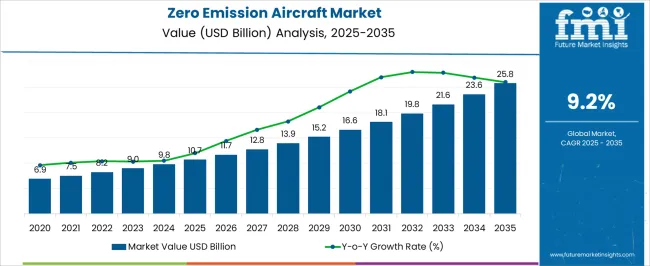
The zero emission aircraft market, valued at USD 10.7 billion in 2025 and projected to reach USD 25.8 billion by 2035 at a CAGR of 9.2%, exhibits pronounced regional growth disparities between Asia-Pacific, Europe, and North America. Asia-Pacific is expected to emerge as a dominant contributor to market value over the forecast period, driven by expanding commercial aviation infrastructure, increasing investments in sustainable aviation technologies, and supportive governmental policies for low-emission aircraft deployment.
Rapid adoption of hydrogen and electric propulsion systems in regional carriers and aerospace manufacturing hubs underpins the relatively higher growth trajectory of this region. Europe maintains a steady contribution to the market, supported by stringent environmental regulations, subsidies for green aviation initiatives, and early adoption of zero-emission technologies by established aerospace firms. Despite these advantages, growth is moderated by higher regulatory compliance costs and slower fleet replacement cycles compared to Asia-Pacific. North America demonstrates moderate growth, underpinned by early technology adoption, research and development in electric and hydrogen-powered aircraft, and significant investments by key manufacturers. However, adoption is partially constrained by the size of the existing fleet and longer certification timelines for zero-emission aircraft.
The regional market composition reflects a clear imbalance, with Asia-Pacific driving accelerated value expansion, Europe sustaining regulated growth, and North America contributing a moderate yet technologically advanced share. By 2035, Asia-Pacific is expected to dominate the market value share, while Europe and North America continue to support innovation and regulatory alignment within the zero-emission aircraft sector.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Zero Emission Aircraft Market Estimated Value in (2025 E) | USD 10.7 billion |
| Zero Emission Aircraft Market Forecast Value in (2035 F) | USD 25.8 billion |
| Forecast CAGR (2025 to 2035) | 9.2% |
The zero emission aircraft market represents a specialized segment within the global aviation and sustainable transport industry, emphasizing reduced greenhouse gas emissions, alternative propulsion, and future mobility solutions. Within the broader aircraft market, it accounts for about 3.9%, driven by demand for short and medium-haul electric, hydrogen, and hybrid aircraft. In the commercial and regional aviation segment, it holds nearly 4.5%, reflecting adoption for passenger transport and cargo operations with environmental compliance.
Across the aerospace propulsion and power systems sector, the market captures 4.1%, supporting electric motors, fuel cells, and hybrid powertrain integration. Within the green aviation and sustainable air mobility category, it represents 3.6%, highlighting initiatives to meet regulatory emission targets. In the research and innovation-driven aerospace technology sector, it secures 3.2%, emphasizing prototype development, certification, and operational testing. Recent developments in this market have focused on electric propulsion, hydrogen fuel cells, and battery energy density improvements. Innovations include hybrid-electric regional aircraft, hydrogen-powered demonstrators, and modular electric propulsion units to optimize efficiency and range.
Key players are collaborating with aerospace OEMs, government research agencies, and energy providers to accelerate adoption and meet strict emission standards. Advanced lightweight materials, aerodynamic optimization, and AI-based energy management systems are being integrated to improve performance and reduce operational costs. Additionally, airport infrastructure is being adapted for hydrogen and electric aircraft charging, refueling, and maintenance.
The zero emission aircraft market is gaining strong momentum, propelled by the aviation industry’s decarbonization goals and stringent international emission regulations. Aerospace industry publications and corporate sustainability reports have underscored the role of alternative propulsion technologies, such as battery-electric, hydrogen fuel cell, and hybrid systems, in reshaping future air travel. Significant investment from aircraft manufacturers, airlines, and government-funded research programs is accelerating prototype development and certification processes.
Advances in lightweight materials, battery energy density, and electric propulsion efficiency have improved operational feasibility for short-haul and regional routes. Infrastructure development for charging and refueling, along with policy incentives for zero-emission fleets, is enhancing adoption prospects.
The market’s near-term focus remains on smaller-capacity aircraft suited for regional connectivity, with scalability expected as technology matures. Segmental growth is being driven by battery electric aircraft for their operational efficiency, turboprop configurations for short regional routes, and the 9 to 30 passenger capacity class due to its commercial viability in early zero-emission deployments.
The zero emission aircraft market is segmented by aircraft type, type, capacity, end-use, and geographic regions. By aircraft type, zero emission aircraft market is divided into Battery electric aircraft, Hydrogen fuel cell aircraft, Hybrid electric aircraft, and Solar electric aircraft. In terms of type, zero emission aircraft market is classified into Turboprop, Turbofan system, Blended-Wing Body (BWB), and Fully electrical concept. Based on capacity, zero emission aircraft market is segmented into 9 to 30, 31 to 60, 61 to 100, 101 to 150, and More than 150. By end-use, zero emission aircraft market is segmented into Commercial, Military, and General. Regionally, the zero emission aircraft industry is classified into North America, Latin America, Western Europe, Eastern Europe, Balkan & Baltic Countries, Russia & Belarus, Central Asia, East Asia, South Asia & Pacific, and the Middle East & Africa.
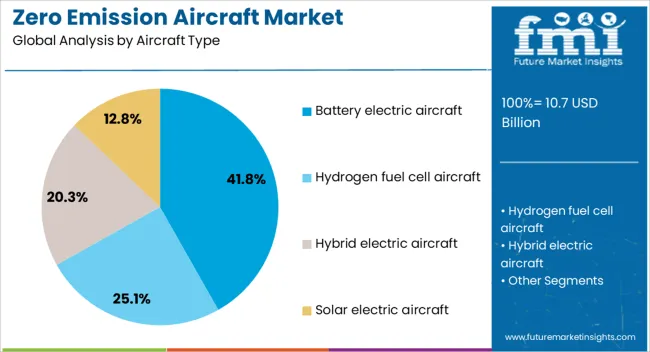
The battery electric aircraft segment is projected to hold 41.8% of the zero emission aircraft market revenue in 2025, maintaining its leadership position due to advancements in battery technology and the suitability of electric propulsion for short-haul flights. This segment’s growth has been supported by substantial R&D funding targeting improved battery energy density, faster charging capabilities, and extended cycle life.
Industry trial programs have demonstrated that battery electric aircraft offer lower operational costs, reduced noise, and minimal maintenance compared to conventional combustion engines. Early adoption has been particularly strong among regional carriers and charter services operating within short ranges, where infrastructure for charging can be readily developed.
Additionally, regulatory bodies have streamlined certification pathways for electric propulsion systems, accelerating time-to-market for new models. With battery performance improving annually and renewable electricity integration into aviation operations, the battery electric aircraft segment is expected to retain its lead in the early stages of zero-emission aviation commercialization.
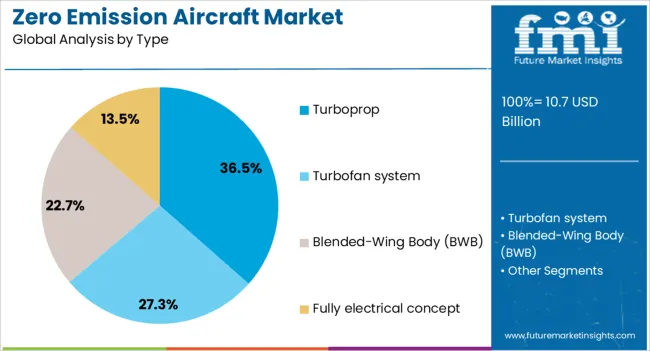
The turboprop segment is projected to account for 36.5% of the zero emission aircraft market revenue in 2025, driven by its efficiency in regional and short-haul operations. Turboprop designs have been widely favored for their ability to operate from shorter runways, access smaller airports, and deliver better fuel efficiency at lower cruising speeds.
In the context of zero-emission propulsion, turboprop configurations are well-suited for integrating electric and hybrid-electric powertrains due to their relatively lower power requirements compared to jet engines. Manufacturers have leveraged existing turboprop platforms as testbeds for new propulsion technologies, reducing development timelines and costs.
Additionally, the segment benefits from established market familiarity and pilot training pathways, facilitating faster adoption by airlines. As regional aviation markets continue to prioritize sustainability, the turboprop segment is expected to remain a preferred configuration for zero-emission aircraft deployments in the foreseeable future.
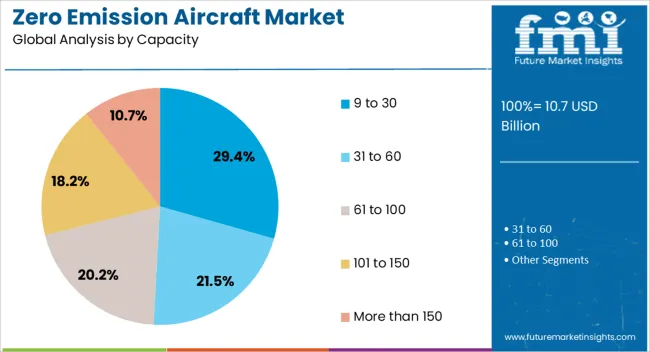
The 9 to 30 passenger capacity segment is projected to contribute 29.4% of the zero emission aircraft market revenue in 2025, reflecting its commercial viability for early-stage adoption. This category offers a balance between operational efficiency and route flexibility, making it suitable for regional connectivity and commuter air services.
Development programs targeting this capacity range have been prioritized by manufacturers due to the lower certification complexity and quicker market entry timelines compared to larger aircraft. Regional airlines and charter operators have shown strong interest in replacing aging fleets with zero-emission models in this class, particularly for routes under 500 kilometers.
Additionally, smaller capacity aircraft require less charging or refueling infrastructure, reducing upfront investment for operators. With policy incentives and public funding supporting sustainable regional transportation, the 9 to 30 capacity segment is expected to remain a key driver of zero-emission aviation growth in the short to medium term.
The market has expanded rapidly as aviation stakeholders focus on reducing carbon footprints and meeting global environmental targets. Aircraft powered by hydrogen fuel cells, electric propulsion, or hybrid systems offer cleaner alternatives to conventional fossil-fuel engines. Growing regulatory pressure, government incentives, and airline commitments toward net-zero emissions have accelerated development and adoption. Advancements in lightweight materials, energy-dense batteries, and efficient propulsion systems have improved feasibility and operational performance. Despite technological, infrastructure, and cost challenges, zero emission aircraft are increasingly recognized as viable solutions for regional, short-haul, and urban air mobility routes.
Hydrogen and electric propulsion technologies have been central drivers for zero emission aircraft development. Hydrogen fuel cells provide high energy efficiency and zero carbon emissions during flight, while electric motors enable quieter, low-maintenance operations. Aircraft manufacturers are integrating lightweight hydrogen storage systems, high-capacity batteries, and efficient power management units to extend flight range and operational reliability. Research initiatives focus on hybrid-electric propulsion for short-haul and regional aircraft, combining traditional engines with electric systems to reduce fuel consumption. Airlines and aerospace companies collaborate on test programs and pilot projects to validate performance and safety. These innovations are essential to overcome range limitations and establish commercial viability, driving adoption of zero emission aircraft in future aviation fleets.
Urban air mobility (UAM) and regional flight services have become key applications for zero emission aircraft. Electric vertical takeoff and landing (eVTOL) aircraft and short-range hydrogen planes offer sustainable solutions for urban commuting, intercity travel, and cargo transport. Noise reduction, low operational costs, and emissions-free operation make these aircraft attractive for city authorities and operators. Infrastructure development, including charging stations, hydrogen refueling networks, and vertiports, is being prioritized to support deployment. Governments and municipalities provide incentives and regulatory frameworks to encourage UAM adoption. The growing need for fast, clean, and efficient urban and regional air transport continues to create opportunities for zero emission aircraft manufacturers and service providers worldwide.
Advancements in battery technology, lightweight composite materials, and propulsion efficiency have strengthened the feasibility of zero emission aircraft. High energy-density batteries and fuel cells reduce weight while extending flight duration, while aerodynamic improvements minimize drag and optimize energy usage. Integration of advanced avionics, power electronics, and thermal management systems ensures safe and reliable operations. Digital twin simulations and predictive maintenance tools allow manufacturers and operators to optimize aircraft performance and reduce operational risks. Collaboration between aerospace companies, research institutes, and energy providers is accelerating innovation in propulsion, energy storage, and aircraft design. These technological improvements are pivotal for scaling production, expanding range, and ensuring commercial adoption of zero emission aircraft in the aviation industry.
Despite progress, the market faces challenges related to infrastructure, regulation, and operational adoption. Limited hydrogen refueling stations, electric charging networks, and maintenance facilities constrain deployment, particularly in remote or regional airports. Certification processes, safety standards, and air traffic integration require rigorous testing and compliance measures. High initial investment costs for aircraft, energy storage, and supporting infrastructure may slow adoption, especially for smaller operators. The flight range limitations and energy density constraints remain technological barriers. Addressing these challenges through public-private partnerships, infrastructure investment, and streamlined certification processes is essential to support widespread adoption. Overcoming these hurdles ensures that zero emission aircraft can achieve operational scalability and contribute meaningfully to sustainable aviation goals.
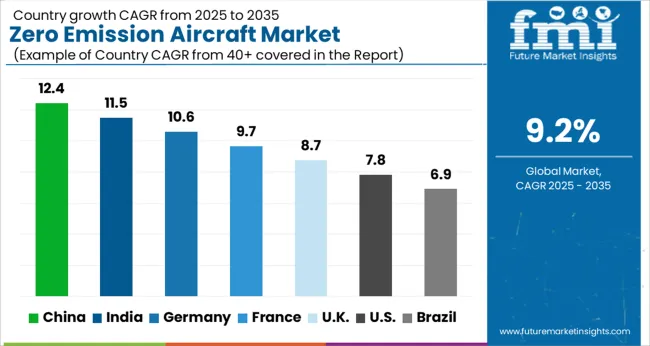
| Country | CAGR |
|---|---|
| China | 12.4% |
| India | 11.5% |
| Germany | 10.6% |
| France | 9.7% |
| UK | 8.7% |
| USA | 7.8% |
| Brazil | 6.9% |
The market is witnessing robust adoption across key regions. India is expanding at 11.5%, driven by investments in electric propulsion systems and sustainable aviation initiatives. China follows closely with 12.4%, supported by large-scale aircraft development programs and government incentives for carbon reduction. Germany shows 10.6% growth, fueled by advancements in hybrid-electric and hydrogen-powered aircraft technologies. The United Kingdom records 8.7%, with focus on urban air mobility and low-emission aviation projects. The United States grows at 7.8%, propelled by aerospace innovation and regulatory support for green aviation solutions. Collectively, these countries demonstrate a strong mix of production, deployment, and technological innovation shaping the global zero emission aircraft market. This report includes insights on 40+ countries; the top markets are shown here for reference.
China’s market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 12.4%, driven by increasing government initiatives to reduce carbon emissions in aviation and strengthen sustainable air transport solutions. Airlines are actively exploring electric and hydrogen-powered aircraft for domestic and regional routes. Technological advancements in battery efficiency, lightweight materials, and propulsion systems are accelerating the adoption of zero emission aircraft. Collaborations between aircraft manufacturers, research institutions, and aviation authorities are enhancing design and operational capabilities. Growing environmental awareness among consumers and regulatory incentives further reinforce market expansion, positioning China as a leading hub for sustainable aviation innovation.
India is anticipated to grow at a CAGR of 11.5%, supported by increasing investments in green aviation technology and clean energy solutions. Efforts to reduce carbon footprints in regional and domestic aviation are driving interest in electric and hydrogen-powered aircraft. Technological developments, including efficient energy storage, lightweight composite materials, and next-generation propulsion systems, are creating favorable conditions for market expansion. Public and private partnerships, government incentives for sustainable aviation, and rising environmental consciousness are enhancing adoption. The integration of innovative designs with operational efficiency and safety measures strengthens India’s position as an emerging market for zero emission aircraft.
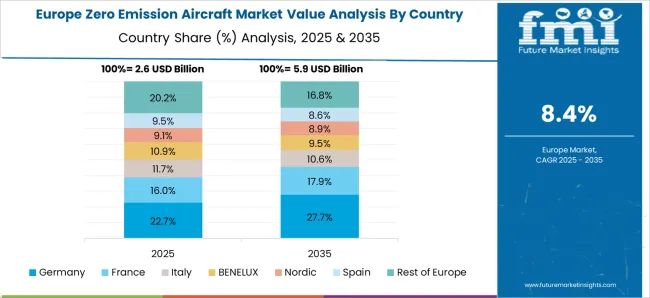
Germany is expected to grow at a CAGR of 10.6%, driven by strict environmental regulations and commitments to reduce aviation-related emissions. Airlines and aircraft manufacturers are investing in electric and hydrogen-based propulsion systems for regional routes. Research in lightweight materials, energy-dense batteries, and hybrid propulsion technologies supports operational efficiency and performance. Government initiatives supporting sustainable aviation, including subsidies, pilot projects, and infrastructure development, foster adoption. Collaborations with European aviation organizations and focus on eco-friendly designs position Germany as a leader in innovative and sustainable aviation solutions.
The United Kingdom’s market is projected to expand at a CAGR of 8.7%, fueled by adoption of electric and hydrogen-powered aircraft for regional and short-haul travel. Government initiatives to reduce aviation emissions and support sustainable air mobility accelerate demand. Investments in research, pilot programs, and airport infrastructure create favorable conditions for deployment. Technological improvements in battery systems, hybrid propulsion, and lightweight designs enhance aircraft performance. Airlines and aircraft manufacturers are increasingly focusing on operational efficiency and environmental compliance, positioning the United Kingdom as a progressive market for zero emission aviation solutions.
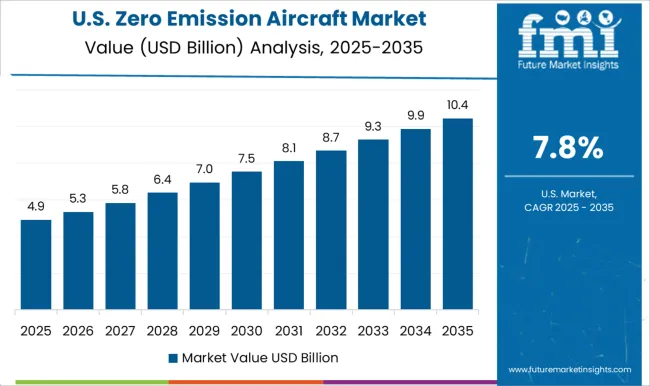
The United States is anticipated to grow at a CAGR of 7.8%, driven by rising investments in clean aviation technology and environmentally responsible operations. Development of electric and hydrogen-powered aircraft for regional flights is gaining momentum. Research in advanced energy storage, aerodynamics, and propulsion systems enhances efficiency and performance. Government policies, regulatory incentives, and sustainability programs foster adoption among commercial operators. Strategic collaborations between manufacturers, research institutions, and airlines strengthen the design and operational deployment of zero emission aircraft. Growing public and corporate interest in carbon reduction further accelerates the market’s growth potential.
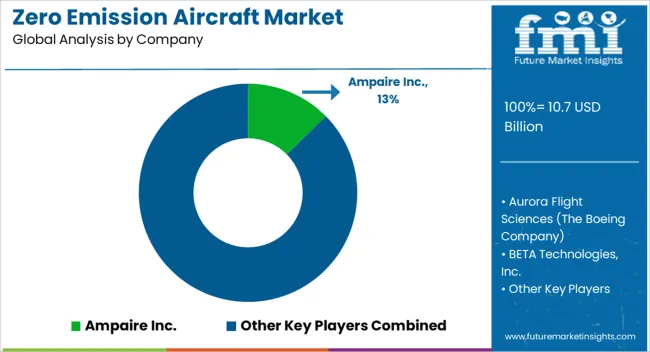
The market is experiencing rapid development as aerospace manufacturers and startups focus on reducing carbon footprints and enabling sustainable aviation. Ampaire Inc. and Bye Aerospace are pioneering hybrid-electric and fully electric propulsion systems for regional and short-haul flights, emphasizing efficiency, noise reduction, and operational cost savings. Aurora Flight Sciences, part of The Boeing Company, is advancing electric and hybrid-electric aircraft technologies, integrating innovative energy storage and propulsion solutions. BETA Technologies, Lilium GmbH, and Joby Aero, Inc. are concentrating on vertical takeoff and landing (VTOL) aircraft, targeting urban air mobility and on-demand air transport with zero-emission propulsion.
Eviation and Heart Aerospace focus on all-electric commuter aircraft, addressing regional connectivity and low-carbon flight operations. Rolls-Royce plc and ZeroAvia, Inc. are developing hydrogen-electric powertrains for larger aircraft, combining long-range capabilities with sustainability goals. Equator Aircraft AS, Evektor, and Pipistrel d.o.o. provide specialized aircraft solutions for training, leisure, and short-distance travel, integrating electric propulsion technologies to minimize environmental impact.
| Item | Value |
|---|---|
| Quantitative Units | USD 10.7 Billion |
| Aircraft Type | Battery electric aircraft, Hydrogen fuel cell aircraft, Hybrid electric aircraft, and Solar electric aircraft |
| Type | Turboprop, Turbofan system, Blended-Wing Body (BWB), and Fully electrical concept |
| Capacity | 9 to 30, 31 to 60, 61 to 100, 101 to 150, and More than 150 |
| End-Use | Commercial, Military, and General |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America, Middle East & Africa |
| Country Covered | United States, Canada, Germany, France, United Kingdom, China, Japan, India, Brazil, South Africa |
| Key Companies Profiled | Ampaire Inc., Aurora Flight Sciences (The Boeing Company), BETA Technologies, Inc., Bye Aerospace, Equator Aircraft AS, Evektor, spol. s r. o., Eviation, Heart Aerospace, Joby Aero, Inc., Lilium GmbH, PIPISTREL d.o.o., Rolls-Royce plc, Wright Electric, and ZeroAvia, Inc. |
| Additional Attributes | Dollar sales by aircraft type and propulsion system, demand dynamics across commercial, regional, and urban air mobility sectors, regional trends in sustainable aviation adoption, innovation in electric and hydrogen propulsion, lightweight materials, and energy storage, environmental impact of reduced carbon emissions and lifecycle energy use, and emerging use cases in short-haul flights, regional connectivity, and eco-friendly air transport. |
The global zero emission aircraft market is estimated to be valued at USD 10.7 billion in 2025.
The market size for the zero emission aircraft market is projected to reach USD 25.8 billion by 2035.
The zero emission aircraft market is expected to grow at a 9.2% CAGR between 2025 and 2035.
The key product types in zero emission aircraft market are battery electric aircraft, hydrogen fuel cell aircraft, hybrid electric aircraft and solar electric aircraft.
In terms of type, turboprop segment to command 36.5% share in the zero emission aircraft market in 2025.






Full Research Suite comprises of:
Market outlook & trends analysis
Interviews & case studies
Strategic recommendations
Vendor profiles & capabilities analysis
5-year forecasts
8 regions and 60+ country-level data splits
Market segment data splits
12 months of continuous data updates
DELIVERED AS:
PDF EXCEL ONLINE
Zero Liquid Discharge System Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Zero-Waste Packaging Technologies Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Zero-Waste Refill Packaging Market Analysis - Size, Share, and Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Zero-Fishmeal Feed Market Analysis - Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Zero Friction Coatings Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Zero Trust Security Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Zero-Touch Provisioning (ZTP) Market - Growth & Demand 2025 to 2035
Zero Calorie Chips Market Outlook - Growth, Demand & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Zero Sugar Beverages Market Analysis by Product Type and Sales Channel Through 2035
Zero-Waste Packaging Market Report – Sustainable Growth & Trends 2023-2033
Zero Emission Vehicle Market Growth - Trends & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Africa’s Zero Liquid Discharge System Market - Size, Share, and Forecast 2025 to 2035
Emissions Management Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Emission Control Catalyst for Small Engines Market - Size, Share, and Forecast 2025 to 2035
Motorcycle Emission Control Catalyst Market Growth - Trends & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Emission Control Catalyst Market Growth – Trends & Forecast 2024-2034
Emission Monitoring Software Market
Emission Monitoring Systems Market
Marine Emission Control Catalyst Market - Size, Share, and Forecast 2025 to 2035
Optical Emission Spectroscopy Market Report – Trends 2019-2027

Thank you!
You will receive an email from our Business Development Manager. Please be sure to check your SPAM/JUNK folder too.
Chat With
MaRIA