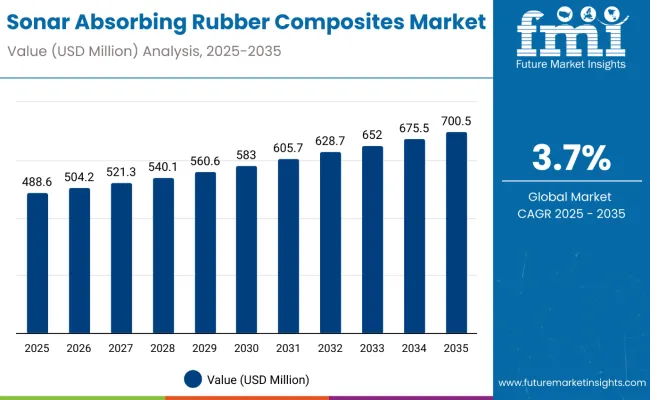
The global sonar absorbing rubber composites market is expected to be valued at USD 488.6 million in 2025 and projected to reach approximately USD 700.5 million by 2035. This represents an absolute value increase of USD 211.9 million, marking a 43.4% expansion over the forecast period. The market is forecast to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 3.7%, with overall size projected to increase by nearly 1.43X between 2025 and 2035.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Industry Size (2025E) | USD 488.6 million |
| Industry Size (2035F) | USD 700.5 million |
| CAGR (2025 to 2035) | 3.7% |
Between 2025 and 2030, the market is projected to rise from USD 488.6 million to USD 583.0 million, contributing approximately USD 94.4 million, or 44.5% of the total ten-year growth. This early phase is likely to be shaped by increased deployment of acoustic signature reduction technologies across naval defense platforms, supported by global maritime security investments and submarine fleet modernization.
During the 2030 to 2035 period, the market is expected to grow from USD 583.0 million to USD 700.5 million, generating the remaining USD 117.5 million in value. Growth in this later phase is anticipated to be driven by advancements in composite formulation, increased integration with autonomous underwater vehicles (AUVs), and broader adoption in dual-use civil-military applications such as offshore infrastructure and undersea surveillance systems.
Between 2020 and 2025, the sonar absorbing rubber composites market expanded, with total industry value rising from USD 422.3 million in 2020 to USD 488.6 million in 2025. This growth trajectory was primarily supported by increased naval modernization programs across major defense economies, particularly in submarine stealth optimization, sonar decoy shielding, and acoustic dampening linings for hull structures.
During this period, rising geopolitical tensions in strategic maritime zones such as the South China Sea, Baltic Sea, and Eastern Mediterranean prompted accelerated investments in undersea warfare capabilities. Countries including the United States, China, India, and Russia increased procurement of sonar-absorbing composites for fleet upgrades and new vessel classes. The shift toward quieter and stealthier naval platforms also fueled demand for elastomeric rubber composites embedded with microbubble or matrix-based sound absorption technologies.
Material suppliers focused on enhancing polymer durability, water resistance, and low-frequency absorption efficiency. Developments in polyurethane rubber blends, reinforced EPDM compounds, and filled silicone elastomers allowed for broader adoption across hull geometries and composite panel architectures.
The market is segmented by frequency absorption into low, medium, and broadband ranges to suit various underwater acoustic needs. Material types include natural rubber, EPDM, silicone rubber, PU rubber, and others, each offering unique damping properties. Applications span submarines, defense systems, unmanned underwater vehicles, sonar buoy housings, and more, indicating core use in naval stealth operations. Regional analysis covers North America, Latin America, Western and Eastern Europe, East Asia, South Asia and Pacific, and the Middle East and Africa, capturing global demand variations and growth trends.
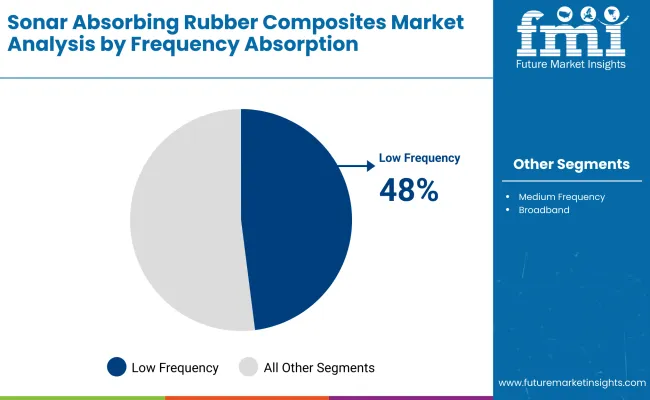
Low frequency absorption composites are projected to hold a 48% share in the frequency absorption segment in 2025, emerging as the dominant category through the forecast period. Their usage is prioritized for stealth applications in submarine and naval vessel design, where low-frequency sonar detection poses significant strategic risks. These composites effectively dampen longer wavelength sonar signals, reducing acoustic signatures in deep-sea conditions. As navies expand anti-submarine warfare capabilities and stealth infrastructure, material solutions with optimal attenuation at low frequencies are expected to witness continued specification in new designs and retrofits.
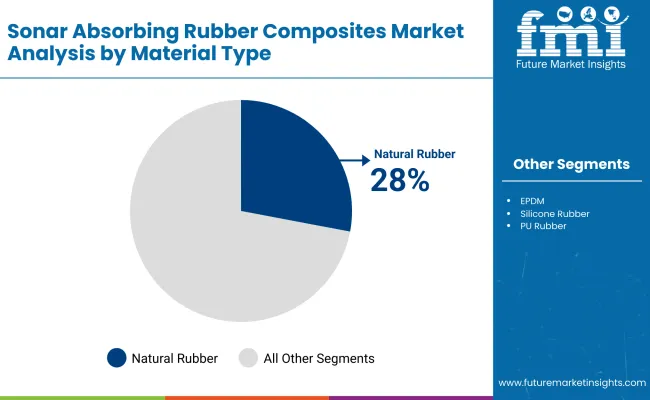
Natural rubber is expected to contribute 28% of the market in the material type segment in 2025. Its continued preference is based on favorable acoustic impedance properties, high flexibility, and cost efficiency. Natural rubber blends well with fillers and additives to produce composites with superior sound absorption at target frequencies, particularly in mid-to-low ranges. Its ease of processing and compatibility with lamination and molding processes also support widespread deployment in sonar-absorbing panels, tiles, and conformal coatings across naval platforms.
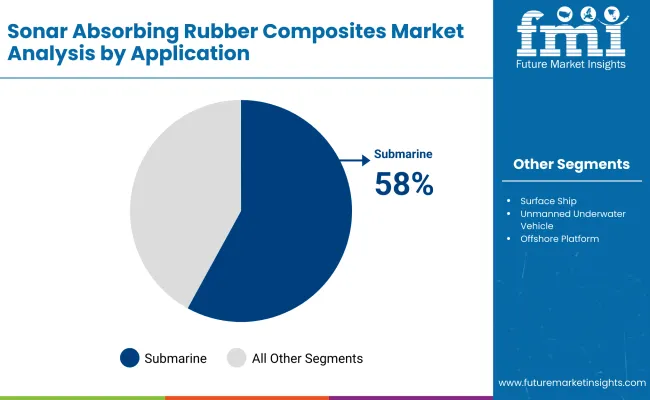
Submarine platforms are projected to account for 58% of the application share in 2025, solidifying their position as the core application area. The adoption of sonar absorbing composites in submarine hulls and sail structures is driven by operational imperatives of minimizing detectability in hostile waters. The growing global fleet of conventional and nuclear submarines, particularly in Asia-Pacific and NATO countries, continues to fuel demand for tailored rubber composites. Long-term naval procurement cycles and modernization programs are further anchoring submarine-based applications as the primary growth vector for the market.
The sonar absorbing rubber composites market is witnessing sustained growth due to the confluence of rising underwater stealth requirements, expanded naval procurement budgets, and technological advances in acoustic dampening materials. Global defense priorities are increasingly emphasizing sonar signature reduction as an essential capability for next-generation submarines, surface vessels, and autonomous underwater systems. This trend is reinforced by evolving naval strategies focused on operating in contested littoral and deep-sea environments where acoustic detectability is a critical limitation.
Geopolitical rivalries in maritime corridors and the proliferation of advanced sonar systems have led to growing investments in passive stealth materials that reduce the acoustic reflectivity of hull structures. National security programs across the United States, China, South Korea, India, and NATO countries are incorporating rubber-based acoustic composites into existing and new fleets to reduce sonar return signatures and increase mission survivability.
Parallel to military drivers, increased offshore infrastructure development—including subsea pipelines, research stations, and ocean monitoring systems—has catalyzed adoption of sonar-absorbing composites for civil marine applications. These systems require materials capable of minimizing acoustic interference and improving the fidelity of underwater signal processing.
Material innovation remains a key enabler of market expansion. Developments in microcellular elastomer design, viscoelastic damping layers, and composite lamination techniques have led to improved acoustic attenuation across a broad frequency range. Moreover, the integration of sonar-absorbing composites with lightweight fiber reinforcements and modular panel structures is enhancing installation efficiency across vessel classes and subsea modules.
The market for sonar absorbing rubber composites is being driven by growing demand for acoustic stealth in naval defense systems, expanded use of autonomous underwater vehicles (AUVs), and increased deployment of subsea communication networks. However, adoption remains constrained by the high cost of specialized elastomers, complex molding requirements, and the lack of standardization across international procurement programs. Environmental degradation, biofouling, and performance variability in extreme marine conditions present additional challenges to material reliability and lifecycle economics.
Underwater Stealth Demands Push Composite Adoption in Next-Gen Naval Platforms
Navies across North America, Europe, and Asia are investing heavily in sonar-absorbing technologies to minimize vessel detectability and counter the growing sophistication of active sonar systems. Submarine hulls, torpedo casings, and sonar dome enclosures are increasingly lined with rubber composites that attenuate acoustic waves and reduce reflected energy signatures. Modern combat vessels are required to operate in multi-threat environments, reinforcing the need for passive acoustic cloaking materials that function without emitting counter-signals. The shift toward low-frequency and broadband sonar coverage has further necessitated customized elastomeric formulations with layered absorption profiles.
Material Engineering Advances Improve Frequency Band Performance and Durability
Technological progress in composite rubber design—particularly the incorporation of viscoelastic polymers, microcellular fillers, and fiber-reinforced elastomers—is enabling tailored sound absorption across targeted frequency bands. These engineered materials can now absorb energy from sonar pulses in both low and mid-frequency ranges while maintaining hydrodynamic shape stability. Surface treatments that resist marine biofouling and microcracking have also improved long-term deployment outcomes. Additionally, multilayered laminate constructions combining rubber with metallic or ceramic barriers are extending the utility of these composites to harsh underwater terrains and fluctuating thermal environments.
| Country | 2025 |
|---|---|
| Germany | 16% |
| Italy | 12% |
| France | 18% |
| UK | 14% |
| Spain | 7% |
| BENELUX | 2% |
| Russia | 15% |
| Rest of Europe | 16% |
| Country | 2035 |
|---|---|
| Germany | 17% |
| Italy | 11% |
| France | 19% |
| UK | 13% |
| Spain | 8% |
| BENELUX | 3% |
| Russia | 16% |
| Rest of Europe | 13% |
France is projected to remain the largest contributor to Europe's sonar absorbing rubber composites market, growing from 18% in 2025 to 19% in 2035. The country continues to lead due to its extensive naval defense modernization, including upgrades to the Barracuda-class submarines and investments in sonar stealth capabilities.
Germany follows with a steady increase from 16% to 17%, backed by high-value shipbuilding contracts and export-oriented sonar system production. Russia maintains a strong share, growing from 15% to 16%, supported by fleet renewals and domestic composite material sourcing.
Meanwhile, the UK’s share is projected to decline slightly from 14% to 13%, although defense-led demand remains significant. Spain is expected to grow marginally from 7% to 8% due to increased coastal surveillance infrastructure. Italy’s share is forecast to decline from 12% to 11%, while BENELUX is expected to gain a slight uptick from 2% to 3%. Rest of Europe is projected to decrease from 16% to 13%.
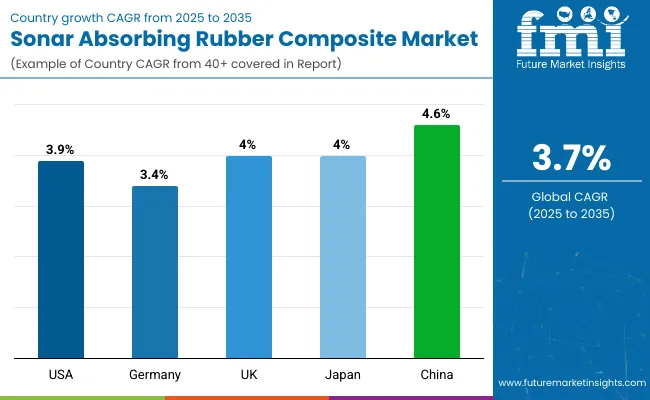
The USA market is expected to expand at a CAGR of 3.9%, driven by growing procurement of advanced submarine and naval assets. Ongoing investments in stealth technologies, including sonar attenuation materials for Virginia-class submarines and AUV programs, are driving demand.
Germany is projected to grow at a CAGR of 3.4%, supported by naval exports and advanced shipyard capabilities. Rubber composites are increasingly used in hull-mounted sonar domes and propulsion noise dampening.
The UK is forecast to grow at a CAGR of 4.0% owing to its long-term naval modernization strategy and expansion of undersea drone fleets. Lightweight rubber composites are being integrated into both defense and civilian subsea systems.
Japan’s sonar absorbing rubber composites market is expected to post a CAGR of 4.0%, driven by maritime border surveillance and modern submarine fleet expansion. Demand is increasing for rubber composites compatible with layered hull insulation systems.
China is projected to be the fastest-growing market with a CAGR of 4.6%, led by expansive submarine manufacturing, coastal surveillance deployment, and rising exports of naval systems.
EPDM rubber is projected to hold a 29% share in Japan's sonar absorbing composite material usage by 2025. Its weather resilience and consistent acoustic performance make it ideal for naval systems exposed to saltwater, pressure variation, and long deployment cycles. Natural rubber (24%) continues to serve in older sonar architectures, while silicone rubber (18%) is favored for electronics shielding in shallow-water or research-grade sonar units. PU rubber (16%) supports localized vibration isolation in sonar panel arrays.
South Korea’s composite materials market is led by low-frequency absorption technologies, comprising 42% of the demand. These are tailored for stealth missions, long-range acoustic sensing, and naval intelligence systems on submarines and frigates. Medium frequency absorbers (38%) are common in surface vessel installations and unmanned underwater vehicles (UUVs). Broadband absorption holds a 20% share and is gradually expanding in anti-submarine warfare and ship-mounted array upgrades.
Competition in the sonar-absorbing rubber composites market is being shaped by advancements in materials and acoustic technologies. New coatings and composite solutions are being developed to reduce vessel detection risk and enhance underwater stealth capabilities. Investment in research and development is being prioritized to improve absorption efficiency, durability, and performance under diverse operational conditions.
| Item | Value |
|---|---|
| Quantitative Units | USD 488.6 Million (2025) |
| Material Type | Natural Rubber, EPDM, Silicone Rubber, PU Rubber, Others |
| Frequency Absorption | Low Frequency, Medium Frequency, Broadband |
| Application | Naval Submarines, Surface Ships, Unmanned Underwater Vehicles (UUVs), Offshore Platforms, Research Equipment |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, East Asia, South Asia & Pacific, Latin America, Middle East & Africa |
| Countries Covered | United States, Germany, United Kingdom, Japan, China |
| Key Companies Profiled | Trelleborg AB, Meggitt PLC, Furuno Electric Co. Ltd., Thales Group, Ultra Electronics, KENNO Corporation, Cuming Microwave Corporation, CompositeTechs LLC, Hunan Zhongke Shield Technology Co. Ltd., Sonatech Inc. |
The global market is estimated to reach USD 2.5 billion in 2025, with strong growth expected through 2035.
The market is forecast to grow at a CAGR of 7.4% during the 2025 to 2035 period
Panoramic sunroof systems hold a 66% share in Japan, favored for their enhanced cabin aesthetics.
Brazil, Australia, and the United States are projected to witness robust growth, each with a CAGR above 7%.
The increasing penetration of electric vehicles and preference for quiet, durable motor systems are boosting demand for brushless DC drives.






Full Research Suite comprises of:
Market outlook & trends analysis
Interviews & case studies
Strategic recommendations
Vendor profiles & capabilities analysis
5-year forecasts
8 regions and 60+ country-level data splits
Market segment data splits
12 months of continuous data updates
DELIVERED AS:
PDF EXCEL ONLINE
Sonar Absorbing Rubber Composites Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Radar Absorbing Materials Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Food Oil Absorbing Sheet Market Trends & Industry Growth Forecast 2024-2034
Microwave Absorbing Material Market Size, Growth, and Forecast 2025 to 2035
Near Infrared Absorbing Material Market Growth – Trends & Forecast 2024-2034
Low Frequency Sound Absorbing Insulation Material Market Growth – Trends & Forecast 2024-2034
Composite Resin Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Composite Pin Insulator Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Composite Roller Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Composite Insulator Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Composite Paper Cans Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Composite Drums Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Composite Textile Production Equipment Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Composite Cans Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Composite Film Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Composite Cardboard Tube Packaging Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Composite Cylinder Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Composite Tooling Market Outlook- Share, Growth and Forecast 2025 to 2035
Composite Cardboard Tubes Market from 2025 to 2035
Composite IBCs System Market from 2025 to 2035

Thank you!
You will receive an email from our Business Development Manager. Please be sure to check your SPAM/JUNK folder too.
Chat With
MaRIA