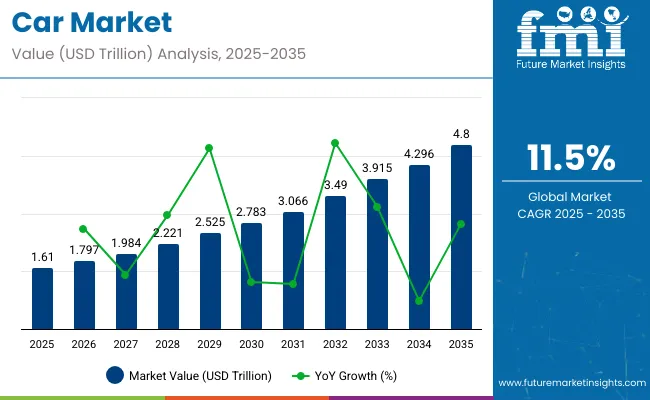
The global car market has been valued at USD 1.61 trillion in 2025 and is forecast to reach nearly USD 4.8 trillion by 2035, expanding at a CAGR of 11.5%.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Industry Size (2025E) | USD 1.61 trillion |
| Industry Value (2035F) | USD 4.8 trillion |
| CAGR (2025 to 2035) | 11.5% |
The market trajectory reflects a stable pattern of long-range accumulation, driven by rising fleet modernization, higher adoption of electric vehicle lines, and increased consumer preference for connected transport systems. Between 2025 and 2028, the rolling CAGR is estimated at 10.6%, with consistent uplift from hybrid variants across ASEAN and gradual internal combustion engine phase-out across select OECD zones. The 2028 to 2031 period indicates a rolling CAGR close to 11.4%, showing amplified contribution from AI-based driver assistance integrations.
Rolling CAGR between 2031 and 2035 trends higher at approximately 12.2%, led by rising demand for software-defined vehicle platforms, premium electric sedans, and performance utility vehicles. Price elasticity has remained stable during these transition phases, allowing inventory cycles to rebalance without margin compression.
The rolling CAGR framework confirms structural strength without reliance on sharp peaks. Manufacturers are projected to retain pricing power as digital mobility platforms widen access and usage metrics. Each sub-period exhibits consistent gains, avoiding volatility typical of single-trend reliance, which reinforces a long-term growth outlook.
The car industry has formed a substantial part of the global mobility ecosystem. Around 45% of vehicle manufacturing operations have been directed toward car assembly, reflecting its dominant share in the overall automotive production base. Roughly 55% of the light-duty transport sector has been influenced by car models, especially in commuter and personal use categories.
About 30% of emissions mitigation investments across the transport value chain have been linked to passenger cars due to evolving regulatory frameworks. In automotive sensor deployment, car models have contributed to nearly 50% of system integration across driver assistance and navigation applications. Nearly 40% of structural metals used in road vehicles have been assigned to car manufacturing for body and underframe design.
The shift toward electrified cars have reshaped product planning across global automakers, accounting for 20% of current rollouts. Hybridized platforms have been introduced in 35% of new launches, while connected services now feature in 40% of new car deliveries. Flexible ownership formats have accounted for 10% of market distribution. In-house assembly of critical subcomponents has been prioritized to stabilize procurement. Real-time analytics and digital twin frameworks have been utilized by 25% of global plants to streamline output precision.
Fuel-flexible models and city-adapted SUVs have been prioritized by OEMs to meet regional mandates. Advanced infotainment and semi-autonomous features have been introduced across mid-tier variants to maintain competitiveness. Nearly 60% of car buyers in ASEAN and MENA regions have relied on digital platforms for research and financing.
Localized production clusters have been developed in Indonesia, Morocco, and Mexico to manage costs and improve supply agility. Shifts in emission laws and powertrain innovation have directly influenced vehicle design and distribution strategies.
Over 65% of first-time car buyers in India and Southeast Asia have opted for vehicles below 1,500 cc engine capacity. Rising urban employment and two-wheeler to four-wheeler migration have supported compact hatchback and sedan sales. Monthly bookings for compact SUVs increased by 22% in Brazil between Q1 and Q2 2025. In South Africa, more than 40% of new passenger cars sold in 2024 were financed through subscription or flexible leasing models.
Dual-fuel options, including petrol-CNG and petrol-ethanol, have been introduced in low-emission zones. Automakers have released models with high ground clearance and shorter turning radii to match dense traffic and poor road quality. Regional variants featuring simplified digital dashboards, wireless mirroring, and rear sensors have dominated demand in the sub-USD 15,000 bracket. Local assembly operations have enabled delivery timelines below six weeks across selected metro zones.
Lithium carbonate prices fluctuated by over 45% in 2024, disrupting EV battery cost structures. Semiconductor lead times have averaged 38 weeks, delaying final assembly of infotainment-heavy vehicles. In Europe and Japan, energy-intensive stamping and paint shop operations saw cost increases exceeding 20% year-over-year. Manufacturers in India reported a 12-15% increase in total production costs for B-segment vehicles between 2023 and 2025.
Container shipping rates remained volatile, with key routes from East Asia to the EU rising by 18% in Q1 2025. Multiple OEMs experienced unit shortages in fleet channels, especially in hybrid and petrol-automatic trims. High reliance on a limited pool of tier-1 vendors has restricted platform scalability. In ASEAN, government-imposed localization thresholds delayed homologation of imported components, lengthening rollout timelines for new model introductions across key markets like Vietnam and Malaysia.
Electric vehicle production in China surpassed 10 million units in 2024, capturing nearly 30% of global EV output. India’s FAME-linked incentives pushed battery EV sales to over 140,000 units in the same year. Localized cell manufacturing has started in Thailand, South Korea, and Brazil, reducing import costs by up to 17%. Indonesia and South Africa have both committed to policy frameworks supporting low-cost urban EV assembly under 100 km range.
Entry-level EVs priced below USD 20,000 have gained visibility across Latin America due to duty exemptions. Software-defined vehicle architecture has been integrated into new launches to enable OTA upgrades. Battery-swapping networks have been piloted in selected Indian cities to support delivery fleets. Manufacturing units optimized for modular chassis have been commissioned in Mexico and Eastern Europe to supply neighboring trade blocks, meeting origin-specific compliance without reengineering.
In Japan and Germany, subscription-based car ownership grew by over 35% year-over-year during 2024, focused on compact and urban crossover models. Over 20,000 active car subscriptions have been recorded across Delhi, Mumbai, and Bengaluru combined, with average usage durations of 6-11 months. In the United States, more than 12% of Gen Z car buyers opted for pay-per-mile ownership via digital platforms.
OEMs have included flexible monthly plans bundled with insurance, scheduled maintenance, and roadside assistance. Electric variants now account for over 25% of active subscriptions in London and Oslo due to zero-emission zone mandates. Real-time usage data has been leveraged by fleet operators to adjust pricing models and control wear-related expenses. Contactless onboarding and digital key systems have shortened delivery and return cycles. Subscription models are being localized for college towns, gated housing societies, and tech parks.
In 2025, the car market will be led by SUVs, gasoline-powered vehicles, and franchised dealer networks. These segments account for the highest global market shares and continue to attract both consumer interest and OEM investment. Individual ownership remains the dominant end-use, although taxi, rental, and fleet models are showing marginal growth due to operational cost efficiency.
While electric propulsion is expanding, traditional gasoline platforms remain dominant. The market is being shaped by consumer preferences for performance, design flexibility, and accessible servicing, which explains the resilience of certain high-share segments across developing and developed regions alike.
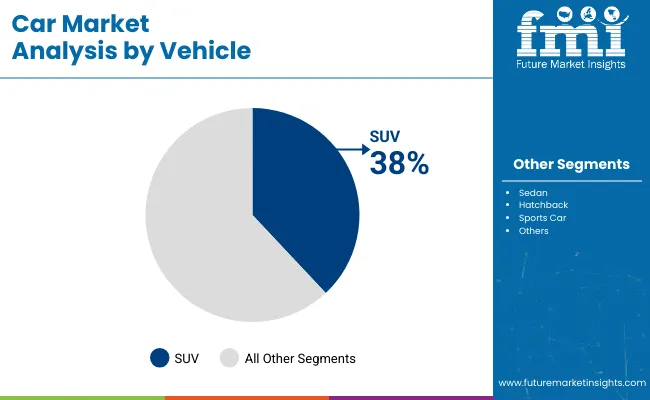
SUVs are projected to maintain dominance in the vehicle segment with a 38% market share in 2025, driven by consumer preference for larger cabin space, road visibility, and all-terrain utility. Manufacturers such as Toyota, Ford, and Hyundai have aggressively expanded their SUV offerings, including compact and crossover variants. The high seating position, safety features, and flexibility for family and recreational use support steady sales volumes. Regions such as North America, the Middle East, and Australia continue to prefer SUVs due to road infrastructure and lifestyle alignment. The segment benefits from strong resale value and consistent model refresh cycles among leading OEMs.
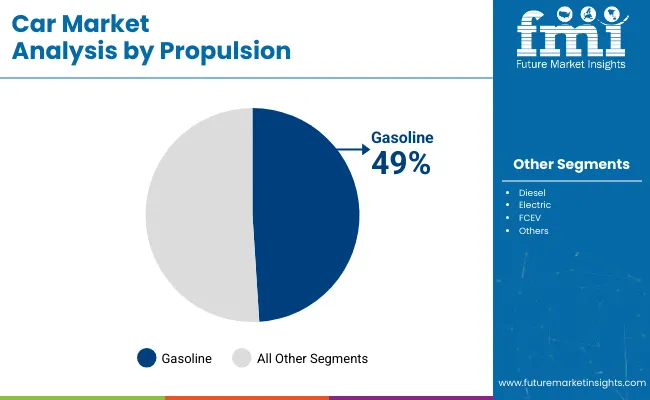
Gasoline-powered vehicles are forecasted to maintain their lead with a 49% market share in 2025, driven by broad refueling infrastructure and improved engine efficiency. Automakers such as Honda, Chevrolet, and Kia continue to launch gasoline-based models that are more compliant with emission standards without drastically increasing costs.
In markets like Southeast Asia, Africa, and South America, gasoline remains more accessible and less regulated compared to diesel and EV alternatives. The affordability of repairs and maintenance further sustains interest in gasoline cars. While electrification grows, the gasoline segment offers performance consistency, longer range, and better support in second-hand vehicle markets.
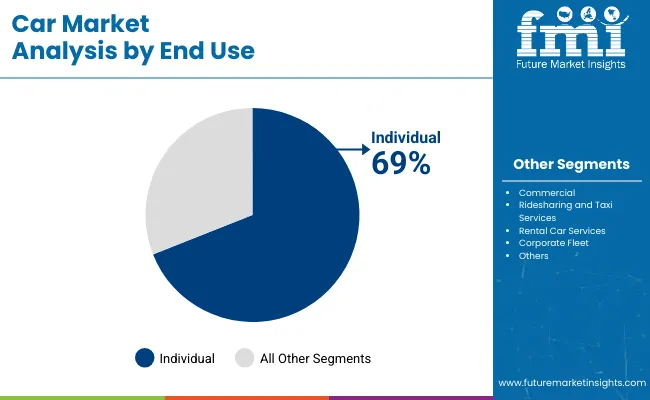
Individual car ownership remains the dominant end-use category with 69% market share in 2025, as personal vehicles offer autonomy, flexibility, and status value across socio-economic classes. Brands such as Volkswagen, Skoda, and Nissan continue to design vehicles tailored for personal daily use, including compact sedans and urban hatchbacks.
In rural and semi-urban areas of developing economies, personal car ownership is often the only viable transport option. Financing options, resale value, and personal control over maintenance schedules contribute to sustained demand. While commercial use and shared mobility are growing, their expansion remains constrained by usage limitations and regulatory concerns.
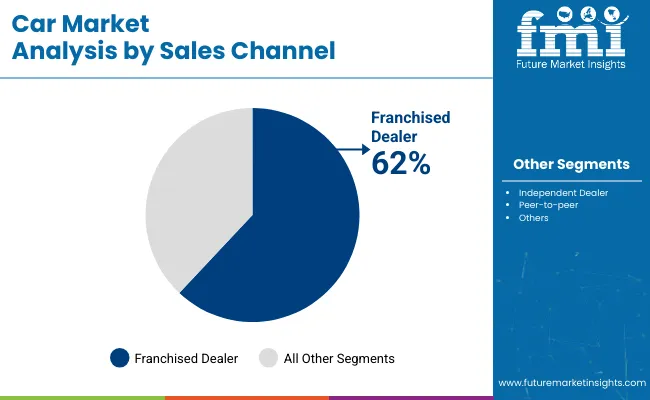
Franchised dealers are projected to account for 62% of car sales globally in 2025, maintaining their lead due to structure after-sales services, manufacturer-backed warranties, and financing assistance. OEMs including Toyota, BMW, and Chevrolet rely heavily on franchised dealer networks for launch events, customer retention, and servicing integration.
These dealerships offer consistent pricing transparency and authorized servicing, making them preferable for new buyers. Franchised dealers are especially prominent in North America, Europe, and parts of Asia where manufacturer trust and product assurance play a critical role in high-value transactions. Digital extensions of these dealers are also growing via hybrid service models.
Electric vehicles are estimated to account for 26% of the global car market by propulsion in 2025, owing to regulatory pressure, rising consumer awareness, and product diversification. Tesla, BYD, and Volkswagen have launched new models with longer range and lower charging times, driving mainstream adoption.
Subsidies and import duty exemptions are improving affordability in regions like Europe and China. Charging infrastructure in urban zones has also expanded significantly. However, challenges remain in rural areas and emerging economies where power access and battery cost still limit reach. Dedicated EV platforms are helping OEMs reduce manufacturing complexity and boost profit margins.
| Countries | CAGR (%) |
|---|---|
| Global CAGR | 11.5 |
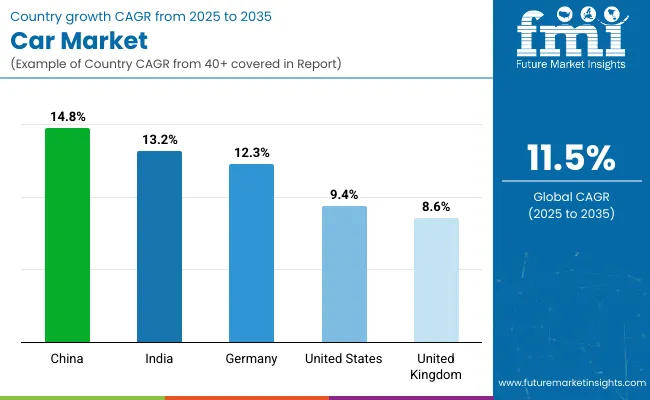
| China (BRICS) | 14.8 |
| India (BRICS) | 13.2 |
| Germany (OECD) | 12.3 |
| United States (OECD) | 9.4 |
| United Kingdom (OECD) | 8.6 |
The global car market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 11.5% between 2025 and 2035. China (BRICS) leads with a CAGR of 14.8%, outperforming the global average by 3.3%. India (BRICS) follows at 13.2%, maintaining a 1.7% advantage. Among OECD countries, Germany records 12.3%, slightly above the global rate by 0.8%. The United States is expected to grow at 9.4%, which is 2.1% below the global average, while the United Kingdom posts the lowest among the listed nations at 8.6%, trailing by 2.9%.
BRICS countries show stronger momentum due to domestic vehicle demand, assembly localization, and production-linked programs. OECD markets register slower growth as a result of maturity in ownership rates and regulatory transitions. ASEAN countries, though not shown in this table, are expected to approach or exceed double-digit growth in selected markets, supported by intra-bloc trade frameworks and rising local manufacturing investments.
China is forecast to grow at a CAGR of 14.8%, outperforming the global average by 29%. Demand is being driven by affordable EV adoption, subsidy-driven urban vehicle replacement, and export-led production. Compact electric sedans and long-range SUVs have dominated domestic registrations.
OEM strategies have focused on vertically integrated battery sourcing and embedded vehicle intelligence. Charging infrastructure has expanded beyond Tier-1 cities. Provincial compliance targets have been met using AI-integrated powertrain design and OTA update capabilities.
India is expected to register a CAGR of 13.2%, growing 15% faster than the global average. Affordability, road infrastructure upgrades, and EV penetration in urban centers have boosted new registrations. Mid-size cars and compact electric hatchbacks are leading purchases.
Production-linked incentive schemes have enabled local assembly of EVs and lithium-ion battery units. Growth in Tier-2 and Tier-3 cities is being supported by competitive financing and low maintenance costs. Battery swapping and micro-charging infrastructure are under pilot testing in several districts.
Germany is set to grow at a CAGR of 12.3%, 7% above the global mean. Premium electric vehicles, hydrogen fuel cell variants, and modular EV platforms are being prioritized. Tier-1 suppliers have deployed autonomous braking modules and driver monitoring systems.
New assembly units are focused on AI-enhanced quality control and heat-efficient battery layouts. Exports have expanded due to increased demand for smart performance vehicles in Nordic and East Asian regions. Cross-border EV collaborations with France and Italy are ongoing.
The United States is projected to record a CAGR of 9.4%, falling 18% below the global rate. Demand continues to favor SUVs and pickup trucks with higher torque specifications. Urban EV adoption has grown, but suburban and rural segments remain slow-moving.
Model upgrades have been focused on infotainment systems, battery range enhancement, and integration of safety assist features. Federal incentives have shifted focus toward zero-emission vehicles. Supply chains for critical parts remain partially reliant on imports from East Asia.
The United Kingdom is anticipated to grow at a CAGR of 8.6%, 25% below the global average. Output has been partially restored following capacity upgrades and supply chain localization. Emphasis is being placed on converting combustion-based assembly lines to EV-centric formats.
Tax credits and emission-linked benefits have encouraged electric fleet procurement. OEMs are emphasizing compact electric hatchbacks with enhanced battery safety profiles. Domestic demand has favored brands with integrated AI driving assistance.
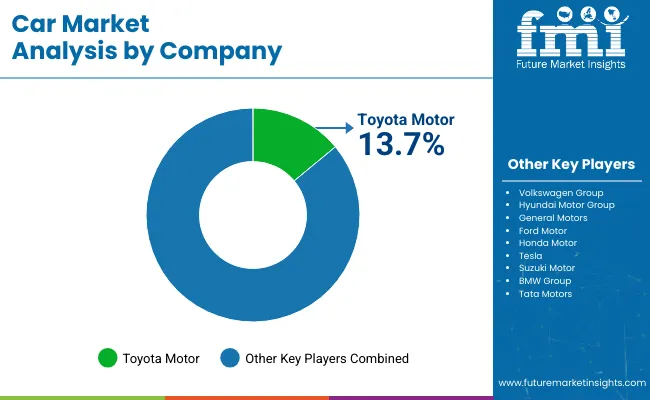
The market continues to be led by established companies such as Toyota Motor, Volkswagen, Ford Motor, and General Motors. Product portfolio expansion has been prioritized by Toyota Motor through the launch of hybrid variants across ASEAN and Latin American countries. Volkswagen has widened its sedan and crossover offerings in Europe through regional manufacturing tie-ups. Ford Motor has optimized platform sharing for cost reduction and volume flexibility in the US and Canadian markets.
General Motors has directed capital towards large SUV and pickup segments, especially within North America. BMW has concentrated on expanding electric vehicle output across Europe while maintaining leadership in the premium sedan segment. Tesla has scaled output through expanded Gigafactory operations in Germany and China. Hyundai Motor has increased its dealership footprint across Asia and the Middle East, while also streamlining exports from South Korea.
Second-tier players such as Tata Motors, Suzuki Motor, and Honda Motor have focused on value-driven segments. Tata Motors has launched compact electric cars in India to meet demand for low-cost personal transport. Suzuki Motor has expanded low-emission ICE and hybrid offerings across African and ASEAN nations. Honda Motor has diversified mid-segment vehicles for Latin America. Direct-to-consumer models, R&D into drive-cycle efficiency, and cross-platform production partnerships are now being pursued by several regional entrants.
Recent Industry News
| Report Attributes | Details |
|---|---|
| Market Size (2025) | USD 1.61 trillion |
| Projected Market Size (2035) | USD 4.8 trillion |
| CAGR (2025 to 2035) | 11.5% |
| Base Year for Estimation | 2024 |
| Historical Period | 2020 to 2024 |
| Projections Period | 2025 to 2035 |
| Quantitative Units | USD trillion for value and volume units as applicable |
| Vehicle Types Analyzed (Segment 1) | Hatchback, Sedan, SUV, Sports Car, Others |
| Propulsion Types (Segment 2) | Gasoline, Diesel, Electric, FCEV |
| End-Use Segments (Segment 3) | Commercial, Ridesharing and Taxi Services, Rental Car Services, Corporate Fleet, Individual |
| Sales Channels (Segment 4) | Peer-to-peer, Franchised Dealer, Independent Dealer |
| Regions Covered | North America; Latin America; Western Europe; Eastern Europe; Asia Pacific; Middle East and Africa |
| Countries Covered | United States, Canada, Brazil, Mexico, Germany, United Kingdom, France, Italy, China, Japan, India, UAE, South Africa |
| Key Players Influencing the Market | Toyota Motor, Volkswagen Group, Hyundai Motor Group, General Motors, Ford Motor, Honda Motor, Tesla, Suzuki Motor, BMW Group, Tata Motors |
| Additional Attributes | Dollar sales by fuel type (gasoline, diesel, hybrid, EV) and class (SUV, sedan, hatchback), demand influenced by urban mobility shifts, regional gains in Asia and Europe, innovation in ADAS and vehicle connectivity, environmental push through EV adoption, and emerging uses in car sharing, subscription models, and smart city integration. |
The global car market is expected to reach USD 4.8 trillion by 2035, growing at a CAGR of 11.5%.
Electric cars are projected to secure 26% of the global market share by 2025.
SUVs are forecasted to lead with a 38% share of the global car market in 2025.
Franchised dealers are expected to account for 62% of total global car sales in 2025.
Toyota Motor is the leading player with a 13.7% share of the global car market.






Our Research Products

The "Full Research Suite" delivers actionable market intel, deep dives on markets or technologies, so clients act faster, cut risk, and unlock growth.

The Leaderboard benchmarks and ranks top vendors, classifying them as Established Leaders, Leading Challengers, or Disruptors & Challengers.

Locates where complements amplify value and substitutes erode it, forecasting net impact by horizon

We deliver granular, decision-grade intel: market sizing, 5-year forecasts, pricing, adoption, usage, revenue, and operational KPIs—plus competitor tracking, regulation, and value chains—across 60 countries broadly.

Spot the shifts before they hit your P&L. We track inflection points, adoption curves, pricing moves, and ecosystem plays to show where demand is heading, why it is changing, and what to do next across high-growth markets and disruptive tech

Real-time reads of user behavior. We track shifting priorities, perceptions of today’s and next-gen services, and provider experience, then pace how fast tech moves from trial to adoption, blending buyer, consumer, and channel inputs with social signals (#WhySwitch, #UX).

Partner with our analyst team to build a custom report designed around your business priorities. From analysing market trends to assessing competitors or crafting bespoke datasets, we tailor insights to your needs.
Supplier Intelligence
Discovery & Profiling
Capacity & Footprint
Performance & Risk
Compliance & Governance
Commercial Readiness
Who Supplies Whom
Scorecards & Shortlists
Playbooks & Docs
Category Intelligence
Definition & Scope
Demand & Use Cases
Cost Drivers
Market Structure
Supply Chain Map
Trade & Policy
Operating Norms
Deliverables
Buyer Intelligence
Account Basics
Spend & Scope
Procurement Model
Vendor Requirements
Terms & Policies
Entry Strategy
Pain Points & Triggers
Outputs
Pricing Analysis
Benchmarks
Trends
Should-Cost
Indexation
Landed Cost
Commercial Terms
Deliverables
Brand Analysis
Positioning & Value Prop
Share & Presence
Customer Evidence
Go-to-Market
Digital & Reputation
Compliance & Trust
KPIs & Gaps
Outputs
Full Research Suite comprises of:
Market outlook & trends analysis
Interviews & case studies
Strategic recommendations
Vendor profiles & capabilities analysis
5-year forecasts
8 regions and 60+ country-level data splits
Market segment data splits
12 months of continuous data updates
DELIVERED AS:
PDF EXCEL ONLINE
Carboxymethyl Tamarind Kernel Powder Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Car Tail Light Mould Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Car OS Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Caramel Malt Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Carbon Capture and Sequestration Market Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Cardiac Rehabilitation Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Carbon Dioxide Incubators Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Carboxymethyl Tamarind Gum (CMT) Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Car Cover Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Cardiology Information System Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Cardiopulmonary Functional Testing Platform Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Carbon Enhanced Lead Acid Battery Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Car Bushing Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Carbon-negative Cement Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Card Printer Ribbon Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Carbon Tetrabromide Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Carbon Steel Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Carpet Spot Remover Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Cardiovascular CT Systems Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Carbon Brush Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035

Thank you!
You will receive an email from our Business Development Manager. Please be sure to check your SPAM/JUNK folder too.
Chat With
MaRIA