The global ultra-thin glass market is projected to grow from USD 13.15 billion in 2025 to approximately USD 29.5 billion by 2035, reflecting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 8.7%. Market expansion is primarily driven by the growing demand for lightweight and durable materials in electronic displays, solar panels, and automotive applications.
| Attributes | Description |
|---|---|
| Estimated Global Industry Size (2025E) | USD 13.15 billion |
| Projected Global Value (2035F) | USD 29.5 billion |
| Value-based CAGR (2025 to 2035) | 8.7% |
Demand for ultra-thin glass is increasing across sectors that prioritize both functional performance and space efficiency. In consumer electronics, the material is being adopted for foldable smartphones, tablets, and wearable devices, where its combination of flexibility, scratch resistance, and transparency is essential. Foldable OLED and Micro LED displays represent a key growth vector, with ultra-thin glass replacing plastic films in applications that require higher durability and visual clarity.
In the automotive sector, manufacturers are using ultra-thin glass to reduce component weight in head-up displays, infotainment systems, and sunroofs, which aligns with broader goals to enhance energy efficiency in electric vehicles. The material’s thermal stability and optical properties also support its integration into advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) and interior smart surfaces.
In the solar energy domain, ultra-thin glass is gaining traction in the production of high-efficiency photovoltaic modules. Its lightweight nature and superior light transmittance enhance energy capture while reducing structural load in rooftop and portable solar applications. Manufacturers are expanding investments in ultra-thin glass for bifacial solar modules and building-integrated photovoltaics (BIPV), particularly in China, South Korea, and Japan.
Despite these drivers, the market faces certain limitations. High capital investment required for precision manufacturing, along with yield losses due to breakage during processing, remain critical cost barriers. Technological complexity in handling and laminating ultra-thin sheets, especially those below 0.1 mm thickness, further constrains adoption in some mid-tier applications. Moreover, competition from flexible polymers and coated films continues in price-sensitive segments.
China and the broader Asia-Pacific region are expected to retain dominant market share due to robust consumer electronics manufacturing, supportive industrial policies, and domestic supply chains.
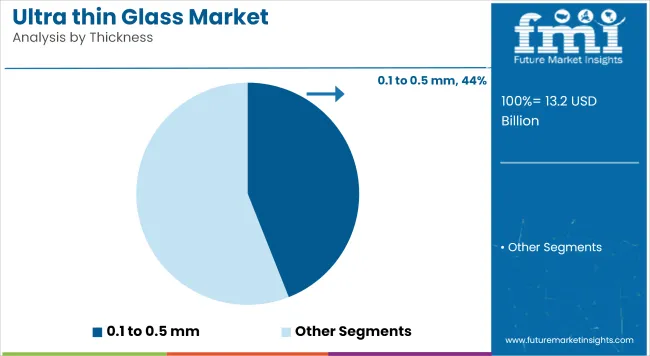
The 0.1 mm to 0.5 mm segment is projected to hold approximately 44% of the global ultra-thin glass market share in 2025 and is expected to grow at a CAGR of 8.9% through 2035. This thickness range offers the necessary flexibility and mechanical strength required in foldable smartphones, curved displays, and advanced wearable electronics.
Its adoption is supported by ongoing innovation in screen lamination, low-temperature processing, and optical clarity enhancement. Manufacturers are increasingly adopting roll-to-roll manufacturing techniques and laser-assisted cutting for this segment, which makes it suitable for high-volume applications in consumer electronics and automotive interior displays.
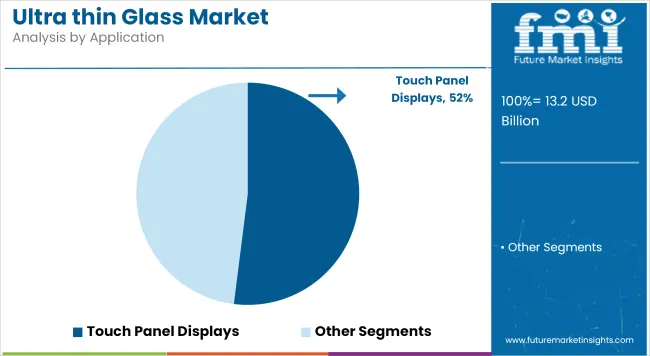
The touch panel display segment is estimated to account for approximately 52% of the global ultra-thin glass market share in 2025 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 8.8% through 2035. Ultra-thin glass is favored in capacitive and resistive touchscreens for its excellent surface smoothness, scratch resistance, and ability to transmit light without distortion.
Its use spans smartphones, tablets, infotainment systems, and industrial control panels. The shift toward bezel-less designs, foldable screens, and thinner consumer devices is further accelerating demand in this application. As OEMs seek robust materials that meet both aesthetic and functional requirements, ultra-thin glass continues to replace plastic and conventional thicker glass alternatives.
| Key Drivers | Key Restraints |
|---|---|
| Increasing Demand in Consumer Electronics: The growing use of ultra-thin glass in consumer electronics such as smartphones, tablets, wearables, and foldable displays is a significant driver. Its flexibility, lightweight nature, and superior optical clarity make it ideal for advanced electronics. | High Production Costs: The manufacturing of ultra-thin glass, especially through advanced techniques like fusion and float processes, can be costly. The high production costs involved can hinder the market's expansion, especially for small and medium-sized manufacturers. |
| Rise of Foldable Displays and Wearable Devices: Ultra-thin glass is essential for foldable displays and wearable devices. As these technologies gain popularity in the consumer electronics market, the demand for ultra-thin glass is increasing, driving market growth. | Limited Thickness Range: Although ultra-thin glass has many applications, its limited thickness range can be a constraint. For instance, thicker glass is required for certain heavy-duty applications, and ultra-thin glass may not be suitable for such needs. |
| Advancements in Semiconductor Industry: The use of ultra-thin glass as substrates for semiconductor manufacturing is expanding. With the growing demand for high-performance semiconductors in the electronics and automotive sectors, this application is a key driver for market growth. | Lack of Standardization: As the market for ultra-thin glass is still evolving, a lack of standardisation across various industries and manufacturers can create barriers to widespread adoption and reduce operational efficiency. |
| Growth in the Automotive Sector: Ultra-thin glass is becoming increasingly popular in the automotive industry, particularly in lightweight vehicle design, energy-efficient solutions, and advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS). The need for durable yet lightweight materials to improve fuel efficiency and reduce emissions supports market growth. | Fragility of Ultra-Thin Glass: Ultra-thin glass, while lightweight and flexible, may lack the strength and durability needed for certain applications, such as heavy-duty industrial uses or extreme conditions. This limitation could restrict its adoption in some markets. |
| Improved Optical Properties: Ultra-thin glass is highly valued for its superior optical clarity and ability to transmit light with minimal reflection loss. Its use in applications like touch panels, fingerprint sensors, and solar panels drives market demand, especially as technological advancements improve its performance. | Competition from Alternative Materials: The ultra-thin glass market faces competition from other materials, such as plastic and flexible films, which can offer similar benefits at a lower cost. Alternatives may limit the widespread adoption of ultra-thin glass in some industries. |
| Growing Renewable Energy Applications: Ultra-thin glass is increasingly being used in solar panels and other renewable energy applications due to its light-transmitting capabilities, enhancing the performance of solar cells. As the renewable energy market expands, the demand for ultra-thin glass for these applications is also increasing. | Environmental and Sustainability Concerns: The production of ultra-thin glass can have environmental impacts, including the use of energy-intensive processes and the production of waste materials. Additionally, concerns about the recyclability of ultra-thin glass could hinder its acceptance in certain markets. |
| Technological Innovations: The continuous development of new manufacturing techniques, including chemical vapour deposition (CVD) and physical vapour deposition (PVD), is expected to improve the properties of ultra-thin glass, opening up new applications and markets. | Fragile Supply Chain: The market for ultra-thin glass relies on specific raw materials, such as certain types of sand or silica, which can create supply chain vulnerabilities. Fluctuations in raw material prices or scarcity can affect production and impact the overall market. |
| Increasing Adoption in Medical Devices: Ultra-thin glass is gaining traction in the medical and healthcare industries, especially in diagnostic equipment, devices, and healthcare applications. Its biocompatibility, strength, and durability make it an ideal choice for various medical uses. | Lack of Consumer Awareness: Despite the advantages of ultra-thin glass, there is still a lack of widespread consumer and industrial awareness regarding its benefits and potential applications. This knowledge gap may slow down the adoption rate across various sectors. |
Key Driver
| Driver | Impact |
|---|---|
| Increasing demand from consumer electronics for lightweight, durable materials | High |
| Growing adoption of foldable and flexible displays | High |
| Advancements in the automotive industry towards lightweight designs and electric vehicles | Medium |
| Rising use in solar energy applications for enhanced efficiency | Medium |
| Technological advancements in display technologies like OLED and Micro LED | High |
| Expansion in the Asia-Pacific region due to robust domestic demand and supportive policies | High |
Key Restraints
| Restraint | Impact |
|---|---|
| High production costs | High |
| Technological complexities | Medium |
| Competition from alternative materials | Medium |
| Limited awareness in emerging markets | Low |
| Environmental and safety regulations | Medium |
| Supply chain disruptions | Medium |
The Ultra-thin glass sector is one of the most prominent markets in the United States, with its surging demand, especially in the North American region. The ultra-thin glass is extensively used in consumer electronics and the automotive industry. Countries, including Israel, have an advanced manufacturing ecosystem and extensive R&D infrastructure that encourages innovation in the field of ultra-thin glass. The industry is projected to continue growing in the North American market, especially in high-tech and renewable energy applications.
Ultra-thin glass has a robust market in the UK, primarily due to intense research and development related to consumer electronics and automotive applications. The ultra-thin glass in renewable energy and medical devices is one of the areas explored in the UK, which is also one of the reasons behind the fast-growing market in this region.
The ultra-thin glass market in France is supported by its well-organized manufacturing industry and strong sustainability focus. The automotive and consumer electronics industries drive the European market, and the country's import demand plays an important role. With a strong commitment to renewable energy, France is taking all measures, including investing in ultra-thin glass that can be used in solar energy applications.
Germany is a key player in ultra-thin glass production relative to other countries, with a high focus on high-quality production and technological advancements. The industry’s growth is driven by demand from the automotive, consumer electronics and renewable energy sectors. The nation’s strong industrial base and focus on innovation led to a rapid surge in its growth.
The ultra-thin glass industry in South Korea is dominated by a few local firms, which have been especially successful in the consumer electronics space. Ultra-thin glass is in high demand in this country due to the country's comparatively high-end technology and well-known electronics manufacturers. South Korea is also investing in research and development to broaden the use of ultra-thin glass in many other industries.
The ultra-thin glass market in Japan is highly quality and precision-driven. The country is a leading producer of ultra-thin glass used in consumer electronics, automotive and medical applications. The growth of the ultra-thin glass market is supported by the innovative technologies and advanced manufacturing facilities of Japan.
With demand from consumer electronics and automotive industries expanding steadily, China is dominating the ultra-thin glass market. The nation's strong manufacturing base and substantial domestic market contribute to robust growth. When it comes to renewable applications, China is working on ultra-thin glass, which represents a growing market to expand.
With the growth of consumer electronics and automotive sectors, the Indian thin glass market is booming. The increasing market is due in part to the large population in the country and its growing middle class. Such factors help support market growth in India, which is investigating the use of ultra-thin glass in renewable power and medical devices.
Market participants are focusing on vertical integration and collaborative R&D to advance material handling capabilities and reduce production costs. This trajectory is expected to define the market’s transition toward high-performance, eco-efficient applications over the next decade.
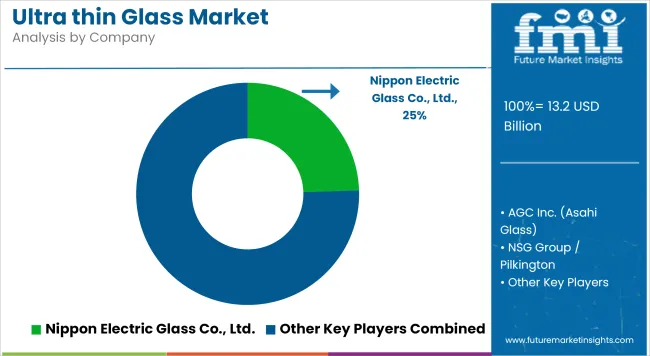
Ultra-thin glass is used in touch panel displays, semiconductor substrates, fingerprint sensors, and solar panels.
Ultra-thin glass is lightweight, durable, flexible, and offers excellent optical clarity.
Consumer electronics, automotive, and renewable energy industries are the main consumers.
High production costs, technological complexities, and competition from alternative materials are the main challenges.






Full Research Suite comprises of:
Market outlook & trends analysis
Interviews & case studies
Strategic recommendations
Vendor profiles & capabilities analysis
5-year forecasts
8 regions and 60+ country-level data splits
Market segment data splits
12 months of continuous data updates
DELIVERED AS:
PDF EXCEL ONLINE
Glass Bottles Market Forecast and Outlook 2025 to 2035
Glass Laser Engraving Machine Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Glass Restoration Kit Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Glass Bottle and Container Market Forecast and Outlook 2025 to 2035
Glass Additive Market Forecast and Outlook 2025 to 2035
Glass Reactor Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Glass Cosmetic Bottle Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Glass & Metal Cleaner Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Glass Product Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Glassine Paper Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Glass Container Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Glass Fibre Yarn Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Glass Cloth Electrical Insulation Tape Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Glass Bonding Adhesive Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Glass Mat Thermoplastic Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Glass Table Bacteria Tank Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Glassine Paper Industry Analysis in Western Europe Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Glassine Paper Industry Analysis in Korea Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Glassine Paper Industry Analysis in Japan Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Glass Mat Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035

Thank you!
You will receive an email from our Business Development Manager. Please be sure to check your SPAM/JUNK folder too.
Chat With
MaRIA