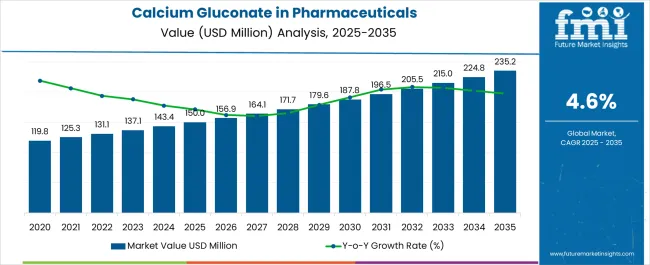
Demand for calcium gluconate in pharmaceuticals globally is estimated at USD 150.0 million in 2025, with projections indicating a rise to USD 235.2 million by 2035, reflecting a CAGR of approximately 4.6% over the forecast period. This growth reflects both expanding healthcare infrastructure and increased per capita consumption in key therapeutic areas. The rise in demand is linked to growing critical care protocols, aging populations, and evolving treatment standards for hypocalcemia and hyperkalemia management. By 2025, per capita spending on calcium gluconate pharmaceuticals in leading countries such as India, China, and the United States varies significantly based on healthcare infrastructure and clinical protocols.
The largest contribution to demand continues to come from injectable calcium gluconate formulations, which are expected to account for 58% of total sales in 2025, owing to their critical role in emergency medicine, intensive care units, and peri-operative settings. By distribution channel, hospital pharmacies represent the dominant format, responsible for 62% of all sales, while retail pharmacies and online platforms serve outpatient and chronic care segments.
Clinical adoption is particularly concentrated among acute care facilities and specialized treatment centers, with healthcare infrastructure development and protocol standardization emerging as significant drivers of demand. While cost considerations remain important in price-sensitive regions, the essential nature of calcium gluconate in emergency and critical care applications maintains steady consumption across diverse healthcare systems. Regional disparities persist in per capita utilization, but expanding hospital networks and improved emergency care protocols are driving broader adoption patterns globally.
The increasing clinical demand for effective calcium supplementation and emergency care is driving growth of calcium gluconate in the pharmaceutical sector. Its high solubility, safety profile, and reliable bioavailability make it the preferred calcium salt for intravenous use in hospitals and clinics. Widely utilized in the treatment of hypocalcemia, cardiac arrest management, tetany, and as an antidote for magnesium sulfate overdose or hydrofluoric acid exposure, calcium gluconate remains a critical component in emergency and intensive care protocols.
Pharmaceutical formulations of calcium gluconate including injectables, oral solutions, and tablets offer dosing flexibility and broad applicability across age groups. Rising incidence of calcium-related deficiencies, expansion of hospital-based treatments, and integration into essential medicine lists worldwide are boosting its adoption. Additionally, increasing use in parenteral nutrition therapies, growing availability in both generic and branded forms, and alignment with global healthcare guidelines are strengthening market growth and providing competitive advantages for pharmaceutical manufacturers.
The calcium gluconate pharmaceutical segment worldwide is classified across several categories. By dosage form, the key segments include injectable solutions, oral tablets, oral solutions and syrups, and other formats such as chewables and powders. By clinical indication, the segment spans acute hypocalcemia treatment including peri-operative and pancreatitis cases, supplementation for osteoporosis, hyperkalemia cardioprotection, calcium-channel-blocker overdose management, and neonatal or pediatric hypocalcemia treatment. By distribution channel, the segment covers hospital pharmacies, retail pharmacies, and online pharmacy platforms. By therapeutic application, formulations serve emergency medicine, critical care, chronic disease management, pediatric care, and specialized treatment protocols. By regional coverage, major countries analyzed include India, China, the United States, Brazil, Germany, Japan, and the United Kingdom.
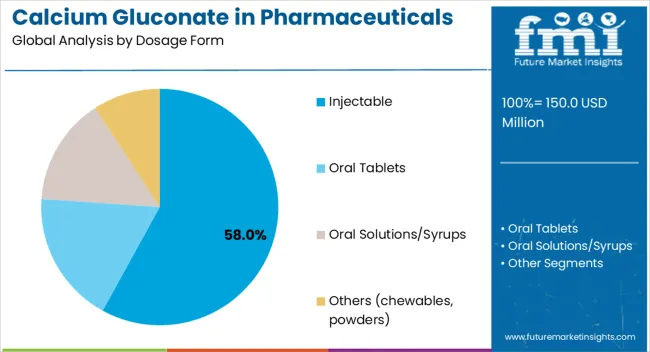
Injectable calcium gluconate formulations are projected to dominate sales in 2025, supported by their essential role in acute care settings, rapid onset of action, and clinical preference in emergency protocols. Other formats such as oral tablets and solutions serve chronic supplementation and outpatient care needs.
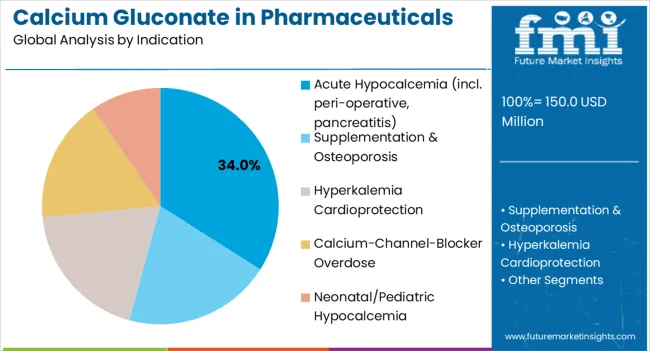
Calcium gluconate pharmaceuticals serve diverse clinical indications, with acute hypocalcemia management representing the largest therapeutic application. Emergency and critical care protocols drive primary demand, while chronic conditions contribute to steady baseline consumption patterns.
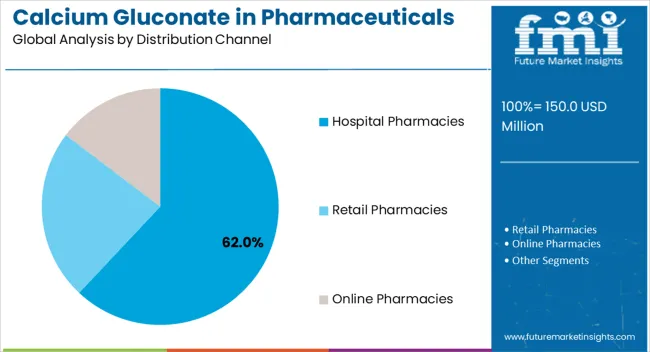
Calcium gluconate pharmaceutical distribution reflects the acute care nature of primary applications, with hospital-based channels dominating sales patterns. Distribution strategies align with clinical usage patterns, emphasizing institutional procurement and emergency preparedness requirements.
Calcium gluconate is widely adopted in the pharmaceutical sector due to its role in managing hypocalcemia, tetany, cardiac resuscitation, and electrolyte imbalances. Its high solubility and safety profile make it suitable for injectable formulations, oral supplements, and IV infusions. In emergency medicine, calcium gluconate is a critical antidote for hyperkalemia and magnesium toxicity and for neutralizing calcium-channel blocker overdoses. Rising hospital admissions linked to osteoporosis, renal dysfunction, and critical care needs are driving demand. Expanding applications in parenteral nutrition and oncology supportive care strengthen its pharmaceutical relevance. Regulatory approvals and inclusion in WHO’s essential medicines list further ensure consistent clinical adoption.
Despite strong clinical demand, calcium gluconate faces supply-side vulnerabilities tied to raw material availability and GMP-compliant production. Its low calcium content (9%) compared to carbonate or citrate salts requires larger doses, increasing treatment costs and storage volumes. In injectables, stringent stability, sterility, and cold-chain requirements raise production costs for pharma manufacturers. Competition from other calcium formulations and generic alternatives puts pricing pressure on suppliers. In some therapeutic areas, patient adherence to oral supplements is hindered by taste and gastrointestinal side effects. Additionally, regulatory hurdles and the need for rigorous clinical quality standards can slow product approvals and market entry.
Pharmaceutical innovation is shifting toward advanced injectable forms of calcium gluconate with improved stability and compatibility for critical care use. Development of fixed-dose combinations with vitamins (e.g., Vitamin D3) and minerals is addressing multi-deficiency treatment needs in hospitals and outpatient care. Micronization and nanotechnology are being applied to enhance absorption, reduce side effects, and optimize dosing efficiency. AI-driven formulation platforms are helping drug developers simulate stability, predict patient outcomes, and shorten R&D timelines. Growth in biosimilar and specialty injectable markets is creating opportunities for calcium gluconate as part of integrated therapy regimens. Increasing demand in emerging markets’ hospital infrastructure positions calcium gluconate as a vital component of the pharmaceutical calcium portfolio.
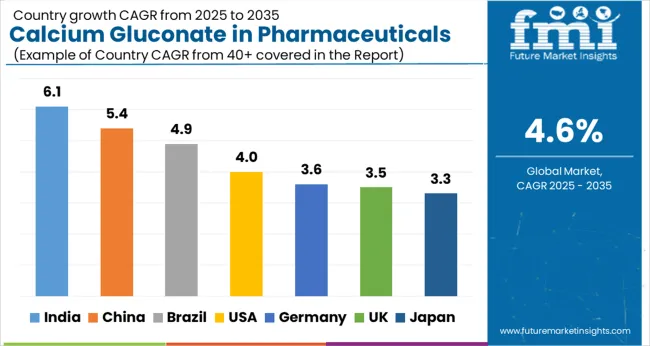
Calcium gluconate pharmaceutical demand varies significantly across countries based on healthcare infrastructure, clinical protocols, and population demographics. Emerging economies with expanding hospital networks show faster growth rates, while developed countries maintain steady consumption from established healthcare systems.
India demonstrates the fastest projected growth in calcium gluconate pharmaceutical demand, with a CAGR of 6.1% between 2025 and 2035. This acceleration stems from rapid expansion of intensive care and emergency department capacity across both public and private hospital networks. The country's large patient population requiring dialysis and chronic kidney disease management drives consistent demand for injectable calcium supplementation protocols.
Healthcare infrastructure development, particularly in tier-2 and tier-3 cities, increases access to critical care services where calcium gluconate plays an essential role in emergency medicine protocols. The substantial neonatal population requires specialized calcium management in expanding neonatal intensive care units nationwide.
China's calcium gluconate pharmaceutical demand is forecast to grow at a 5.4% CAGR through 2035, supported by extensive hospital construction and standardization of emergency care protocols. The country's aging population increases demand for calcium supplementation in both acute and chronic care settings, while expanding urban healthcare networks drive broader access to injectable formulations.
Government healthcare reforms emphasize emergency care capabilities, leading to increased procurement of essential pharmaceuticals including calcium gluconate across municipal and provincial hospital systems. Protocolized treatment approaches for hyperkalemia and hypocalcemia become more widespread as medical education and clinical guidelines reach smaller healthcare facilities.
The United States maintains steady calcium gluconate pharmaceutical demand growth of 4.0% CAGR, reflecting mature healthcare infrastructure and established clinical protocols. Emergency departments increasingly favor calcium gluconate over calcium chloride for hyperkalemia management due to reduced tissue irritation and broader compatibility with peripheral intravenous access, supporting consistent consumption patterns.
Stable dialysis patient populations and standardized critical care protocols maintain predictable demand patterns across hospital systems. The country's well-developed hospital pharmacy networks ensure broad availability and consistent procurement of calcium gluconate formulations for both emergency and routine clinical applications.
Brazil's calcium gluconate pharmaceutical demand is projected to expand at a 4.9% CAGR, driven by growing private hospital networks and increasing prevalence of chronic kidney disease requiring dialysis support. Urban emergency department throughput growth creates higher demand for acute care pharmaceuticals, while expanding healthcare infrastructure improves access to critical care services.
Economic development supports private healthcare expansion, leading to increased procurement of essential pharmaceuticals for emergency and critical care applications. Rising dialysis prevalence, linked to diabetes and hypertension epidemics, drives steady consumption of calcium supplementation protocols in specialized treatment centers.
Germany demonstrates moderate calcium gluconate pharmaceutical demand growth of 3.6% CAGR, reflecting its mature healthcare system and aging population demographics. Strong critical care standards ensure consistent utilization of calcium gluconate in intensive care units and emergency departments, while elderly patient populations drive demand for calcium supplementation protocols.
Healthcare cost containment measures and competitive pharmaceutical procurement practices create price pressures that moderate overall growth rates despite steady clinical demand. The country's well-established healthcare infrastructure maintains predictable consumption patterns across hospital networks and specialized care facilities.
Japan's calcium gluconate pharmaceutical demand is forecast to grow at 3.3% CAGR, supported by one of the world's most aged populations requiring calcium supplementation and critical care services. High standards of emergency and critical care medicine ensure consistent utilization of calcium gluconate in hospital settings, while demographic trends support long-term demand stability.
Mature pharmaceutical procurement systems and established clinical protocols maintain steady consumption patterns across the country's extensive hospital network. Advanced geriatric care practices and specialized treatment protocols for elderly patients support consistent demand for both acute and chronic calcium supplementation applications.
The United Kingdom projects calcium gluconate pharmaceutical demand growth of 3.5% CAGR, supported by National Health Service guidelines that embed calcium gluconate use in emergency department protocols for hyperkalemia and cardioprotection. Standardized treatment approaches across NHS facilities ensure consistent procurement and utilization patterns.
NHS formulary inclusion provides stable access to calcium gluconate across hospital networks, while clinical guidelines favor its use in emergency settings. Healthcare system efficiency measures and controlled procurement practices maintain steady but moderate growth rates aligned with demographic and clinical demand patterns.
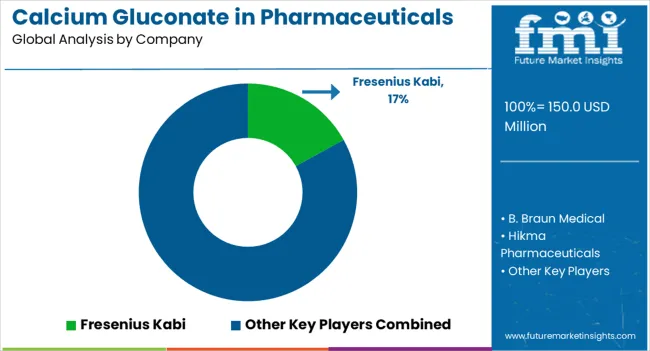
The competitive environment is characterized by a mix of established pharmaceutical manufacturers and specialized injectable product companies. Manufacturing quality standards and regulatory compliance rather than product innovation remain the decisive success factors, as calcium gluconate represents a mature pharmaceutical compound with established clinical applications.
Fresenius Kabi leads the segment with a 17% share, leveraging its global presence in hospital pharmaceuticals and injectable products. The company's extensive distribution network reaches critical care facilities worldwide, while its manufacturing capabilities ensure consistent supply of both standard and specialized calcium gluconate formulations.
Other major participants include B. Braun Medical, Hikma Pharmaceuticals, WG Critical Care, and American Regent, each maintaining significant positions in regional or therapeutic segments. These companies focus on regulatory compliance, quality manufacturing, and reliable supply chain management rather than product differentiation.
The segment also includes specialized active pharmaceutical ingredient suppliers such as Global Calcium Pvt. Ltd., Dr. Paul Lohmann, and Jungbunzlauer, which provide raw materials to finished dosage form manufacturers. Tomita Pharmaceutical contributes to API supply chains serving global pharmaceutical production networks.
Competition centers on manufacturing efficiency, regulatory approvals, and distribution capabilities rather than novel formulations, as calcium gluconate represents a well-established pharmaceutical compound with standardized therapeutic applications across diverse clinical settings.
| Attribute | Details |
|---|---|
| Study Coverage | Global demand and consumption of calcium gluconate pharmaceuticals from 2020 to 2035 |
| Base Year | 2025 |
| Historical Data | 2020 |
| Forecast Period | 2025 to 2035 |
| Units of Measurement | USD Million (sales), CAGR (growth rates) |
| Geography Covered | Global analysis with country-level focus on India, China, USA, Brazil, Germany, Japan, UK |
| By Dosage Form | Injectable, Oral Tablets, Oral Solutions/Syrups, Others (chewables, powders) |
| By Clinical Indication | Acute Hypocalcemia, Supplementation & Osteoporosis, Hyperkalemia Cardioprotection, Calcium-Channel-Blocker Overdose, Neonatal/Pediatric Hypocalcemia |
| By Distribution Channel | Hospital Pharmacies, Retail Pharmacies, Online Pharmacies |
| Metrics Provided | Sales (USD Million), CAGR (2025-2035), Share by segment |
| Competitive Landscape | Company profiles, API suppliers, regional presence |
| Forecast Drivers | Healthcare infrastructure expansion, aging populations, clinical protocol standardization |
The global Calcium Gluconate in Pharmaceuticals Demand is estimated to be valued at USD 150.0 million in 2025.
The market size for the Calcium Gluconate in Pharmaceuticals Demand is projected to reach USD 235.2 million by 2035.
The Calcium Gluconate in Pharmaceuticals Demand is expected to grow at a 4.6% CAGR between 2025 and 2035.
The key product types in Calcium Gluconate in Pharmaceuticals Demand are injectable, oral tablets, oral solutions/syrups and others (chewables, powders).
In terms of indication, acute hypocalcemia (incl. peri-operative, pancreatitis) segment to command 34.0% share in the Calcium Gluconate in Pharmaceuticals Demand in 2025.






Full Research Suite comprises of:
Market outlook & trends analysis
Interviews & case studies
Strategic recommendations
Vendor profiles & capabilities analysis
5-year forecasts
8 regions and 60+ country-level data splits
Market segment data splits
12 months of continuous data updates
DELIVERED AS:
PDF EXCEL ONLINE
Calcium Hypochlorite Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Calcium Carbonate Biocement Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Calcium Sulfate Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Calcium Chloride Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Calcium Bromide Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Calcium Hydrogen Sulphite Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Calcium Phosphate Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Calcium Diglutamate Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Calcium Carbonate Market - Trends & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Calcium Supplement Market Analysis - Size, Share & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Calcium Propionate Market Size, Growth, and Forecast for 2025 to 2035
Assessing Calcium Propionate Market Share & Industry Leaders
Calcium Lactate Market Analysis by Form, End Use Application and Region Through 2025 to 2035
Calcium Ammonium Nitrate Market Growth - Trends & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Calcium Oxide Market Growth - Trends & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Calcium D-Pantothenate Market
Calcium Acetate Market Growth – Trends & Forecast 2019-2029
Calcium Peroxide Market
Calcium Silicate Market
Calcium stearoyl-2-lactylate Market

Thank you!
You will receive an email from our Business Development Manager. Please be sure to check your SPAM/JUNK folder too.
Chat With
MaRIA