About The Report
The Advanced Wound Management Market is estimated to reach USD 12,385.4 Million by 2025. Between 2025 and 2035, the market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 3.4%, reaching a total value of USD 17,302.8 Million by the end of the assessment period.
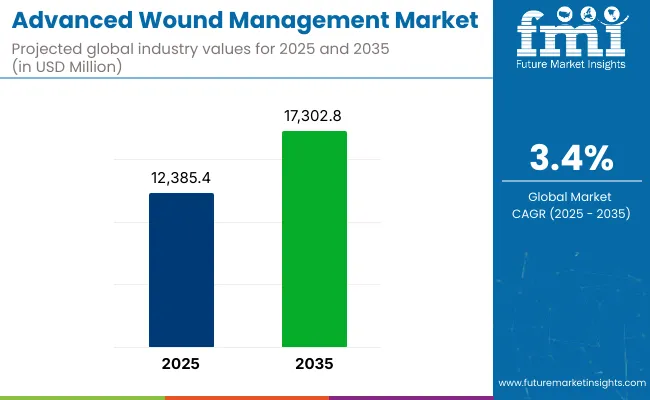
| Attribute | Values |
|---|---|
| Estimated Industry Size (2025E) | USD 12,385.4 Million |
| Projected Industry Value (2035F) | USD 17,302.8 Million |
| CAGR (2025 to 2035) | 3.4% |
The advanced wound management market is experiencing consistent growth, driven by rising incidence of chronic wounds such as diabetic foot ulcers, pressure injuries, and venous leg ulcers. The shift toward outpatient care and the expansion of home health services are accelerating demand for advanced dressings, negative pressure wound therapy (NPWT), and bioactive materials. Innovations in antimicrobial technologies, including silver-impregnated foam dressings and oxygen-enriched therapies, are improving healing rates and reducing infection risk.
Regulatory agencies have endorsed streamlined approvals for novel biologics and skin substitutes, creating a supportive environment for commercialization. Additionally, payer policies increasingly favor advanced wound care to reduce hospital readmissions and total treatment costs. With healthcare systems focusing on value-based care and aging demographics driving higher chronic wound prevalence, the market is well-positioned for robust expansion in the coming decade.
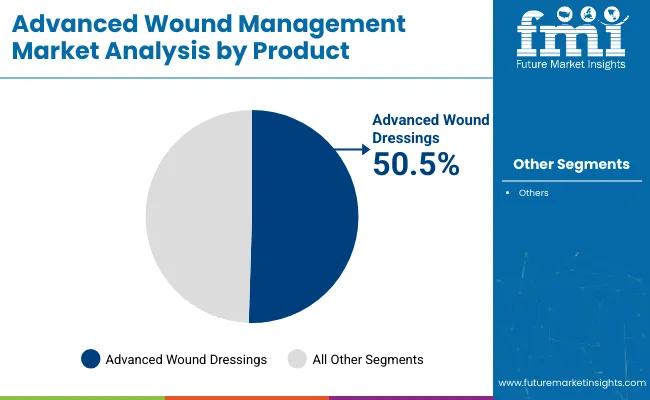
In 2025, advanced wound dressings are anticipated to hold a 50.5% revenue share in the advanced wound management market. This leadership has been attributed to their ability to create optimal healing environments that maintain moisture balance, manage exudate, and prevent infection. Clinical practice guidelines have increasingly endorsed advanced dressings over traditional gauze, strengthening clinician confidence and encouraging wider use across acute and chronic wound indications.
Product development efforts have resulted in dressings incorporating antimicrobial agents, hydrocolloids, and foam technologies, which have been recognized for improving healing rates and patient comfort. Additionally, procurement policies in hospitals and outpatient centers have favored advanced dressings due to their proven cost-effectiveness in reducing wound recurrence and lowering long-term care costs. These factors have reinforced their dominance in the product landscape.
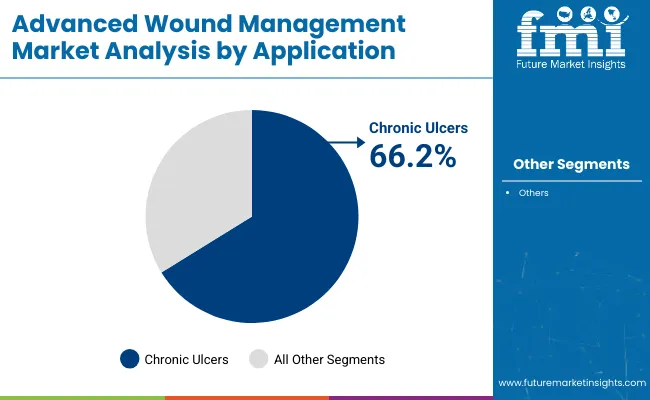
Chronic ulcers are projected to account for 66.2% of the application segment share in 2025. This leadership has been driven by the increasing incidence of diabetic foot ulcers, pressure injuries, and venous leg ulcers, which have been identified as significant contributors to healthcare expenditures and patient morbidity. Advances in wound assessment protocols and early-stage intervention strategies have supported earlier identification and treatment of chronic ulcers.
Clinicians have prioritized advanced wound care modalities for these cases, recognizing their impact on accelerating tissue regeneration and minimizing the risk of infection. Reimbursement frameworks have progressively expanded to cover advanced therapies for chronic wounds, further supporting adoption in hospital and community settings. As a result, chronic ulcers are expected to remain the largest application area within advanced wound management.
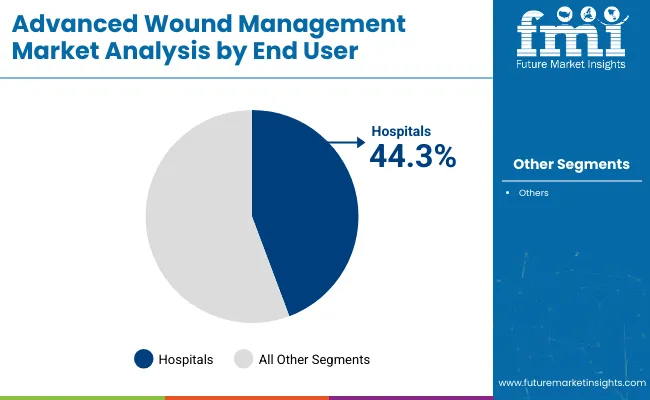
Hospitals are expected to capture 44.3% of the end user segment share in 2025. Their leadership has been attributed to their role as primary treatment centers for acute and chronic wounds requiring complex management and multidisciplinary care.
Hospital-based wound care teams have increasingly adopted evidence-based protocols and advanced dressings to improve patient outcomes and reduce length of stay. Investments in dedicated wound care units and specialized staff training have strengthened institutional capabilities in managing complex wound cases.
Additionally, hospitals have leveraged integrated electronic health records and remote monitoring solutions to standardize care pathways and track healing progress. Procurement practices have favored bulk purchasing of advanced wound products, ensuring consistent availability and cost control. Collectively, these dynamics have established hospitals as the principal end users of advanced wound management solutions.
High product costs, limited access in low-resource settings, and patient adherence issues
Despite significant clinical benefits, advanced form products for wound care are expensive. Such costs prevent access in low- and middle-income countries. Improper reimbursement, lack of awareness among primary care providers, and variable practices of wound care protocol are some of the barriers to accessing the advanced products and technology needed for optimal patient care.
Patient nonadherence with regard to dressing changes or self-care instructions also impacts the results of treatment. According to WHO, improving chronic wound management requires much more integration of primary and specialty care and improved patient education.
Smart dressings, home-based care, and bioengineered therapies
Smart wound dressings, embedded with sensors for moisture and pH monitoring, are allowing for real-time tracking and early infection detection. The advancement of home healthcare has been in concert with apps for remote wound monitoring and tele-wound care services.
Biologically active products like skin substitutes, collagen dressings, and growth factor-infused therapies are becoming more appealing for complex and slow-healing wound treatment. WHO estimates that technology-enabled wound care can significantly reduce complications and hospitalization rates.
The USA market for advanced wound care is growing at a continuous rate owing to a high prevalence of chronic wounds in respect of diabetic foot ulcers, pressure injuries, and postoperative complications. While hospitals and outpatient centers use NPWT (negative pressure wound therapy) and bioactive wound care solutions, in this regard according to OECD, with an ever-aging population, the increasing rates of diabetes are playing a big role in the long-term requirement of wound care. This includes innovations in moist-retentive and antimicrobial dressings along with reimbursement support, helping to fuel momentum in the market in acute care as well as home care.
| Country | CAGR (2025 to 2035) |
|---|---|
| United States | 3.6% |
In the UK, the advanced wound management market is supported by NHS initiatives aimed at reducing the clinical and economic burden of chronic wounds. According to OECD, clinical guidelines and national audits are promoting evidence-based use of advanced therapies, including foam dressings, alginates, and antimicrobial silver-based products. Prevalence of venous leg ulcers and pressure ulcers among the elderly is creating sustained demand for advanced wound care especially for community nursing and home healthcare.
| Country | CAGR (2025 to 2035) |
|---|---|
| United Kingdom | 3.2% |
In the EU advanced wound management market, Germany, France, and Italy constitute the areas that are presently developing driving by the aging populations and strong health care systems toward acceptance of newer wound healing technologies.
According to UN, recovery by the European Commission for research-going and smart dressings and bioengineered skin substitutes is under the Horizon Europe framework. Added hospital-acquired wound prevention initiatives and improved reimbursement for advanced wound therapies are further pushing for acceptance from both inpatient and outpatient environments.
| Country | CAGR (2025 to 2035) |
|---|---|
| European Union | 3.4% |
The advanced wound management market offers promising growth opportunities in Japan. The country homes many elderly people and follows a high standard of clinical wound care. Most hospitals and long-term care facilities utilize hydrocolloid, hydrogel, and NPWT systems for effective healing of chronic wounds.
Government support in home-based medical care and pressure injury prevention programs results in constant utilization of advanced dressings. Japanese manufacturing industries innovate bioactive and biocompatible materials with the aim of improving tissue regeneration and infection control.
| Country | CAGR (2025 to 2035) |
|---|---|
| Japan | 3.1% |
Advanced wound management has extended its market in South Korea, increased consumer demand for advanced wound dressings, and a rise in surgical and outpatient volume. According to OECD studies, medical device innovation in chronic disease management being emphasized by government investment includes those for cuts and wounds related to diabetes.
All of which have synergized in developing hydro fiber, collagen, and growth factor-infused dressings found in most tertiary care hospitals and outpatient clinics. Meanwhile, affordable advanced wound care solutions are also being developed by Korean companies with the focus of exporting such to the Southeast Asian as well as the Middle Eastern market.
| Country | CAGR (2025 to 2035) |
|---|---|
| South Korea | 3.5% |
The advanced wound management market is highly competitive, shaped by innovation in moisture-balancing dressings, negative pressure wound therapy (NPWT), and bioactive products. Leading companies are investing in antimicrobial technologies, foam dressings, and integrated digital wound monitoring platforms to improve healing outcomes and reduce infection risks. Strategic acquisitions, global expansion, and partnerships with healthcare providers are central to maintaining market leadership and accelerating adoption.
Additionally, the rising prevalence of chronic wounds such as diabetic foot ulcers and pressure injuries is fueling demand across acute and community care settings. Emphasis on patient-centric designs, cost-effectiveness, and evidence-based protocols is reshaping competitive differentiation.
Key Development
In 2024, Solventum launched the V.A.C.® Peel and Place Dressing, an all-in-one, extended-wear wound dressing for Negative Pressure Wound Therapy (NPWT). This new dressing simplifies application to under two minutes and can be worn for up to seven days, reducing application time by 61% and potentially cutting costs and home nursing visits. It features a non-adherent layer for less painful removal and is indicated for various wound types.
In 2024, Arch Therapeutics announced it would present its AC5® Advanced Wound System at the 2024 SAWC Spring Meeting (May 14-18, 2024). A poster featuring a pilot study on AC5® for lower extremity wounds would be showcased. AC5®, an FDA-cleared self-assembling peptide technology, offers a novel approach to wound care for various acute and chronic wounds.
The overall market size for the advanced wound management market was approximately USD 12,385.4 Million in 2025.
The advanced wound management market is expected to reach approximately USD 17,302.8 Million by 2035.
The demand for advanced wound management is rising due to the increasing prevalence of chronic wounds, diabetic ulcers, and pressure injuries.
The top 5 countries driving the development of the advanced wound management market are the United States, Germany, China, Japan, and the United Kingdom.
Advanced wound dressings and chronic ulcer applications are expected to command significant shares over the assessment period.






Our Research Products

The "Full Research Suite" delivers actionable market intel, deep dives on markets or technologies, so clients act faster, cut risk, and unlock growth.

The Leaderboard benchmarks and ranks top vendors, classifying them as Established Leaders, Leading Challengers, or Disruptors & Challengers.

Locates where complements amplify value and substitutes erode it, forecasting net impact by horizon

We deliver granular, decision-grade intel: market sizing, 5-year forecasts, pricing, adoption, usage, revenue, and operational KPIs—plus competitor tracking, regulation, and value chains—across 60 countries broadly.

Spot the shifts before they hit your P&L. We track inflection points, adoption curves, pricing moves, and ecosystem plays to show where demand is heading, why it is changing, and what to do next across high-growth markets and disruptive tech

Real-time reads of user behavior. We track shifting priorities, perceptions of today’s and next-gen services, and provider experience, then pace how fast tech moves from trial to adoption, blending buyer, consumer, and channel inputs with social signals (#WhySwitch, #UX).

Partner with our analyst team to build a custom report designed around your business priorities. From analysing market trends to assessing competitors or crafting bespoke datasets, we tailor insights to your needs.
Supplier Intelligence
Discovery & Profiling
Capacity & Footprint
Performance & Risk
Compliance & Governance
Commercial Readiness
Who Supplies Whom
Scorecards & Shortlists
Playbooks & Docs
Category Intelligence
Definition & Scope
Demand & Use Cases
Cost Drivers
Market Structure
Supply Chain Map
Trade & Policy
Operating Norms
Deliverables
Buyer Intelligence
Account Basics
Spend & Scope
Procurement Model
Vendor Requirements
Terms & Policies
Entry Strategy
Pain Points & Triggers
Outputs
Pricing Analysis
Benchmarks
Trends
Should-Cost
Indexation
Landed Cost
Commercial Terms
Deliverables
Brand Analysis
Positioning & Value Prop
Share & Presence
Customer Evidence
Go-to-Market
Digital & Reputation
Compliance & Trust
KPIs & Gaps
Outputs
Full Research Suite comprises of:
Market outlook & trends analysis
Interviews & case studies
Strategic recommendations
Vendor profiles & capabilities analysis
5-year forecasts
8 regions and 60+ country-level data splits
Market segment data splits
12 months of continuous data updates
DELIVERED AS:
PDF EXCEL ONLINE
Advanced Wound Dressing Market by Product, Wound Type, End User and Region 2025 to 2035
Advanced Water Management And Filtration Equipment Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
The Advanced Drill Data Management Solutions Market is segmented by Drilling Type (Directional Drilling, Horizontal Drilling, Percussive Drilling, Rotary Drilling, Vertical Drilling), Application (Oil and Gas Exploration, Environmental Remediation, Geotechnical Site Investigation, Groundwater Management, Mining and Exploration), Functionalities (Data Analysis and Visualization, Collaboration and Data Sharing, Drilling Data Collection and Storage, Predictive Analytics for Drill Bit Performance, Real-Time Drilling Optimization), and Region. Forecast for 2026 to 2036.
Advanced Cancer Pain Management Market Insights - Trends & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Advanced Distribution Management Systems Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Traditional Wound Management Market is segmented by product type, application and end user from 2025 to 2035
The Advanced Driver Assistance System (ADAS) Testing Equipment Market is segmented by Product Type (Hardware, Software, and Laboratory Testing Services), End-User (Automotive OEMs, Tier-1 Suppliers, Testing Laboratories, Research Institutes, and Regulatory Bodies), and Region, by FMI.
The Advanced Functional Materials Market is segmented by Material Type (Nanomaterials, Ceramics, Composites, Conductive Polymers, Energy Materials, and Other Types), End-use Industry (Electrical and Electronics, Automotive, Healthcare, Aerospace and Defence, Energy and Power, and Other Industries), and Region, with a forecast period from 2026 to 2036.
Wound Debridement Products Market Analysis - Growth & Forecast 2026 to 2036
Advanced Recycled Polyolefin Resins Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2026 to 2036
Advanced Recycled Circular Polyolefin Packaging and Durables Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2026 to 2036
Advanced Recycled PE E-Commerce Packaging Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2026 to 2036
Wound Healing Ultrasound Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2026 to 2036
Advanced Polymeric Separator Films for EV Traction Batteries Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2026 to 2036
Advanced Strain-Engineered Microbial Platforms for Bioplastic Precursors Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2026 to 2036
Advanced Flocculants for Wastewater Treatment Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2026 to 2036
Advanced Oxidation Chemicals for Emerging Contaminants Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2026 to 2036
Wound Antifungals Market Analysis - Size, Share, and Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Wound Wash Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Advanced Process Control Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035

Thank you!
You will receive an email from our Business Development Manager. Please be sure to check your SPAM/JUNK folder too.