The Chemicals And Petrochemicals Electrostatic Precipitator Market is estimated to be valued at USD 2.2 billion in 2025 and is projected to reach USD 4.0 billion by 2035, registering a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.2% over the forecast period. A rolling CAGR analysis highlights steady acceleration across the forecast horizon with no significant volatility. From 2025 to 2030, the market grows from USD 2.2 billion to USD 3.0 billion, reflecting an annualized growth rate of 6.3%, driven by stricter emission regulations, capacity expansions in petrochemical complexes, and the adoption of advanced particulate control systems for high-efficiency dust removal.
This early phase emphasizes investments in wet electrostatic precipitators for sulfuric acid mist and fine particulate filtration. In the following period (2030-2035), the market advances from USD 3.0 billion to USD 4.0 billion, maintaining a rolling CAGR of approximately 6.1%, signaling stable demand as retrofitting projects gain prominence in mature economies and new installations continue in emerging markets. Late-stage growth is reinforced by digitalization trends, with integration of IoT-enabled monitoring systems and predictive maintenance to optimize operational efficiency and compliance reporting. Vendors focusing on modular designs, energy-efficient power supplies, and hybrid filtration solutions will strengthen their competitive position as environmental performance becomes a critical differentiator in global chemical and petrochemical operations.
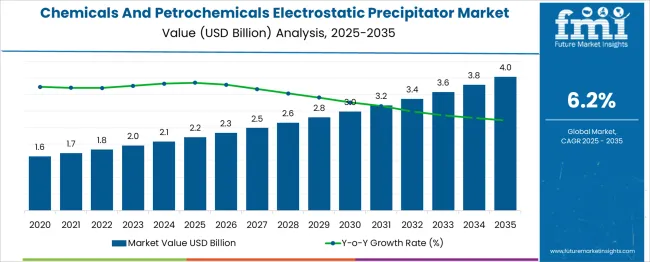
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Chemicals And Petrochemicals Electrostatic Precipitator Market Estimated Value in (2025E) | USD 2.2 billion |
| Chemicals And Petrochemicals Electrostatic Precipitator Market Forecast Value in (2035F) | USD 4.0 billion |
| Forecast CAGR (2025 to 2035) | 6.2% |
The chemicals and petrochemicals ESP segment holds distinct shares across these broader equipment and compliance-oriented markets. Within the air pollution control equipment market, chemical‑plant ESPs represent 12–14%, reflecting their predominant use in large-scale process gas cleaning applications. In the chemical and petrochemical plant utilities equipment market, their share is 8–10%, given they are foundational for emissions compliance in boilers and process off-gases.
Within the industrial air quality and emissions compliance systems segment, ESPs used in refining or chemical contexts account for 15–17%, owing to their ability to handle high particulate-load exhaust streams efficiently. In the industrial utility equipment retrofit and modernization market, their share reaches 20-22%, driven by upgrades of older scrubbers or filters in response to tightening emissions regulations.
Finally, in the power generation support equipment market within refining and petrochemical complexes, ESPs comprise 5–6%, reflecting their role in particulate removal from captive power plant exhausts. Drivers include stricter air quality mandates, rising investment in refinery upgrades, and demand for reliable, low-maintenance particulate control. Advances such as high-temperature ESP designs, pulse-jet cleaning, and modular retrofit skid systems are improving performance and cost-effectiveness. These attributes position chemical‑plant ESP installations as a mission-critical solution in modern compliance-driven process industries.
Growing regulatory mandates related to particulate matter control in chemical and petrochemical processing units have positioned electrostatic precipitators as a critical technology for air pollution control. The increasing installation of advanced emission reduction systems in refineries, chemical manufacturing units, and gas processing plants has supported this. Industries are actively investing in high-efficiency systems that reduce fine particulate discharge while maintaining cost and energy efficiency.
The future outlook remains positive due to growing global concern about air quality, government-led industrial audits, and the integration of pollution control systems into long-term ESG strategies. As emerging markets expand their petrochemical and chemical capacities, and developed economies prioritize plant modernization, the demand for robust, scalable, and low-maintenance electrostatic precipitator solutions is expected to accelerate steadily over the coming years..
The chemicals and petrochemicals electrostatic precipitator market is segmented by design, system, and geographic regions. By design of the chemicals and petrochemicals, the electrostatic precipitator market is divided into Plate and Tubular. In terms of the system of chemicals and petrochemicals, the electrostatic precipitator market is classified into Dry and Wet. Regionally, the chemicals and petrochemicals electrostatic precipitator industry is classified into North America, Latin America, Western Europe, Eastern Europe, Balkan & Baltic Countries, Russia & Belarus, Central Asia, East Asia, South Asia & Pacific, and the Middle East & Africa.
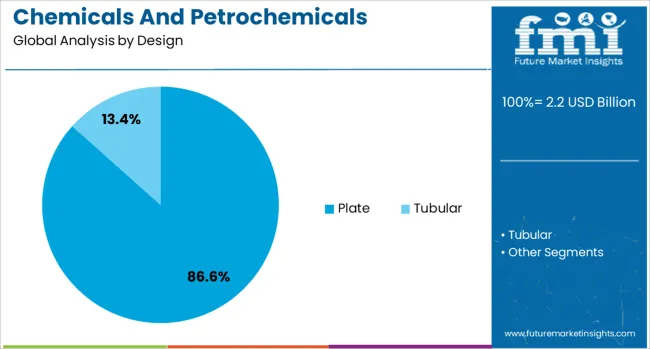
The plate design segment is expected to contribute 86.60% of the Chemicals and Petrochemicals Electrostatic Precipitator market revenue share in 2025, making it the leading design configuration. This segment has benefited from its well-established efficiency in capturing fine particulate matter at high temperatures and high gas flow rates, which are common in chemical and petrochemical environments.
Plate designs have been favored for their stable performance across varying load conditions and ease of cleaning, ensuring long operational cycles with minimal downtime. The large collection surface area provided by plates allows for effective dust accumulation and enhances particle capture efficiency, making them highly suitable for applications involving acidic, corrosive, or dust-laden gas streams.
Additionally, their mechanical simplicity reduces the need for complex maintenance routines, increasing their appeal for continuous operations. Regulatory pressures to reduce PM2.5 and other hazardous emissions have reinforced the dominance of the plate design configuration in modern air filtration infrastructure..
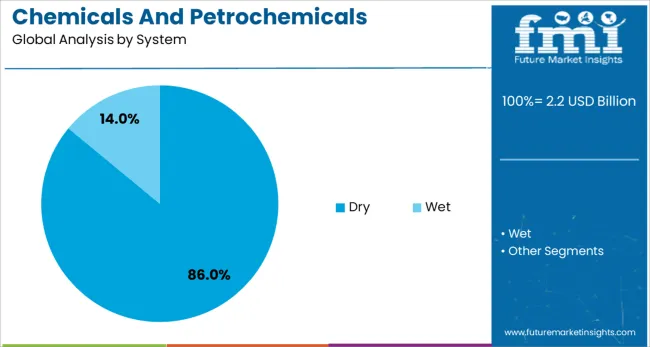
The dry system segment is anticipated to hold 86% of the Chemicals and Petrochemicals Electrostatic Precipitator market revenue share in 2025, positioning it as the most dominant system type. Growth in this segment has been driven by its operational suitability in handling high-temperature flue gases without the need for gas conditioning or liquid injection.
The dry configuration has been particularly favored in petrochemical and chemical processing due to its efficiency in collecting solid particles from exhaust streams while maintaining minimal water usage and reducing secondary waste generation. The system's structural robustness, combined with low operating costs and compatibility with corrosive environments, has further contributed to its widespread adoption.
Additionally, advancements in dry electrostatic precipitator designs have allowed for improved collection efficiency, even under fluctuating process conditions. As facilities increasingly seek environmentally sustainable and cost-effective emission control technologies, dry systems continue to offer an ideal balance of performance, reliability, and ease of integration into complex industrial operations..
Electrostatic precipitators (ESPs) utilized in chemicals and petrochemical plants are air pollution control systems designed to capture dust, particulate, and fume from process streams. These systems are widely deployed in refineries, petrochemical complexes, and chemical processing units to meet emission control standards and protect downstream equipment. Demand has been supported by strict air quality regulations, high dust load operations, and the need to control process emissions. Suppliers offering ESPs with enhanced collection efficiency, compact footprint designs, and modular maintenance access have gained preference. Plants requiring predictable particulate removal and minimal downtime continue to prioritize ESP solutions to ensure compliance and process integrity.
Growth in service adoption has been enabled by rapid expansion of EV fleets among both individuals and corporations. Operators and site hosts have preferred managed charging networks to avoid upfront hardware costs and simplify ongoing operations. Regulations encouraging electrification of transport and emission reduction objectives have amplified demand for accessible AC and DC charging locations. Real estate sectors such as workplaces, multifamily residences, and retail centres have pursued site hosts arrangements to attract EV-driving users. Platforms supporting multi-site deployment and usage analytics have helped accelerate service rollouts across urban and suburban catchment zones.
Deployment of electrostatic precipitators in harsh chemical or high-temperature environments involves design, material, and operational complexity. High dust resistivity, corrosive or acid-laden flue gas, and variable particle load impact collection efficiency and require specialized electrode and insulator design. Chamber configurations must account for thermal expansion, electrode spacing, and voltage control adaptation to changing process chemistry. Maintenance requirements—such as electrode rapping, ash removal, and insulation cleaning require downtime and skilled technicians. Initial cost for large custom ESP installations and costs associated with system accessories such as high-voltage power supplies are often substantial. Inconsistent installation quality and performance test uncertainty have further hampered adoption in projects with tight lead times.
Opportunities exist in retrofitting older cyclone or fabric filter systems with high-efficiency ESP modules to improve particulate capture without expanding plant footprint. Advances in power supply control and field instrumentation enable real-time voltage adjustment, sparking detection, and optimized rapping algorithms that improve performance in demanding chemical processing conditions. Modular ESP units in skid or container modules may support rapid deployment in brownfield or modular plant expansion. Partnerships with equipment OEMs to offer bundled solutions and recurring maintenance or condition monitoring services create long-term engagement. Application of ESP systems in new petrochemical units, combined with catalyst regeneration or accident risk management systems, is creating value beyond basic particulate control.
New trends in ESP application include integration of digital systems offering real-time performance monitoring, spark detection, and predictive maintenance alerts via SCADA dashboards. Adoption of corrosion-resistant alloys, ceramic-coated electrodes, and acid-resistant insulators is increasing for prolonged service in aggressive flue gas streams. Automatic voltage control systems with feedback loops allow for consistent efficiency under variable load and temperature conditions. Compact multi-chamber ESP designs that allow staged cleaning and minimal downtime are gaining traction. Standardization of remote data logging for emissions performance tracking supports regulatory compliance and process optimization.
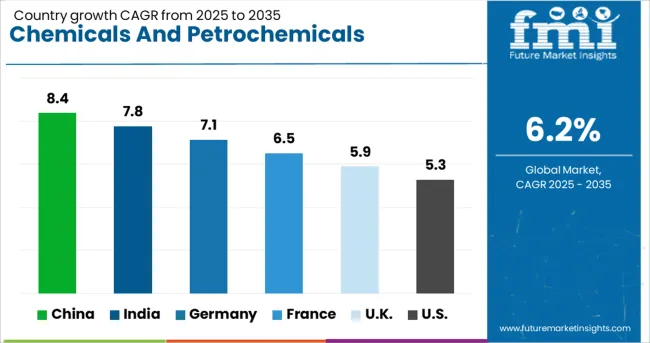
| Country | CAGR |
|---|---|
| China | 8.4% |
| India | 7.8% |
| Germany | 7.1% |
| France | 6.5% |
| UK | 5.9% |
| USA | 5.3% |
The chemicals and petrochemicals electrostatic precipitator market is projected to expand at a CAGR of 6.2% from 2025 to 2035, driven by the rising demand for advanced air pollution control systems, stricter emission compliance norms, and modernization of chemical production facilities. China leads with 8.4%, supported by rapid industrialization and large-scale refinery operations, while India follows at 7.8%, driven by capacity expansions in petrochemical clusters. Among developed markets, France posts 6.5%, the United Kingdom grows at 5.9%, and the United States records 5.3%, influenced by stringent environmental standards and investments in emission-reduction technologies. Increasing adoption of high-efficiency precipitators integrated with digital monitoring systems continues to define market advancements. The analysis includes over 40 countries, with the top five detailed below.
China is projected to register a CAGR of 8.4% through 2035, driven by stringent emission norms and large-scale investments in refineries, petrochemical complexes, and fertilizer plants. The need to control particulate emissions from high-capacity boilers and catalytic cracking units is prompting significant adoption of dry and wet electrostatic precipitator systems. Leading domestic manufacturers are focusing on high-efficiency designs to meet national clean-air targets, while global players invest in smart precipitators with automated voltage optimization and real-time emission monitoring. Rising demand from downstream chemical industries and energy-intensive sectors reinforces the market outlook. Additionally, government-backed infrastructure projects in industrial hubs create opportunities for advanced filtration systems.
India is forecasted to achieve a CAGR of 7.8% through 2035, supported by expansion of petrochemical complexes, refinery upgradation programs, and chemical manufacturing clusters. Increasing focus on reducing particulate matter emissions in power-intensive chemical production drives demand for advanced ESP technologies. Domestic manufacturers are introducing modular, low-maintenance systems, while global vendors emphasize energy-efficient solutions integrated with digital performance analytics. Government initiatives under emission compliance frameworks encourage adoption of retrofitted ESP systems across aging industrial setups. The rapid development of industrial corridors and increased foreign investments in specialty chemicals further accelerate demand for electrostatic precipitators in India’s petrochemical sector.
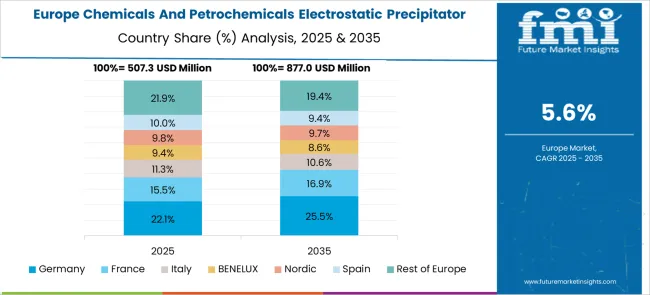
France is expected to grow at a CAGR of 6.5% through 2035, driven by regulatory mandates for emission reduction in chemical and petrochemical facilities. Demand is strong for compact and high-efficiency ESP systems to manage particulate emissions in energy-intensive processes. Manufacturers are focusing on integrating corrosion-resistant materials and digital controls for enhanced operational reliability. Adoption of wet electrostatic precipitators is increasing in facilities dealing with sulfuric acid production and fine particulate removal. The emphasis on energy optimization within emission control equipment aligns with France’s environmental objectives, creating opportunities for innovation in low-energy, high-performance ESP designs.
The United Kingdom is forecasted to post a CAGR of 5.9% through 2035, supported by stringent particulate emission limits and modernization programs in chemical facilities. Adoption of ESP systems is concentrated in petrochemical refineries, polymer manufacturing, and specialty chemical plants where high particulate load handling is required. Manufacturers are deploying dry-type ESP solutions with automated rapping systems to improve operational efficiency. Increased integration of AI-based emission monitoring platforms enhances compliance management in real time. Retrofitting projects across older refineries and chemical complexes further fuel demand, as companies work to meet upcoming air quality directives.
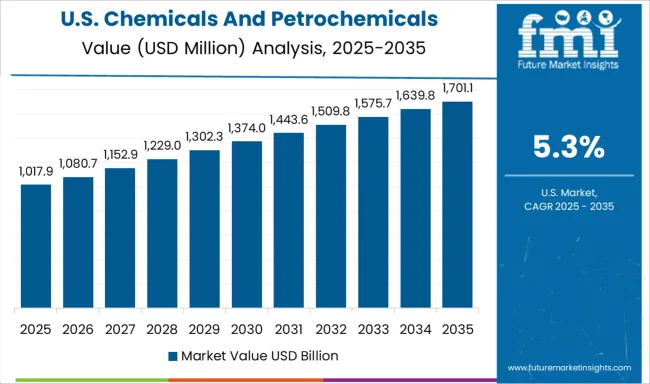
The United States is expected to grow at a CAGR of 5.3% through 2035, supported by implementation of federal emission standards and technological upgrades in petrochemical plants. The adoption of wet and hybrid ESP systems is expanding, especially in chemical processes involving acid mist and fine particulate control. Manufacturers are emphasizing energy-efficient ESP configurations combined with IoT-based diagnostics, enabling predictive maintenance and cost optimization. Investment in greenfield petrochemical projects and modernization of older plants contributes to steady demand for electrostatic precipitators across the US market. Partnerships between ESP technology providers and environmental compliance firms enhance long-term growth prospects.
The chemicals and petrochemicals electrostatic precipitator (ESP) market is led by prominent industrial equipment manufacturers such as Babcock & Wilcox Enterprises, Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, and the Dürr Group, alongside other major contributors including GE Energy, GEA Group, FLSmidth, and KC Cottrell. Babcock & Wilcox maintains a strong foothold with advanced ESP solutions engineered for large-scale emission control, integrating high-efficiency collection systems tailored for chemical and petrochemical processing facilities. Mitsubishi Heavy Industries emphasizes energy-efficient designs and modular ESP systems optimized for high-dust environments, ensuring compliance with stringent emission regulations. Dürr Group leverages its expertise in industrial air pollution control systems to deliver customized ESP units integrated with smart monitoring for real-time performance optimization. GE Energy and GEA Group focus on supplying scalable ESP systems compatible with multiple chemical processing operations, while FLSmidth and KC Cottrell strengthen their competitive positions by offering turnkey solutions, including design, installation, and after-sales maintenance services. Competitive differentiation revolves around collection efficiency, adaptability to corrosive environments, and integration of digital monitoring platforms for predictive maintenance.
Entry barriers remain high due to technological complexity, regulatory requirements, and significant capital investment needed for manufacturing and installation. Future market growth will be influenced by increasingly strict environmental regulations, rising chemical production capacity, and demand for energy-efficient pollution control technologies. Companies investing in advanced control systems, IoT-enabled monitoring, and hybrid ESP designs that combine filtration technologies for superior particle capture will secure long-term advantages.
On June 26, 2024, Babcock & Wilcox announced securing over $18 million in contracts to design and supply wet and dry electrostatic precipitator rebuilds for utility and industrial facilities in the U.S. and Europe, supporting particulate emissions control in sectors including petrochemical, power, and waste-to-energy industries.
| Item | Value |
|---|---|
| Quantitative Units | USD 2.2 Billion |
| Design | Plate and Tubular |
| System | Dry and Wet |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America, Middle East & Africa |
| Country Covered | United States, Canada, Germany, France, United Kingdom, China, Japan, India, Brazil, South Africa |
| Key Companies Profiled | Babcock and Wilcox Enterprises, Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, DÜRR Group, and GE Energy / GEA Group / FLSmidth / KC Cottrell / Others |
| Additional Attributes | Dollar sales by ESP type (dry ESP, wet ESP) and application (chemical manufacturing, petrochemical processing, fertilizer production), driven by regulatory compliance and the need for improved air quality in industrial zones. Regional dynamics highlight strong demand in Asia-Pacific due to rapid chemical industry expansion, while North America and Europe focus on upgrading existing emission control infrastructure. Innovation trends include digitalized performance monitoring, modular ESP designs for retrofit installations, and development of corrosion-resistant materials to extend equipment lifespan in harsh operating conditions. |
The global chemicals and petrochemicals electrostatic precipitator market is estimated to be valued at USD 2.2 billion in 2025.
The market size for the chemicals and petrochemicals electrostatic precipitator market is projected to reach USD 4.0 billion by 2035.
The chemicals and petrochemicals electrostatic precipitator market is expected to grow at a 6.2% CAGR between 2025 and 2035.
The key product types in chemicals and petrochemicals electrostatic precipitator market are plate and tubular.
In terms of system, dry segment to command 86.0% share in the chemicals and petrochemicals electrostatic precipitator market in 2025.






Our Research Products

The "Full Research Suite" delivers actionable market intel, deep dives on markets or technologies, so clients act faster, cut risk, and unlock growth.

The Leaderboard benchmarks and ranks top vendors, classifying them as Established Leaders, Leading Challengers, or Disruptors & Challengers.

Locates where complements amplify value and substitutes erode it, forecasting net impact by horizon

We deliver granular, decision-grade intel: market sizing, 5-year forecasts, pricing, adoption, usage, revenue, and operational KPIs—plus competitor tracking, regulation, and value chains—across 60 countries broadly.

Spot the shifts before they hit your P&L. We track inflection points, adoption curves, pricing moves, and ecosystem plays to show where demand is heading, why it is changing, and what to do next across high-growth markets and disruptive tech

Real-time reads of user behavior. We track shifting priorities, perceptions of today’s and next-gen services, and provider experience, then pace how fast tech moves from trial to adoption, blending buyer, consumer, and channel inputs with social signals (#WhySwitch, #UX).

Partner with our analyst team to build a custom report designed around your business priorities. From analysing market trends to assessing competitors or crafting bespoke datasets, we tailor insights to your needs.
Supplier Intelligence
Discovery & Profiling
Capacity & Footprint
Performance & Risk
Compliance & Governance
Commercial Readiness
Who Supplies Whom
Scorecards & Shortlists
Playbooks & Docs
Category Intelligence
Definition & Scope
Demand & Use Cases
Cost Drivers
Market Structure
Supply Chain Map
Trade & Policy
Operating Norms
Deliverables
Buyer Intelligence
Account Basics
Spend & Scope
Procurement Model
Vendor Requirements
Terms & Policies
Entry Strategy
Pain Points & Triggers
Outputs
Pricing Analysis
Benchmarks
Trends
Should-Cost
Indexation
Landed Cost
Commercial Terms
Deliverables
Brand Analysis
Positioning & Value Prop
Share & Presence
Customer Evidence
Go-to-Market
Digital & Reputation
Compliance & Trust
KPIs & Gaps
Outputs
Full Research Suite comprises of:
Market outlook & trends analysis
Interviews & case studies
Strategic recommendations
Vendor profiles & capabilities analysis
5-year forecasts
8 regions and 60+ country-level data splits
Market segment data splits
12 months of continuous data updates
DELIVERED AS:
PDF EXCEL ONLINE
Biochemicals Control Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Oxo Chemicals Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Soy Chemicals Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Fine Chemicals Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Zinc Chemicals Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Green Chemicals Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Fluorochemicals Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Paper Chemicals Market Growth – Trends & Forecast 2023-2033
Leather Chemicals Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Roofing Chemicals Market Size & Trends 2025 to 2035
Sulphur Chemicals Market
Cosmetic Chemicals Market Growth - Trends & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Membrane Chemicals Market Growth - Trends & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Aluminum Chemicals Market Growth & Demand 2025 to 2035
Oilfield Chemicals Market Report - Growth, Demand & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Pickling Chemicals Market Growth - Trends & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Polishing Chemicals Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Oral Care Chemicals Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Precision Chemicals Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Specialty Chemicals Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035

Thank you!
You will receive an email from our Business Development Manager. Please be sure to check your SPAM/JUNK folder too.
Chat With
MaRIA