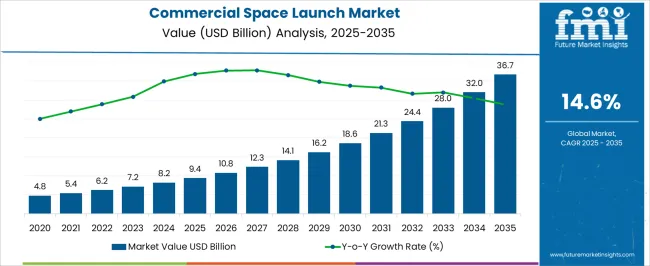
The commercial space launch market is estimated to be valued at USD 9.4 billion in 2025 and is projected to reach USD 36.7 billion by 2035, registering a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 14.6% over the forecast period.
In the early years leading up to 2025, the market value grows steadily from USD 4.8 billion in 2020, driven by satellite deployment for broadband and Earth observation, with established entities like SpaceX and Arianespace securing dominant shares. Between 2026 and 2030, the market accelerates from USD 10.8 billion to USD 18.6 billion, marking a clear redistribution of share where new entrants from Asia and private firms narrow the dominance of early leaders. By 2030, share erosion is observed among traditional operators due to cost competition, reusability, and small satellite launch providers gaining traction.
From 2031 to 2035, growth surges from USD 21.3 billion to USD 36.7 billion, consolidating share gains for reusable launch vehicle developers and firms offering bundled services for satellite integration and in-orbit servicing. Market gains favor companies leveraging economies of scale and diversified payload portfolios, while erosion impacts players unable to adapt to price-sensitive satellite customers. Overall, the decade highlights significant market share redistribution with net gains concentrated among innovators in reusability and cost efficiency.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Commercial Space Launch Market Estimated Value in (2025 E) | USD 9.4 billion |
| Commercial Space Launch Market Forecast Value in (2035 F) | USD 36.7 billion |
| Forecast CAGR (2025 to 2035) | 14.6% |
The commercial space launch market holds a prominent position within the broader space transportation and launch services sector, representing approximately 25–28% of the global space launch ecosystem, driven by increasing private investment and demand for satellite deployment services. Within the overall aerospace and space exploration segment, commercial launches account for around 18–20%, fueled by rapid adoption of small and medium satellite constellations, remote sensing, telecommunications, and Earth observation applications. In the global satellite services and orbital infrastructure sector, the market commands an estimated 12–15% share, reflecting rising reliance on private launch providers such as SpaceX, Blue Origin, Rocket Lab, and Arianespace for cost-efficient and flexible access to low Earth orbit (LEO) and geostationary transfer orbit (GTO). Growth is supported by government and commercial partnerships, technological improvements in reusable launch vehicles, and increasing demand for mega-constellations supporting broadband connectivity, IoT, and defense applications.
Despite regulatory approvals, launch site limitations, and capital-intensive R&D requirements posing challenges, the market has seen strong momentum through international collaborations, investment inflows, and emerging launch hubs in Asia-Pacific and North America. With growing reliance on space-based infrastructure for communications, navigation, and Earth observation, commercial space launches continue to strengthen their critical role within the aerospace value chain globally.
The market is undergoing significant expansion, driven by the rising demand for satellite deployments, advancements in reusable launch technologies, and increased private sector participation in space exploration. Growing investments in communication, navigation, and Earth observation infrastructure have strengthened the demand for cost-efficient and reliable launch solutions.
The evolution of heavy-lift launch vehicles, capable of carrying large and complex payloads, has widened the scope of commercial missions, including crewed spaceflights and deep space exploration. Furthermore, the increasing adoption of Low Earth Orbit deployments for telecommunications and broadband services is creating consistent demand for high-frequency, rapid turnaround launch capabilities.
Supportive government policies, strategic public-private partnerships, and competitive pricing models are fostering market accessibility for emerging space enterprises With technological innovations reducing launch costs and improving payload efficiency, the sector is expected to witness sustained growth, positioning commercial space launches as a cornerstone of the global space economy over the coming years.
The commercial space launch market is segmented by payload type, launch vehicle type, orbit type, end use, and geographic regions. By payload type, commercial space launch market is divided into Satellites, Cargo & logistics, Human spaceflight, and Interplanetary missions. In terms of launch vehicle type, commercial space launch market is classified into Heavy-lift launch vehicles (> 20,000 kg), Small-lift launch vehicles (< 2,000 kg), and Medium-lift launch vehicles (2,000–20,000 kg). Based on orbit type, commercial space launch market is segmented into Low earth orbit (LEO), Geostationary orbit (GEO), Medium earth orbit (MEO), Polar & sun-synchronous orbit (SSO), and Deep space. By end use, commercial space launch market is segmented into Private satellite operators, Government-commercial partnerships, Space tourism companies, Research & academic institutions, and Defense & military. Regionally, the commercial space launch industry is classified into North America, Latin America, Western Europe, Eastern Europe, Balkan & Baltic Countries, Russia & Belarus, Central Asia, East Asia, South Asia & Pacific, and the Middle East & Africa.
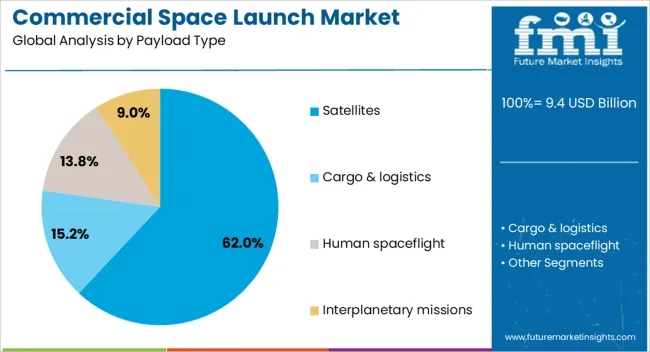
The satellites payload type segment is projected to hold 62% of the market revenue share in 2025, making it the dominant payload category. This leadership position has been driven by the surge in demand for satellite-based services, including communication, navigation, weather monitoring, and Earth observation. Increasing reliance on satellite constellations for global internet coverage and advanced imaging capabilities has significantly boosted launch frequency requirements.
The ability to deploy multiple satellites in a single mission, enabled by advancements in launch vehicle capacity and precision deployment systems, has further enhanced market efficiency. The segment has also benefited from the miniaturization of satellite components, allowing for higher payload density and diversified mission profiles.
Rising investment from private satellite operators and national space agencies has reinforced this growth trajectory As satellite networks continue to expand for both commercial and scientific applications, the dominance of this segment is expected to remain firmly established.
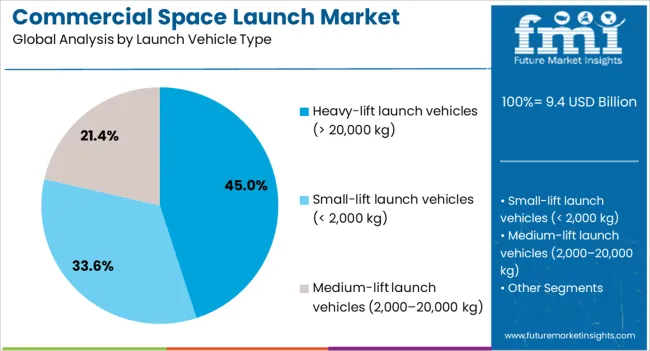
The heavy-lift launch vehicles segment is expected to account for 45% of the market revenue share in 2025, positioning it as the leading launch vehicle type. This growth has been supported by the increasing need to transport large and complex payloads, including space station modules, interplanetary probes, and high-capacity satellite constellations. Heavy-lift vehicles offer unmatched payload capacity, enabling single-launch missions that reduce operational complexity and cost per kilogram.
Technological advancements in reusable booster systems have significantly lowered launch costs while improving turnaround times. These capabilities have attracted both government and private sector missions, particularly those involving deep space exploration and mega-constellation deployments.
The flexibility to carry diverse payloads across various orbits has further strengthened the segment’s market position With continued innovation in propulsion systems and materials engineering, heavy-lift launch vehicles are anticipated to remain a preferred solution for high-demand, high-value space missions.
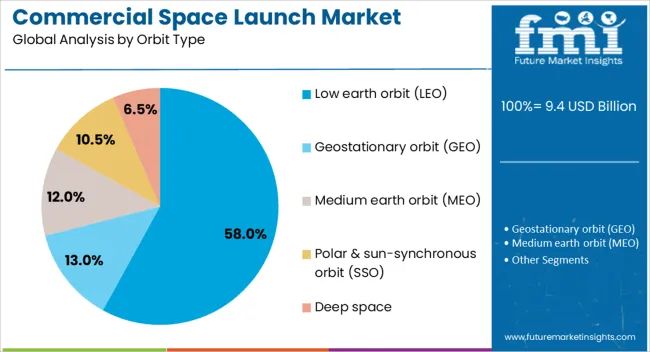
The low Earth orbit (LEO) segment is projected to capture 58% of the market revenue share in 2025, making it the leading orbit type. This dominance has been driven by the increasing deployment of satellite constellations for broadband internet, Earth imaging, and scientific research. The proximity of LEO to Earth allows for reduced latency in communication services and improved imaging resolution, making it highly attractive for both commercial and governmental applications.
The lower energy requirements for reaching LEO compared to higher orbits result in reduced launch costs, enabling more frequent and cost-efficient missions. The segment has also been supported by advancements in small satellite technology, which align well with LEO’s operational characteristics.
Growing demand from industries such as telecommunications, defense, and environmental monitoring continues to reinforce the strategic importance of LEO launches As global connectivity initiatives expand, the segment is expected to maintain its strong market leadership.
The commercial space launch market is being shaped by rising private investments, satellite constellation demand, regulatory support, and advanced payload services. These factors collectively drive sustained growth and strategic adoption globally.
The commercial space launch sector has experienced significant momentum due to growing investments from private players such as SpaceX, Blue Origin, and Rocket Lab. These investments focus on developing reusable launch vehicles, increasing launch frequency, and reducing cost per kilogram of payload. Capital inflows have enabled rapid prototyping, enhanced testing facilities, and strategic partnerships with satellite manufacturers and government agencies. Expansion of venture funding and defense contracts has also contributed to accelerating research and operational capabilities. Emerging companies are entering the market with niche launch solutions for small and medium satellites, fostering competition and stimulating service innovation. These trends have resulted in faster mission timelines, higher reliability rates, and increased adoption of commercial launch services across both civilian and defense segments.
Satellite deployment has become a key driver of commercial space launch growth, particularly with the proliferation of mega-constellations for broadband, IoT, and Earth observation. Companies are increasingly outsourcing orbital insertion to private launch providers to meet strict deployment schedules. The need for rapid, reliable, and frequent launches has prompted service enhancements such as multi-payload integration, rideshare missions, and dedicated launch windows. Rising investments in communication networks and remote sensing applications have made commercial launch services indispensable for both government and private entities. Expansion in space-based data applications, including geospatial analytics and environmental monitoring, is generating higher payload volumes. These factors collectively contribute to sustained growth and the strategic value of commercial launch providers.
Regulatory frameworks and cross-border collaborations play a central role in commercial space launch operations. Compliance with national aerospace authorities, orbital licensing, and safety regulations ensures operational continuity and market credibility. International partnerships facilitate access to emerging launch sites, joint R&D programs, and satellite sharing agreements. Governments are increasingly supporting commercial operators through launch subsidies, tax incentives, and collaborative satellite programs. Export controls, environmental assessments, and spectrum allocations are critical for market access and timely mission execution. The regulatory environment not only safeguards operations but also influences investment decisions, enabling global service expansion while maintaining adherence to safety and operational standards. Efficient licensing and approvals have become differentiators in competitive positioning.
The sector continues to see service diversification through enhanced payload management, mission customization, and integration of specialized launch vehicles. Providers are offering end-to-end solutions, including pre-launch preparation, in-orbit deployment, and post-launch tracking, to reduce complexity for satellite operators. Innovations in modular payload adapters, rapid integration protocols, and rideshare scheduling have improved turnaround times and operational efficiency. Increasing demand for tailored mission planning, orbital insertion precision, and multi-orbit deployment strategies has further boosted service adoption. Advanced analytics and simulation tools are being used to optimize launch sequences and minimize risk, making commercial launches more predictable and cost-effective. These developments strengthen the appeal of commercial launch providers to both defense and civilian clients.
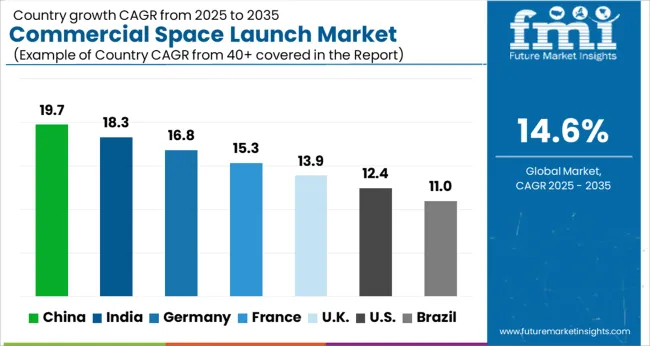
| Country | CAGR |
|---|---|
| China | 19.7% |
| India | 18.3% |
| Germany | 16.8% |
| France | 15.3% |
| UK | 13.9% |
| USA | 12.4% |
| Brazil | 11.0% |
The commercial space launch market is projected to grow globally at a CAGR of 14.6% between 2025 and 2035, fueled by increasing satellite deployments, private aerospace investments, and reusable launch vehicle adoption. China leads with a CAGR of 16.8%, propelled by government-backed space programs, expanding satellite constellations, and domestic launch vehicle development. India follows at 15.7%, supported by growing private sector participation, regional satellite demand, and cost-effective launch services. France records 14.2%, benefiting from European space agency collaborations, innovation in small satellite launch systems, and partnerships with private operators. The United Kingdom grows at 13.8%, shaped by commercial satellite ventures and spaceport expansions, while the United States posts 12.9%, reflecting established aerospace infrastructure, frequent orbital missions, and private sector-led reusable launch initiatives. The analysis spans over 40 countries, with these five serving as benchmarks for investment planning, service adoption, and operational expansion in the global commercial space launch sector.
China is forecasted to post a CAGR of 19.7% for 2025–2035, improving from about 16.4% recorded between 2020–2024, outpacing the global average of 14.6%. The early phase of growth was shaped by steady expansion of satellite launches, state-backed funding, and initial strides in reusable launch vehicles. In the next decade, expansion is expected to be driven by mega-constellations, government–private partnerships, and expanding capacity at new launch sites. Collaborations with global clients for commercial launches, combined with an aggressive push into lunar and Mars missions, are also enhancing the trajectory. Such advances position China as the largest growth hub in the commercial launch industry.
India is projected to grow at a CAGR of 18.3% during 2025–2035, rising from 15.2% between 2020–2024, maintaining its momentum as a cost-efficient launch hub. Earlier growth was largely supported by ISRO-led satellite deployments and collaborations with universities and small payload operators. Post-2024, a surge in private space startups, government incentives for commercialization, and growing demand for regional communication satellites are driving acceleration. India’s competitive pricing and reliable PSLV/GSLV launch vehicles remain critical differentiators. Spaceport expansion in Andhra Pradesh and partnerships with global companies ensure that India emerges as a central player in the global small- and medium-satellite launch market.
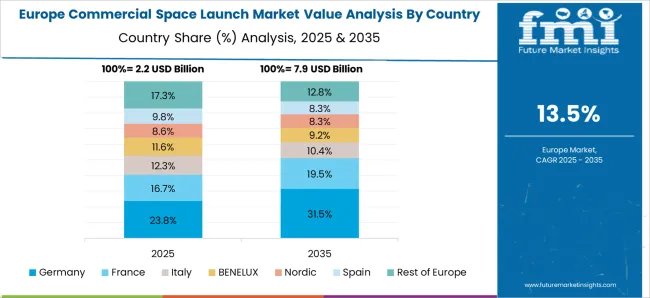
France is set to achieve a CAGR of 15.3% between 2025–2035, rising from around 12.9% during 2020–2024, in line with broader European initiatives. Early progress was shaped by ArianeGroup’s role in ESA-led programs and selective private launches. The sharper rise in the next decade is attributed to demand for mini-launch vehicles, orbital rideshare services, and support for defense-focused satellite programs. Increased funding for reusable vehicle R&D and upgrades at the Guiana Space Centre further contribute to long-term acceleration. France’s close integration within the European Union’s space strategy ensures a steady pipeline of commercial launches, making it a vital player in the global launch ecosystem.
The United Kingdom is forecasted to post a CAGR of 13.9% during 2025–2035, higher than the 11.5% achieved during 2020–2024, reflecting a rise above the global 14.6% benchmark. Early growth was shaped by small satellite launches supported by university programs and collaboration with European contractors. Moving forward, the establishment of spaceports in Scotland and Cornwall, coupled with strong government support for CubeSat launches, is fueling adoption. The UK’s focus on defense-related payloads and expansion into Earth observation and navigation satellites further contributes to its growth. Partnerships with USA and European launch providers are enhancing technology transfer and boosting competitiveness.
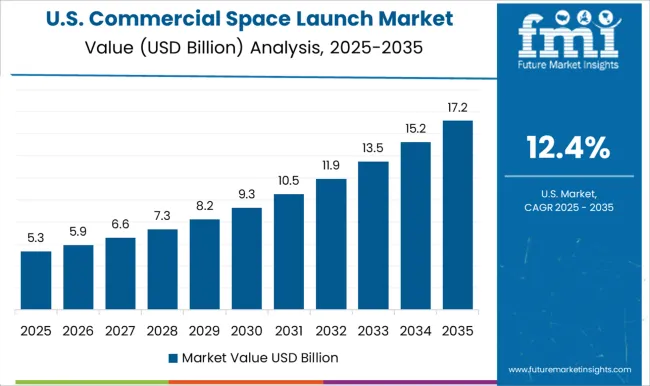
The United States is expected to grow at a CAGR of 12.4% from 2025–2035, compared with 10.6% between 2020–2024, reflecting steady but mature growth. Earlier momentum came from SpaceX’s reusable rockets and NASA partnerships that created confidence in commercial launch reliability. Post-2024, demand from mega-constellations, Mars exploration programs, and increasing DoD investments are expected to maintain adoption. While the USA market is relatively mature, further acceleration is expected through greater satellite rideshare services, growth in private satellite internet programs, and improved integration of defense applications. Its large-scale infrastructure and strong commercial sector presence ensure its continued dominance in global launches.
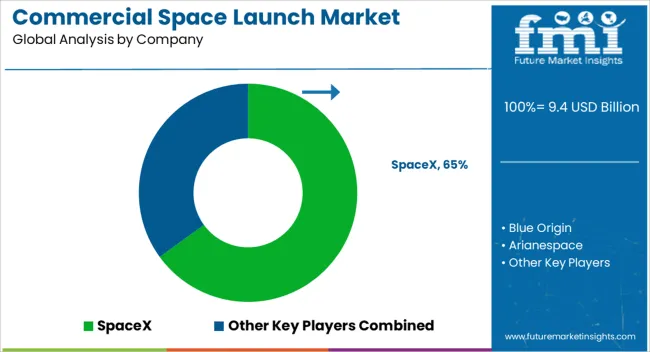
The commercial space launch market is defined by intense competition among global leaders and specialized launch providers, each focusing on cost efficiency, reusable technologies, and diversified payload services. SpaceX dominates with its Falcon 9 and Falcon Heavy reusable rockets, offering unmatched launch cadence, cost reductions, and reliability for satellite constellations and interplanetary missions. Blue Origin emphasizes reusable vertical launch systems, with its New Glenn vehicle targeting both satellite and human spaceflight, backed by strong private investment. Arianespace maintains a leading role in Europe with its Ariane and Vega launchers, specializing in commercial satellites and institutional missions. United Launch Alliance (ULA) focuses on government and defense payloads, leveraging its Atlas V and upcoming Vulcan Centaur for heavy-lift reliability. Rocket Lab has built a strong position in small satellite launches with its Electron vehicle, while its larger Neutron rocket aims at expanding into medium payload markets.
China Aerospace firms, including CASC, continue to scale rapidly with Long March rockets, focusing on state programs and commercial launches, supported by growing domestic demand. The competitive environment is driven by lower launch costs, rapid deployment cycles, and expanding demand for small- to mega-constellations. Strategies include advancing reusable rockets, securing long-term contracts with governments and private satellite operators, and developing diversified orbital access solutions. Future competitiveness will hinge on balancing reliability, scalability, and innovation while meeting the increasing demand for global satellite connectivity and space exploration missions.
| Item | Value |
|---|---|
| Quantitative Units | USD 9.4 Billion |
| Payload Type | Satellites, Cargo & logistics, Human spaceflight, and Interplanetary missions |
| Launch Vehicle Type | Heavy-lift launch vehicles (> 20,000 kg), Small-lift launch vehicles (< 2,000 kg), and Medium-lift launch vehicles (2,000–20,000 kg) |
| Orbit Type | Low earth orbit (LEO), Geostationary orbit (GEO), Medium earth orbit (MEO), Polar & sun-synchronous orbit (SSO), and Deep space |
| End Use | Private satellite operators, Government-commercial partnerships, Space tourism companies, Research & academic institutions, and Defense & military |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America, Middle East & Africa |
| Country Covered | United States, Canada, Germany, France, United Kingdom, China, Japan, India, Brazil, South Africa |
| Key Companies Profiled | SpaceX, Blue Origin, Arianespace, United Launch Alliance (ULA), Rocket Lab, and China Aerospace (various firms) |
| Additional Attributes | Dollar sales, share, CAGR, satellite launch demand by segment, government vs private contracts, reusable launch economics, regional growth hubs, competitive positioning, and investment opportunities in new spaceports. |
The global commercial space launch market is estimated to be valued at USD 9.4 billion in 2025.
The market size for the commercial space launch market is projected to reach USD 36.7 billion by 2035.
The commercial space launch market is expected to grow at a 14.6% CAGR between 2025 and 2035.
The key product types in commercial space launch market are satellites, cargo & logistics, human spaceflight and interplanetary missions.
In terms of launch vehicle type, heavy-lift launch vehicles (> 20,000 kg) segment to command 45.0% share in the commercial space launch market in 2025.






Full Research Suite comprises of:
Market outlook & trends analysis
Interviews & case studies
Strategic recommendations
Vendor profiles & capabilities analysis
5-year forecasts
8 regions and 60+ country-level data splits
Market segment data splits
12 months of continuous data updates
DELIVERED AS:
PDF EXCEL ONLINE
Commercial Water Heater Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Commercial High-Speed Oven Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Commercial Turboprop Aircrafts Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Commercial Vehicle Foundation Brakes Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Commercial Vehicle Brake Chambers Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Commercial Vehicles LED Bar Lights Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Commercial Vehicle AMT Transmission Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Commercial Greenhouse Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Commercial Vessel Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Commercial Slush Machine Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Commercial Medium Voltage Distribution Panel Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Commercial Earth Observation (CEO) Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Commercial Ozone Generator Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Commercial Gas-Fired Boiler Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Commercial Deep Fryer Parts & Accessories Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Commercial Gas Restaurant Ranges Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Commercial Heat Pump Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Commercial Countertop Ranges Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Commercial Electric Restaurant Ranges Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Commercial Distribution Panel Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035

Thank you!
You will receive an email from our Business Development Manager. Please be sure to check your SPAM/JUNK folder too.
Chat With
MaRIA