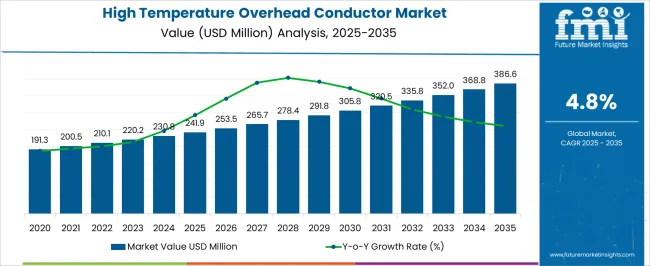
The high temperature overhead conductor (HTOC) market is expected to grow from USD 241.9 million in 2025 to USD 386.6 million by 2035, registering a 4.8% CAGR and generating an absolute dollar opportunity of USD 144.7 million. Growth is driven by increasing electricity demand, modernization of transmission networks, and the need to enhance grid capacity without expanding right-of-way. HTOC systems provide higher current carrying capacity, improved thermal performance, and lower line losses, making them an attractive solution for utilities and industrial power transmission. Market share erosion or gain analysis highlights changing dynamics across regions, product types, and application segments.
North America and Europe currently hold substantial market share due to mature transmission infrastructure and early adoption of high-capacity conductors, but moderate erosion is anticipated as Asia Pacific emerges as the fastest-growing region. China, India, and Southeast Asia are expected to gain significant share driven by rapid urbanization, industrial growth, and large-scale grid expansion projects. Aluminum-based high temperature conductors are likely to capture additional share from conventional copper lines due to lower weight, cost efficiency, and thermal advantages.
On the application front, utility-scale transmission projects are poised to gain share relative to industrial distribution, supported by increasing investment in renewable integration and grid modernization. The USD 144.7 million opportunity reflects regional expansion, product innovation, and shifting adoption patterns between 2025 and 2035.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| High Temperature Overhead Conductor Market Estimated Value in (2025 E) | USD 241.9 million |
| High Temperature Overhead Conductor Market Forecast Value in (2035 F) | USD 386.6 million |
| Forecast CAGR (2025 to 2035) | 4.8% |
The high temperature overhead conductor (HTOC) market is primarily driven by the power transmission and distribution sector, which accounts for approximately 50% of the market share, as utilities upgrade lines to handle higher loads and improve grid reliability. Industrial energy users contribute around 20%, adopting HTOCs to support large-scale manufacturing and process operations. Renewable energy projects, including wind and solar farms, represent nearly 15%, using high-capacity conductors to efficiently transmit power from remote generation sites.
The transportation and railway sector accounts for roughly 10%, integrating HTOCs for electrified lines and urban transit systems. The remaining 5% comes from mining and heavy infrastructure projects that require durable, high-capacity conductors in challenging environments. The HTOC market is advancing with innovations in conductor materials, design, and installation technology. Aluminum composite cores, advanced alloys, and reinforced materials are being adopted to increase current-carrying capacity and reduce sag under high temperatures. Modular and lightweight conductor designs are improving ease of installation and maintenance.
Integration with smart grid monitoring systems enables real-time line performance tracking and predictive maintenance. Strategic partnerships between utilities, manufacturers, and engineering firms are expanding deployment in urban, industrial, and renewable energy projects. Rising demand for reliable electricity, grid modernization, and higher energy transfer efficiency continue to drive market adoption globally.
The high temperature overhead conductor market is expanding steadily, driven by the increasing need for efficient and reliable power transmission infrastructure worldwide. Rising electricity demand, coupled with the modernization of aging power grids, is fueling adoption of conductors that can operate safely at elevated temperatures with improved current-carrying capacity. The market growth is supported by infrastructure investments targeting enhanced grid resilience and reduction of energy losses.
Technological advancements in conductor materials, including improved alloys and composite cores, are increasing durability and thermal performance. Regulatory pressures to minimize power outages and improve grid reliability are encouraging utilities to replace conventional conductors with high temperature variants.
As renewable energy sources continue to penetrate power networks, the requirement for conductors capable of handling variable loads and higher thermal stresses is becoming more pronounced The increasing focus on energy efficiency and system reliability is expected to create further demand for conductors with superior mechanical strength and thermal endurance, positioning the market for sustained growth.
The high temperature overhead conductor market is segmented by product, voltage, rated strength, application, and geographic regions. By product, high temperature overhead conductor market is divided into Tal, ZTAl, and others. In terms of voltage, high temperature overhead conductor market is classified into 132 kV to 220 kV, > 220 kV to 660 kV, and > 660 kV. Based on rated strength, high temperature overhead conductor market is segmented into high strength, extra high strength, and ultra high strength. By application, high temperature overhead conductor market is segmented into high tension, extra high tension, and ultra high tension. Regionally, the high temperature overhead conductor industry is classified into North America, Latin America, Western Europe, Eastern Europe, Balkan & Baltic Countries, Russia & Belarus, Central Asia, East Asia, South Asia & Pacific, and the Middle East & Africa.
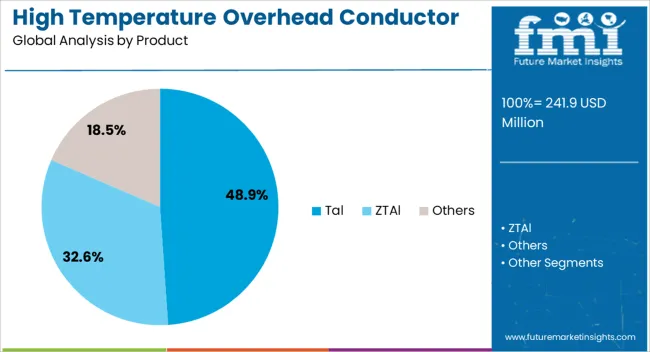
The Tal product segment is forecasted to hold 48.9% of the high temperature overhead conductor market revenue share in 2025, establishing it as the dominant product type. This position is supported by its superior thermal stability and enhanced current-carrying capacity, which allow efficient power transmission even under high operating temperatures.
The segment’s growth is further driven by the increasing adoption of Tal conductors in both urban and rural power grids due to their reliability and reduced sag characteristics. Improved alloy compositions and manufacturing processes have enabled Tal conductors to deliver high mechanical strength and resistance to environmental degradation, including corrosion and fatigue.
These attributes make them well-suited for high-voltage applications where system performance and safety are critical. As utilities prioritize grid upgrades and renewable energy integration, the Tal segment’s ability to meet demanding electrical and mechanical specifications continues to drive its market leadership and revenue growth.
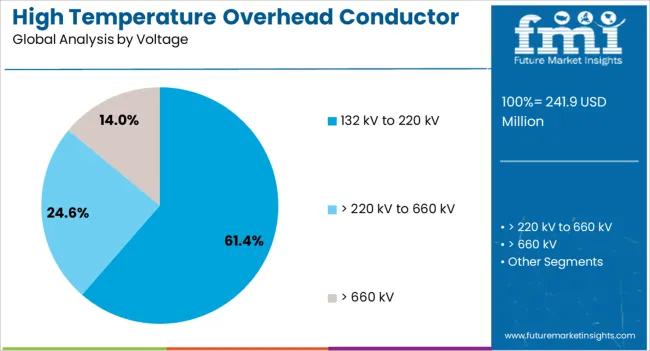
The 132 kV to 220 kV voltage segment is expected to account for 61.4% of the high temperature overhead conductor market revenue share in 2025, making it the leading voltage category. This dominance is attributed to its extensive use in medium to high voltage power transmission networks where balancing efficient energy transfer and infrastructure cost is critical.
The voltage range covers a significant portion of regional and national transmission grids, including sub-transmission systems connecting generation sources to distribution networks. Increasing investments in grid expansion and reinforcement to address growing electricity demand are driving demand for conductors optimized for this voltage class.
High-temperature overhead conductors designed for this range deliver improved thermal performance and load capacity, helping utilities minimize transmission losses and increase reliability. Compliance with grid codes and safety standards requiring enhanced conductor strength and stability further supports adoption in this segment, securing its leadership position in the market.
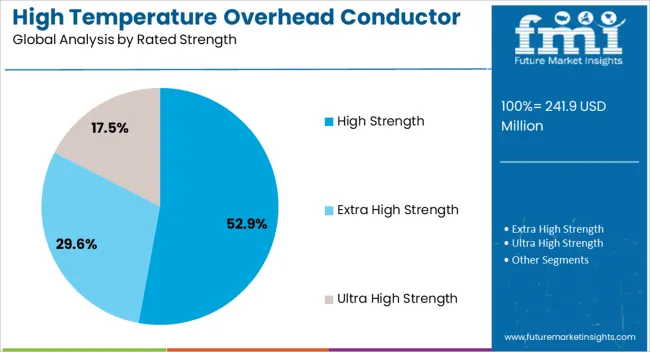
The high strength rated strength segment is projected to hold 52.9% of the high temperature overhead conductor market revenue share in 2025, positioning it as the leading rated strength category. The segment’s growth is being fueled by the demand for conductors capable of withstanding increased mechanical stress due to environmental factors such as high winds, ice loading, and long spans.
High strength conductors provide improved sag control and durability, essential for maintaining transmission line integrity and operational safety. Technological innovations in conductor core materials, including composite and advanced alloy designs, are enhancing tensile strength while allowing for lightweight construction.
This improves installation flexibility and reduces maintenance costs, making high-strength conductors attractive for utilities focused on long-term asset reliability. The segment’s alignment with evolving transmission standards and its suitability for both new installations and retrofits are reinforcing its market dominance, supporting steady revenue growth in the high-temperature overhead conductor market.
The high temperature overhead conductor market is expanding due to rising electricity demand, grid upgrades, and the need to increase transmission capacity. Global revenue exceeded USD 6.4 billion in 2024, with a projected CAGR of 7.8% from 2025 to 2030. Asia Pacific leads with 40% share, driven by China (USD 1.8 billion), India (USD 1.2 billion), and Japan (USD 0.9 billion) focusing on urban and industrial power networks. North America contributes 28% (USD 1.8 billion), primarily the USA, investing in retrofits. Europe accounts for 25% (USD 1.6 billion), led by Germany, France, and UK Advanced aluminum alloys and composite cores support high thermal ratings.
Utilities, industrial facilities, and renewable energy projects account for over 70% of global high temperature overhead conductor adoption. Utility transmission accounts for 40%, supplying high-voltage electricity to metropolitan and industrial zones. Industrial applications represent 20%, including steel plants, chemical refineries, and data centers requiring uninterrupted power. Renewable energy projects contribute 10%, connecting wind farms and solar plants to the grid. Asia Pacific leads with 40% market share, with China investing USD 1.8 billion in transmission projects and India USD 1.2 billion. North America accounts for 28%, while Europe holds 25%. Expanding grid modernization and industrial electrification drive adoption globally.
High temperature overhead conductors are increasingly designed with aluminum conductor composite core (ACCC) technology, achieving 25–30% higher thermal ratings. High-strength steel or composite cores increase span length capacity by 15–20%, reducing sag in long transmission lines. Advanced aluminum alloys improve conductivity by 5–7%, supporting higher current flows. Asia Pacific emphasizes cost-efficient deployment, with China deploying 1,200 km of ACCC lines in 2024 and India 900 km. Europe focuses on lightweight, high-conductivity solutions, installing 750 km of retrofits. North America integrates monitoring systems to track conductor performance, reducing downtime by 12%. These innovations enhance reliability, operational efficiency, and grid capacity globally.
High temperature overhead conductors are increasingly applied in transmission lines (45%), urban distribution (25%), and smart grid integration (10%). Transmission lines support 500–800 kV networks for long-distance electricity flow. Distribution networks utilize high temperature conductors to deliver power to cities and industrial parks with reduced losses. Smart grid projects use sensors and real-time monitoring to optimize load management. Asia Pacific leads with 40% share, with 2,100 km of projects deployed in 2024. Europe contributes 25% (~1,600 km), while North America holds 28% (~1,800 km). Expanding deployment in these sectors strengthens reliability and supports growing electricity demand.
High material costs and regulatory compliance remain barriers. Aluminum alloy and composite core conductors cost USD 30–50 per kg, 15–25% higher than conventional options. Installation requires specialized cranes, tensioning equipment, and trained technicians. Regulatory standards in Europe and North America mandate compliance with environmental, mechanical, and electrical safety norms, adding project complexity. Asia Pacific mitigates costs through local production and mass procurement, e.g., China installed 1,200 km of ACCC lines in 2024. Europe emphasizes certified materials, while North America integrates automated installation and monitoring systems. Despite high performance, elevated costs and compliance requirements remain key adoption constraints.
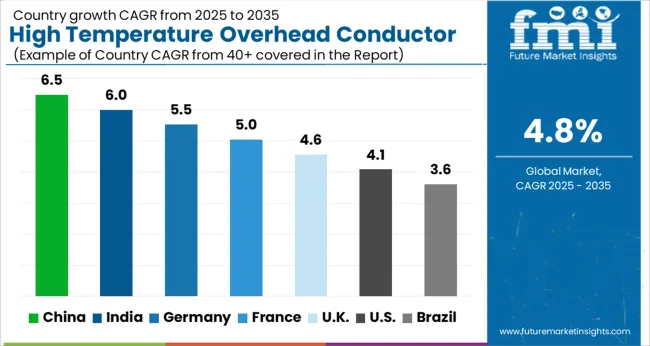
| Country | CAGR |
|---|---|
| China | 6.5% |
| India | 6.0% |
| Germany | 5.5% |
| France | 5.0% |
| UK | 4.6% |
| USA | 4.1% |
| Brazil | 3.6% |
In 2025, the high temperature overhead conductor market is projected to grow at a global CAGR of 4.8% through 2035, driven by increasing demand for efficient power transmission, grid modernization, and industrial electrification. China leads at 6.5%, 35.4% above the global benchmark, supported by BRICS-driven expansion in power infrastructure, urban electrification, and industrial grid projects. India follows at 6.0%, 25% above the global average, reflecting growth in transmission networks, renewable energy integration, and industrial power requirements. Germany records 5.5%, 14.6% above the benchmark, shaped by OECD-driven adoption of advanced conductors, smart grid initiatives, and efficiency-focused energy projects. The United Kingdom posts 4.6%, 4.2% below the global rate, with selective uptake in industrial and utility projects, retrofits, and regional transmission networks. The United States stands at 4.1%, 14.6% below the benchmark, with steady demand in transmission upgrades, industrial electrification, and specialized power infrastructure applications. BRICS economies drive overall market volume, OECD countries emphasize technology and efficiency, while ASEAN nations contribute through expanding grid infrastructure and industrial power demand.
China high temperature overhead conductor market is expanding at a CAGR of 6.5%, above the global 4.8%, supported by increasing electricity demand, grid modernization, and renewable energy integration. The market in China is growing rapidly due to the country’s accelerating investments in power grid modernization and renewable energy integration. Rising electricity demand, driven by urbanization, industrial expansion, and electrification of transport, is pushing utilities to upgrade transmission infrastructure. HTLS conductors enable higher current-carrying capacity without costly tower replacements, making them ideal for China’s dense grid. Additionally, government policies promoting carbon neutrality and reducing transmission losses support adoption. The shift toward ultra-high voltage (UHV) lines and cross-regional power transmission projects further fuels demand, positioning HTLS as a strategic solution for reliable, efficient energy delivery.
India high temperature overhead conductor market is growing at 6.0% CAGR, above the global 4.8%, driven by renewable energy integration, industrial grid expansion, and modernization of existing lines. The market in India is expanding due to the country’s growing power demand, driven by rapid urbanization, industrialization, and rural electrification programs. India’s aging transmission network requires upgrades to handle higher loads without extensive new infrastructure, making HTLS conductors an attractive solution. These conductors allow greater current capacity and reduced transmission losses, supporting integration of large-scale renewable projects, particularly solar and wind. Government initiatives like “Power for All,” investments in smart grids, and green energy corridors further accelerate adoption. Additionally, rising focus on energy efficiency and minimizing right-of-way constraints strengthens HTLS deployment across India’s power sector.
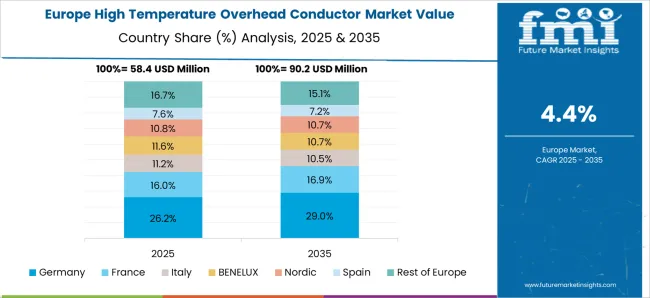
Germany high temperature overhead conductor market is growing at 5.5% CAGR, above the global 4.8%, driven by upgrades of transmission lines for renewable energy and urban infrastructure projects. The market in Germany is growing as the country accelerates its energy transition (Energiewende) and integrates large volumes of renewable energy into the grid. With increasing wind and solar generation, especially from northern regions, Germany faces the challenge of transmitting electricity efficiently across long distances to industrial hubs in the south. HTLS conductors provide higher current-carrying capacity without major tower modifications, reducing congestion and grid losses. Supportive EU regulations, Germany’s commitment to carbon neutrality by 2045, and investments in cross-border interconnections further drive adoption. Additionally, modernization of aging grid infrastructure strengthens market growth.
United Kingdom high temperature overhead conductor market is expanding at 4.6% CAGR, slightly below the global 4.8%, supported by grid modernization and renewable energy integration projects. The market in the U.K. is growing due to increasing electricity demand from electrification of transport, heating, and digital infrastructure, coupled with the rapid expansion of renewable energy projects. As offshore wind and solar generation scale up, the U.K. grid requires enhanced transmission capacity to integrate variable power sources. HTLS conductors provide a cost-effective way to boost line efficiency and capacity without extensive new construction, which aligns with strict land-use and permitting regulations. Government commitments to achieve net-zero emissions by 2050 and investments in grid modernization further drive adoption, ensuring reliable and sustainable power delivery.
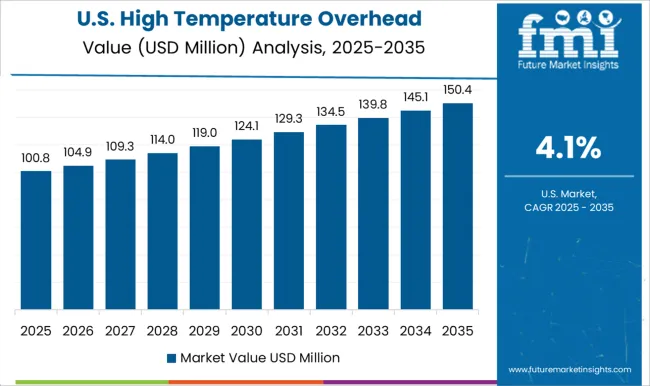
United States high temperature overhead conductor market is growing at 4.1% CAGR, below the global 4.8%, reflecting steady demand from industrial and renewable energy grid expansion projects. The market in the U.S. is growing due to rising electricity demand, driven by electrification of transportation, data centers, and renewable integration. Aging grid infrastructure is under pressure, and utilities are seeking solutions to increase transmission capacity without costly new corridors. HTLS conductors enable higher ampacity and reduced line losses, making them ideal for grid upgrades. Federal investments in infrastructure, clean energy transition policies, and resilience against extreme weather events further accelerate adoption. Additionally, the expansion of wind and solar projects across states requires efficient long-distance transmission, boosting demand for HTLS in modernizing the U.S. grid.
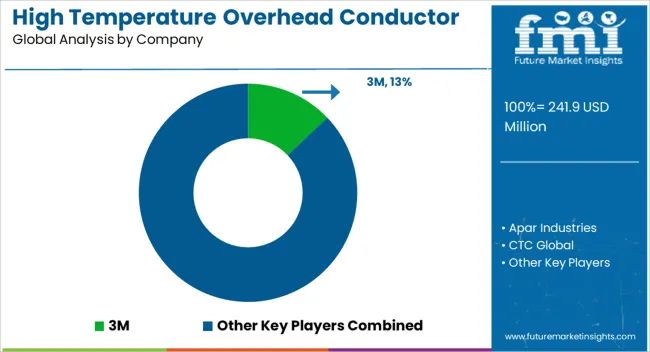
The high temperature overhead conductor market is highly competitive, driven by growing demand for efficient power transmission, grid modernization, and renewable energy integration. Market competition is shaped by conductor type (ACSR, ACSS, ACCC, and composite core), thermal capacity, tensile strength, corrosion resistance, cost, and installation efficiency. Companies differentiate through advanced alloy materials, enhanced conductivity, lightweight designs, and superior heat tolerance that improve energy efficiency and reduce transmission losses.
Key players such as Prysmian Group, Nexans, Southwire Company, Sumitomo Electric Industries, LS Cable & System, Brugg Kabel, General Cable (Now part of Prysmian), ABB, Jiangsu Zhongtian Technology, and Shandong Taikai Power Engineering dominate the market by offering high-performance, durable, and technologically advanced conductors. Strategic collaborations with utilities, EPC contractors, and regional distributors are leveraged to expand market presence. Regional and emerging manufacturers compete by providing cost-effective, customizable, and climate-resilient conductor solutions. The market is moderately consolidated, with leading players focusing on innovation, material optimization, regulatory compliance, and long-term service agreements to maintain market share and support the growing demand for reliable, high-temperature transmission lines.
| Item | Value |
|---|---|
| Quantitative Units | USD 241.9 million |
| Product | Tal, ZTAl, and Others |
| Voltage | 132 kV to 220 kV, > 220 kV to 660 kV, and > 660 kV |
| Rated Strength | High Strength, Extra High Strength, and Ultra High Strength |
| Application | High Tension, Extra High Tension, and Ultra High Tension |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America, Middle East & Africa |
| Country Covered | United States, Canada, Germany, France, United Kingdom, China, Japan, India, Brazil, South Africa |
| Key Companies Profiled | 3M, Apar Industries, CTC Global, Elsewedy Electric, Hendrix Wire and Cable, J-Power Systems, Kec International, Lamifil, Nexans, Prysmian Group, Southwire Company, Sterlite Power, Sumitomo Electric Industries, SWCC Showa Holdings, and Trefinasa |
| Additional Attributes | Dollar sales by conductor type and end use, demand dynamics across power transmission and distribution, regional trends in grid modernization, innovation in heat resistance, conductivity, and mechanical strength, environmental impact of production and disposal, and emerging use cases in renewable integration and smart grid applications. |
The global high temperature overhead conductor market is estimated to be valued at USD 241.9 million in 2025.
The market size for the high temperature overhead conductor market is projected to reach USD 386.6 million by 2035.
The high temperature overhead conductor market is expected to grow at a 4.8% CAGR between 2025 and 2035.
The key product types in high temperature overhead conductor market are tal, ztal and others.
In terms of voltage, 132 kv to 220 kv segment to command 61.4% share in the high temperature overhead conductor market in 2025.






Full Research Suite comprises of:
Market outlook & trends analysis
Interviews & case studies
Strategic recommendations
Vendor profiles & capabilities analysis
5-year forecasts
8 regions and 60+ country-level data splits
Market segment data splits
12 months of continuous data updates
DELIVERED AS:
PDF EXCEL ONLINE
High-performance Dual-core Processor Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
High Purity Magnesium Citrate Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
High Performance Magnet Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
High-frequency RF Evaluation Board Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
High Viscosity Mixer Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
High Voltage Ionising Air Gun Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
High Voltage Equipment Market Forecast and Outlook 2025 to 2035
High Clear Film Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
High Performance Random Packing Market Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
High Precision Microfluidic Pump Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
High Performance Composites Market Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
High Performance Medical Plastic Market Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
High Purity Tungsten Hexachloride Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
High Purity Nano Aluminum Oxide Powder Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
High Mast Lighting Market Forecast and Outlook 2025 to 2035
High-Protein Pudding Market Forecast and Outlook 2025 to 2035
High Voltage Ceramic Zinc Oxide Surge Arrester Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
High-Power Microwave Source Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
High Performance Epoxy Coating Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
High Molecular Ammonium Polyphosphate Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035

Thank you!
You will receive an email from our Business Development Manager. Please be sure to check your SPAM/JUNK folder too.
Chat With
MaRIA