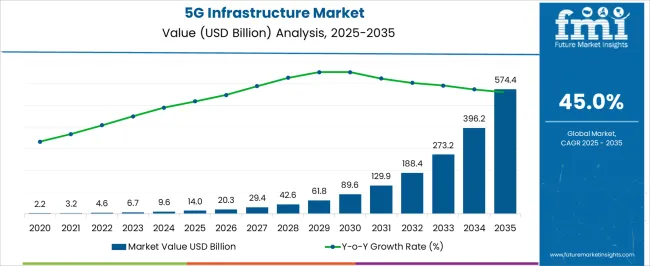
The 5G Infrastructure Market is estimated to be valued at USD 14.0 billion in 2025 and is projected to reach USD 574.4 billion by 2035, registering a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 45.0% over the forecast period. This growth trajectory reflects the rapid pace of technological adoption, large-scale investments, and infrastructure rollouts associated with the next generation of mobile connectivity.
The CAGR of 45.0% signifies that the market nearly doubles in several early forecast years, as seen from the increase to USD 20.3 billion in 2026 and USD 29.4 billion in 2027. Such acceleration in the initial phase is driven by the deployment of small cells, massive MIMO, and core network upgrades to meet low-latency and high-bandwidth demands. Midway through the period, growth momentum remains strong, with the market reaching USD 129.9 billion in 2031, representing more than nine times its 2025 size.
Late-stage expansion, from USD 273.2 billion in 2033 to USD 574.4 billion in 2035, continues at a rapid pace, though incremental gains in absolute value become significantly larger due to the higher base. The calculated CAGR captures this compounding effect, showing how early gains amplify future valuations. Overall, the data indicates a transformative industry shift where the 5G Infrastructure Market experiences exponential scaling throughout the forecast horizon.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| 5G Infrastructure Market Estimated Value in (2025 E) | USD 14.0 billion |
| 5G Infrastructure Market Forecast Value in (2035 F) | USD 574.4 billion |
| Forecast CAGR (2025 to 2035) | 45.0% |
The 5G infrastructure market is undergoing accelerated transformation, driven by large-scale investments in network modernization, data-intensive applications, and government-backed connectivity programs. Increased demand for ultra-reliable low-latency communication (URLLC) and massive machine-type communication (mMTC) is compelling telecom operators to invest in both access and core infrastructure.
Strategic collaborations among chipset manufacturers, equipment vendors, and cloud service providers are creating robust deployment ecosystems. Regulatory support for spectrum auctions and infrastructure sharing is lowering entry barriers in developing economies, while edge computing integration and network slicing capabilities are unlocking new use cases in industries such as manufacturing, automotive, and healthcare.
Future expansion is expected to be supported by the convergence of AI-enabled network optimization, cloud-native architectures, and the rise of private 5G networks catering to enterprise-grade requirements.
The 5G infrastructure market is segmented by component, spectrum, network architecture, deployment mode, organization size, end use, and geographic regions. By component, the 5G infrastructure market is divided into Hardware, Software, and Services. In terms of the spectrum, the 5G infrastructure market is classified into Sub-6 GHz and mmWave. Based on the network architecture of the 5G infrastructure market, it is segmented into Non-Standalone (NSA) and Standalone (SA). The deployment mode of the 5G infrastructure market is segmented into Urban, Rural, and Remote.
The 5G infrastructure market is segmented by organization size into Large enterprises and Small and medium enterprises (SME). The 5G infrastructure market is segmented by end use into Enterprise/Corporate, Residential, Smart City, Industrial, Energy & Utility, Transportation & Logistics, Public Safety & Defense, Healthcare Facilities, Retail, Agriculture, and Others.
Regionally, the 5G infrastructure industry is classified into North America, Latin America, Western Europe, Eastern Europe, Balkan & Baltic Countries, Russia & Belarus, Central Asia, East Asia, South Asia & Pacific, and the Middle East & Africa.
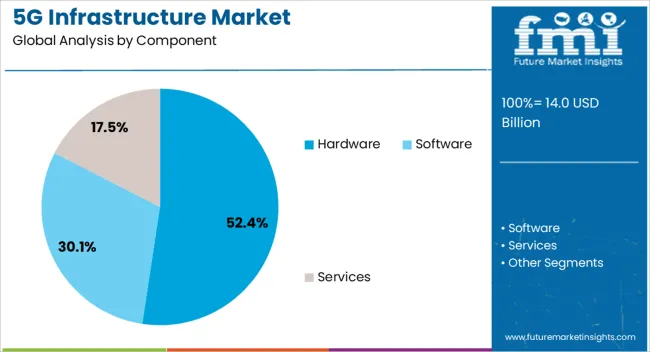
Hardware is expected to account for 52.40% of the total revenue share in the 5G infrastructure market in 2025, establishing it as the leading component segment. The high capital intensity of physical network deployment, including base stations, antennas, routers, and massive MIMO systems, is driving this dominance.
Hardware plays a foundational role in enabling ultra-fast connectivity and supporting millimeter wave frequencies with dense, small cell architecture. Telecom operators are prioritizing scalable and energy-efficient infrastructure that ensures long-term operational stability and performance.
Continued innovations in antenna design and radio units, coupled with increased rollout of Open RAN-compatible hardware, have further strengthened this segment's position in large-scale network expansion plans.
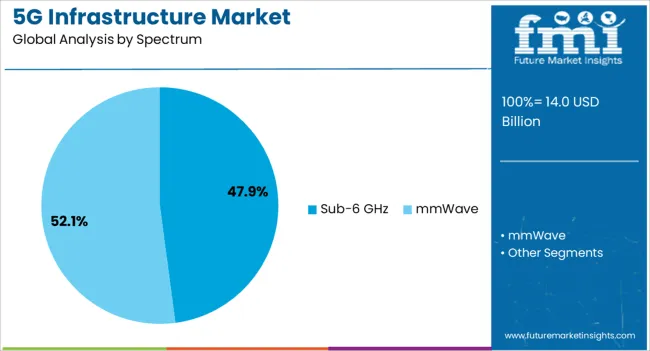
Sub-6 GHz is projected to contribute 47.90% of total market revenue in 2025, making it the most utilized spectrum band in 5G deployments. This segment's lead is being shaped by its optimal balance between coverage and capacity, which enables both urban and suburban rollout at scale.
The availability of mid-band spectrum through global licensing auctions has enabled quicker deployment timelines and compatibility with existing LTE infrastructure. Sub-6 GHz provides stable connections with lower attenuation and broader signal penetration, especially beneficial in densely populated areas.
Its adoption is further supported by advancements in dynamic spectrum sharing (DSS) and carrier aggregation, which allow smoother transitions from 4G to 5G.
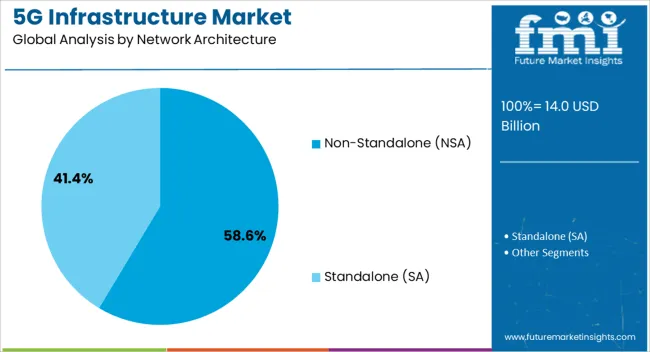
Non-Standalone (NSA) network architecture is anticipated to hold 58.60% of the overall market share in 2025, maintaining its lead as the preferred deployment model. This segment's strength stems from its cost-effectiveness and rapid integration with existing 4G LTE infrastructure, enabling quicker time-to-market for operators.
NSA allows operators to leverage the LTE control plane while using the 5G data plane for improved performance, making it suitable for enhanced mobile broadband (eMBB) services. The reduced need for entirely new infrastructure, combined with compatibility with legacy systems, has made NSA a preferred choice in early and transitional 5G rollouts.
Ongoing improvements in software-defined networking (SDN) and virtualization are further enabling more flexible and scalable NSA deployments across diverse geographies.
The market has been shaped by the rapid evolution of next-generation wireless networks aimed at delivering ultra-low latency, high-speed connectivity, and massive device density. Network operators and equipment manufacturers have been actively deploying small cells, macro cells, and advanced antenna systems to meet the performance requirements of diverse applications ranging from autonomous vehicles to industrial automation. The transition from 4G to 5G has been driven by the need for enhanced mobile broadband, reliable mission-critical communications, and large-scale IoT connectivity.
The proliferation of small cell infrastructure has been central to 5G network rollouts, particularly in densely populated areas where high data demand challenges traditional macro cell coverage. These compact base stations have been deployed on street furniture, buildings, and utility poles to ensure robust signal strength and capacity. Advanced antenna technologies, including massive MIMO and beamforming, have been implemented to optimize spectral efficiency and deliver consistent connectivity. The integration of small cells with existing LTE networks through dynamic spectrum sharing has allowed smoother transitions to 5G. These deployments have enabled network densification, reduced congestion, and improved user experience, particularly in urban centers and enterprise environments.
The adoption of edge computing within 5G infrastructure has enabled faster data processing closer to end-users, significantly reducing latency for time-sensitive applications. Edge data centers and mobile edge computing nodes have been deployed to support use cases such as augmented reality, remote surgery, and real-time industrial control. By decentralizing processing workloads, network efficiency has been improved and backhaul traffic minimized. This integration has also facilitated better scalability for IoT ecosystems, allowing billions of connected devices to operate without compromising network performance. The synergy between edge computing and 5G has positioned the infrastructure as a foundational enabler for next-generation digital transformation initiatives.
Regulatory bodies and governments have played a critical role in accelerating 5G infrastructure development by allocating mid-band and high-band spectrum, streamlining permitting processes, and offering financial incentives for network expansion. National strategies in key markets have prioritized 5G deployment as part of digital economy growth plans. Public funding programs have supported rural and underserved area connectivity, ensuring that the benefits of 5G extend beyond metropolitan regions. Collaboration between telecom operators, infrastructure providers, and municipal authorities has been encouraged to optimize site acquisition and network design. These policy frameworks have ensured a competitive environment for infrastructure deployment while addressing coverage gaps.
High capital expenditure for infrastructure deployment, including base stations, fiber backhaul, and spectrum acquisition, has been a major restraint, particularly for operators in developing markets. The need for dense network coverage in 5G, especially in mmWave bands, has further increased rollout costs. Additionally, cybersecurity threats targeting the expanded attack surface of 5G networks have heightened concerns, necessitating robust security protocols and continuous monitoring. Supply chain vulnerabilities, exacerbated by geopolitical tensions, have also impacted equipment availability and vendor diversity. Addressing these challenges requires strategic investment planning, vendor diversification, and adherence to stringent cybersecurity standards to safeguard network integrity.
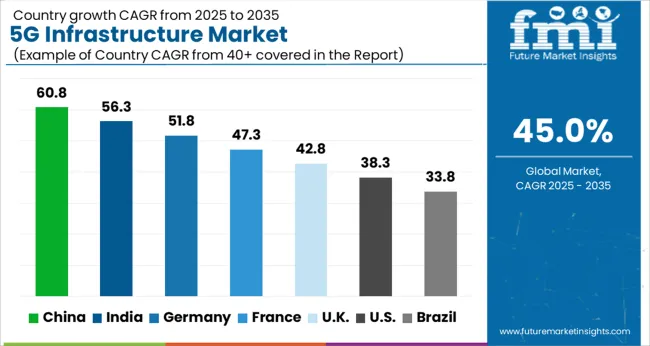
The market is projected to grow at a robust CAGR of 45.0% from 2025 to 2035, fueled by large-scale network deployments, increased spectrum availability, and expanding use cases in industries and smart cities. China, with a 61.0% CAGR, leads through aggressive rollouts, state-backed investments, and rapid adoption in manufacturing and transportation sectors. India follows at 56.0%, benefiting from expanding telecom infrastructure and affordable device penetration.
Germany, at 52.0%, is leveraging industrial IoT applications to accelerate deployment. The UK, growing at 43.0%, is advancing coverage with rural and urban network upgrades, while the USA, at 38.0%, focuses on enterprise 5G solutions and private network developments. This report includes insights on 40+ countries; the top markets are shown here for reference.
The 5G infrastructure industry in China is projected to grow at a CAGR of 61% from 2025 to 2035, driven by large-scale base station deployment and advanced network technologies. Government-led investments and favorable spectrum policies are expediting adoption, embedding high-speed connectivity across manufacturing, logistics, and smart city projects. Domestic telecom giants are investing heavily in ultra-dense networks and fiber backhaul, enabling massive IoT deployment and ultra-low latency applications. These initiatives are expected to consolidate China’s lead as the global center for 5G innovation.
The adoption of advanced 5G systems in India is anticipated to rise at a CAGR of 56% over 2025 to 2035, supported by nationwide fiberization programs and increasing spectrum availability. Telecom operators are accelerating network rollout in urban and semi-urban areas, enhancing mobile broadband capacity and enabling low-latency applications. Affordable data plans and a large smartphone user base are fostering demand for high-speed services, while enterprise adoption in manufacturing and healthcare is strengthening. These developments position India for one of the fastest 5G expansions globally.
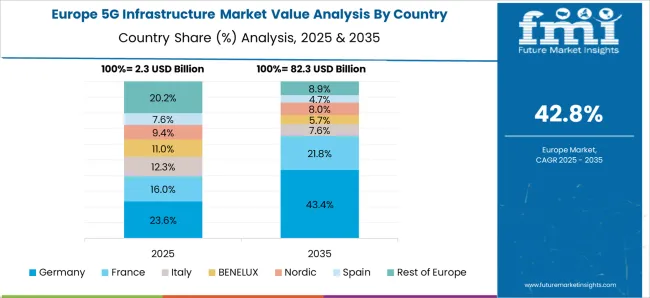
Sales of 5G connectivity solutions in Germany are forecast to expand at a CAGR of 52% between 2025 and 2035, propelled by industrial automation and connected mobility projects. The automotive sector’s shift toward autonomous vehicles and connected supply chains is driving substantial demand for ultra-reliable low-latency communications. Federal initiatives promoting smart manufacturing and energy efficiency are accelerating enterprise network adoption. Strategic partnerships between telecom operators and equipment manufacturers are also enhancing coverage and service quality nationwide.
The expansion of 5G infrastructure deployments in the United Kingdom is set to progress at a CAGR of 43% from 2025 to 2035, supported by investments in rural connectivity and small cell networks. Government-led programs are bridging digital divides, while private telecom operators are accelerating rollout in metropolitan hubs. Key sectors such as finance, healthcare, and media are adopting 5G to support real-time services and immersive applications. The shift toward edge computing is further enhancing network performance and service capabilities.
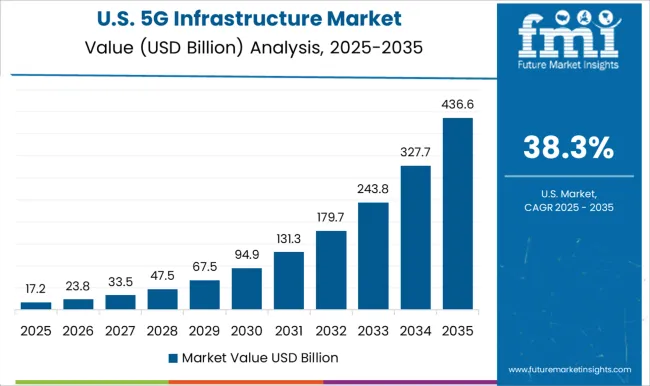
Demand for 5G-enabled technologies in the United States is forecast to grow at a CAGR of 38% during 2025 to 2035, driven by large-scale private network deployments and enhanced spectrum utilization. Leading telecom operators are prioritizing ultra-low latency services for autonomous systems, telemedicine, and advanced manufacturing. Federal funding for rural broadband and small cell expansion is bridging connectivity gaps. Rapid innovation in edge computing and AI-driven network optimization is also supporting the evolution of next-generation communication services.
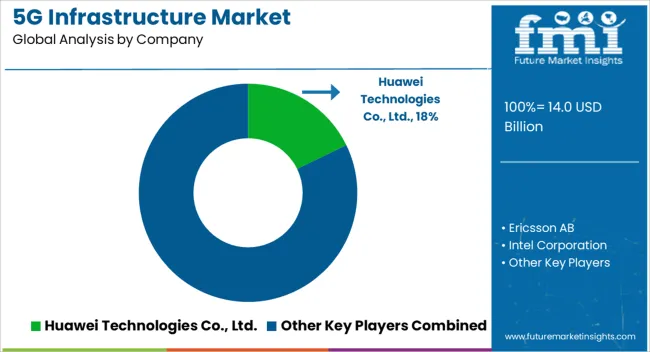
The market is shaped by a concentrated group of multinational corporations that provide network hardware, semiconductors, and integrated solutions to telecom operators worldwide. Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. holds a dominant position through extensive global deployments and partnerships with service providers in Asia, Africa, and parts of Europe.
Ericsson AB and Nokia Corporation maintain strong footholds in Europe and North America, leveraging extensive patent portfolios and long-term contracts with major carriers. Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd. has strengthened its market share by securing multi-billion-dollar agreements in the United States and Asia, offering both radio access and core network solutions. Intel Corporation and Qualcomm Incorporated play crucial roles in supplying advanced chipsets, processors, and connectivity modules that power 5G base stations and devices.
ZTE Corporation focuses on competitive large-scale network rollouts in emerging markets, supported by cost-effective infrastructure offerings. The market is driven by strategies such as spectrum optimization, mass deployment of small cells, expansion of mmWave capabilities, and integration with cloud-native architectures.
Entry into this sector is constrained by high R&D expenditure, stringent network security requirements, intellectual property dominance by incumbents, complex global compliance regulations, and the need for extensive manufacturing and deployment capabilities. These factors create significant challenges for smaller firms attempting to compete on a global scale.
| Item | Value |
|---|---|
| Quantitative Units | USD 14.0 Billion |
| Component | Hardware, Software, and Services |
| Spectrum | Sub-6 GHz and mmWave |
| Network Architecture | Non-Standalone (NSA) and Standalone (SA) |
| Deployment Mode | Urban, Rural, and Remote |
| Organization Size | Large enterprises and Small and medium enterprises (SME) |
| End Use | Enterprise/Corporate, Residential, Smart City, Industrial, Energy & Utility, Transportation & Logistics, Public Safety & Defense, Healthcare Facilities, Retail, Agriculture, and Others |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America, Middle East & Africa |
| Country Covered | United States, Canada, Germany, France, United Kingdom, China, Japan, India, Brazil, South Africa |
| Key Companies Profiled | Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd., Ericsson AB, Intel Corporation, Nokia Corporation, Qualcomm Incorporated, Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd., and ZTE Corporation |
| Additional Attributes | Dollar sales by infrastructure type and end use, demand dynamics across telecom operators, enterprise networks, and industrial automation, regional trends in deployment across Asia-Pacific, North America, and Europe, innovation in massive MIMO, beamforming, and network slicing technologies, environmental impact of energy-efficient base stations and reduced carbon footprint, and emerging use cases in autonomous vehicles, smart cities, augmented reality, and remote healthcare applications. |
The global 5g infrastructure market is estimated to be valued at USD 14.0 billion in 2025.
The market size for the 5g infrastructure market is projected to reach USD 574.4 billion by 2035.
The 5g infrastructure market is expected to grow at a 45.0% CAGR between 2025 and 2035.
The key product types in 5g infrastructure market are hardware, _radio access networks (ran), _core network, _transport network, _backhaul, _antennas, software, _network management software, _network orchestration software, services, _consulting, _implementation & integration and _maintenance & support.
In terms of spectrum, sub-6 ghz segment to command 47.9% share in the 5g infrastructure market in 2025.






Our Research Products

The "Full Research Suite" delivers actionable market intel, deep dives on markets or technologies, so clients act faster, cut risk, and unlock growth.

The Leaderboard benchmarks and ranks top vendors, classifying them as Established Leaders, Leading Challengers, or Disruptors & Challengers.

Locates where complements amplify value and substitutes erode it, forecasting net impact by horizon

We deliver granular, decision-grade intel: market sizing, 5-year forecasts, pricing, adoption, usage, revenue, and operational KPIs—plus competitor tracking, regulation, and value chains—across 60 countries broadly.

Spot the shifts before they hit your P&L. We track inflection points, adoption curves, pricing moves, and ecosystem plays to show where demand is heading, why it is changing, and what to do next across high-growth markets and disruptive tech

Real-time reads of user behavior. We track shifting priorities, perceptions of today’s and next-gen services, and provider experience, then pace how fast tech moves from trial to adoption, blending buyer, consumer, and channel inputs with social signals (#WhySwitch, #UX).

Partner with our analyst team to build a custom report designed around your business priorities. From analysing market trends to assessing competitors or crafting bespoke datasets, we tailor insights to your needs.
Supplier Intelligence
Discovery & Profiling
Capacity & Footprint
Performance & Risk
Compliance & Governance
Commercial Readiness
Who Supplies Whom
Scorecards & Shortlists
Playbooks & Docs
Category Intelligence
Definition & Scope
Demand & Use Cases
Cost Drivers
Market Structure
Supply Chain Map
Trade & Policy
Operating Norms
Deliverables
Buyer Intelligence
Account Basics
Spend & Scope
Procurement Model
Vendor Requirements
Terms & Policies
Entry Strategy
Pain Points & Triggers
Outputs
Pricing Analysis
Benchmarks
Trends
Should-Cost
Indexation
Landed Cost
Commercial Terms
Deliverables
Brand Analysis
Positioning & Value Prop
Share & Presence
Customer Evidence
Go-to-Market
Digital & Reputation
Compliance & Trust
KPIs & Gaps
Outputs
Full Research Suite comprises of:
Market outlook & trends analysis
Interviews & case studies
Strategic recommendations
Vendor profiles & capabilities analysis
5-year forecasts
8 regions and 60+ country-level data splits
Market segment data splits
12 months of continuous data updates
DELIVERED AS:
PDF EXCEL ONLINE
Infrastructure Projects Legal Services Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
5G Electromechanical RF Switch Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
5G Solid State Switches Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
5G Gain Block Amplifier Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
5G Driver Amplifier Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
5G Millimeter Wave RF Transceiver Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
5G Testing Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
5G in Healthcare Market Analysis Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
5G Temperature-Compensated Crystal Oscillator (TCXO) Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
5G Remote Surgery System Market Analysis - Size, Share, and Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
5G Telemedicine Platform Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
5G Industrial IOT Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
5G IoT Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
5G in Defense Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
5G Enterprise Private Network Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
5G Edge Cloud Network and Services Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
5G Automotive Grade Product Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
5G Enterprise Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
5G RAN Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
5G Security Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035

Thank you!
You will receive an email from our Business Development Manager. Please be sure to check your SPAM/JUNK folder too.
Chat With
MaRIA