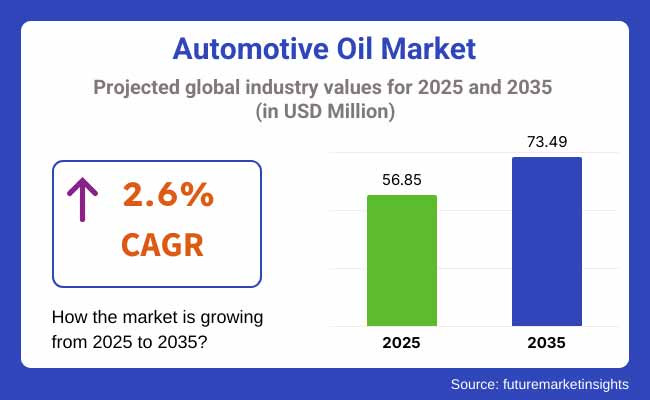
The automotive oil market is valued at USD 56.85 billion in 2025 and is expected to reach USD 73.49 billion by 2035, advancing at a 2.6 % CAGR over the forecast period.
Within the market, the United States remains the most lucrative country in 2025 owing to its vast vehicle parc, stringent GF-6 fuel-economy norms, and high uptake of premium synthetics. Conversely, India is poised to be the fastest-growing national market from 2025 to 2035 as BS-VI regulations, surging vehicle ownership, and aftermarket formalization accelerate demand for synthetic and semi-synthetic engine oils.
Across workshops and assembly lines, decarbonization pledges, extended-warranty programs, and fleet telematics are reshaping the automotive oil market. OEMs now factory-fill 0W-20 and 5W-30 synthetics to meet CO₂ targets, while fleet operators install IoT oil-health sensors that trigger predictive drain cycles.
Volatile base-oil prices restrain adoption in price-sensitive regions, prompting suppliers to launch re-refined Group II+ loops and subscription-based oil-analysis services. Emerging trends include e-transmission fluids for EV drivetrains, bio-based esters for hybrid thermal management, and AI-optimized nano-additive packages that cut friction by up to 6 %.
Looking ahead, the automotive oil market is set to pivot toward closed-loop, carbon-accounted lubrication ecosystems. By 2030, cloud algorithms will blend on-site additive top-ups, extending drain intervals beyond 15,000 km for light-duty vehicles and 75,000 km for long-haul trucks.
Bio-based and waste-oil-derived base stocks are expected to triple their share as OEMs push Scope 3 emission cuts. Vendors that bundle carbon-tracking dashboards, localized re-refining, and EV-specific thermal fluids are forecast to capture outsized share through 2035.
Mineral oils still anchor bulk volumes-particularly in cost-sensitive aftermarket channels-while synthetics dominate OE factory fills for their shear stability at low viscosities (0W-16 / 0W-20). Semi-synthetic blends (Group III mineral + PAO/ester) are hitting a sweet spot of price-performance:
fleets upgrading from monograde mineral lubricants gain up to 2 % fuel-economy savings without paying full-synthetic premiums. Rising uptake of emission-compliant, low-SAPs semi-synthetics in India, ASEAN, and Latin America underpins their outperformance through 2035.
| Grade Segment | CAGR (2025 to 2035) |
|---|---|
| Semi-synthetic Automotive Oils | 3.1% |
Diesel engine oils still command ~57 % value share in 2025, driven by long-haul trucks and off-highway equipment. Petrol grades follow, supported by a growing global passenger-car parc but tempered by longer drain intervals and a gradual shift to hybrids. The fastest expansion comes from alternative-fuel oils (CNG/LNG, hybrid ICE, and dedicated e-transmission & e-axle fluids).
Demand is fuelled by urban clean-air mandates, tax breaks for gas fleets, and surging global EV stock-projected to top 200 million units by 2030-which requires low-conductivity, oxidation-resistant coolants and gear oils.
| Engine-Type Segment | CAGR (2025 to 2035) |
|---|---|
| Alternative-Fuel Engine Oils | 4.2% |
Passenger-vehicle oils remain the largest revenue pool, but growth is maturing in North America and Europe as EV penetration rises. Heavy commercial vehicles (HCVs) add steady but slower gains, constrained by increased freight electrification pilots and longer drain synthetics.
Light commercial vehicles (LCVs) benefit from e-commerce logistics growth, yet the standout performer is the two-wheeler segment-bolstered by booming scooter and motorcycle ownership across India, Indonesia, Vietnam, and Africa. OEM push toward 10W-30/10W-40 fuel-saving grades and the rise of performance-oriented bikes lift per-unit oil spends, propelling above-average CAGR.
| Application Segment | CAGR (2025 to 2035) |
|---|---|
| Two-Wheeler Lubricants | 3.1% |
(Surveyed Q4 2024, n=500 stakeholder participants evenly distributed across manufacturers, suppliers, distributors, and end-users in North America, Europe, and Asia-Pacific)
Regional Variance
Convergent and Divergent Perspectives on Market Adaptation
Differentiation Strategies Among Industry Players
Alignment Across Markets
Regional Divergence
Key Variances
| Countries | Government Regulations & Mandatory Certifications |
|---|---|
| United States | The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) regulates emissions, typically favouring low-viscosity and fuel-efficient lubricants. Technical Specs: Gasoline engine oils are API SN PLUS and ILSAC GF-6 certified. The SAE J300 is a commonly recognized viscosity classification. |
| United Kingdom | The guideline for lubricants under UK REACH Regulation Bio-based lubricants are facing more specific requirements due to the demand for carbon neutrality by 2050. ACEA standards are mandatory for automotive oils in passenger vehicles. |
| France | The product meets the standards for both the EU REACH and ACEA oil. Easing up France's aggressive low-emission vehicle initiatives has spurred demand for hybrid and EV-friendly lubricant products. Indeed, the government offers tax credits for sustainable lubricants. |
| Germany | The German Institute for Standardization (DIN) governs lubricant performance specifications. The German Institute for Standardization (DIN) approves OEM-approved lubricants following ACEA and VW 504.00/507.00 certification. Regulations around carbon capture cause knock-on effects to lubricant formulations. |
| Italy | The product satisfies both ACEA oil standards and EU REACH regulations. Tax shift for the spare on sustainable lubricants in Italy: Disposal of used engine oils as waste is regulated by the Ministry of Environment. |
| South Korea | Standards for lubricant quality in Korea are provided by the Korean Agency for Technology and Standards (KATS). The nation follows API and ACEA certifications, which promote fuel-saving oils. It also has to meet tough CO₂ emissions targets. |
| Japan | Standardization bodies such as the Japan Automotive Standards Organization (JASO) encourage standards like JASO MA/MB for motorcycle oils. Japan, however, is also compliant with API and ILSAC certifications and is moving to hybrid-compatible oils due to a higher ratio of electrified vehicles. |
| China | CNIS governs the regulatory environment for lubricant quality in China. Stringent emissions regulations set to take effect by 2025 ensure a widespread preference for low-sulphur and synthetic oils in much of the domestic industry. API and ACEA often certify high-end lubricants. |
| Australia & New Zealand | Australia's Product Stewardship for Oil (PSO) Scheme promotes recycling and re-refining of used lubricants. In New Zealand, firms like Pacific Bio Lubricants hold ISO 9001 & 14001 certifications for quality and environmental standards. Additionally, Australian manufacturers like Anglomoil have ISO 21469 certification for food-grade lubricants. |
| India | The Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) has already implemented Bharat Stage VI (BS-VI) emission standards that require low-sulphur engine lubricants. Petrol quality is regulated by the Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS), while the Automotive Research Association of India (ARAI) certifies lubricants for OEM approval. |
USA automotive oil consumption is expected to grow at a CAGR of 2.1% during 2025 to 2035, slightly lower than the world average due to a maturing automobile sector and increasing EV penetration. However, demand for synthetic and semi-synthetic oils in passenger vehicles and heavy commercial vehicles (HCVs) is considerable.
Tight EPA emission standards are pushing automakers and lubricant manufacturers to low-viscosity, fuel-efficient engine oils such as 0W-20 and 5W-30. The growing number of hybrid car sales is also driving demand for lubricants specific to hybrids, particularly in urban areas, where government incentives for green vehicles are accelerating the transition.
Heavy-duty diesel fuels dominate the freight and logistics industry, where fleet managers lean toward extended-drain synthetic lubricants to decrease downtime. Further government mandates, such as those from the California Air Resources Board (CARB) and federal fuel economy regulations, will likely accelerate the trend toward high-performance, low-emission engine oils.
Demand for eco-friendly lubricants is expected to rise, and thus the UK automotive lubricant industry is slated to grow at a CAGR of 2.3% from 2025 to 2035. Replacement spurs driven by the growth of electric and hybrid vehicles are conducive factors for industry growth. It is expected that the UK government's plan to end the sale of new petrol and diesel vehicles in 2035 would drive the industry toward specialist EV lubricants, including thermal management fluids and e-gear oils.
At present, low-viscosity technology, which improves compliance with fuel efficiency regulations, dominates the industry for synthetic engine oils, particularly in passenger cars and LCVs. ACEA-approved lubricants must meet challenges set by European emission and performance specifications. The HCV phase is also slowly transitioning to low-sulphur and bio-based lubricants-most notably against urban low-emission zones (LEZs).
The automobile oil industry in the country is expected to expand at a CAGR of 2.4% from 2025 to 2035, higher than the global average due to stringent environmental regulations and increased hybrid vehicle sales. In France, the 2050 carbon neutrality drive by the French government has started influencing lubricant formulations towards bio-based and synthetic oils.
The passenger car sector continues to be the biggest consumer of automotive oils, with fully synthetic automotive oils dominating this field owing to their fuel efficiency and extended oil change intervals. The high-rate consumption of 0W-20 and 5W-30 lubricants has increased remarkably, mainly to adapt to Euro 6 and future Euro 7 regulations.
The government is encouraging the LCV and HCV industries to switch to low-emission diesel engine oils through subsidies and incentives for cleaner fleets. Growing application in commercial vehicles, on account of tax incentives, is propelling the demand for bio-lubricants.
Germany, being the hub for automotive innovation, is expected to grow at a 2.6% CAGR between 2025 and 2035, in line with the global average. The growing inclination in the region towards high-performance, fuel-economical, and eco-friendly lubricants is reshaping the industry dynamics.
The passenger cars are the leading segment, with increasing supplies of synthetic and hybrid-compatible oils. Germany's premium automobile sector, with its numerous BMW, Mercedes-Benz, Audi, and other brands, requires high-performance engine lubricants in the 0W and 5W viscosity range. Furthermore, the HCV and industrial vehicles segment is a key driver of the demand for high-performance, long-life diesel engine oils.
Germany is driving the development of bio-based and hybrid oils to reduce CO2 emissions from commercial traffic. This effort aligns with the country’s broader sustainability goals, promoting alternatives to conventional petroleum-based oils to improve environmental performance in the transport sector.
The luxury and performance car industry in Italy creates a demand for performance synthetic lubricants, sourced from high-revenue manufacturers like Ferrari and Lamborghini. The transition to Euro 7 emission regulations is prompting OEMs to embrace low-viscosity, fuel-efficient lubricants. Rising demand for hybrid and electric vehicles (EVs) is slowing demand for conventional engine oils but is increasing e-transmission fluids and battery cooling systems.
Italy's afterindustry is strong, and demand for OEM-recommended lubricants is growing. In accordance with the vision of the EU having carbon neutrality, the country also backs bio-based lubricants. The Automotive Oil industry in Italy is expected to grow at a 2.0% CAGR between 2025 and 2035.
South Korea, the home of Hyundai, Kia, and Genesis, is a dominant force in the global automotive industry. As the use of hydrogen, electricity, and electrification in transportation grows, so does the need for thermal management fluids (TMFs). This is causing changes in the requirements for lubrication. High-efficiency lubricants and hybrid engine R&D in South Korea are driving the industry.
An increasing demand for high-end synthetic oils cannot be denied due to the rising demand for Korean-manufactured vehicles, which necessitates more commercial vehicles and heavy-duty lubricants. The government will also encourage the use of eco-friendly lubricant, enabling an eco-sustainable industry. The Automotive Oil industry in South Korea is expected to grow at a 2.5% CAGR between 2025 and 2035.
Japan's automotive sector is renowned for its technological efficiency and innovation, with Toyota, Honda, and Nissan being longstanding leaders in this field. The leading nation for hybrid cars keeps demand for low-friction automotive oils high, and growing EV volumes are turning lubricant requirements into e-transmission fluids.
Japan is also aggressively bringing down high-emission lubricants with strict fuel economy specifications that are forcing the use of synthetic and bio-based oils. However, the continued success of the afterindustry is contingent upon Japan's older vehicle population and the ongoing demand for OEM-approved lubricants. The Automotive Oil industry in Japan is expected to grow at a 2.3% CAGR between 2025 and 2035.
China, the largest single-country car industry in the world, witnessed growth in both the passenger andcial vehicle segments. It is one of the key countries in East Asia and is likely to account for more than 70% of the share in Asia-Pacific region. Simultaneously, the government's promotion of new energy vehicles (NEVs), such as electric vehicles (EVs), hybrids, and hydrogen cars, is causing a significant disruption in the lubricants industry.
While conventional engine oils remain in high demand, the shift to synthetic, fuel-saving,, and EV-compatible lubes is gathering momentum. China's industrial growth also drives the demand for heavy-duty lubricants used in logistics and construction equipment.
While domestic lubricant brands are expanding, international brands are gaining a significant industry share through OEM partnerships and localized production. The Automotive Oil industry in China is expected to grow at a 3.2% CAGR between 2025 and 2035.
The Indian automotive oil industry is one of the fastest-growing in the world, fuelled by increasing vehicle ownership, a blossoming infrastructure space, and a booming logistics ecosystem. With the implementation of BS-VI emission standards, there is a greater need for synthetic and semi-synthetic lubricants. These standards call for low-viscosity, high-performance oils.
The commercial vehicle sector is a significant driving force behind this, as fleet operators increasingly select long-drain interval lubricants to minimize maintenance expenses. While the EV adoption in India has still not attained momentum, the lubricant segment is preparing for offerings related to e-mobility.
Local manufacture and collaboration with the OEMs is critical as a drive and government initiatives towards lubricant manufacture that are environmentally friendly in nature. The Automotive Oil industry in India is expected to grow at a 3.5% CAGR between 2025 and 2035.
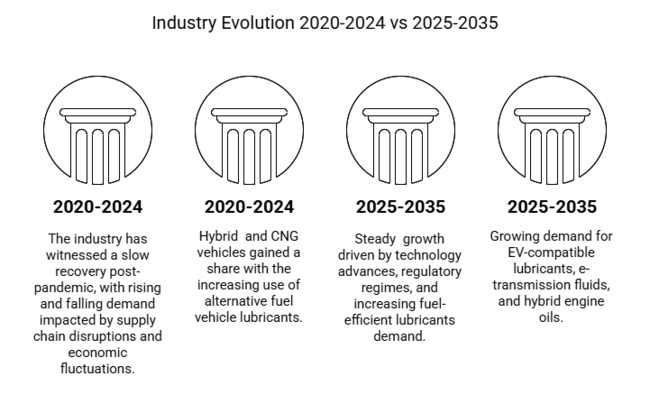
| 2020 to 2024 | 2025 to 2035 |
|---|---|
| The industry has witnessed a slow recovery post-pandemic, with rising and falling demand impacted by supply chain disruptions and economic fluctuations. | Steady growth driven by technology advances, regulatory regimes, and increasing fuel-efficient lubricants demand. |
| There is a strong demand for synthetic oils, especially in maturing regions, owing to better engine performance and longer drain intervals. | Synthetic oils will remain the most popular lubricant by share and become the most popular by tonnage, as penetration rises in emerging industries and the trend towards low-viscosity grades continues. |
| Hybrid and CNG vehicles gained a share with the increasing use of alternative fuel vehicle lubricants. | There is a growing demand for EV-compatible lubricants, e-transmission fluids, and hybrid engine oils. |
| Increasing regulations compelled a shift to lubrication for low-sulphur, low-viscosity, and high-performance lubrication. | Growing worldwide emissions regulations are driving the utilization of bio-based, completely synthetic, and high-efficiency lubricants. |
| Disruptions to the raw material supply chain and volatile crude oil prices affected the profitability and pricing of lubricants. | The robustness of the supply chain builds; investments support sustainable raw material sources, stabilizing the industry. |
| Consumer demand for high-performance lubricants has been shaped by OEM specifications and technology trends. | The Automotive Oil Industry have major collaborations with OEMs to drive lubricant innovation-explorations and implementations around AI-based predictive maintenance and intelligent lubrication solutions. |
Major players operating in the automotive oil segment strives to promote themselves through price, innovation, alliances and geographical expansion. While price competition remains fierce, premium brand choices indicate differentiation by high-performance synthetic and green lubricants.
These investments spread through the work on developing low-viscosity, fuel-efficient and electric vehicles compatible lubricants that comply with emissions standards. Strategically partnered with OEM partnerships help fortify product offerings, whereas M&As land us a foothold in the industry.
Major players are expanding into emerging economies like India and China, prioritizing localized production and efficient delivery. This evolving landscape gives way to digitalization, such as AI-based predictive maintenance solutions, as a prominent differentiator.
The global automotive oil industry is highly fragment, with some key players bearing a largish share of the industry. With the most extensive distribution network and strong OEM partnerships, Shell leads with an estimated 13-15% market share.
ExxonMobil holds approximately 12% market share and is well-positioned due to its advanced lubrication technologies and OEM partnerships. The State-owned oil and gas companies, BP's Castrol which has an industry share of 10-12%, and other competitors in the respective segment strengthen each other's market position with novel and cutting-edge portfolio of products and a major segment of growth from developing economies.
Chevron owns nearly 9% and TotalEnergies about 8% of it. Sustainability and high-performance lubricants have been the two areas where the two companies have developed products to remain competitive in the marketplace.
Valvoline (~7% industry share) remains the leader in the after industry, primarily focusing on DIY customers and quick-lube shops. It retained its position because of its brand loyalty and customer service approach.
FUCHS Petrolub SE, one of the largest independent lubricant manufacturers, commands a notable share in the industry. The German-based company specializes in customized lubrication solutions for passenger cars, heavy-duty vehicles, and industrial applications. Its focus on research and innovation has driven the adoption of high-performance, fuel-efficient oils tailored to meet stringent European emission standards.
PETRONAS Lubricants International, a subsidiary of the Malaysian energy giant PETRONAS, has also expanded its global presence. With strong OEM partnerships, the company has positioned itself as a leader in premium synthetic lubricants. Its commitment to motorsports, particularly through its collaboration with Mercedes-AMG Petronas Formula One Team, has helped solidify its brand image and technological advancements in high-performance engine oils.
The industry is segmented into mineral, synthetic and semi-synthetic
It is fragmented into diesel, petrol and alternative fuel
The sector is segmented into passenger vehicle, heavy commercial vehicle, light commercial vehicle and two wheelers
It is fragmented into North America, Latin America, Europe, East Asia, South Asia & Pacific and Middle East & Africa.
The industry is experiencing growth in vehicle production, rising demand for high-performance lubricant, stringent emission regulations, and growing penetration of bio and synthetic oils.
The rise of EVs reduces demand for traditional engine oils but drives growth in e-transmission fluids, thermal management lubricants, and hybrid oils.
Asia-Pacific, including China and India, is experiencing a rapid expansion of vehicle fleets, while the rest of North America and Europe is focusing on premium and environmentally friendly oils.
Demand for bio-based, low-viscosity lubricants is split into lower viscosity products. This is because of stricter rules on fuel efficiency and emissions, like the ones that apply to lighter oils (0W and 5W) in some regional industries.
To meet these evolving industry needs, companies invest in artificial oils, long-drain lubricants, predictive maintenance based on artificial intelligence, and eco-friendly formulations.
Table 1: Global Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Region, 2018 to 2033
Table 2: Global Market Volume (Liters) Forecast by Region, 2018 to 2033
Table 3: Global Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Grade, 2018 to 2033
Table 4: Global Market Volume (Liters) Forecast by Grade, 2018 to 2033
Table 5: Global Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Engine Type, 2018 to 2033
Table 6: Global Market Volume (Liters) Forecast by Engine Type, 2018 to 2033
Table 7: Global Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Application, 2018 to 2033
Table 8: Global Market Volume (Liters) Forecast by Application, 2018 to 2033
Table 9: North America Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Country, 2018 to 2033
Table 10: North America Market Volume (Liters) Forecast by Country, 2018 to 2033
Table 11: North America Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Grade, 2018 to 2033
Table 12: North America Market Volume (Liters) Forecast by Grade, 2018 to 2033
Table 13: North America Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Engine Type, 2018 to 2033
Table 14: North America Market Volume (Liters) Forecast by Engine Type, 2018 to 2033
Table 15: North America Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Application, 2018 to 2033
Table 16: North America Market Volume (Liters) Forecast by Application, 2018 to 2033
Table 17: Latin America Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Country, 2018 to 2033
Table 18: Latin America Market Volume (Liters) Forecast by Country, 2018 to 2033
Table 19: Latin America Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Grade, 2018 to 2033
Table 20: Latin America Market Volume (Liters) Forecast by Grade, 2018 to 2033
Table 21: Latin America Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Engine Type, 2018 to 2033
Table 22: Latin America Market Volume (Liters) Forecast by Engine Type, 2018 to 2033
Table 23: Latin America Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Application, 2018 to 2033
Table 24: Latin America Market Volume (Liters) Forecast by Application, 2018 to 2033
Table 25: Western Europe Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Country, 2018 to 2033
Table 26: Western Europe Market Volume (Liters) Forecast by Country, 2018 to 2033
Table 27: Western Europe Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Grade, 2018 to 2033
Table 28: Western Europe Market Volume (Liters) Forecast by Grade, 2018 to 2033
Table 29: Western Europe Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Engine Type, 2018 to 2033
Table 30: Western Europe Market Volume (Liters) Forecast by Engine Type, 2018 to 2033
Table 31: Western Europe Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Application, 2018 to 2033
Table 32: Western Europe Market Volume (Liters) Forecast by Application, 2018 to 2033
Table 33: Eastern Europe Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Country, 2018 to 2033
Table 34: Eastern Europe Market Volume (Liters) Forecast by Country, 2018 to 2033
Table 35: Eastern Europe Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Grade, 2018 to 2033
Table 36: Eastern Europe Market Volume (Liters) Forecast by Grade, 2018 to 2033
Table 37: Eastern Europe Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Engine Type, 2018 to 2033
Table 38: Eastern Europe Market Volume (Liters) Forecast by Engine Type, 2018 to 2033
Table 39: Eastern Europe Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Application, 2018 to 2033
Table 40: Eastern Europe Market Volume (Liters) Forecast by Application, 2018 to 2033
Table 41: South Asia and Pacific Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Country, 2018 to 2033
Table 42: South Asia and Pacific Market Volume (Liters) Forecast by Country, 2018 to 2033
Table 43: South Asia and Pacific Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Grade, 2018 to 2033
Table 44: South Asia and Pacific Market Volume (Liters) Forecast by Grade, 2018 to 2033
Table 45: South Asia and Pacific Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Engine Type, 2018 to 2033
Table 46: South Asia and Pacific Market Volume (Liters) Forecast by Engine Type, 2018 to 2033
Table 47: South Asia and Pacific Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Application, 2018 to 2033
Table 48: South Asia and Pacific Market Volume (Liters) Forecast by Application, 2018 to 2033
Table 49: East Asia Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Country, 2018 to 2033
Table 50: East Asia Market Volume (Liters) Forecast by Country, 2018 to 2033
Table 51: East Asia Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Grade, 2018 to 2033
Table 52: East Asia Market Volume (Liters) Forecast by Grade, 2018 to 2033
Table 53: East Asia Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Engine Type, 2018 to 2033
Table 54: East Asia Market Volume (Liters) Forecast by Engine Type, 2018 to 2033
Table 55: East Asia Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Application, 2018 to 2033
Table 56: East Asia Market Volume (Liters) Forecast by Application, 2018 to 2033
Table 57: Middle East and Africa Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Country, 2018 to 2033
Table 58: Middle East and Africa Market Volume (Liters) Forecast by Country, 2018 to 2033
Table 59: Middle East and Africa Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Grade, 2018 to 2033
Table 60: Middle East and Africa Market Volume (Liters) Forecast by Grade, 2018 to 2033
Table 61: Middle East and Africa Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Engine Type, 2018 to 2033
Table 62: Middle East and Africa Market Volume (Liters) Forecast by Engine Type, 2018 to 2033
Table 63: Middle East and Africa Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Application, 2018 to 2033
Table 64: Middle East and Africa Market Volume (Liters) Forecast by Application, 2018 to 2033
Figure 1: Global Market Value (US$ Million) by Grade, 2023 to 2033
Figure 2: Global Market Value (US$ Million) by Engine Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 3: Global Market Value (US$ Million) by Application, 2023 to 2033
Figure 4: Global Market Value (US$ Million) by Region, 2023 to 2033
Figure 5: Global Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Region, 2018 to 2033
Figure 6: Global Market Volume (Liters) Analysis by Region, 2018 to 2033
Figure 7: Global Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Region, 2023 to 2033
Figure 8: Global Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Region, 2023 to 2033
Figure 9: Global Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Grade, 2018 to 2033
Figure 10: Global Market Volume (Liters) Analysis by Grade, 2018 to 2033
Figure 11: Global Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Grade, 2023 to 2033
Figure 12: Global Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Grade, 2023 to 2033
Figure 13: Global Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Engine Type, 2018 to 2033
Figure 14: Global Market Volume (Liters) Analysis by Engine Type, 2018 to 2033
Figure 15: Global Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Engine Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 16: Global Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Engine Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 17: Global Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Application, 2018 to 2033
Figure 18: Global Market Volume (Liters) Analysis by Application, 2018 to 2033
Figure 19: Global Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Application, 2023 to 2033
Figure 20: Global Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Application, 2023 to 2033
Figure 21: Global Market Attractiveness by Grade, 2023 to 2033
Figure 22: Global Market Attractiveness by Engine Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 23: Global Market Attractiveness by Application, 2023 to 2033
Figure 24: Global Market Attractiveness by Region, 2023 to 2033
Figure 25: North America Market Value (US$ Million) by Grade, 2023 to 2033
Figure 26: North America Market Value (US$ Million) by Engine Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 27: North America Market Value (US$ Million) by Application, 2023 to 2033
Figure 28: North America Market Value (US$ Million) by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 29: North America Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Country, 2018 to 2033
Figure 30: North America Market Volume (Liters) Analysis by Country, 2018 to 2033
Figure 31: North America Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 32: North America Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 33: North America Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Grade, 2018 to 2033
Figure 34: North America Market Volume (Liters) Analysis by Grade, 2018 to 2033
Figure 35: North America Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Grade, 2023 to 2033
Figure 36: North America Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Grade, 2023 to 2033
Figure 37: North America Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Engine Type, 2018 to 2033
Figure 38: North America Market Volume (Liters) Analysis by Engine Type, 2018 to 2033
Figure 39: North America Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Engine Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 40: North America Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Engine Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 41: North America Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Application, 2018 to 2033
Figure 42: North America Market Volume (Liters) Analysis by Application, 2018 to 2033
Figure 43: North America Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Application, 2023 to 2033
Figure 44: North America Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Application, 2023 to 2033
Figure 45: North America Market Attractiveness by Grade, 2023 to 2033
Figure 46: North America Market Attractiveness by Engine Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 47: North America Market Attractiveness by Application, 2023 to 2033
Figure 48: North America Market Attractiveness by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 49: Latin America Market Value (US$ Million) by Grade, 2023 to 2033
Figure 50: Latin America Market Value (US$ Million) by Engine Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 51: Latin America Market Value (US$ Million) by Application, 2023 to 2033
Figure 52: Latin America Market Value (US$ Million) by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 53: Latin America Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Country, 2018 to 2033
Figure 54: Latin America Market Volume (Liters) Analysis by Country, 2018 to 2033
Figure 55: Latin America Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 56: Latin America Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 57: Latin America Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Grade, 2018 to 2033
Figure 58: Latin America Market Volume (Liters) Analysis by Grade, 2018 to 2033
Figure 59: Latin America Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Grade, 2023 to 2033
Figure 60: Latin America Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Grade, 2023 to 2033
Figure 61: Latin America Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Engine Type, 2018 to 2033
Figure 62: Latin America Market Volume (Liters) Analysis by Engine Type, 2018 to 2033
Figure 63: Latin America Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Engine Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 64: Latin America Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Engine Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 65: Latin America Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Application, 2018 to 2033
Figure 66: Latin America Market Volume (Liters) Analysis by Application, 2018 to 2033
Figure 67: Latin America Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Application, 2023 to 2033
Figure 68: Latin America Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Application, 2023 to 2033
Figure 69: Latin America Market Attractiveness by Grade, 2023 to 2033
Figure 70: Latin America Market Attractiveness by Engine Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 71: Latin America Market Attractiveness by Application, 2023 to 2033
Figure 72: Latin America Market Attractiveness by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 73: Western Europe Market Value (US$ Million) by Grade, 2023 to 2033
Figure 74: Western Europe Market Value (US$ Million) by Engine Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 75: Western Europe Market Value (US$ Million) by Application, 2023 to 2033
Figure 76: Western Europe Market Value (US$ Million) by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 77: Western Europe Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Country, 2018 to 2033
Figure 78: Western Europe Market Volume (Liters) Analysis by Country, 2018 to 2033
Figure 79: Western Europe Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 80: Western Europe Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 81: Western Europe Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Grade, 2018 to 2033
Figure 82: Western Europe Market Volume (Liters) Analysis by Grade, 2018 to 2033
Figure 83: Western Europe Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Grade, 2023 to 2033
Figure 84: Western Europe Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Grade, 2023 to 2033
Figure 85: Western Europe Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Engine Type, 2018 to 2033
Figure 86: Western Europe Market Volume (Liters) Analysis by Engine Type, 2018 to 2033
Figure 87: Western Europe Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Engine Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 88: Western Europe Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Engine Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 89: Western Europe Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Application, 2018 to 2033
Figure 90: Western Europe Market Volume (Liters) Analysis by Application, 2018 to 2033
Figure 91: Western Europe Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Application, 2023 to 2033
Figure 92: Western Europe Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Application, 2023 to 2033
Figure 93: Western Europe Market Attractiveness by Grade, 2023 to 2033
Figure 94: Western Europe Market Attractiveness by Engine Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 95: Western Europe Market Attractiveness by Application, 2023 to 2033
Figure 96: Western Europe Market Attractiveness by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 97: Eastern Europe Market Value (US$ Million) by Grade, 2023 to 2033
Figure 98: Eastern Europe Market Value (US$ Million) by Engine Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 99: Eastern Europe Market Value (US$ Million) by Application, 2023 to 2033
Figure 100: Eastern Europe Market Value (US$ Million) by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 101: Eastern Europe Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Country, 2018 to 2033
Figure 102: Eastern Europe Market Volume (Liters) Analysis by Country, 2018 to 2033
Figure 103: Eastern Europe Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 104: Eastern Europe Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 105: Eastern Europe Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Grade, 2018 to 2033
Figure 106: Eastern Europe Market Volume (Liters) Analysis by Grade, 2018 to 2033
Figure 107: Eastern Europe Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Grade, 2023 to 2033
Figure 108: Eastern Europe Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Grade, 2023 to 2033
Figure 109: Eastern Europe Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Engine Type, 2018 to 2033
Figure 110: Eastern Europe Market Volume (Liters) Analysis by Engine Type, 2018 to 2033
Figure 111: Eastern Europe Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Engine Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 112: Eastern Europe Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Engine Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 113: Eastern Europe Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Application, 2018 to 2033
Figure 114: Eastern Europe Market Volume (Liters) Analysis by Application, 2018 to 2033
Figure 115: Eastern Europe Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Application, 2023 to 2033
Figure 116: Eastern Europe Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Application, 2023 to 2033
Figure 117: Eastern Europe Market Attractiveness by Grade, 2023 to 2033
Figure 118: Eastern Europe Market Attractiveness by Engine Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 119: Eastern Europe Market Attractiveness by Application, 2023 to 2033
Figure 120: Eastern Europe Market Attractiveness by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 121: South Asia and Pacific Market Value (US$ Million) by Grade, 2023 to 2033
Figure 122: South Asia and Pacific Market Value (US$ Million) by Engine Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 123: South Asia and Pacific Market Value (US$ Million) by Application, 2023 to 2033
Figure 124: South Asia and Pacific Market Value (US$ Million) by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 125: South Asia and Pacific Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Country, 2018 to 2033
Figure 126: South Asia and Pacific Market Volume (Liters) Analysis by Country, 2018 to 2033
Figure 127: South Asia and Pacific Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 128: South Asia and Pacific Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 129: South Asia and Pacific Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Grade, 2018 to 2033
Figure 130: South Asia and Pacific Market Volume (Liters) Analysis by Grade, 2018 to 2033
Figure 131: South Asia and Pacific Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Grade, 2023 to 2033
Figure 132: South Asia and Pacific Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Grade, 2023 to 2033
Figure 133: South Asia and Pacific Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Engine Type, 2018 to 2033
Figure 134: South Asia and Pacific Market Volume (Liters) Analysis by Engine Type, 2018 to 2033
Figure 135: South Asia and Pacific Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Engine Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 136: South Asia and Pacific Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Engine Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 137: South Asia and Pacific Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Application, 2018 to 2033
Figure 138: South Asia and Pacific Market Volume (Liters) Analysis by Application, 2018 to 2033
Figure 139: South Asia and Pacific Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Application, 2023 to 2033
Figure 140: South Asia and Pacific Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Application, 2023 to 2033
Figure 141: South Asia and Pacific Market Attractiveness by Grade, 2023 to 2033
Figure 142: South Asia and Pacific Market Attractiveness by Engine Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 143: South Asia and Pacific Market Attractiveness by Application, 2023 to 2033
Figure 144: South Asia and Pacific Market Attractiveness by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 145: East Asia Market Value (US$ Million) by Grade, 2023 to 2033
Figure 146: East Asia Market Value (US$ Million) by Engine Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 147: East Asia Market Value (US$ Million) by Application, 2023 to 2033
Figure 148: East Asia Market Value (US$ Million) by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 149: East Asia Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Country, 2018 to 2033
Figure 150: East Asia Market Volume (Liters) Analysis by Country, 2018 to 2033
Figure 151: East Asia Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 152: East Asia Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 153: East Asia Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Grade, 2018 to 2033
Figure 154: East Asia Market Volume (Liters) Analysis by Grade, 2018 to 2033
Figure 155: East Asia Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Grade, 2023 to 2033
Figure 156: East Asia Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Grade, 2023 to 2033
Figure 157: East Asia Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Engine Type, 2018 to 2033
Figure 158: East Asia Market Volume (Liters) Analysis by Engine Type, 2018 to 2033
Figure 159: East Asia Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Engine Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 160: East Asia Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Engine Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 161: East Asia Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Application, 2018 to 2033
Figure 162: East Asia Market Volume (Liters) Analysis by Application, 2018 to 2033
Figure 163: East Asia Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Application, 2023 to 2033
Figure 164: East Asia Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Application, 2023 to 2033
Figure 165: East Asia Market Attractiveness by Grade, 2023 to 2033
Figure 166: East Asia Market Attractiveness by Engine Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 167: East Asia Market Attractiveness by Application, 2023 to 2033
Figure 168: East Asia Market Attractiveness by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 169: Middle East and Africa Market Value (US$ Million) by Grade, 2023 to 2033
Figure 170: Middle East and Africa Market Value (US$ Million) by Engine Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 171: Middle East and Africa Market Value (US$ Million) by Application, 2023 to 2033
Figure 172: Middle East and Africa Market Value (US$ Million) by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 173: Middle East and Africa Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Country, 2018 to 2033
Figure 174: Middle East and Africa Market Volume (Liters) Analysis by Country, 2018 to 2033
Figure 175: Middle East and Africa Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 176: Middle East and Africa Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 177: Middle East and Africa Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Grade, 2018 to 2033
Figure 178: Middle East and Africa Market Volume (Liters) Analysis by Grade, 2018 to 2033
Figure 179: Middle East and Africa Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Grade, 2023 to 2033
Figure 180: Middle East and Africa Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Grade, 2023 to 2033
Figure 181: Middle East and Africa Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Engine Type, 2018 to 2033
Figure 182: Middle East and Africa Market Volume (Liters) Analysis by Engine Type, 2018 to 2033
Figure 183: Middle East and Africa Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Engine Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 184: Middle East and Africa Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Engine Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 185: Middle East and Africa Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Application, 2018 to 2033
Figure 186: Middle East and Africa Market Volume (Liters) Analysis by Application, 2018 to 2033
Figure 187: Middle East and Africa Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Application, 2023 to 2033
Figure 188: Middle East and Africa Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Application, 2023 to 2033
Figure 189: Middle East and Africa Market Attractiveness by Grade, 2023 to 2033
Figure 190: Middle East and Africa Market Attractiveness by Engine Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 191: Middle East and Africa Market Attractiveness by Application, 2023 to 2033
Figure 192: Middle East and Africa Market Attractiveness by Country, 2023 to 2033






Our Research Products

The "Full Research Suite" delivers actionable market intel, deep dives on markets or technologies, so clients act faster, cut risk, and unlock growth.

The Leaderboard benchmarks and ranks top vendors, classifying them as Established Leaders, Leading Challengers, or Disruptors & Challengers.

Locates where complements amplify value and substitutes erode it, forecasting net impact by horizon

We deliver granular, decision-grade intel: market sizing, 5-year forecasts, pricing, adoption, usage, revenue, and operational KPIs—plus competitor tracking, regulation, and value chains—across 60 countries broadly.

Spot the shifts before they hit your P&L. We track inflection points, adoption curves, pricing moves, and ecosystem plays to show where demand is heading, why it is changing, and what to do next across high-growth markets and disruptive tech

Real-time reads of user behavior. We track shifting priorities, perceptions of today’s and next-gen services, and provider experience, then pace how fast tech moves from trial to adoption, blending buyer, consumer, and channel inputs with social signals (#WhySwitch, #UX).

Partner with our analyst team to build a custom report designed around your business priorities. From analysing market trends to assessing competitors or crafting bespoke datasets, we tailor insights to your needs.
Supplier Intelligence
Discovery & Profiling
Capacity & Footprint
Performance & Risk
Compliance & Governance
Commercial Readiness
Who Supplies Whom
Scorecards & Shortlists
Playbooks & Docs
Category Intelligence
Definition & Scope
Demand & Use Cases
Cost Drivers
Market Structure
Supply Chain Map
Trade & Policy
Operating Norms
Deliverables
Buyer Intelligence
Account Basics
Spend & Scope
Procurement Model
Vendor Requirements
Terms & Policies
Entry Strategy
Pain Points & Triggers
Outputs
Pricing Analysis
Benchmarks
Trends
Should-Cost
Indexation
Landed Cost
Commercial Terms
Deliverables
Brand Analysis
Positioning & Value Prop
Share & Presence
Customer Evidence
Go-to-Market
Digital & Reputation
Compliance & Trust
KPIs & Gaps
Outputs
Full Research Suite comprises of:
Market outlook & trends analysis
Interviews & case studies
Strategic recommendations
Vendor profiles & capabilities analysis
5-year forecasts
8 regions and 60+ country-level data splits
Market segment data splits
12 months of continuous data updates
DELIVERED AS:
PDF EXCEL ONLINE
Automotive Oil Management Module Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Automotive Oil Pressure Control Valve Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Automotive Oil Strainer Market
Automotive Oil Pressure Switch Market
Automotive Coil Spring Market
Automotive Engine Oil Coolers Market
Automotive Variable Oil Pump Market Growth – Trends & Forecast 2024-2034
Automotive Ignition Coil Market Growth - Trends & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Automotive Variable Discharge Oil Pump Market
Automotive Direct Liquid Cooling IGBT Module Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Automotive Hoses and Assemblies Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Automotive Network Testing Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Automotive Performance Part Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Oily Waste Can Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Oil and Gas Seal Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Oil Coalescing Filter Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Automotive Carbon Ceramic Brake Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Automotive Camshaft Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Automotive Stamping Industry Analysis in India Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Automotive Cylinder Liner Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035

Thank you!
You will receive an email from our Business Development Manager. Please be sure to check your SPAM/JUNK folder too.
Chat With
MaRIA