The phase shifting transformer (PST) market is expected to grow from USD 183.8 million in 2025 to USD 348.2 million by 2035, registering a 6.6% CAGR and generating an absolute dollar opportunity of USD 164.4 million. Growth is driven by increasing demand for power flow control, grid stability, and congestion management in transmission networks. PSTs are essential in modern electricity grids to optimize power distribution, prevent overloads, and enhance operational efficiency, particularly in regions with high renewable energy integration and cross-border power exchange.
Saturation point analysis identifies phases where market expansion approaches maximum adoption levels within existing infrastructure and technology constraints. From 2025 to 2028, growth is robust, driven by the replacement of aging transformers and the expansion of high-voltage transmission networks in North America, Europe, and the Asia Pacific. Between 2029 and 2032, the market begins to approach saturation in mature regions, as major transmission networks adopt PSTs and new installations become incremental, focusing on upgrades and optimization rather than new deployments. From 2033 to 2035, growth continues but at a moderated pace, as emerging markets drive incremental adoption while mature regions rely on maintenance, retrofits, and system enhancements.
Overall, the USD 164.4 million opportunity illustrates that while the market has strong potential, it is gradually approaching a saturation point in established regions, with late-stage growth increasingly influenced by efficiency improvements and replacement demand.
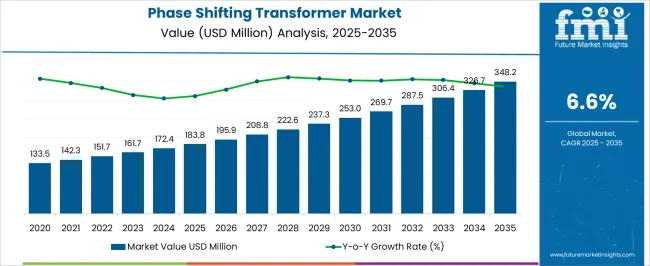
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Phase Shifting Transformer Market Estimated Value in (2025 E) | USD 183.8 million |
| Phase Shifting Transformer Market Forecast Value in (2035 F) | USD 348.2 million |
| Forecast CAGR (2025 to 2035) | 6.6% |
The phase shifting transformer market is driven by five primary parent markets with specific shares. Power transmission leads with 40%, as these transformers manage power flow and reduce congestion in high-voltage networks. Renewable energy integration contributes 25%, enabling efficient grid connection of wind, solar, and hydroelectric sources. Industrial and commercial facilities account for 15%, using transformers to optimize power distribution and improve stability. Utilities and energy providers represent 10%, leveraging phase shifting transformers for load balancing and grid reliability. Rail and transportation electrification hold 10%, requiring controlled power flow for safe and efficient operation.
These sectors collectively shape global demand. Recent developments in the phase shifting transformer market focus on efficiency, grid modernization, and smart integration. Manufacturers are improving transformer designs with advanced insulation, low-loss cores, and digital monitoring to enhance performance and reliability. Integration with smart grids and energy management systems allows real-time control, predictive maintenance, and improved power flow management. Growth in renewable energy installations, urbanization, and industrial electrification is driving an increase in demand for high-capacity transformers. Companies are also exploring modular and compact designs for easier installation and maintenance.
The phase shifting transformer market is advancing steadily, driven by the growing need to regulate power flow and enhance grid reliability across complex transmission networks. As global electricity demand continues to rise, utilities and grid operators are increasingly deploying phase shifting transformers to mitigate loop flows, control active power, and optimize load distribution.
The modernization of aging grid infrastructure, combined with the integration of renewable energy sources, has further emphasized the importance of these systems in maintaining grid stability. The market outlook remains favorable due to the heightened focus on reducing transmission losses and improving cross-border electricity trade efficiency.
Increased capital expenditure in power transmission projects and advancements in transformer technology are expected to drive further adoption. As countries reinforce their high-voltage networks, demand for phase shifting transformers is projected to remain strong, especially in industrialized regions and emerging economies investing in energy infrastructure.
The phase shifting transformer market is segmented by rating, application, and geographic regions. By rating, phase shifting transformer market is divided into 400 MVA, 400 MVA - 800 MVA, and > 800 MVA. In terms of application, phase shifting transformer market is classified into Industrial, Utility, and Others. Regionally, the phase shifting transformer industry is classified into North America, Latin America, Western Europe, Eastern Europe, Balkan & Baltic Countries, Russia & Belarus, Central Asia, East Asia, South Asia & Pacific, and the Middle East & Africa.
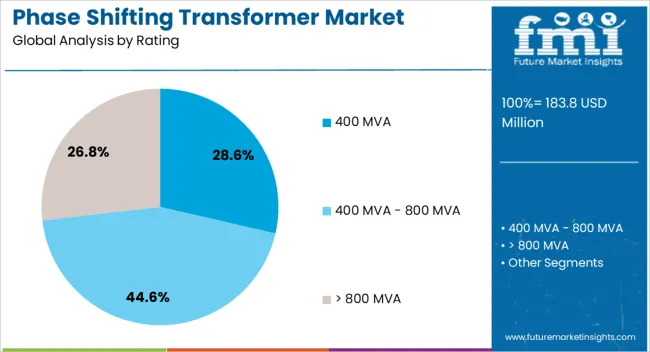
The 400 MVA segment accounts for 29% of the phase shifting transformer market, representing a critical solution for high-load, high-voltage applications within complex power transmission systems. This rating is preferred for its ability to manage substantial power flows while minimizing losses and maintaining voltage stability across interconnectors.
Its deployment is particularly relevant in large-scale grid reinforcement projects where precise control over power direction and magnitude is essential. The segment’s growth is further supported by increasing utility-scale investments and infrastructure upgrades aimed at strengthening transmission corridors.
Manufacturers are focused on developing robust, thermally optimized designs to handle long-term operational stresses in high-load scenarios. As inter-regional and international power transfers become more frequent, 400 MVA-rated units are expected to witness sustained demand, particularly in projects involving bulk power exchange and renewable integration.
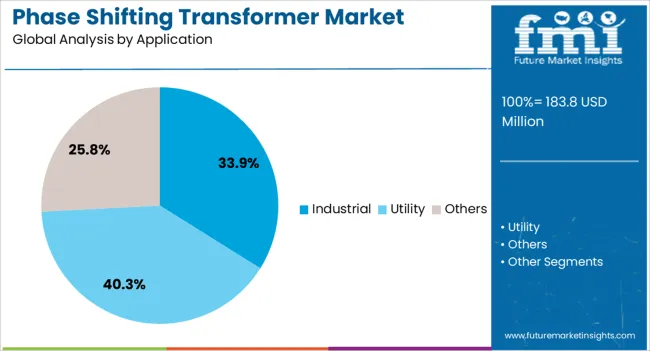
The industrial application segment leads with a 34% market share, highlighting the critical role of phase shifting transformers in supporting heavy-load manufacturing and processing operations. Industrial facilities often face challenges related to load balancing, voltage fluctuations, and power quality—issues that are effectively addressed through the deployment of phase shifting transformers.
These units enable stable and efficient power distribution, particularly in sectors such as steel, petrochemicals, and mining, where uninterrupted power flow is essential. As industries increasingly rely on automation and high-energy equipment, the need for power regulation and system protection has intensified, driving the adoption of advanced transformer solutions.
Additionally, expanding industrial infrastructure in emerging economies is contributing to new installations. With continued industrialization and energy consumption growth, this segment is poised to maintain a prominent share in the overall market landscape.
The global phase shifting transformer (PST) market is expanding due to increasing demand for grid stability, efficient power flow control, and congestion management in transmission networks. Asia Pacific accounts for over 35% of installations, led by China and India, while North America and Europe focus on high-voltage, high-capacity PSTs for renewable integration and interregional power transfer. Technological innovations in solid-state and conventional PSTs improve voltage regulation, reactive power control, and load balancing. Rising electricity demand, renewable penetration, and cross-border grid interconnections are creating measurable opportunities for market growth worldwide.
The primary driver for the PST market is the need for efficient power flow management in high-voltage transmission systems. PSTs enable precise phase angle adjustment, controlling real and reactive power, mitigating congestion, and enhancing network reliability. Integration of renewable energy, such as wind and solar, introduces variability in grid load, increasing the need for PST deployment to balance fluctuations. Asia Pacific, particularly China and India, invests heavily in high-voltage AC and DC transmission corridors requiring PSTs with ratings of 200–1,000 MVA. PSTs also support interregional power transfer, reduce transmission losses by 5–10%, and facilitate energy trading, driving adoption in commercial and utility-scale projects.
Opportunities in the PST market arise from smart grid initiatives, high-voltage interconnections, and cross-border power trading. Europe and North America are adopting PSTs in renewable-rich regions to manage wind and solar variability while ensuring grid stability. Asia Pacific expansion includes high-voltage AC and DC corridors connecting power surplus regions to urban load centers. PSTs integrated with SCADA, digital monitoring, and predictive maintenance enable optimized real-time load control. Upgrades of aging transmission infrastructure, construction of new ultra-high-voltage lines, and international energy trade agreements present additional market potential. Manufacturers investing in modular, solid-state, and compact PST designs can capture growing demand from utilities and grid operators globally.
Key trends in the PST market include solid-state transformers, digital monitoring, and integration with energy management systems. Solid-state PSTs offer faster response times, lower losses, and enhanced reliability compared with conventional magnetic designs. Integration with digital sensors and SCADA systems allows predictive maintenance, real-time phase angle adjustments, and load optimization. Asia Pacific is leading in deployment of high-capacity conventional PSTs, while Europe and North America emphasize advanced solid-state solutions for renewable integration. Modular designs and compact configurations enable retrofitting in existing substations. Increasing use of PSTs in interregional and international transmission corridors reflects a trend toward automated, flexible, and smart power grid management worldwide.
Despite advantages, the PST market faces challenges related to high capital investment, technical complexity, and operational risks. Conventional PSTs with ratings above 500 MVA can cost $5–15 million per unit, limiting adoption in smaller utilities. Installation requires precise engineering, foundation work, and coordination with protective relays and grid systems. Solid-state PSTs, though efficient, remain expensive and less commercially proven at ultra-high-voltage levels. Maintenance requires specialized expertise, and malfunction or phase angle misalignment can impact grid stability. Regulatory approvals, environmental compliance, and extended lead times for large transformers further constrain growth. Manufacturers must focus on cost reduction, modular designs, and digital integration to overcome these barriers and support global grid modernization.
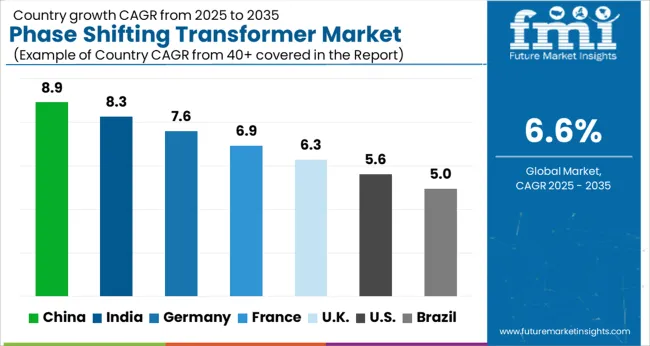
| Country | CAGR |
|---|---|
| China | 8.9% |
| India | 8.3% |
| Germany | 7.6% |
| France | 6.9% |
| UK | 6.3% |
| USA | 5.6% |
| Brazil | 5.0% |
The phase shifting transformer market is expected to grow at a global CAGR of 6.6% through 2035, driven by the need for improved power flow control, grid stability, and renewable energy integration. China leads at 8.9%, a 1.35× multiple of the global rate, supported by BRICS-focused investments in smart grid projects, transmission infrastructure, and renewable energy integration. India follows at 8.3%, a 1.26× multiple, reflecting the expansion of national grids, industrial demand, and adoption of power flow management solutions. Germany records 7.6%, a 1.15× multiple, shaped by OECD-backed energy efficiency initiatives and advanced transformer technologies. The United Kingdom posts 6.3%, slightly below the global CAGR, with adoption concentrated in regional transmission networks and grid modernization projects. The United States stands at 5.6%, 0.85× the benchmark, supported by steady grid upgrades and renewable energy integration. BRICS nations drive volume growth, OECD countries emphasize technological advancements, while ASEAN markets contribute through expanding power infrastructure. This report includes insights on 40+ countries; the top markets are shown here for reference.
The phase shifting transformer market in China is projected to grow at a CAGR of 8.9%, driven by rapid expansion of high-voltage transmission networks and grid modernization projects. Utilities and industrial players are increasingly adopting transformers to control power flow, minimize losses, and improve grid stability in regional interconnections. Domestic manufacturers are focusing on high-capacity, low-loss designs suitable for integration with renewable energy sources. Technological trends include digital monitoring, adaptive control systems, and high-efficiency insulation materials. Investments in ultra-high voltage (UHV) networks and smart grid upgrades are further supporting adoption. Strong government emphasis on energy efficiency, reliability, and renewable integration reinforces growth prospects for phase shifting transformers in China.
The phase shifting transformer market in India is expected to expand at a CAGR of 8.3%, supported by demand for grid stability, renewable integration, and congestion management in transmission networks. Utilities and large industrial users are investing in advanced transformers to optimize power flow, reduce losses, and maintain voltage regulation. Domestic and international manufacturers are introducing high-efficiency, digitally monitored transformers suitable for both conventional and renewable power sources. Government programs promoting grid modernization, renewable energy, and smart grids are accelerating adoption. Strong industrial and urban energy demand drives deployment in regional interconnections. Investments in high-capacity and flexible transformer designs further enhance growth opportunities.
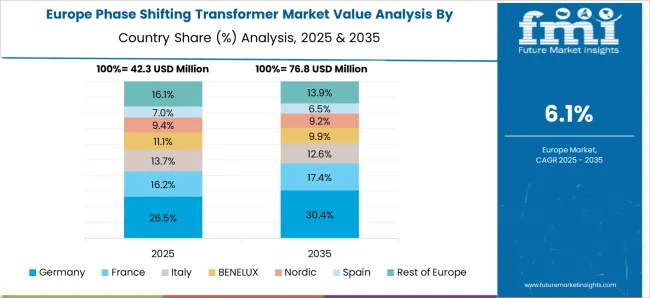
The phase shifting transformer market in Germany is projected to grow at a CAGR of 7.6%, driven by adoption for high-voltage transmission networks, renewable energy integration, and cross-border interconnections. Manufacturers are focusing on high-efficiency, low-loss transformers with advanced control systems suitable for both onshore and offshore wind power integration. Deployment is concentrated in industrial regions, renewable hubs, and grid interconnection points. Technological trends include real-time monitoring, adaptive phase control, and eco-friendly insulation materials. Government policies promoting grid modernization, renewable energy integration, and carbon emission reduction further support market growth. The focus remains on enhancing energy efficiency, reliability, and grid stability.
The phase shifting transformer market in the United Kingdom is forecast to grow at a CAGR of 6.3%, supported by renewable energy expansion, grid interconnections, and industrial demand for voltage regulation. Utilities are investing in digitally controlled transformers to enhance grid stability and manage congestion in high-voltage networks. Technological trends focus on adaptive phase control, remote monitoring, and efficient insulation materials. Deployment is concentrated in offshore wind connection points, high-load urban regions, and industrial zones. Government initiatives supporting smart grids, renewable energy integration, and energy efficiency further reinforce adoption. Emphasis on environmental compliance and long-term reliability drives transformer upgrades across the UK.
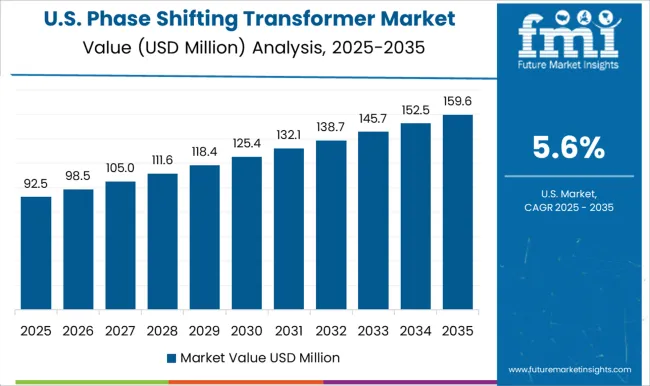
The phase shifting transformer market in the United States is expected to grow at a CAGR of 5.6%, driven by adoption for transmission optimization, grid stability, and renewable energy integration. Utilities and industrial customers are deploying high-efficiency transformers with digital monitoring, adaptive phase control, and low-loss insulation. Investment in modernizing aging grid infrastructure and expanding interconnection capabilities supports market growth. Technological trends include smart grid compatibility, predictive maintenance, and high-voltage application designs. Federal and state-level initiatives promoting renewable energy and reliable transmission reinforce demand. Industrial and regional interconnections are key segments contributing to growth.
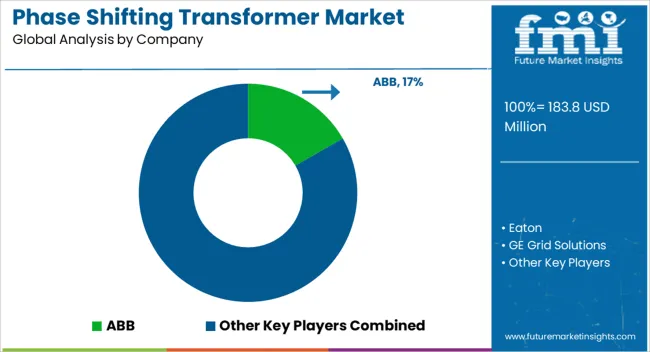
Competition in the phase shifting transformer sector is driven by demand for advanced grid stability, voltage regulation, and power flow optimization across high-voltage networks. ABB is enhancing its position with transformers designed for flexible power distribution and reduced transmission losses. Eaton provides high-capacity, reliable units that support industrial and utility-scale grid applications. GE Grid Solutions develops digitally enabled transformers capable of precise phase angle adjustments to improve grid efficiency. Hitachi Energy integrates smart monitoring and control systems, enabling real-time management of power flows and reactive power compensation.
Hyosung Heavy Industries focuses on compact, high-performance transformers suitable for both conventional and renewable energy grids. Schneider Electric delivers scalable solutions that optimize voltage regulation while minimizing energy loss across transmission lines. SGB-SMIT Group emphasizes customization and robust design, serving utility operators with transformers that meet diverse network requirements. Siemens Energy combines advanced materials and engineering to enhance thermal performance and reduce operational downtime. Tamini Transformers and Toshiba International Corporation produce transformers with high reliability, designed for demanding power distribution environments. Wilson Transformers addresses niche industrial and utility applications with precision-engineered units, completing a competitive landscape where performance, durability, and intelligent control define market leadership.
| Item | Value |
|---|---|
| Quantitative Units | USD 183.8 Million |
| Rating | 400 MVA, 400 MVA - 800 MVA, and > 800 MVA |
| Application | Industrial, Utility, and Others |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America, Middle East & Africa |
| Country Covered | United States, Canada, Germany, France, United Kingdom, China, Japan, India, Brazil, South Africa |
| Key Companies Profiled | ABB, Eaton, GE Grid Solutions, Hitachi Energy, Hyosung Heavy Industries, Schneider Electric, SGB-SMIT Group, Siemens Energy, Tamini Transformers, Toshiba International Corporation, and Wilson Transformers |
| Additional Attributes | Dollar sales by transformer type and end use, demand dynamics across utilities, industrial, and commercial power networks, regional trends in grid modernization and load balancing, innovation in voltage control, efficiency, and monitoring, environmental impact of material use and oil disposal, and emerging use cases in renewable integration and smart grids. |
The global phase shifting transformer market is estimated to be valued at USD 183.8 million in 2025.
The market size for the phase shifting transformer market is projected to reach USD 348.2 million by 2035.
The phase shifting transformer market is expected to grow at a 6.6% CAGR between 2025 and 2035.
The key product types in phase shifting transformer market are 400 mva, 400 mva - 800 mva and > 800 mva.
In terms of application, industrial segment to command 33.9% share in the phase shifting transformer market in 2025.






Our Research Products

The "Full Research Suite" delivers actionable market intel, deep dives on markets or technologies, so clients act faster, cut risk, and unlock growth.

The Leaderboard benchmarks and ranks top vendors, classifying them as Established Leaders, Leading Challengers, or Disruptors & Challengers.

Locates where complements amplify value and substitutes erode it, forecasting net impact by horizon

We deliver granular, decision-grade intel: market sizing, 5-year forecasts, pricing, adoption, usage, revenue, and operational KPIs—plus competitor tracking, regulation, and value chains—across 60 countries broadly.

Spot the shifts before they hit your P&L. We track inflection points, adoption curves, pricing moves, and ecosystem plays to show where demand is heading, why it is changing, and what to do next across high-growth markets and disruptive tech

Real-time reads of user behavior. We track shifting priorities, perceptions of today’s and next-gen services, and provider experience, then pace how fast tech moves from trial to adoption, blending buyer, consumer, and channel inputs with social signals (#WhySwitch, #UX).

Partner with our analyst team to build a custom report designed around your business priorities. From analysing market trends to assessing competitors or crafting bespoke datasets, we tailor insights to your needs.
Supplier Intelligence
Discovery & Profiling
Capacity & Footprint
Performance & Risk
Compliance & Governance
Commercial Readiness
Who Supplies Whom
Scorecards & Shortlists
Playbooks & Docs
Category Intelligence
Definition & Scope
Demand & Use Cases
Cost Drivers
Market Structure
Supply Chain Map
Trade & Policy
Operating Norms
Deliverables
Buyer Intelligence
Account Basics
Spend & Scope
Procurement Model
Vendor Requirements
Terms & Policies
Entry Strategy
Pain Points & Triggers
Outputs
Pricing Analysis
Benchmarks
Trends
Should-Cost
Indexation
Landed Cost
Commercial Terms
Deliverables
Brand Analysis
Positioning & Value Prop
Share & Presence
Customer Evidence
Go-to-Market
Digital & Reputation
Compliance & Trust
KPIs & Gaps
Outputs
Full Research Suite comprises of:
Market outlook & trends analysis
Interviews & case studies
Strategic recommendations
Vendor profiles & capabilities analysis
5-year forecasts
8 regions and 60+ country-level data splits
Market segment data splits
12 months of continuous data updates
DELIVERED AS:
PDF EXCEL ONLINE
Dual-Phase Cleanser Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Three-Phase Unbalanced Regulating Device Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Solid Phase Carrier Resin for Peptide Drug Synthesis Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Early Phase Clinical Trial Outsourcing Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Three Phase Commercial Voltage Regulator Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Three Phase String Inverter Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Three Phase Inverter Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Three Phase Residential Voltage Regulator Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Three Phase Recloser Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Three Phase Micro Inverter Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Three Phase Residential Power Conditioner Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Three Phase Shunt Reactor Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Three Phase Power Device Analyzer Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Three Phase Green Power Transformer Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Single Phase Spot Welder Machine Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Single Phase Spot Welder Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Single Phase Recloser Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Single Phase Portable Conventional Gensets Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Single Phase Residential Voltage Regulator Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Single Phase Shunt Reactor Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035

Thank you!
You will receive an email from our Business Development Manager. Please be sure to check your SPAM/JUNK folder too.
Chat With
MaRIA