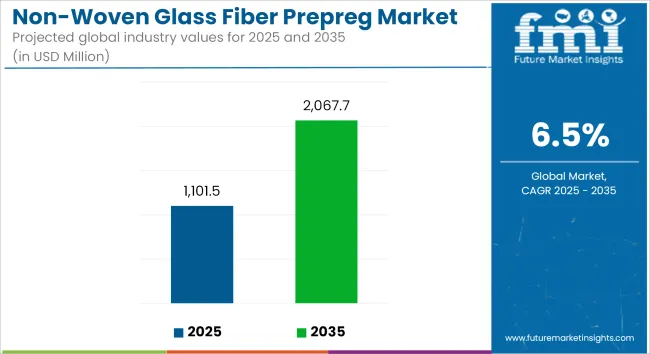
The global non-woven glass fiber prepreg market is estimated at USD 1,101.5 million in 2025 and is projected to expand to USD 2,067.7 million by 2035, registering a CAGR of 6.5%. Market growth is supported by increasing demand from sectors such as wind energy, aerospace, and construction, where lightweight and high-strength composite materials are used for structural reinforcement and durability.
Key Market Metrics
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Industry Size (2025E) | USD 1,101.5 million |
| Industry Value (2035F) | USD 2,067.7 million |
| CAGR (2025 to 2035) | 6.5% |
The non-woven glass fiber prepreg market is expanding due to increasing demand across aerospace, automotive, wind energy, and infrastructure sectors. These materials, which consist of glass fibers pre-impregnated with resin, are used in structural and insulating applications where weight reduction, corrosion resistance, and dimensional stability are critical.
Their compatibility with automated manufacturing and uniform resin distribution make them suitable for mass production and complex designs.
One significant development is the adoption of thermosetting resins such as epoxy and phenolic, which cure irreversibly to form high-strength, thermally stable composites. These resins are widely used in load-bearing applications where mechanical performance and reliability are essential.
In aerospace, prepregs are used in nacelles, fuselage linings, and cabin panels. In the automotive industry, they are integrated into body panels, battery enclosures, and underbody shields to reduce weight and enhance impact resistance.
Advancements in resin formulation have addressed earlier limitations such as long cure cycles and handling sensitivity. The introduction of snap-cure epoxies and bio-based resins has enabled faster processing while improving sustainability. Manufacturers are also implementing automated layup systems to ensure consistent fiber orientation and reduce production variability.
Regionally, countries like the United States are using prepregs in electric vehicle platforms and wind turbine blades. In the European Union, adoption is driven by lightweight mobility and emissions regulations. In South Korea and Japan, prepregs are applied in renewable energy components and electronic insulation.
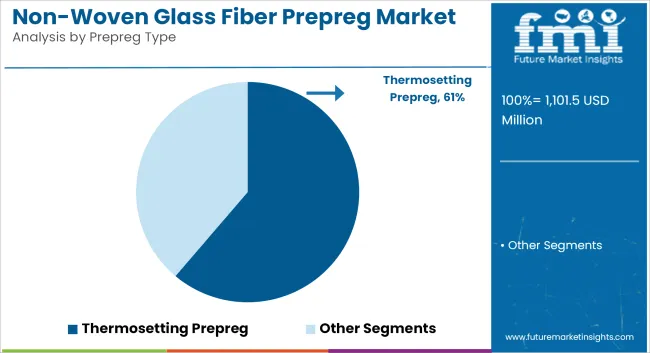
Thermosetting prepreg is projected to account for 61.2% of the market in 2025 and is expected to grow at a CAGR of 6.4% through 2035. This segment includes epoxy, phenolic, and vinyl ester resin systems impregnated into non-woven glass fiber mats.
These prepregs are widely adopted in structural applications such as wind turbine blades, electrical panels, and transportation interiors due to their thermal stability and resistance to deformation under heat. Once cured, thermosetting matrices provide rigid, crosslinked structures that maintain mechanical properties under prolonged stress. The prepreg is applied through compression molding, layup, and resin transfer molding.
Adoption is expanding in East Asia and Western Europe, driven by investments in infrastructure and renewable energy. Processing and storage stability, along with controlled shelf life, make this segment viable for large-volume production environments. Market growth is reinforced by consistent demand from composite product manufacturers seeking strength-to-weight advantages.
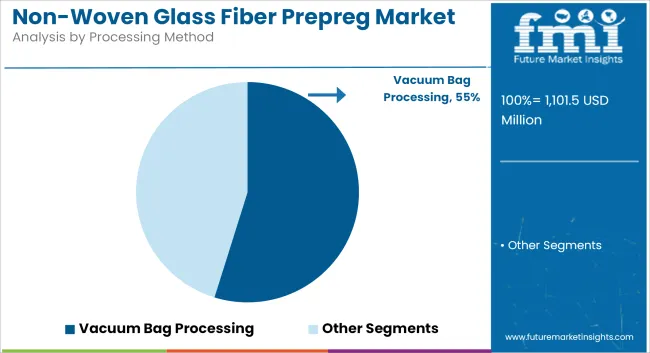
Vacuum bag processing is expected to account for 54.8% of the non-woven glass fiber prepreg market in 2025 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 6.6% through 2035. This method involves placing prepreg laminates into molds and covering them with a vacuum bag, which compresses the layers during curing to remove air pockets and improve resin distribution.
The technique is used across wind blade manufacturing, boat hulls, and aerospace interior panels. It provides moderate pressure control without the need for autoclave systems and is applicable in settings where component dimensions are large or tooling investment is limited. Industries prefer vacuum bagging due to reduced capital expenditure, compatibility with thermosetting systems, and simplicity in layout.
Market expansion is observed in regions scaling up wind energy and light vehicle composite components, especially in Asia and Latin America, where manual or semi-automated processes remain prevalent.
Challenge: Processing Complexity and Resin Compatibility Limitations
Non-woven glass fiber prepreg presents challenges related to complete resin impregnation and interlinear strength in different applications. Although such non-woven structures would have good conformability, the mechanical consistency of nonwoven structures is sometimes insufficient, relative to woven substitutes.
Distributing fibers consistently and enabling adhesion during curing especially at variable temperature or pressure can be a challenge.
Moreover, multi-material compatibility (epoxy, phenolic, and polyester) becomes a limitation for high-performance industries such as aerospace or automotive, where mechanical precision is essential.
High production costs, narrow recycling pathways, and sensitivity in handling further restrict usage in cost-sensitive or high-throughput manufacturing contexts.
Opportunity: Lightweight Composites and High-Speed Manufacturing Demand
Lightweight, high-strength, and ease of molding are driving adoption of composites, and more specifically, use of non-woven glass fiber prepreg, despite some ongoing processing challenges.
Such materials are commonly used in automotive panels, wind turbine blades, marine structures, or components of sports equipment whose utility is afforded by their versatility and cost effectiveness.
Non-woven prepregs enable faster cycle times and improved surface finish in high-speed molding processes, responding to manufacturers’ demands for fast layup solutions. New developments in resin chemistry including snap-cure epoxies and bio-based matrices are improving compatibility and sustainability.
As electrification and structural optimization transform transportation and construction, non-woven prepregs are coming into their own as composite enablers.
In the USA, the non-woven glass fiber prepreg market is expected to move towards steady growth due to strong demand from the aerospace, automotive, and wind energy verticals. Thermal resistance and dimensional stability make these prepregs excellent for lightweight structural applications with a superior strength-to-weight ratio.
Non-woven glass fiber prepregs are being increasingly integrated by USA manufacturers into electric vehicle body panels, as well as being used in aircraft interiors. Increasing interest in renewable energy has also driven demand for prepregs used in turbine blade fabrication where fatigue resistance and uniform alignment are essential.
| Country | CAGR (2025 to 2035) |
|---|---|
| USA | 6.2% |
Non-woven glass fiber prepregs have seen stable growth in the United Kingdom due to advances in automotive light weighting and aerospace innovation. British engineering companies are using these prepregs to help reduce emissions from vehicles and improve the structural integrity of demands from electronic vehicle (EV) platforms.
In aerospace, high fire resistance and process uniformity drive the adoption of prepregs for parts such as nacelles, fuselage linings and cabin panels. Market fundamentals are being strengthened by ongoing investments in composite research and export-driven production.
| Country | CAGR (2025 to 2035) |
|---|---|
| UK | 6.3% |
The European Union dominates the non-woven glass fiber prepreg market based on applications in composite applications, including an automotive segment, rail, marine, and wind. The production of high-performance composite parts will diffuse from Germany, France, and Spain to other countries, covering design for structural and semi-structural applications.
The growing pressure on the EU to prioritize fuel efficiency and lower emissions in mobility sectors has accelerated the adoption of lightweight, recyclable materials. Regional manufacturers are also working on thermoset and thermoplastic prepregs that adhere to strict REACH and ECHA regulations.
| Region | CAGR (2025 to 2035) |
|---|---|
| European Union | 6.5% |
The market in Japan for the non-woven glass fiber prepreg is on a steady path, owing to its increasing requirement in electronic components and automotive applications. Long-time Japanese automakers are integrating these prepregs into door panels, battery enclosures, and underbody shields for enhanced crash resistance and less mass.
Prepregs also provide electrical insulation and thermal stability, which renders them usable in multilayer PCB reinforcement. This high precision prepreg production and surface finish control is also stimulating domestic innovation within Japan.
| Country | CAGR (2025 to 2035) |
|---|---|
| Japan | 6.0% |
With the fast expansion of renewable energy sources, shipbuilding & electric mobility, South Korea continues to emerge as a potential industry for non-woven glass fiber prepregs. To capitalize on export opportunities in the wind and defense sectors, South Korean manufacturers are increasingly investing in prepreg-based composite tooling and high-performance laminates.
Korean manufacturers, placing a high priority on innovative approaches and materials science, are improving resin systems and fiber orientation methods to produce prepregs with superior resistance to fatigue and environmental degradation.
| Country | CAGR (2025 to 2035) |
|---|---|
| South Korea | 6.9% |
The non-woven glass fiber prepreg market is defined by shifts in supply chain alignment and end-use diversification across aerospace, wind energy, and construction sectors. Major suppliers are expanding production near key manufacturing hubs to reduce lead times and logistics expenses. Investments in process automation and quality control systems are being implemented to maintain consistency and throughput.
Collaborations between resin producers and composite fabricators are enabling tailored material solutions for structural applications. Raw material fluctuations, particularly in glass fiber and resin feedstocks, are affecting pricing strategies and inventory management.
The overall market size for the non-woven glass fiber prepreg market was USD 1,101.5 million in 2025.
The non-woven glass fiber prepreg market is expected to reach USD 2,067.7 million in 2035.
The increasing demand for lightweight, high-strength composite materials, rising application in aerospace and automotive sectors, and growing preference for thermosetting prepregs and autoclave processing fuel the non-woven glass fiber prepreg market during the forecast period.
The top 5 countries driving the development of the non-woven glass fiber prepreg market are the USA, UK, European Union, Japan, and South Korea.
Thermosetting prepregs and autoclave processing lead market growth to command a significant share over the assessment period.






Full Research Suite comprises of:
Market outlook & trends analysis
Interviews & case studies
Strategic recommendations
Vendor profiles & capabilities analysis
5-year forecasts
8 regions and 60+ country-level data splits
Market segment data splits
12 months of continuous data updates
DELIVERED AS:
PDF EXCEL ONLINE
Glass Laser Engraving Machine Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Glass Restoration Kit Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Glass Bottle and Container Market Forecast and Outlook 2025 to 2035
Glass Additive Market Forecast and Outlook 2025 to 2035
Glass Reactor Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Glass Cosmetic Bottle Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Glass & Metal Cleaner Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Glass Product Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Glassine Paper Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Glass Container Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Glass Fibre Yarn Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Glass Cloth Electrical Insulation Tape Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Glass Bonding Adhesive Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Glass Mat Thermoplastic Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Glass Table Bacteria Tank Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Glassine Paper Industry Analysis in Western Europe Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Glassine Paper Industry Analysis in Korea Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Glassine Paper Industry Analysis in Japan Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Glass Mat Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Glassware Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035

Thank you!
You will receive an email from our Business Development Manager. Please be sure to check your SPAM/JUNK folder too.
Chat With
MaRIA