The Japan automotive grade inductor demand is valued at USD 134.6 million in 2025 and is forecasted to reach USD 166.9 million by 2035, recording a CAGR of 2.2%. Demand reflects the steady integration of inductive components in vehicle power electronics, including onboard chargers, DC-DC converters, engine control modules, and infotainment units. Increased utilization in electric and hybrid vehicles supports continued component upgrades that ensure thermal stability, vibration resistance, and high-current handling.
Products in the 1 to 10 microhenry inductance range hold the largest share due to their broad applicability across vehicle electronic architectures. These inductors provide stable current flow, reduced electromagnetic interference, and improved circuit efficiency. Performance improvements focus on miniaturization, high-temperature tolerance, and compliance with automotive quality standards.
Kyushu & Okinawa, Kanto, and Kansai account for the highest volumes due to the presence of automotive manufacturing clusters, Tier-1 suppliers, and electronics assembly operations. Component procurement in these regions reflects established EV production capabilities and investments in advanced automotive electronics. Key suppliers include TDK Corporation, Murata Manufacturing Co., Ltd., Vishay Intertechnology, Inc., Panasonic Corporation, and Taiyo Yuden Co., Ltd. Their product portfolios cover surface-mount and power inductors used in electrified powertrains, safety electronics, and vehicle communication systems.
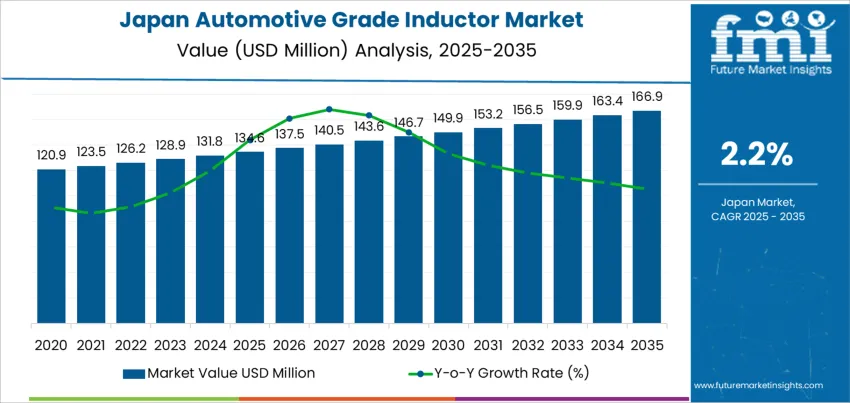
Demand for automotive-grade inductors in Japan follows a phased growth curve shaped by electronics penetration in vehicle platforms. In the early period, growth is supported by advanced driver-assistance systems, infotainment upgrades, and incremental electrification. These features increase the number of inductive components per vehicle, though the scale remains linked to selective adoption in mid-to-high-end models. Early-stage growth is therefore steady but not rapid, grounded in gradual technology integration across domestic automakers.
Late-period dynamics show stronger contribution as electrified mobility becomes more widely embedded in the national fleet. EV power electronics, onboard chargers, DC-DC converters, and battery-management systems expand unit requirements, accelerating the curve. Component reliability standards drive replacement demand within supply chains, further supporting the later phase. Growth moderation may reappear once electrification penetration stabilizes and efficiency engineering reduces component counts. The comparison indicates that the larger share of cumulative expansion is expected in the second half of the decade. The growth curve transitions from electronics-feature adoption to powertrain-centric demand, reflecting a sector moving from incremental enhancement toward accelerated electrification maturity.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Japan Automotive Grade Inductor Sales Value (2025) | USD 134.6 million |
| Japan Automotive Grade Inductor Forecast Value (2035) | USD 166.9 million |
| Japan Automotive Grade Inductor Forecast CAGR (2025-2035) | 2.2% |
Demand for automotive grade inductors in Japan is increasing because vehicles rely on more electronic control systems that require stable power conversion and noise filtering. Hybrid and battery electric vehicles use inductors in onboard chargers, inverters and battery management units, which expands demand as electrification advances. Japanese automakers emphasise compact and efficient designs, so inductors that operate reliably under high heat and vibration conditions are essential for safety and performance.
Advanced driver assistance, infotainment and communication systems add further electronic modules, increasing the number of inductors installed per vehicle. Domestic automotive suppliers invest in next generation power electronics and higher voltage architectures that require inductors with better magnetic characteristics and smaller footprints. Efforts to enhance energy efficiency and reduce emissions reinforce the need for precise control of power electronics that inductors support. Constraints include high development and production costs for advanced materials, certification requirements that extend qualification timelines and competitive pressure to secure stable supply of components during manufacturing cycles. Smaller manufacturers may delay upgrades until platform changes justify new specifications.
Demand for automotive grade inductors in Japan is driven by electrification growth, advanced driver assistance system integration, and stable power regulation requirements in vehicle electronics. Japanese automakers prioritize inductors with high thermal tolerance, vibration resistance, and compact geometries for EV powertrains, onboard chargers, infotainment systems, and safety electronics. Supply chain reliability, compliance with AEC-Q200 standards, and long operational lifecycles remain core purchasing factors for manufacturers operating within Japan’s precision-focused automotive sector.
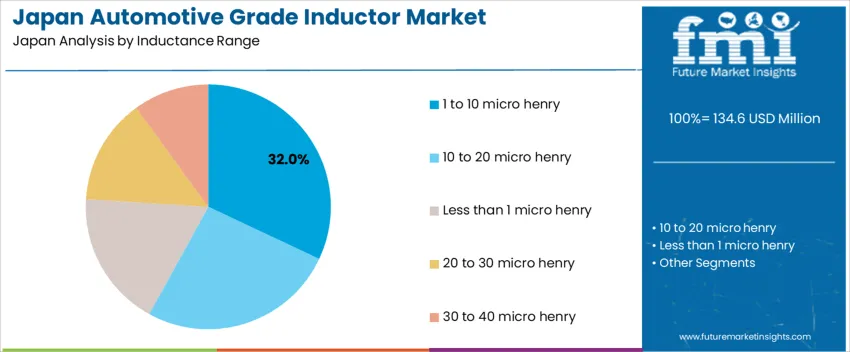
Inductors in the 1 to 10 µH range account for 32.0%, commonly used in DC-DC converters, battery management systems, and LED headlights across Japanese vehicles. They deliver efficient electromagnetic noise suppression while minimizing board space, meeting design constraints in hybrid and electric cars. The 10 to 20 µH segment holds 26.0%, serving infotainment hardware and low-frequency filtering circuits. Less than 1 µH inductors represent 18.0%, typically supporting high-switching power modules and fast response requirements. 20 to 30 µH units contribute 14.0%, while 30 to 40 µH components hold 10.0%, used in specialized drive and actuator controls. Range selection aligns with performance tuning, current capacity, and thermal load tolerance.
Key Points:
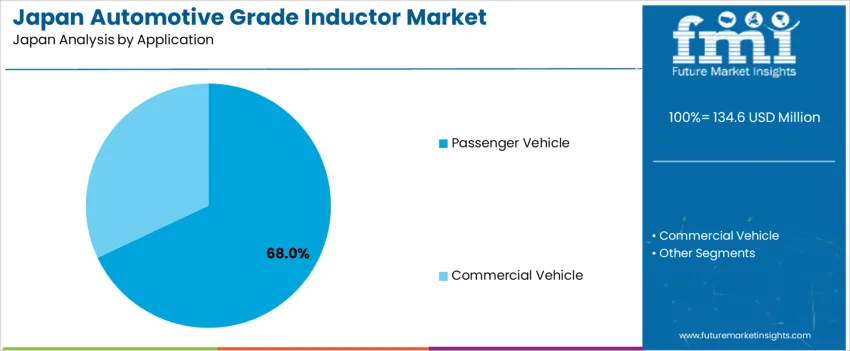
Passenger vehicles hold 68.0%, reflecting Japan’s strong hybrid and electric passenger car production where circuit reliability and compact integration define component use. Inductors enable stable voltage conversion in ADAS sensors, display modules, and active suspension controls. Commercial vehicles represent 32.0%, including buses and delivery fleets adopting electrified powertrains and telematics upgrades. Application trends follow increased electronic content per vehicle, strict emissions reduction goals, and safety-critical system expansion across major Japanese automakers.
Key Points:
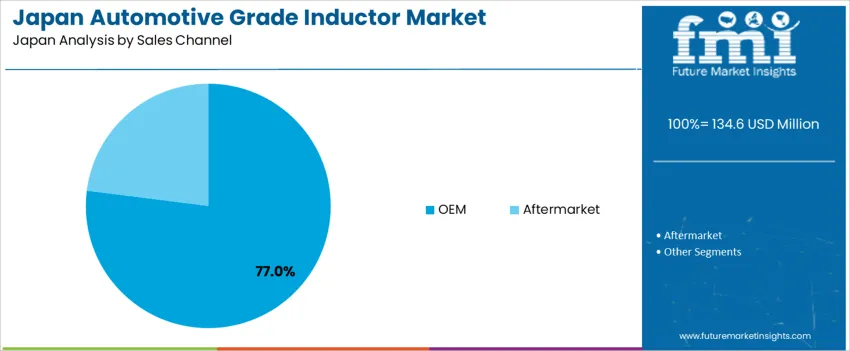
OEM channels account for 77.0%, driven by direct sourcing relationships with tier-1 suppliers to ensure component traceability and adherence to Japanese production specifications. Early design involvement supports precise electrical matching and lifecycle durability testing. The aftermarket holds 23.0%, serving repair and replacement needs for power electronics used in aging transport fleets. The predominant OEM focus reflects Japan’s centralized automotive manufacturing model, emphasizing quality assurance and standardized electronics architecture.
Key Points:
Expansion of electrified vehicle production, increased electronics content in safety systems and strong domestic supply chains for passive components are driving demand.
In Japan, automotive grade inductors benefit from the national shift toward hybrid and battery electric vehicles, which require efficient power conversion in inverters, onboard chargers and DC-DC converters. Major automakers located in Aichi, Tochigi and Hiroshima increase use of inductors in ADAS modules, including cameras and radar systems that demand stable current filtering. Domestic electronics suppliers in regions such as Tochigi and Gunma maintain established manufacturing capacity for passive components used in vehicle body control, engine management and infotainment systems. Japan’s commitment to advanced automotive production supports continuous integration of inductors optimized for thermal stability and vibration resistance in long-life vehicle architectures.
High qualification requirements, long design cycles and sensitivity to import costs for magnetic materials restrain adoption.
Automotive grade inductors must comply with strict reliability and safety standards, which extend validation timelines for new designs across Japanese OEM platforms. Once approved, components remain locked in for several years, slowing rapid transitions to next-generation inductor technologies. Many magnetic materials and wire coatings used in premium inductors rely on imported inputs, exposing manufacturers to exchange-rate volatility that affects pricing. These operational and cost constraints reduce short-term flexibility in design changes and procurement strategies.
Shift toward high-temperature inductors for EV powertrains, increased collaboration with semiconductor suppliers and rising miniaturization for compact vehicle platforms define key trends.
EV platforms require inductors that maintain inductance stability under high heat loads created by fast-charging and high-power drive modules, driving demand for advanced ferrite and metal composite cores. Chip manufacturers and passive-component producers in Japan are collaborating to ensure electromagnetic compatibility between controllers and inductors used in ADAS and body network systems. Kei and mid-size vehicle segments encourage miniaturized components to support limited available space without compromising electrical performance. Pilot projects for autonomous fleet vehicles also prioritize inductors optimized for higher power density and continuous operation in commercial duty cycles. These trends indicate steady and technology-aligned demand for automotive grade inductors across Japan.
Demand for automotive grade inductors in Japan reflects increasing electronic component density per vehicle, support for power conversion in hybrid architectures, and stable procurement cycles linked to tiered automotive suppliers. System reliability, vibration tolerance, and compact packaging influence sourcing decisions. Kyushu & Okinawa leads at 2.7%, followed by Kanto (2.5%), Kansai (2.2%), Chubu (1.9%), Tohoku (1.7%), and the Rest of Japan (1.6%).
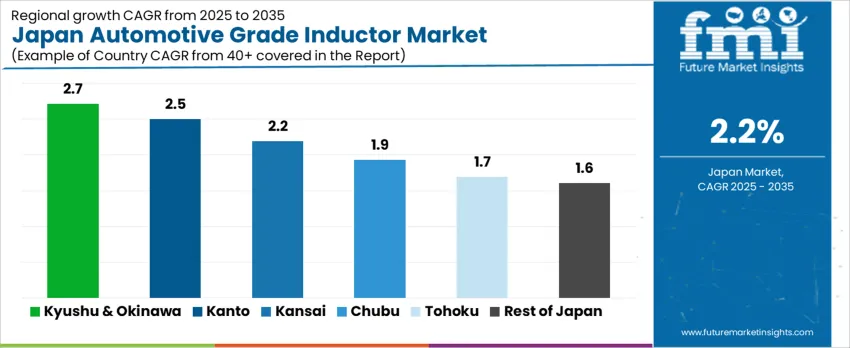
| Region | CAGR (2025-2035) |
|---|---|
| Kyushu & Okinawa | 2.7% |
| Kanto | 2.5% |
| Kansai | 2.2% |
| Chubu | 1.9% |
| Tohoku | 1.7% |
| Rest of Japan | 1.6% |
Kyushu & Okinawa posts 2.7% CAGR, driven by automotive parts production across hubs such as Fukuoka and Kumamoto where inductors are essential for DC-DC conversion, in-vehicle control modules, and noise-filtering in power electronics. Regional suppliers focus on components supporting stable current regulation in compact layouts used in electric sub-systems. Tier-2 manufacturing facilities adopt inductors designed to withstand mechanical vibration from suspension-area placement. Short lead-time procurement supports continuous assembly scheduling as localized production reduces dependence on cross-region shipments. Electrical testing labs validate temperature stability for under-hood placement. Packaging decisions emphasize traceability and solder-joint strength to align with automotive qualification standards. Logistical access to port facilities in Kyushu enables export support.
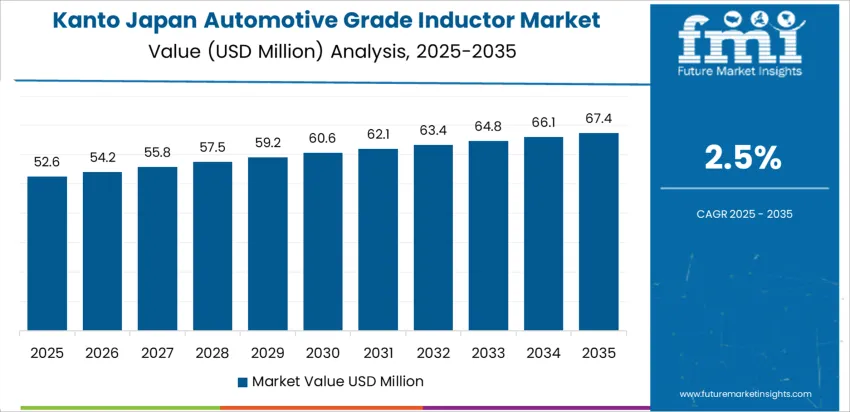
Kanto records 2.5% CAGR, supported by major electronics developers and automotive system integrators operating in Tokyo, Kanagawa, and Saitama. In-vehicle displays, safety controllers, and power steering modules require inductors for signal conditioning and energy conversion stability. Procurement teams prioritize high-reliability surface-mount components that maintain performance through extended duty cycles. Engineering evaluations focus on magnetic core materials that sustain consistent inductance measurements under thermal fluctuation. Production plants adopt packaging suited to automated pick-and-place lines used in high-output electronics manufacturing. E-commerce channels for B2B supply allow technical buyers to source variants meeting exact power ratings.
Kansai posts 2.2% CAGR, driven by automotive electronics manufacturing centered in Osaka and Kobe. Components support functions including body-electronics control, LED lighting drivers, and audio-system noise suppression. Procurement choices emphasize compact shielded inductors that minimize electromagnetic interference in multi-board layouts. Regional suppliers maintain moderate-volume production aligned to diversified automotive programs rather than single-platform dependency. Testing facilities monitor quality characteristics such as saturation current performance across continuous operational loads.
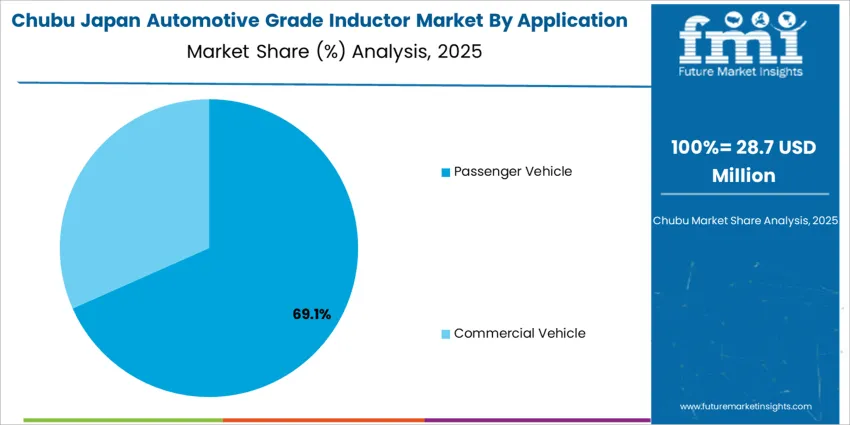
Chubu records 1.9% CAGR, centered on automotive component production clusters across Aichi, Gifu, and Shizuoka. Demand relates to electronic control modules used in powertrain systems, vehicle safety subsystems, and cabin-comfort components. Procurement teams rely on components that meet extended certification durations to maintain platform stability over multi-year production cycles. Engineering teams evaluate inductors based on vibration endurance and copper-loss performance under high-load conditions common in engine-adjacent placements. Contract manufacturers focus on integrating inductors with standardized pad layouts that ensure predictable placement accuracy. Thermal resilience testing supports stable usage in environments exposed to repeated temperature shifts from frequent vehicle operation. Logistics networks serving automotive OEM lines require accurate JIT supply schedules that support uninterrupted assembly flow. Procurement cost sensitivity reinforces reliance on established domestic suppliers familiar with design expectations across Chubu automotive facilities.
Tohoku posts 1.7% CAGR, shaped by regional automotive electronics production in Miyagi, Iwate, and Fukushima, with component sourcing designed around stable supply contracts. Inductors support electronic modules in lighting control, seat-adjustment systems, and instrument-panel functions. Cold-weather driving across the region requires components that maintain magnetic stability and solder-joint integrity through low-temperature exposure. Smaller production facilities emphasize traceability for each component shipment to reinforce defect-response visibility and supplier accountability. Procurement teams favor compact shielded inductors that assist with noise control in products exposed to EMI-dense cabin environments. Batch-based scheduling supports procurement predictability for suppliers serving multiple low-to-moderate volume programs.
The Rest of Japan posts 1.6% CAGR, influenced by demand for electronics in smaller-scale automotive manufacturing and localized tier-2 supplier operations. Inductors support functions in HVAC actuators, mirror-adjustment systems, and accessory power units that require stable current management. Procurement cycles match periodic component refresh periods instead of rapid design change. Buyers maintain inventories that minimize production stoppage risks due to supply delays. Compact standardized package formats help assembly teams maintain process stability without production-line reconfiguration. Reliability expectations reflect long-operating vehicles that dominate regional mobility patterns. Distribution routing spans wide geographic areas requiring accurate forecast alignment to avoid under-stocking or over-storage.
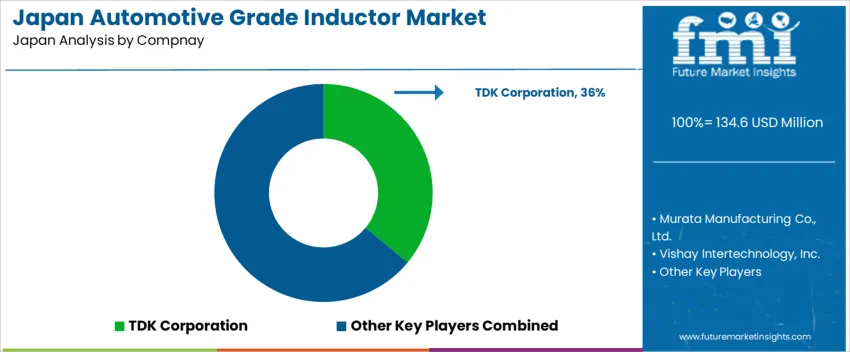
Demand for automotive-grade inductors in Japan is driven by suppliers supporting power-conversion, filtering, and signal-conditioning functions in electric-drive systems, ADAS electronics, and in-vehicle infotainment. TDK Corporation holds an estimated 36% share, supported by controlled inductance tolerance, vibration-resistant construction, and strong supply relationships with Japanese automotive OEMs and Tier-1 electronics integrators. Its components maintain stable magnetic characteristics under elevated temperatures and electrical-noise exposure common in mobility applications. Murata Manufacturing Co., Ltd. maintains strong participation with compact multilayer inductors that provide predictable impedance performance for high-frequency automotive electronics. Its devices offer secure solder-joint reliability and verified AEC-Q200 qualification for long-term system durability. Vishay Intertechnology, Inc. contributes presence through shielded inductors used in power electronics where precise current handling and minimal core losses support efficiency in hybrid and EV platforms.
Panasonic Corporation supports selective demand in noise-suppression and DC-DC converter assemblies, offering inductors with consistent thermal behaviour and stable saturation characteristics required in high-density electronics packaging. Taiyo Yuden Co., Ltd. adds capability in miniaturized automotive inductors designed for reliable EMC performance in sensor and control electronics. Competition in Japan focuses on temperature-stability performance, mechanical robustness, inductance accuracy, electromagnetic-noise control, and dependable delivery to automotive production schedules. Demand continues as Japanese mobility manufacturers adopt higher-efficiency power electronics and expand electrification across passenger-vehicle and commercial-fleet platforms.
| Items | Values |
|---|---|
| Quantitative Units | USD million |
| Inductance Range | Less than 1 micro henry, 1 to 10 micro henry, 10 to 20 micro henry, 20 to 30 micro henry, 30 to 40 micro henry |
| Application | Passenger Vehicle, Commercial Vehicle |
| Sales Channel | OEM, Aftermarket |
| Regions Covered | Kyushu & Okinawa, Kanto, Kansai, Chubu, Tohoku, Rest of Japan |
| Key Companies Profiled | TDK Corporation, Murata Manufacturing Co., Ltd., Vishay Intertechnology, Inc., Panasonic Corporation, Taiyo Yuden Co., Ltd. |
| Additional Attributes | Focus on high-reliability and AEC-Q200-certified inductors supporting ADAS, infotainment, powertrain control, and EV power electronics; demand driven by miniaturization, low core loss, high current tolerance, and electromagnetically efficient designs; integration with DC-DC converters and onboard chargers; adoption trends show higher usage in hybrid and battery electric vehicles across major Japanese automotive manufacturers. |
The demand for automotive grade inductor in Japan is estimated to be valued at USD 134.6 million in 2025.
The market size for the automotive grade inductor in Japan is projected to reach USD 166.9 million by 2035.
The demand for automotive grade inductor in Japan is expected to grow at a 2.2% CAGR between 2025 and 2035.
The key product types in automotive grade inductor in Japan are 1 to 10 micro henry, 10 to 20 micro henry, less than 1 micro henry, 20 to 30 micro henry and 30 to 40 micro henry.
In terms of application, passenger vehicle segment is expected to command 68.0% share in the automotive grade inductor in Japan in 2025.






Our Research Products

The "Full Research Suite" delivers actionable market intel, deep dives on markets or technologies, so clients act faster, cut risk, and unlock growth.

The Leaderboard benchmarks and ranks top vendors, classifying them as Established Leaders, Leading Challengers, or Disruptors & Challengers.

Locates where complements amplify value and substitutes erode it, forecasting net impact by horizon

We deliver granular, decision-grade intel: market sizing, 5-year forecasts, pricing, adoption, usage, revenue, and operational KPIs—plus competitor tracking, regulation, and value chains—across 60 countries broadly.

Spot the shifts before they hit your P&L. We track inflection points, adoption curves, pricing moves, and ecosystem plays to show where demand is heading, why it is changing, and what to do next across high-growth markets and disruptive tech

Real-time reads of user behavior. We track shifting priorities, perceptions of today’s and next-gen services, and provider experience, then pace how fast tech moves from trial to adoption, blending buyer, consumer, and channel inputs with social signals (#WhySwitch, #UX).

Partner with our analyst team to build a custom report designed around your business priorities. From analysing market trends to assessing competitors or crafting bespoke datasets, we tailor insights to your needs.
Supplier Intelligence
Discovery & Profiling
Capacity & Footprint
Performance & Risk
Compliance & Governance
Commercial Readiness
Who Supplies Whom
Scorecards & Shortlists
Playbooks & Docs
Category Intelligence
Definition & Scope
Demand & Use Cases
Cost Drivers
Market Structure
Supply Chain Map
Trade & Policy
Operating Norms
Deliverables
Buyer Intelligence
Account Basics
Spend & Scope
Procurement Model
Vendor Requirements
Terms & Policies
Entry Strategy
Pain Points & Triggers
Outputs
Pricing Analysis
Benchmarks
Trends
Should-Cost
Indexation
Landed Cost
Commercial Terms
Deliverables
Brand Analysis
Positioning & Value Prop
Share & Presence
Customer Evidence
Go-to-Market
Digital & Reputation
Compliance & Trust
KPIs & Gaps
Outputs
Full Research Suite comprises of:
Market outlook & trends analysis
Interviews & case studies
Strategic recommendations
Vendor profiles & capabilities analysis
5-year forecasts
8 regions and 60+ country-level data splits
Market segment data splits
12 months of continuous data updates
DELIVERED AS:
PDF EXCEL ONLINE
Automotive Grade Inductors Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Automotive Grade Inductor Market Growth - Trends & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Demand for Automotive Grade Inductor in USA Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Japan Automotive Load Floor Industry Analysis Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Japan Automotive Turbocharger Market Insights – Demand, Size & Industry Trends 2025–2035
Japan Automotive Airbag Market Report – Trends & Innovations 2025-2035
Japan Automotive Composite Leaf Springs Market Insights – Growth & Demand 2025-2035
Japan Automotive Turbocharger Market Growth – Trends & Forecast 2023-2033
Japan Automotive Lighting Market Growth – Trends & Forecast 2023-2033
Japan Automotive Interior Leather Market Growth – Trends & Forecast 2023-2033
Automotive-grade Inertial Navigation System Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
5G Automotive Grade Product Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Demand for Automotive NFC in Japan Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Demand for Automotive Fabrics in Japan Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Demand for Automotive Brackets in Japan Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Demand for Automotive Headliner in Japan Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Demand for Automotive Light Bars in Japan Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Demand for Automotive Brake Tube in Japan Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Demand for Automotive AI Chipset in Japan Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Demand for Automotive Racing Seats in Japan Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035

Thank you!
You will receive an email from our Business Development Manager. Please be sure to check your SPAM/JUNK folder too.
Chat With
MaRIA