The transport fuel cell market, valued at 6.21 USD billion in 2025, is projected to reach 14.71 USD billion by 2035, reflecting a CAGR of 9.0% over the period. The market maturity curve shows a steady climb from niche usage in 2020–2024 to a defined growth path. In 2025 the curve bends upward as unit deployments, supply chains, and refueling networks reach repeatable scale.
Between 2025–2030, annual volumes step from the mid-single-digits toward double-digits, pushing the curve into its steepest section as fleets standardize models and costs fall with volume learning. From 2030–2035 the slope moderates, reflecting wider availability, clearer standards, and tighter competition. By 2035, at 14.71 USD billion, the curve approaches mid-maturity with stable replacement cycles and fewer greenfield launches.
The adoption lifecycle mirrors this arc. In 2020–2024, pioneers and pilot-heavy fleets validate duty cycles and total cost, shaping early references. From 2025–2030, early-to-mainstream buyers expand orders across buses, trucks, and specialty vehicles; ecosystem partners lock multiyear contracts; aftersales footprints broaden; and financing evolves from bespoke to programmatic. In 2030–2035, late entrants follow proven templates, procurement gets price-led, incumbents consolidate via partnerships and M&A, and performance gaps narrow. Diffusion thus shifts from proof and learning, to scale and replication, to disciplined, margin-focused competition.
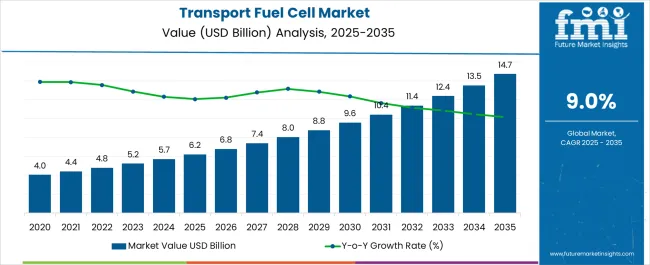
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Transport Fuel Cell Market Estimated Value in (2025 E) | USD 6.2 billion |
| Transport Fuel Cell Market Forecast Value in (2035 F) | USD 14.7 billion |
| Forecast CAGR (2025 to 2035) | 9.0% |
Seasonality in the transport fuel cell market is moderate but visible through order clustering, policy deadlines, and fleet cycles. For example, procurement data shows that up to 35–40% of annual vehicle orders close in Q4 as fleet operators utilize budgets before fiscal year-end, compared to just 15–20% in Q1. Deployment peaks often coincide with government incentive disbursements; in markets where subsidies reset annually, activity surges by 20–25% in the months leading to cutoff dates. Infrastructure rollouts also create seasonal spikes: a new corridor launch can lift local quarterly demand by 10–15%, pulling forward fleet purchases tied to station availability. Cyclicality reflects longer investment and replacement horizons.
Heavy-duty fleets typically replace assets on 5–7 year intervals, creating visible waves in order books, e.g., a large transit operator shifting 300–500 buses can swing annual demand by USD 0.3–0.5 billion. Similarly, policy cycles drive temporary accelerations: in markets with subsidy windows closing in 2030, adoption is projected to spike 20–30% above baseline CAGR between 2028–2030 before normalizing. On a macro basis, demand cycles track capital expenditure trends, where downturns can reduce procurement volumes by 10–15% for 12–18 months, followed by recovery-led surges as deferred replacements are executed.
The transport fuel cell market is progressing rapidly, supported by a global shift toward clean energy solutions and the decarbonization of the transportation sector. Governments and private sector players are actively investing in hydrogen infrastructure, enabling large scale deployment of fuel cell technologies. Advances in fuel cell efficiency, durability, and cost reduction have accelerated adoption in both commercial and passenger transport applications.
Strategic collaborations among automakers, energy providers, and technology developers are fostering an ecosystem that supports the growth of fuel cell powered vehicles. Incentives and regulatory frameworks promoting zero emission transportation are further strengthening demand.
The integration of fuel cells in heavy duty applications, including buses, trucks, and marine transport, is expanding the addressable market As green hydrogen production scales and distribution networks mature, transport fuel cell systems are expected to play an increasingly central role in sustainable mobility strategies, ensuring long term market growth.
The transport fuel cell market is segmented by capacity, product, end use, and geographic regions. By capacity, transport fuel cell market is divided into < 200 kW, 200 kW - 1 MW, and ≥ 1 MW. In terms of product, transport fuel cell market is classified into PEMFC, DMFC, SOFC, PAFC & AFC, and MCFC. Based on end use, transport fuel cell market is segmented into FCEVs, Marine, Railways, and Others. Regionally, the transport fuel cell industry is classified into North America, Latin America, Western Europe, Eastern Europe, Balkan & Baltic Countries, Russia & Belarus, Central Asia, East Asia, South Asia & Pacific, and the Middle East & Africa.
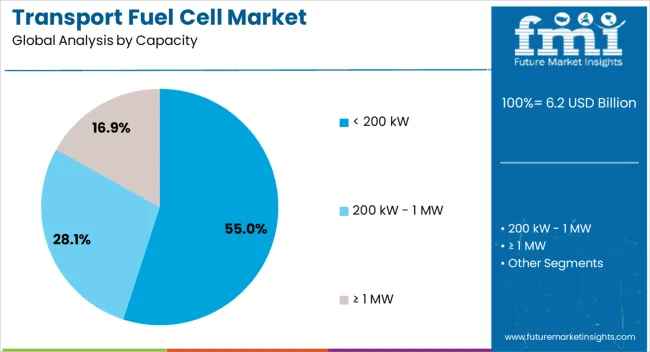
The capacity segment of less than 200 kW is projected to hold 55% of the transport fuel cell market revenue share in 2025, establishing it as the leading category. Growth in this segment has been driven by its suitability for light duty vehicles, small commercial fleets, and certain public transport applications where compact, efficient systems are required.
Fuel cells in this capacity range have been favored for their ability to deliver high power density while maintaining a lightweight design, enhancing vehicle performance and range. The adoption has also been supported by advancements in stack technology, which have improved operational lifespans and reduced costs.
Flexibility in integrating these systems into various vehicle platforms has widened their appeal across automotive manufacturers In addition, supportive policies and subsidies have encouraged the use of fuel cells in urban and regional transport networks, consolidating the dominant position of this capacity range in the overall market.
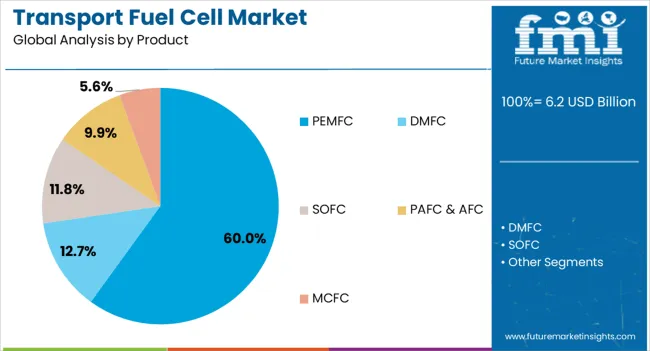
The proton exchange membrane fuel cell (PEMFC) segment is anticipated to account for 60% of the transport fuel cell market revenue share in 2025, making it the dominant product type. Its leadership has been attributed to high efficiency, rapid start up capability, and adaptability to varying power demands in transportation applications. PEMFCs operate at relatively low temperatures, allowing for quick response and suitability in automotive use cases.
Their compatibility with pure hydrogen as a fuel source has aligned well with the growing investments in hydrogen refueling infrastructure. The segment has also benefited from ongoing advancements in membrane durability and catalyst performance, which have reduced operational costs and enhanced commercial viability.
Lightweight design and scalability have allowed PEMFCs to be deployed across a wide range of vehicles, from passenger cars to heavy-duty trucks. These characteristics, combined with supportive government initiatives, have reinforced the segment’s leadership position in the global market.
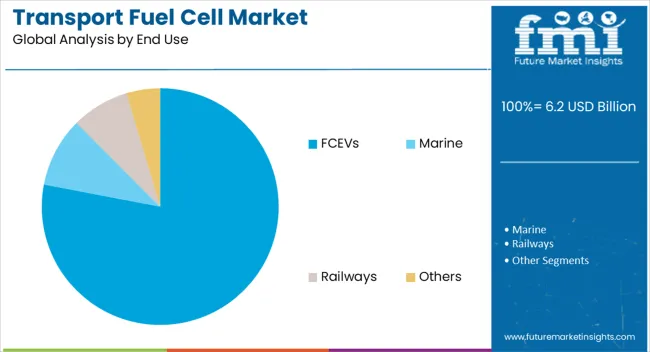
The fuel cell electric vehicle (FCEV) segment is expected to capture 78% of the transport fuel cell market revenue share in 2025, securing its position as the leading end-use category. Growth in this segment has been propelled by increasing demand for zero-emission vehicles that combine long driving ranges with short refueling times. FCEVs have gained strong acceptance in regions with well-established hydrogen infrastructure, where operational efficiency and environmental benefits align with policy goals.
The integration of advanced fuel cell systems in passenger cars, buses, and trucks has expanded their adoption across both commercial and private transportation sectors. Competitive performance compared to internal combustion and battery electric vehicles has further strengthened market penetration.
Strategic partnerships between vehicle manufacturers and energy providers have accelerated deployment, while incentives and regulatory measures have reduced the cost barrier for consumers and fleet operators. These factors have collectively positioned FCEVs as the primary driver of transport fuel cell market growth.
The transport fuel cell market is gaining momentum as industries shift toward cleaner propulsion technologies for vehicles, trains, ships, and aircraft. Fuel cells convert hydrogen into electricity with minimal emissions, making them attractive for decarbonizing heavy-duty and long-range transport. Asia-Pacific leads deployment, driven by government initiatives in Japan, China, and South Korea, while Europe and North America expand through clean mobility policies. Manufacturers are working on improving cost-efficiency, hydrogen infrastructure compatibility, and durability for large-scale commercial adoption.
Fuel cells are particularly suited for buses, trucks, trains, and ships that require long ranges and rapid refueling. Unlike battery-electric systems, fuel cells offer high energy density and faster turnaround times, making them practical for logistics fleets, intercity buses, and freight locomotives. Adoption in heavy-duty transport is accelerating as operators prioritize low-emission solutions that do not compromise payload capacity. Until alternative zero-emission technologies can match the efficiency and range of fuel cells in large transport applications, fuel cell systems will remain a preferred option for decarbonizing long-haul mobility.
The growth of transport fuel cells is closely linked to the development of hydrogen production and refueling infrastructure. Limited availability of hydrogen stations, especially outside Asia, restricts widespread adoption. Governments and private investors are funding hydrogen corridors, port facilities, and urban refueling hubs to support vehicle rollout. Regions with established hydrogen supply chains, such as Japan and parts of Europe, see faster adoption. Until hydrogen infrastructure is expanded globally to ensure convenient refueling access, the scalability of transport fuel cells will remain dependent on infrastructure development.
High costs of fuel cell stacks, catalysts, and hydrogen storage systems continue to challenge market competitiveness. Manufacturers are focusing on reducing platinum content in catalysts, improving membrane longevity, and optimizing balance-of-plant components. Increased durability, with lifespans matching those of conventional engines, is essential for heavy transport fleets to justify investment. Collaborative projects between fuel cell suppliers, automotive manufacturers, and material scientists aim to achieve cost parity with diesel and hybrid alternatives. Until costs decline and operational lifespans increase, adoption will remain concentrated in pilot programs and subsidized fleets.
Government regulations, emission mandates, and funding incentives strongly influence fuel cell adoption. Asia-Pacific leads with strong state backing in Japan, South Korea, and China, focusing on buses, trucks, and fuel cell passenger vehicles. Europe supports deployment through clean hydrogen strategies and public transport projects, while North America emphasizes freight and transit buses. Policy-driven programs create early demand, but long-term growth depends on aligning fuel cell vehicle production with hydrogen availability. Until global policy frameworks stabilize and align with infrastructure development, adoption patterns will remain regionally uneven.
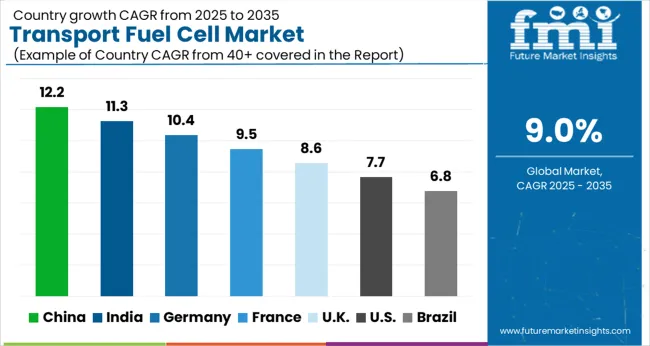
| Country | CAGR |
|---|---|
| China | 12.2% |
| India | 11.3% |
| Germany | 10.4% |
| France | 9.5% |
| UK | 8.6% |
| USA | 7.7% |
| Brazil | 6.8% |
The global transport fuel cell market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 9.0% through 2035, supported by increasing adoption in electric mobility, hydrogen infrastructure, and clean transport initiatives. Among BRICS nations, China has been recorded with 12.2% growth, driven by large-scale investment in hydrogen-powered vehicles and fuel cell infrastructure, while India has been observed at 11.3%, supported by government initiatives and rising adoption in public and commercial transport fleets. In the OECD region, Germany has been measured at 10.4%, reflecting strong industrial deployment and innovation in transport fuel cell technologies, while France has been noted at 9.5%, with demand supported by clean energy policies and transport electrification. The United Kingdom has been recorded at 8.6%, where commercialization and adoption in automotive and heavy-transport sectors have been steadily expanding, while the USA has been observed at 7.7%, reflecting consistent investment in hydrogen mobility and transport decarbonization. This report includes insights on 40+ countries; the top six markets are shown here for reference.
The transport fuel cell market in China is growing at a robust CAGR of 12.2%, supported by government policies promoting clean mobility and reduction of carbon emissions. With China leading the world in new energy vehicle adoption, fuel cells are gaining traction as a complementary technology to battery-electric systems, particularly for heavy-duty transport. Hydrogen infrastructure expansion, subsidies for fuel cell vehicles (FCVs), and strong investment in hydrogen production drive market growth. Public-private partnerships are accelerating large-scale deployment of hydrogen-powered buses, trucks, and commercial fleets. Domestic manufacturers are investing in R&D to improve fuel cell efficiency, durability, and cost-effectiveness, further strengthening China’s position in the global market. Rising focus on energy security and reducing reliance on fossil fuels ensures continued momentum for transport fuel cell adoption.
Transport fuel cell market in India is expanding at a CAGR of 11.3%, driven by increasing government initiatives to promote hydrogen-based mobility and reduce urban pollution. Hydrogen fuel cells are being positioned as a viable alternative to conventional fuels, especially for buses, trucks, and long-haul vehicles. The National Hydrogen Mission and pilot projects in major cities are key growth enablers. India’s growing industrial sector and focus on renewable hydrogen production also provide a strong foundation for transport fuel cell adoption. Collaborations between global technology providers and domestic manufacturers are accelerating the development of cost-effective and efficient systems. Although infrastructure challenges remain, strategic investments in hydrogen fueling stations are expected to improve accessibility. Rising awareness of sustainable transport and stricter emission norms support market penetration in urban and intercity transport segments.
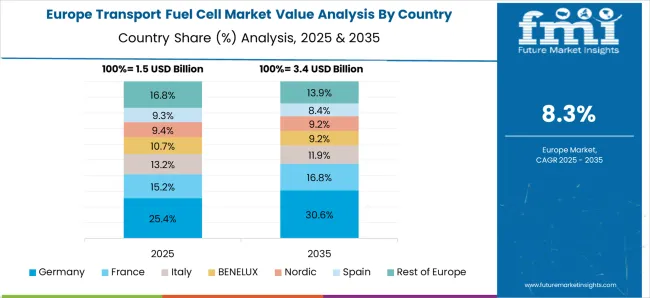
The transport fuel cell market in Germany is witnessing steady growth at a CAGR of 10.4%, supported by strong environmental policies and emphasis on green hydrogen. Germany’s commitment to carbon neutrality and leadership in clean mobility technologies makes it a frontrunner in fuel cell adoption. The government is investing heavily in hydrogen fueling networks, with focus on buses, trucks, and rail transport. Collaboration between automakers, energy companies, and research institutions accelerates innovation and deployment. Fuel cells are being increasingly integrated into heavy-duty vehicles, logistics fleets, and public transport systems. Germany’s industrial base and technological expertise support the development of high-efficiency and durable systems. Continued focus on renewable hydrogen production enhances sustainability, making fuel cell transport a strategic pillar in Germany’s clean mobility roadmap.
The UK transport fuel cell market is growing at a CAGR of 8.6%, supported by decarbonization goals and adoption of hydrogen-powered transport solutions. Hydrogen buses, trucks, and trains are being deployed in pilot projects across major cities, supported by government funding and regional initiatives. Fuel cells are seen as vital for long-haul and heavy-duty mobility, complementing the country’s electric vehicle transition. Investments in hydrogen production and distribution networks are underway, though at a slower pace compared to leading European counterparts. Collaborations between energy companies, automakers, and public transport operators strengthen market growth. Rising focus on achieving net-zero emissions and promoting clean energy technologies ensures steady adoption of transport fuel cells in the UK
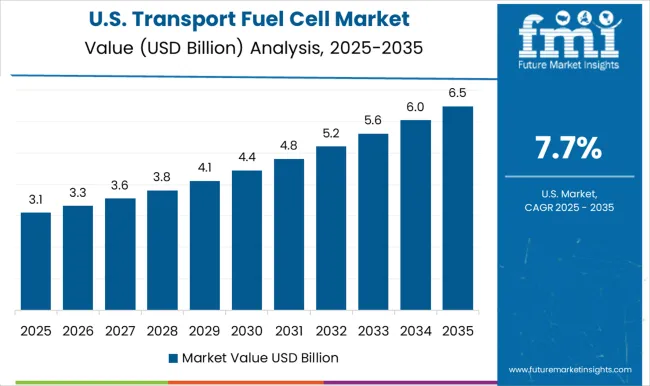
The transport fuel cell market in the United States is expanding at a CAGR of 7.7%, driven by federal and state-level initiatives promoting clean energy and hydrogen adoption. California leads deployment, with hydrogen-powered buses, trucks, and passenger cars integrated into transportation systems. The USA Department of Energy and private companies are investing heavily in hydrogen infrastructure and fuel cell R&D. Growing interest in decarbonizing freight, logistics, and public transit is pushing adoption, particularly in regions with strong policy support. Partnerships between automakers, energy firms, and government agencies enhance market development. While battery-electric vehicles currently dominate, fuel cells are gaining momentum in heavy-duty and long-range transport where high efficiency and fast refueling are critical. Increasing green hydrogen production further strengthens the long-term outlook.
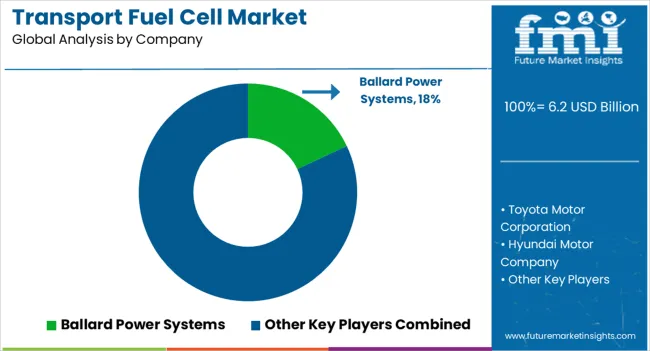
The transport fuel cell market is expanding rapidly as industries and governments push for cleaner mobility solutions to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and dependence on fossil fuels. Fuel cells, particularly hydrogen-based systems, are gaining momentum in applications such as passenger vehicles, buses, trucks, trains, and even maritime transport due to their high efficiency, long range, and fast refueling capabilities compared to conventional batteries. Global decarbonization goals, government incentives for zero-emission transport, and investments in hydrogen infrastructure strongly support the market growth. Ballard Power Systems is a pioneer in proton exchange membrane (PEM) fuel cell technology and a leader in supplying fuel cells for buses, trucks, and rail transport.
Toyota Motor Corporation is at the forefront of commercial fuel cell vehicles (FCVs) with its Mirai sedan and partnerships to scale fuel cell applications in heavy-duty vehicles. Hyundai Motor Company has advanced fuel cell integration in passenger cars, trucks, and buses with its NEXO and XCIENT Fuel Cell models. Plug Power Inc. has positioned itself as a key player in hydrogen-powered mobility solutions, particularly in logistics and material handling. Cummins Inc. leverages its power systems expertise to develop fuel cell solutions for commercial vehicles and large-scale transport. Together with other emerging players, these companies are advancing innovation in hydrogen storage, fuel cell stack efficiency, and cost reduction strategies. As infrastructure for hydrogen refueling expands and production costs decline, transport fuel cells are expected to play a critical role in the transition to sustainable mobility, particularly in sectors where long range and high power are essential.
| Item | Value |
|---|---|
| Quantitative Units | USD 6.2 Billion |
| Capacity | < 200 kW, 200 kW - 1 MW, and ≥ 1 MW |
| Product | PEMFC, DMFC, SOFC, PAFC & AFC, and MCFC |
| End Use | FCEVs, Marine, Railways, and Others |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America, Middle East & Africa |
| Country Covered | United States, Canada, Germany, France, United Kingdom, China, Japan, India, Brazil, South Africa |
| Key Companies Profiled | Ballard Power Systems, Toyota Motor Corporation, Hyundai Motor Company, Plug Power Inc., Cummins Inc., and Others |
| Additional Attributes | Dollar sales in the Transport Fuel Cell Market vary by type including proton exchange membrane fuel cells, solid oxide fuel cells, and alkaline fuel cells, application across passenger vehicles, buses, trucks, trains, and marine transport, and region covering North America, Europe, and Asia-Pacific. Growth is driven by rising demand for zero-emission vehicles, government incentives for clean energy adoption, and advancements in hydrogen infrastructure. |
The global transport fuel cell market is estimated to be valued at USD 6.2 billion in 2025.
The market size for the transport fuel cell market is projected to reach USD 14.7 billion by 2035.
The transport fuel cell market is expected to grow at a 9.0% CAGR between 2025 and 2035.
The key product types in transport fuel cell market are < 200 kw, 200 kw - 1 mw and ≥ 1 mw.
In terms of product, pemfc segment to command 60.0% share in the transport fuel cell market in 2025.






Full Research Suite comprises of:
Market outlook & trends analysis
Interviews & case studies
Strategic recommendations
Vendor profiles & capabilities analysis
5-year forecasts
8 regions and 60+ country-level data splits
Market segment data splits
12 months of continuous data updates
DELIVERED AS:
PDF EXCEL ONLINE
Transport Cases & Boxes Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Transportation and Security System Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Transport Management System Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Transportation Infrastructure Construction Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Transportation Aggregators Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Transportation Based Hydrogen Energy Storage Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Transportation Analytics Market Analysis - Size, Share, and Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Transport Protein Assays Kits Market Trends - Industry Forecast 2025 to 2035
Transportation Condensing Units Market Growth – Trends & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Market Share Distribution Among Transport Cases & Boxes Providers
Transport Packaging Market from 2025 to 2035
Transportation Composites Market Growth – Trends & Forecast 2022 to 2032
Transportable Ventilator Market
Transportation Coating Market Analysis 2022 to 2032
Transportation Predictive Analytics Market Report – Growth & Forecast 2017-2027
Transportation Biofuel Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
MRI Transport Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Pet Transporting Service Market Growth - Demand & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Air Transport MRO Market Trends - Growth & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Ice Transport Buckets Market

Thank you!
You will receive an email from our Business Development Manager. Please be sure to check your SPAM/JUNK folder too.
Chat With
MaRIA