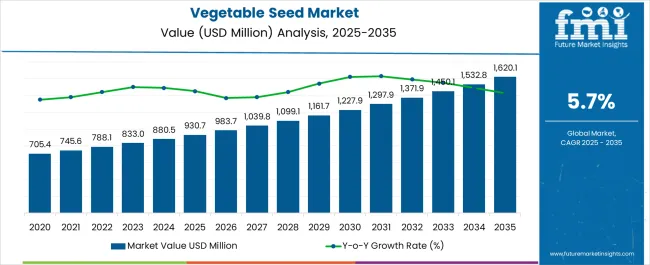
The vegetable seed market is estimated to be valued at USD 930.7 million in 2025 and is projected to reach USD 1620.1 million by 2035, registering a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.7% over the forecast period.
The period of 2020–2024 represents early adoption, with the market expanding from USD 705.4 million in 2020 to USD 880.5 million in 2024, showing a steady rise in adoption among growers and suppliers. This stage reflects gradual improvements in distribution channels, structured demand from organized farming groups, and expanding regional adoption. The market here establishes a stable base, with gradual awareness and penetration setting the groundwork for a more accelerated growth phase.
Between 2025 and 2030, the scaling phase dominates, as values climb from USD 930.7 million in 2025 to USD 1,227.9 million by 2030, indicating wider acceptance, stronger purchasing cycles, and increased use of hybrid and high-yield seed types. By 2030–2035, consolidation defines the market as it rises to USD 1,620.1 million in 2035, with growth driven by more concentrated demand among large growers and consistent regional adoption. At this stage, expansion continues, but at a more controlled pace, with established suppliers focusing on refining distribution, securing long-term contracts, and maintaining stable growth trajectories.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Vegetable Seed Market Estimated Value in (2025 E) | USD 930.7 million |
| Vegetable Seed Market Forecast Value in (2035 F) | USD 1620.1 million |
| Forecast CAGR (2025 to 2035) | 5.7% |
The vegetable seed market, valued at USD 930.7 million in 2025 and projected to reach USD 1,620.1 million by 2035 at a CAGR of 5.7%, shows clear seasonality influenced by agricultural planting and harvesting cycles. Sales typically peak before major planting seasons, particularly in spring and early summer, when demand for seeds surges across key regions. This cyclicality is shaped by crop calendars, climate conditions, and regional agricultural practices, with high-volume crops such as tomatoes, peppers, and leafy vegetables creating distinct demand spikes. In contrast, off-season periods see lower seed orders as growers shift focus to harvesting, storage, and sales activities.
From 2025 to 2035, the cyclicality of the market becomes more evident as the value progresses from USD 930.7 million to USD 1,620.1 million, aligning with consistent annual planting schedules. Vegetable seeds demonstrate relatively predictable cycles, where reordering is tied directly to seasonal production needs, creating a dependable rhythm in supply chain flows. Regional variations, such as winter demand in tropical zones versus spring demand in temperate areas, reinforce global cyclicality. This structured demand pattern provides stability for suppliers, while periodic peaks enable producers to optimize inventory, forecast sales, and balance production with recurring market cycles.
The market is experiencing sustained growth, supported by rising global demand for high-quality crops, improvements in agricultural practices, and the expansion of protected cultivation systems. Advancements in seed breeding technologies, coupled with increased investment in genetic research, have allowed seed developers to offer varieties with improved yield, disease resistance, and climate adaptability. Growing population pressures and shifting dietary preferences toward nutrient-rich vegetables have further increased the need for efficient seed solutions.
Government initiatives promoting agricultural productivity, along with collaborations between seed companies and research institutions, are creating opportunities for product innovation. The shift toward precision farming and the adoption of sustainable cultivation practices are also influencing the market’s trajectory.
With evolving consumer preferences and the need to ensure food security, vegetable seed producers are focusing on both yield enhancement and quality improvement These factors, along with growing international trade in horticultural products, are anticipated to maintain the market’s growth momentum in the coming years.
The vegetable seed market is segmented by crop family, form, trait, and geographic regions. By crop family, vegetable seed market is divided into solanaceae, brassicas, cucurbits, roots & bulbs, and others. In terms of form, vegetable seed market is classified into inorganic and organic. Based on trait, vegetable seed market is segmented into conventional and genetically modified. Regionally, the vegetable seed industry is classified into North America, Latin America, Western Europe, Eastern Europe, Balkan & Baltic Countries, Russia & Belarus, Central Asia, East Asia, South Asia & Pacific, and the Middle East & Africa.
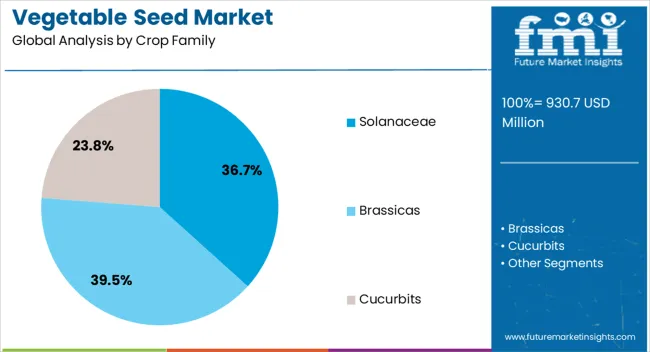
The solanaceae crop family segment is projected to hold 36.70% of the vegetable seed market revenue share in 2025, making it the leading crop family segment. This dominance has been supported by the high commercial value and wide cultivation of crops within this family, which includes varieties known for their strong market demand and adaptability. The consistent global consumption of Solanaceae crops has driven significant investment in seed development, focusing on yield improvement and resistance to pests and diseases. The segment’s growth has also been driven by the suitability of these crops for protected cultivation and modern farming systems, allowing year-round production. Breeding programs have leveraged genetic advancements to produce varieties with extended shelf life, better transport tolerance, and superior taste profiles As consumer preferences align with the nutritional benefits offered by Solanaceae crops, and farmers seek profitable and resilient cultivation options, this segment continues to retain its market leadership position.
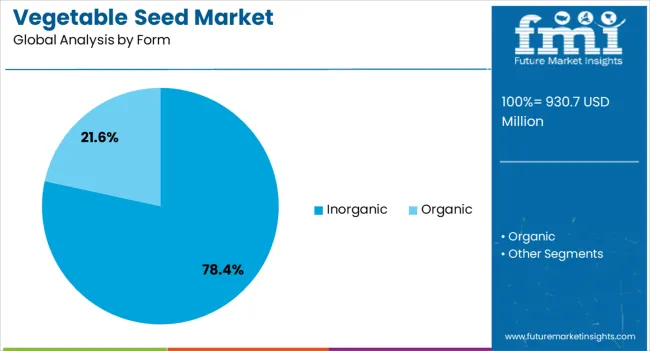
The inorganic form segment is expected to command 78.40% of the market revenue share in 2025, emerging as the dominant form category. This leadership position has been achieved due to the extensive use of conventional synthetic inputs during the cultivation of crops from inorganic seeds, which often yield faster and more predictable results. Farmers have favored this form for its cost efficiency, availability, and compatibility with high-intensity farming systems. The segment benefits from established supply chains and the ability to produce in bulk to meet global demand. Advancements in breeding have ensured that inorganic seeds maintain high germination rates, uniform growth, and resistance to specific regional challenges. The scalability of production, along with supportive infrastructure for storage and distribution, has further reinforced its dominance Inorganic seeds continue to be the preferred choice for many large-scale agricultural enterprises seeking consistent output and optimized resource use.
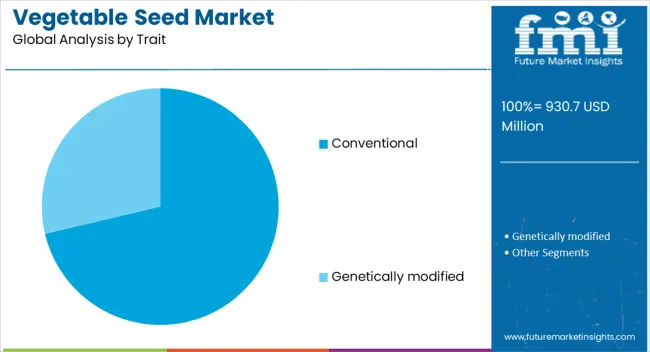
The conventional trait segment is anticipated to hold 71.30% of the market revenue share in 2025, making it the leading trait category. Its growth has been reinforced by the long-standing acceptance and familiarity of conventional seeds among farmers worldwide. These seeds have been valued for their predictable performance, affordability, and adaptability across diverse climatic conditions. The segment’s resilience stems from minimal regulatory hurdles compared to genetically modified alternatives, allowing faster market availability. Conventional breeding techniques have steadily improved disease resistance, yield potential, and quality traits without reliance on complex genetic modification processes. Additionally, the market has been supported by consumer preferences in regions where genetically modified crops face regulatory or cultural resistance The combination of farmer trust, cost-effectiveness, and strong market demand has ensured that conventional seeds remain the primary choice for vegetable production across both developed and emerging agricultural economies.
The vegetable seed market is experiencing solid growth due to rising demand for high-yield, disease-resistant varieties that meet consumer preferences for flavor, size, and appearance. Adoption of hybrid and genetically enhanced seeds is strongest in regions with commercial-scale farming, while developing economies focus on affordable open-pollinated varieties. Key players such as BASF, Bayer CropScience, Syngenta, Sakata Seed, East-West Seed, and Rijk Zwaan dominate through strong R&D pipelines, partnerships with growers, and distribution networks. Growth is also supported by the expansion of protected cultivation, such as greenhouses and vertical farming, which require specialized seeds. While hybrid seeds increase productivity and profitability, affordability and access in rural areas remain barriers. Until open-access breeding programs expand, established multinationals continue to shape global production and consumption patterns in the vegetable seed sector.
Hybrid vegetable seeds are increasingly preferred for their higher yields, uniformity, and resistance to diseases and pests. Farmers in North America, Europe, and Asia-Pacific invest heavily in hybrids to maximize output, reduce pesticide usage, and meet market demand for consistent produce quality. Companies like Syngenta and Bayer CropScience lead with strong hybrid portfolios in tomatoes, peppers, cucumbers, and leafy vegetables. In developing regions, adoption remains slower due to high costs, yet hybrid seeds are gradually penetrating markets where commercial farming is expanding. Hybrid seeds help growers meet consumer expectations for size, taste, and longer shelf life, ensuring greater profitability. Rising demand from organized retail chains and food processing industries further drives hybrid adoption. Until cost barriers are reduced for smallholder farmers, hybrids will remain more accessible to commercial growers, creating a divide in adoption rates across developed and developing regions.
Protected cultivation methods such as greenhouses, polyhouses, and vertical farming are expanding rapidly, creating demand for vegetable seeds optimized for controlled environments. These seeds are developed to thrive under artificial lighting, precise irrigation, and climate control, producing higher yields with less resource input. Companies like Rijk Zwaan and Sakata Seed specialize in breeding seeds suited for hydroponic and indoor farming systems, including lettuce, cucumbers, and herbs. Farmers using these seeds benefit from year-round production, uniform quality, and reduced vulnerability to external weather conditions. Adoption is rising in Europe, North America, and urban regions of Asia-Pacific where space-efficient farming is prioritized. While investment costs for protected cultivation remain high, profitability through premium produce attracts commercial growers. Until broader access to affordable indoor-farming seeds develops, specialized seed suppliers will continue to dominate this segment, catering mainly to urban agriculture and high-value farming enterprises.
In developing markets across Africa, South Asia, and parts of Latin America, affordability and accessibility of quality vegetable seeds remain significant hurdles. Farmers often rely on open-pollinated varieties or saved seeds, which are lower-cost but yield less and have weaker resistance to pests and diseases. Companies like East-West Seed have gained strong positions by offering affordable, locally adapted hybrid varieties and building farmer education programs. Despite their efforts, limited distribution channels, lack of awareness, and high upfront costs restrict large-scale adoption of advanced seeds. Local seed companies face challenges in scaling production and competing with multinational firms. Governments and NGOs play a vital role in improving access through subsidies and training. Until more inclusive systems for smallholder farmers are developed, the market will continue to show a divide between resource-rich commercial growers and subsistence-level farmers in developing regions.
The vegetable seed market is highly competitive, with global players emphasizing R&D investments and breeding technologies to maintain leadership. BASF and Syngenta focus on developing disease-resistant hybrids, while Rijk Zwaan is known for flavor-driven varieties. East-West Seed has built strong market share in Asia by focusing on affordability and farmer support, while Sakata Seed specializes in crops like broccoli and melons. These companies employ strategies such as contract farming, farmer education programs, and collaborations with food processors to secure market demand. Intellectual property rights and seed patents play a critical role in competitive positioning, often limiting new entrants. While large firms dominate global markets, regional companies with locally adapted varieties offer competitive alternatives. Until open-source breeding programs expand further, leading players will maintain market leadership through technological edge, strong branding, and extensive farmer networks across diverse geographies.
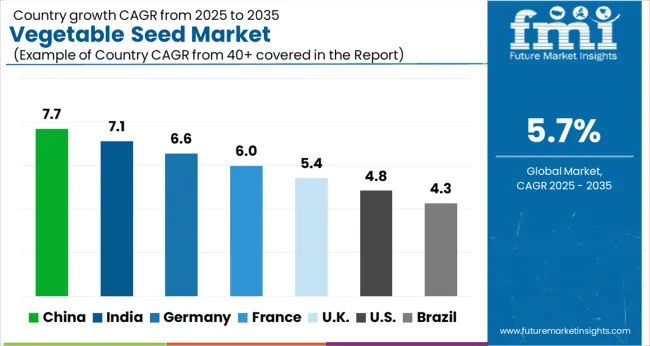
| Country | CAGR |
|---|---|
| China | 7.7% |
| India | 7.1% |
| Germany | 6.6% |
| France | 6.0% |
| UK | 5.4% |
| USA | 4.8% |
| Brazil | 4.3% |
The global vegetable seed market is projected to expand at a CAGR of 5.7% through 2035, driven by advancements in hybrid seed technology and rising demand for high-yield crop varieties. Within BRICS nations, China has been recorded at 7.7%, supported by large-scale adoption of hybrid and genetically improved seeds, while India has been observed at 7.1%, with growth fueled by expanding agricultural modernization and food security initiatives. In the OECD region, Germany has been measured at 6.6%, reflecting strong emphasis on research-driven seed development and regulated commercial farming. The United Kingdom has been noted at 5.4%, influenced by sustainable farming practices and regulatory compliance, while the USA has been recorded at 4.8%, supported by precision agriculture and demand for improved vegetable varieties. This report includes insights on 40+ countries; the top five markets are highlighted here.
The vegetable seed market in China is growing at a CAGR of 7.7%, supported by rising demand for fresh vegetables and higher production needs. Farmers are increasingly using hybrid and high-yield seeds to improve crop output. The demand for a wide range of vegetable varieties, including tomatoes, cucumbers, peppers, and leafy greens, is strong. Distribution networks through agricultural suppliers, cooperatives, and direct sales channels help farmers access seeds more easily. Government initiatives that encourage crop productivity and food security also support the market. The steady rise in both large-scale and small-scale farming boosts demand for vegetable seeds in China.
The vegetable seed market in India is expanding at a CAGR of 7.1%, driven by rising consumption of vegetables and the need for better crop performance. Farmers are adopting hybrid seeds and region-specific varieties to meet market demand. Popular crops include onions, okra, tomatoes, and leafy vegetables. The market benefits from agricultural input suppliers, seed distributors, and cooperatives that make seeds available across rural and semi-urban areas. Government programs that encourage higher crop productivity add to the growth. The need for consistent supply of vegetables throughout the year continues to drive the market in India.
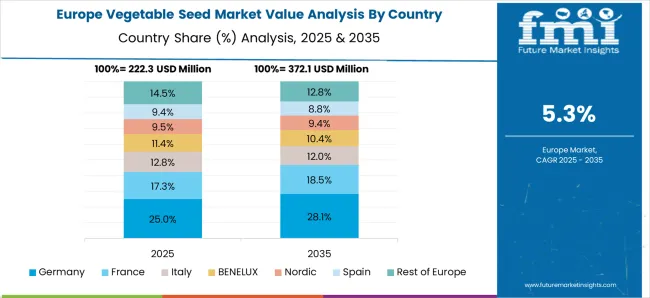
The vegetable seed market in Germany is growing at a CAGR of 6.6%, supported by strong demand for fresh produce and diverse vegetable varieties. Farmers and growers are adopting high-quality seeds to ensure steady supply for local consumption and exports. Key vegetable crops include lettuce, tomatoes, carrots, and cabbage. Distribution is handled by agricultural cooperatives, suppliers, and specialized seed companies. Strict government regulations ensure seed quality and crop performance. The demand for reliable and high-yield seed varieties is expected to maintain market growth in Germany.
The vegetable seed market in the UK is growing at a CAGR of 5.4%, with steady demand from both commercial farming and household gardening. Popular crops include tomatoes, carrots, beans, and leafy greens. Agricultural suppliers, retail stores, and online platforms provide easy access to seeds. Farmers focus on seed varieties that provide good yields and resilience across growing seasons. Regulations for quality standards help ensure reliable supply. With continued interest in fresh produce and gardening, the market is expected to expand gradually in the UK.
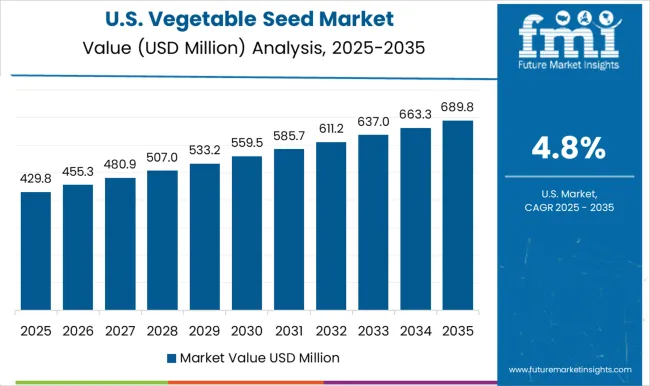
The vegetable seed market in the USA is growing at a CAGR of 4.8%, driven by demand from commercial farming and home gardening. Key crops include lettuce, tomatoes, peppers, beans, and leafy greens. Distribution channels include agricultural cooperatives, seed suppliers, and retail outlets. Farmers and gardeners prefer high-quality seed varieties to improve yield and crop reliability. Government regulations on seed quality and certification provide assurance for buyers. The combination of commercial demand and strong interest in gardening continues to support the market in the USA
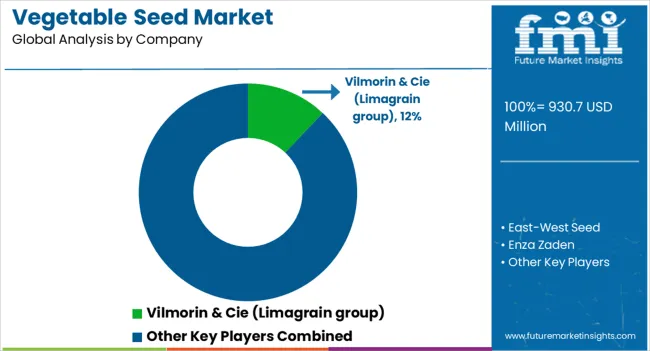
The vegetable seed market plays a central role in ensuring food security and supporting global agricultural productivity. Rising demand for high-yielding, disease-resistant, and climate-adapted seed varieties is shaping this sector, alongside the growing adoption of hybrid and genetically improved seeds. Population growth, expanding vegetable consumption, and sustainable farming practices are further accelerating the market’s momentum. Vilmorin & Cie (Limagrain group), East-West Seed, Enza Zaden, Sakata Seed Corporation, and Takii & Co., Ltd. are among the global leaders, offering extensive vegetable seed portfolios that cater to farmers worldwide.
Companies like Bejo Zaden and Rijk Zwaan focus strongly on innovation, investing in R&D to produce varieties with enhanced nutrition, taste, and resilience against pests and diseases. On the multinational side, Bayer (Bayer Vegetable Seeds) and BASF leverage biotechnology and breeding expertise to strengthen the seed market with advanced hybrid solutions, while KWS emphasizes high-quality breeding programs adapted to diverse regions. Regional and local seed companies play a vital role, particularly in Asia-Pacific, Africa, and Latin America, where they provide affordable, locally adapted seed varieties to smallholder farmers. With precision agriculture, digital seed platforms, and sustainable farming practices gaining ground, the vegetable seed market is expected to expand significantly, balancing global food supply needs with climate resilience and nutritional demands.
| Item | Value |
|---|---|
| Quantitative Units | USD 930.7 million |
| Crop Family | Solanaceae, Brassicas, Cucurbits, Roots & bulbs, and Others |
| Form | Inorganic and Organic |
| Trait | Conventional and Genetically modified |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America, Middle East & Africa |
| Country Covered | United States, Canada, Germany, France, United Kingdom, China, Japan, India, Brazil, South Africa |
| Key Companies Profiled | Vilmorin & Cie (Limagrain group), East-West Seed, Enza Zaden, Sakata Seed Corporation, Takii & Co., Ltd., Bejo Zaden, Rijk Zwaan, Bayer / Bayer Vegetable Seeds, BASF, KWS, and Other local and regional seed companies |
| Additional Attributes | Dollar sales in the Vegetable Seed Market vary by type including open-pollinated, hybrid, and genetically modified seeds, application across commercial farming, home gardening, and horticulture, and region covering North America, Europe, and Asia-Pacific. Growth is driven by increasing demand for high-yield crops, rising focus on food security, and advancements in seed biotechnology. |
The global vegetable seed market is estimated to be valued at USD 930.7 million in 2025.
The market size for the vegetable seed market is projected to reach USD 1,620.1 million by 2035.
The vegetable seed market is expected to grow at a 5.7% CAGR between 2025 and 2035.
The key product types in vegetable seed market are solanaceae, chilli, eggplant, tomato, and others.
In terms of form, inorganic segment to command 78.4% share in the vegetable seed market in 2025.






Full Research Suite comprises of:
Market outlook & trends analysis
Interviews & case studies
Strategic recommendations
Vendor profiles & capabilities analysis
5-year forecasts
8 regions and 60+ country-level data splits
Market segment data splits
12 months of continuous data updates
DELIVERED AS:
PDF EXCEL ONLINE
Vegetable Glycerin Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Vegetable Sugar Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Vegetable Parchment Paper Market Size, Share & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Vegetable Shortening Market Trends and Forecast 2025 to 2035
Vegetable Dicing Machines Market Growth – Food Processing Efficiency 2025 to 2035
Vegetable Carbon Market Trends - Functional Uses & Industry Demand 2025 to 2035
Vegetable Powders Market Insights - Growth & Functional Benefits 2025 to 2035
Vegetable Concentrates Market Growth - Nutrient-Dense Foods & Industry Demand 2025 to 2035
Vegetable Sorting Machine Market Analysis by Processing Capacity, Technology, Operation Type, Vegetable Type, and Region Through 2035
Vegetable Waste Products Market
IQF Vegetables Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Fresh Vegetables Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Frozen Vegetable Market Analysis - Size, Share, and Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Brined Vegetable Market Analysis by Nature, Type, End-use, Distribution Channel and Region through 2035
Savory Vegetable Flavours Market Insights - Applications & Industry Growth 2025 to 2035
Canned Vegetable Market Growth – Preservation & Industry Demand 2024-2034
Textured Vegetable Protein Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Upcycled Vegetable Snacks Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Fruit And Vegetable Juice Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Fruit and Vegetable Ingredient Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035

Thank you!
You will receive an email from our Business Development Manager. Please be sure to check your SPAM/JUNK folder too.
Chat With
MaRIA