The small cell network market is estimated to be valued at USD 3.3 billion in 2025 and is projected to reach USD 71.8 billion by 2035, registering a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 36.2% over the forecast period. The market is being driven by the global rollout of 5G technology, the rapid surge in mobile data traffic, and increasing demand for low-latency, high-bandwidth connectivity to support applications such as IoT, smart cities, and autonomous vehicles.
Enterprises are also adopting private LTE and 5G small cell solutions to enhance in-building connectivity and ensure reliable, secure communication networks. Despite high growth potential, challenges such as deployment costs, regulatory hurdles, and site acquisition complexities remain. However, advancements in plug-and-play solutions, open RAN (Radio Access Network), and cloud-native architectures are expected to mitigate these barriers.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Small Cell Network Market Estimated Value in (2025 E) | USD 3.3 billion |
| Small Cell Network Market Forecast Value in (2035 F) | USD 71.8 billion |
| Forecast CAGR (2025 to 2035) | 36.2% |
The increasing strain on macrocell networks defines the current market landscape due to surging data traffic, which is driving the need for densified network architectures. Small cells are playing a vital role in enabling low-latency communication and high-speed connectivity in both densely populated urban zones and remote areas. Network operators are prioritizing the integration of small cells to offload traffic and enhance coverage, particularly in areas where macrocell expansion is limited by space or regulatory constraints.
The market outlook remains positive due to continued investments in telecom infrastructure, spectrum availability, and increased data consumption from IoT devices, smart cities, and mobile users. As carriers push for seamless connectivity and energy-efficient network layers, the small cell ecosystem is expected to grow further, with strategic deployment in both public and private networks.
The small cell network market is segmented by component, cell, deployment mode, end use, organization size, and geographic regions. By component, the small cell network market is divided into Solution and Services. In terms of cells, the small cell network market is classified into Femtocells, Picocells, Microcells, and Metro cells.
Based on the deployment mode, the small cell network market is segmented into Indoor and Outdoor. By end use, the small cell network market is segmented into Telecom Operators & Service Providers, Enterprises, Smart Cities & Public Infrastructure, Healthcare, Education, Retail & Hospitality, and Industrial & Manufacturing. By organization size, the small cell network market is segmented into Large enterprises and SME. Regionally, the small cell network industry is classified into North America, Latin America, Western Europe, Eastern Europe, Balkan & Baltic Countries, Russia & Belarus, Central Asia, East Asia, South Asia & Pacific, and the Middle East & Africa.
The solution segment is expected to hold 61.4% of the total Small Cell Network market revenue in 2025, making it the leading component type. This dominant position is being attributed to the growing demand for end-to-end network capabilities that enable intelligent management, traffic optimization, and service orchestration.
Telecom operators are increasingly deploying software-defined and virtualized small cell solutions to support dynamic bandwidth allocation and centralized control, which reduces operational complexity and cost. The evolution of small cell solutions to support multi-access edge computing and private LTE networks has further strengthened this segment's adoption.
Additionally, the scalability and interoperability offered by advanced software platforms have enabled smooth integration into existing core networks As operators seek to future-proof their infrastructure and improve user experience across dense and heterogeneous environments, the preference for comprehensive solutions over standalone hardware is reinforcing the segment’s continued growth.
The femtocells segment is projected to account for 34.7% of the Small Cell Network market revenue in 2025, establishing it as a key cell type in the ecosystem. This growth is being driven by the increased need for enhanced indoor mobile coverage in residential and enterprise environments where macrocell signals are often weak or inconsistent.
Femtocells have gained traction due to their ease of installation, cost-efficiency, and ability to deliver high-quality voice and data services using standard broadband connections. The segment's expansion is also supported by their compatibility with existing mobile devices and operator networks, requiring minimal infrastructure changes.
As user expectations for seamless connectivity rise, especially in homes and small offices, the demand for localized and energy-efficient small cells has increased. Femtocells also play a critical role in network densification strategies, particularly for operators aiming to expand coverage while managing capital expenditure effectively.
The indoor deployment mode is anticipated to contribute 69.2% of the total Small Cell Network market revenue in 2025, highlighting its dominant role in network expansion strategies. This leadership is being driven by the growing volume of mobile data traffic generated indoors, which accounts for the majority of total data usage globally.
Enterprises, public venues, and residential spaces are increasingly requiring robust and uninterrupted indoor connectivity to support high-bandwidth applications and mission-critical services. The deployment of small cells indoors allows for enhanced network performance, reduced latency, and better quality of service in areas where outdoor signals face attenuation or interference.
The segment’s growth is also being enabled by the integration of indoor small cells with building infrastructure and enterprise IT systems, providing flexible deployment models. As demand continues to rise for secure, high-speed wireless access in enclosed environments, indoor deployment remains a priority for network operators seeking to enhance user experience and support digital transformation initiatives.
Small cell networks are expanding as a critical enabler of 5G rollout and enterprise connectivity. Rising data traffic, favorable regulations, and private network adoption are strengthening their long-term relevance across telecom and enterprise ecosystems.
Small cell networks are positioned as a cornerstone for the expansion of 5G coverage worldwide. Their role in boosting network density and enabling seamless data transfer at high speeds has been viewed as indispensable for mobile operators. Deployment is being encouraged by the rising demand for ultra-low latency communication, which has become essential in sectors like autonomous mobility, healthcare, and industrial automation. The concentration of mobile data traffic in high-density areas has highlighted the limitations of traditional macrocells, creating greater reliance on small cell deployments. These solutions improve indoor and outdoor connectivity, addressing call drops and coverage gaps. Their growing use in enterprise networks highlights their strategic importance in ensuring reliable mobile broadband experiences.
The unprecedented rise in mobile data traffic has intensified the adoption of small cell networks as a complementary infrastructure layer. Consumers have been consuming more data due to video streaming, gaming, and immersive media, creating strain on existing networks. Small cells are addressing this surge by providing localized, high-capacity coverage that eases network congestion. Enterprises are also implementing them to support employee connectivity in office campuses and production facilities. Operators are increasingly relying on these networks to balance coverage efficiency and cost-effectiveness. With the global digital economy expanding, the adoption of small cells is no longer limited to telecom carriers but is being explored across multiple commercial applications. This widening scope is expected to drive consistent growth.
Private enterprise networks have become an important growth area for small cell deployment. Businesses in manufacturing, logistics, and healthcare are using private LTE and 5G systems enabled by small cells to enhance productivity and reliability. These localized networks improve real-time monitoring, machine connectivity, and secure data transfer, all while minimizing dependence on traditional macro infrastructures. Industries requiring mission-critical communication view small cell installations as a strategic investment for operational efficiency. Vendors are tailoring offerings to match specific enterprise requirements, combining hardware with flexible software-defined management platforms. As organizations continue to demand secure and uninterrupted connectivity for IoT and automation, small cells are playing an increasingly central role in the enterprise communication landscape.
Regulatory frameworks and spectrum allocation policies have had a profound influence on the adoption of small cell networks. Governments and telecom regulators are recognizing the importance of spectrum sharing and cost-efficient licensing models to accelerate deployment. Policies supporting shared spectrum initiatives are helping operators reduce expenses and expand coverage in both rural and urban clusters. National programs promoting smart infrastructure investments are also driving demand for these systems. Regulatory approvals have encouraged partnerships between telecom providers, neutral hosts, and enterprises, making deployment smoother and faster. The focus on easing approval processes for site installation is helping to reduce deployment delays, ensuring faster rollout. This supportive regulatory environment is expected to reinforce long-term growth prospects.
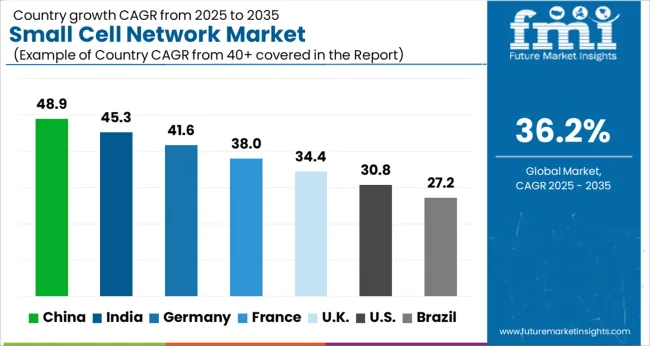
The small cell network market is projected to grow globally at a CAGR of 36.2% from 2025 to 2035, with China leading the expansion at 48.9%, supported by accelerated 5G deployments and government-backed infrastructure upgrades. India follows closely at 45.3%, driven by rising mobile data usage and initiatives to improve rural and urban network density. France posts a CAGR of 38.0%, influenced by demand for in-building wireless solutions and rising adoption of private networks. The UK stands at 34.4%, supported by small cell rollouts in transportation hubs and city centers. The USA shows 30.8%, as adoption is steady but moderated by established macro networks and a more gradual 5G densification strategy.
The CAGR for the small cell network market in the United Kingdom was nearly 28.7% during 2020–2024 and improved to 34.4% for the 2025–2035 period. This upward shift occurred due to the acceleration of 5G rollouts, spectrum allocation reforms, and neutral-host partnerships that expanded coverage in city centers and transport corridors. The earlier period saw moderate expansion, as deployments were largely confined to pilot projects across select metropolitan areas. Growth after 2025 has been supported by enterprise adoption in logistics, healthcare, and commercial real estate where in-building solutions became critical. Regulatory support for easing installation approvals also aided faster deployments. The combination of operator investments and enterprise reliance has reinforced the United Kingdom as a strong contributor to the sector’s regional expansion.
The CAGR for the small cell network market in China was recorded at 42.2% between 2020–2024 and surged to 48.9% during 2025–2035. This sharp rise was supported by large-scale government investments in telecom infrastructure and the nation’s ambitious 5G coverage plans. Early growth was influenced by widespread adoption of smart connectivity projects, rising mobile data usage, and massive infrastructure spending. From 2025 onward, the expansion of millimeter wave networks and deployment in industrial parks, public spaces, and high-speed rail networks provided an additional boost. China’s focus on network densification positioned small cells as a backbone for ultra-reliable communication. The strategy of combining consumer-driven adoption with enterprise networks has ensured China’s dominance in the global landscape.
The CAGR for the small cell network market in India was nearly 39.1% during 2020–2024 and advanced to 45.3% in the 2025–2035 period. The momentum picked up due to rising mobile internet penetration, spectrum allocation reforms, and the expansion of enterprise-level networks. Growth during the early period was powered by concentrated deployments in metro cities, supporting 4G densification. After 2025, adoption accelerated as telecom operators prioritized 5G readiness, focusing on localized high-capacity coverage. Private networks for IT campuses, manufacturing plants, and healthcare facilities further elevated expansion. The demographic strength of India, combined with its fast-growing internet economy, ensured that small cell adoption became central to bridging coverage gaps and handling surging data demand.
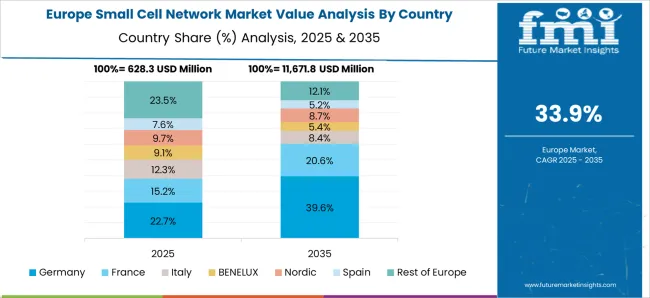
The CAGR for the small cell network market in France was about 33.4% between 2020–2024 and strengthened to 38.0% for the 2025–2035 period. Early growth was influenced by investments in telecom upgrades across urban hubs and large public infrastructure such as stadiums and airports. The transition to 5G pushed operators toward denser networks capable of supporting applications like connected mobility and industrial automation. By 2025, demand rose for in-building wireless deployments in corporate offices and commercial facilities. Regulatory authorities encouraged spectrum sharing initiatives and reduced approval delays for site installations, which made deployments faster in the later phase. With strong emphasis on enterprise connectivity and public infrastructure upgrades, France positioned itself as a European leader in small cell adoption.
The CAGR for the small cell network market in the United States was nearly 27.5% during 2020–2024 and rose to 30.8% during 2025–2035. The more moderate rise compared to other regions was due to reliance on macrocell networks, as operators had heavily invested in existing infrastructure. During the earlier years, adoption was concentrated in specific urban zones such as stadiums, universities, and dense metropolitan corridors. Growth accelerated post-2025, as operators required dense coverage for millimeter wave 5G networks and enterprises began to implement private networks across logistics hubs and technology parks. Regulatory initiatives promoting quicker site approvals and spectrum availability also helped the adoption process. Although slower than emerging economies, the United States remains a steady contributor, supported by enterprise-driven deployments and gradual 5G densification strategies.
The small cell network market is characterized by the presence of leading global telecom equipment providers, networking companies, and technology vendors focused on strengthening mobile connectivity and 5G densification. Huawei plays a dominant role with its wide-ranging small cell solutions tailored for urban and rural coverage, supported by its strong position in 5G infrastructure.
Airspan is recognized for its expertise in open RAN-based small cell technology, offering flexible and cost-effective deployment options for operators. Cisco contributes through its enterprise-driven small cell solutions, integrating advanced networking and cloud-based management systems. CommScope provides infrastructure-focused small cell solutions, particularly for in-building and enterprise connectivity. Corning is known for fiber-backed small cell deployments, enhancing capacity in dense urban areas. Ericsson remains a key player with its operator-focused small cell offerings designed for seamless 5G integration. Fujitsu is expanding its role with network densification solutions and collaborative projects in advanced 5G rollouts. Nokia delivers innovative small cell systems emphasizing private networks and enterprise solutions.
Samsung leverages its 5G expertise to supply compact small cell units for both public and private network use cases. ZTE is enhancing its portfolio with small cells designed for mass deployment in high-traffic zones, strengthening its global position. Competitive differentiation in this market revolves around integration with 5G architecture, enterprise-driven private network solutions, and scalable deployments that ensure efficient coverage and low-latency performance.
| Item | Value |
|---|---|
| Quantitative Units | USD 3.3 Billion |
| Component | Solution and Services |
| Cell | Femtocells, Picocells, Microcells, and Metro cells |
| Deployment Mode | Indoor and Outdoor |
| End Use | Telecom Operators & Service Providers, Enterprises, Smart Cities & Public Infrastructure, Healthcare, Education, Retail & Hospitality, and Industrial & Manufacturing |
| Organization Size | Large enterprises and SME |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America, Middle East & Africa |
| Country Covered | United States, Canada, Germany, France, United Kingdom, China, Japan, India, Brazil, South Africa |
| Key Companies Profiled | Huawei, Airspan, Cisco, CommScope, Corning, Ericsson, Fujitsu, Nokia, Samsung, and ZTE |
| Additional Attributes | Dollar sales, share, regional demand trends, competitive landscape, enterprise adoption, technology integration, pricing strategies, regulatory impact, and growth opportunities. |
The global small cell network market is estimated to be valued at USD 3.3 billion in 2025.
The market size for the small cell network market is projected to reach USD 71.8 billion by 2035.
The small cell network market is expected to grow at a 36.2% CAGR between 2025 and 2035.
The key product types in small cell network market are solution, _network management software, _performance optimization software, services, _professional service and _managed service.
In terms of cell, femtocells segment to command 34.7% share in the small cell network market in 2025.






Full Research Suite comprises of:
Market outlook & trends analysis
Interviews & case studies
Strategic recommendations
Vendor profiles & capabilities analysis
5-year forecasts
8 regions and 60+ country-level data splits
Market segment data splits
12 months of continuous data updates
DELIVERED AS:
PDF EXCEL ONLINE
Small Cell 5G Network Market
Small Gas Engine Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Small Molecule CDMO Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Small Molecule CMO/CDMO Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Small Animal Metabolic Monitoring System Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Small Animal Running Wheel System Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Small Molecule-Drug Conjugates Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Small Caliber Ammunition Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Small Boats Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Small Capacity Electrolyzer Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Small Animal Imaging (In Vivo) Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Small Molecule Innovator CDMO Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Small Wind Turbine Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Small Satellite Market by Ticketing Infrastructure, by Orbit Type, by Application & Region Forecast till 2035
Small Off-Road Engines Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Small Continuous Fryer Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Small Molecule Inhibitors Market Analysis – Size, Share, and Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Small Signal Transistor Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Small Bowel Enteroscopes Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Small Paint Pail Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035

Thank you!
You will receive an email from our Business Development Manager. Please be sure to check your SPAM/JUNK folder too.
Chat With
MaRIA