The eosinophilia therapeutics market is segmented on the basis of type and geography. Classes of important medication are corticosteroids, monoclonal antibodies (biologics), immunosuppressants and targetted small molecule therapies.
Market growth is driven by the increasing prevalence of eosinophilic disorders, hoeing awareness of precision medicine and innovative biologics targeting (IL-5, IL-4, IL-13) pathways. In addition, ongoing clinical trials of novel eosinophil-targeting therapeutic agents are pushing the field forward.
In 2025, the global eosinophilia therapeutics market is projected to reach approximately USD 464.0 million, with expectations to grow to around USD 800.2 million by 2035, reflecting a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 5.6% during the forecast period.
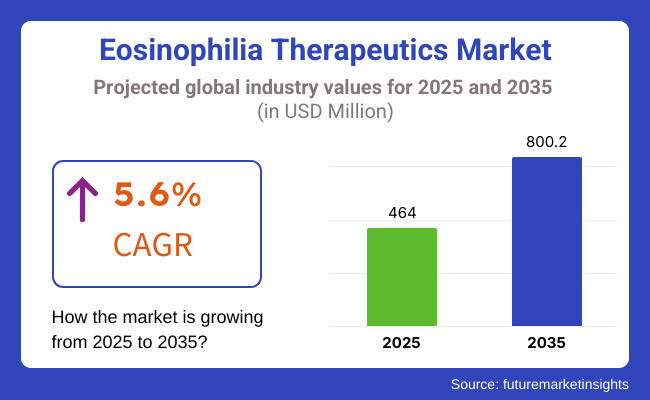
The anticipated CAGR highlights the expanding pipeline of monoclonal antibodies, increasing adoption of biologics for eosinophilic disorders, and improved diagnostic capabilities for rare eosinophilia-related conditions. High patient accessibility to specialty treatment and reimbursement support of biologic therapy also contribute to increase adoption in market.
The eosinophilia therapeutics market in North America held the largest share owing to high prevalence rates of allergic and inflammatory diseases, rapid adoption of personalized medicine and strong investment in biologic drug development.
EO disorders were one of the first diseases to be targeted with monoclonal antibody therapy (polizumab, reslizumab, benralizumab) in the USA and joint FDA approval (Canada). The growth of the market is also aided by insurance provisions as well as access to health care for specialty treatments.
With a significant share of the eosinophilic disorder market, Germany, France, and the United Kingdom hold the largest share of eosinophilic disorder clinical research and biologic drug uptake in Europe boosting its growth. This has broadened the treatment armamentarium with the availability of new eosinophil-targeted therapy recently approved by the European Medicines Agency (EMA).
The growth of the market in the region is also driven by the growing awareness pertaining to eosinophilic gastrointestinal disorders (EGIDs) and improved diagnosis guidelines.
The highest growth for eosinophilia therapeutics is anticipated to be observed in the Asia-Pacific, as the countries are leading in terms of healthcare expenditure, incidence of allergic diseases, and better access to biologic therapy particularly in China, India, Japan, and South Korea.
The diffusion of the marker into the market is being driven by the evolving pharmaceutical industry of the area, and an increase in clinical trials for eosinophilic disorders. Augment Market growth owing to rising government initiative drugs for rare disease treatment and rise in drug approvals of specialty drugs.
Challenges
Delayed Diagnosis and High Treatment Costs
The eosinophilia therapeutics market also have their own sets of challenges such as auto-immune condition leading to misdiagnosis and underreporting as they often present with non-specific symptoms. Additionally, the soaring price tags on biologic therapies - the mAbs especially, and corticosteroids, put treatment out of reach for a great many, particularly in developing markets. A lack of awareness among some primary care physicians also stymies early treatment initiation.
Opportunity
Growth in Targeted Biologic Therapies and Precision Medicine
The increasing prevalence of eosinophilia-associated disorders, including eosinophilic esophagitis (EOE), hyper eosinophilic syndrome (HES), and eosinophilic asthma, is driving demand for targeted biologic therapies.
The introduction of IL-5 inhibitors (mepolizumab, reslizumab, benralizumab) and precision medicine (treatment tailored and predicted to each patient responding) as well as artificial intelligence (AI)-based biomarker development (biomarker guided therapy) along with the rising field of gene-based therapy are bound to change the paradigms of how eosinophilia is treated. Furthermore, governmental initiatives to expand awareness and reimbursement policies will increase patient access to innovative therapies.
Between 2020 and 2024, the market experienced an increase in biologic therapy adoption for eosinophilic disorders, particularly in severe eosinophilic asthma and hyper eosinophilic syndrome. However, high costs, insurance coverage limitations, and inadequate diagnostic infrastructure restricted widespread access to novel treatments.
Between 2025 to 2035, the market will then move toward that AI-assisted tailored medicine, biomarker to guide eosinophilia therapy and next-gen biologics. The emergence of therapies with gene therapy, oral small molecules, and novel cytokine inhibitors that act on the IL-4, IL-13, and IL-33 pathways will hopefully make long-term control of disease with better patient outcomes a reality.
Near real-time eosinophilia monitoring and prevention strategies offered by digital health platforms will supplement and enhance clinical improvements in patient adherence to care.
Market Shifts: A Comparative Analysis 2020 to 2024 vs. 2025 to 2035
| Market Shift | 2020 to 2024 Trends |
|---|---|
| Regulatory Landscape | Compliance with FDA, EMA, and WHO guidelines for biologic approvals |
| Technology Innovations | Adoption of monoclonal antibodies targeting IL-5 and corticosteroid therapies |
| Market Adoption | Growth in biologic therapies for eosinophilic asthma and HES |
| Affordability & Accessibility | High cost of biologic therapies limiting widespread adoption |
| Market Competition | Dominated by biopharma leaders (GSK, AstraZeneca, Sanofi, Regeneron, Teva Pharmaceuticals) |
| Consumer Trends | Demand for effective, long-term eosinophilia management solutions |
| Market Shift | 2025 to 2035 Projections |
|---|---|
| Regulatory Landscape | Stricter regulations on personalized therapies, AI-driven diagnostics, and genetic-based treatments |
| Technology Innovations | Advancements in AI-driven biomarker discovery, gene therapy, and next-generation IL-targeting drugs |
| Market Adoption | Expansion into oral eosinophilia therapeutics, gene-based treatments, and precision medicine approaches |
| Affordability & Accessibility | Increased availability of biosimilar, cost-effective targeted therapies, and insurance-covered treatments |
| Market Competition | Rise of biotech startups and AI-powered drug discovery firms specializing in eosinophilic diseases |
| Consumer Trends | Growth in patient-centric, personalized treatments with real-time eosinophilia monitoring |
This is attributable to growing awareness about eosinophilic disorders, increasing prevalence of asthma and allergic disorders, and significant investment in biologics therapeutics. This has led to the market launch of new drugs, which is fueled by recent clinical trials, the growing incidence of eosinophilia, coupled with the power of global pharma companies- all contributing to the expansion of eosinophilia market.
An approval by the FDA of monoclonal antibody treatments such as IL-5 inhibitors continues to boost the market. The growing utilization of precision medicine and biomarker-based diagnostics in eosinophilic disorders along with rising demand for advance therapeutics are acting as major growth factors.
| Country | CAGR (2025 to 2035) |
|---|---|
| USA | 5.9% |
The UK eosinophilia therapeutics market is anticipated to witness a growth due to rising cases of eosinophilic esophagitis (EOE) and other allergic disorders. The market is primarily driven by the increasing application of biologics and corticosteroids in the treatment of eosinophilic disorders.
The growth of this market is further supported by the national health bodies (NHS) and regulatory bodies (MHRA) encouraging early diagnosis and treatment of eosinophilic disorders. In addition to that the development of the biotechnology pharmaceutical alliances also should promote remedies development in the arena.
| Country | CAGR (2025 to 2035) |
|---|---|
| UK | 5.4% |
Increasing investments for the research of immunology and respiratory diseases is driving the growth of the European Union (EU) Eosinophilia Therapeutics market. Higher prevalence of allergic and inflammatory diseases in the region is accelerating the demand for targeted eosinophilia treatments.
Germany, France, and Italy are individually important markets with significantly high uptake of biologics and corticosteroids for eosinophilic disorders Moreover, the European Medicines Agency (EMA) is actively promoting the approval of new therapies, thereby driving the growth of the market.
Furthermore, The EU’s focus on precision medicine and early diagnosis initiatives is also contributing significantly to the eosinophilia therapeutics market.
| Country | CAGR (2025 to 2035) |
|---|---|
| EU | 5.3% |
Japan eosinophilia therapeutics market is increasing due to a rise in incidence of eosinophilic asthma and gastrointestinal disorders. The country's advanced healthcare system and robust regulatory framework are driving the adoption of targeted biologic therapies in the country.
The market is further driven by an upsurge in investment linked with immunotherapy and monoclonal antibody treatments. Additionally, since Japan is focused towards personalized medicine and biomarker based therapies, this will lead to the wider adoption of eosinophilia therapeutics during the forecast period.
| Country | CAGR (2025 to 2035) |
|---|---|
| Japan | 5.6% |
Eosinophilia therapeutics market in South Korea - market landscape, covering metrics such as market size, revenue, and key growth indicators, as well as current innovations catered to patients with eosinophilia in South Korea. Immunology-based drug development is being invested in by strong pharmaceutical and biotechnology sectors the country has.
Market demand is propelled by rising prevalence of asthma and allergic disorders, along with government efforts to facilitate access to target specific therapies. The rising utilization of telemedicine and artificial intelligence-based diagnostic options to manage eosinophilia ultimately will dictate future market trends, as well.
| Country | CAGR (2025 to 2035) |
|---|---|
| South Korea | 5.5% |
Corticosteroids are classified among the most important agents we have in the management of eosinophilic conditions, as they are the first line treatment for eosinophil-associated inflammatory and allergic diseases. These drugs help modify immune responses, reduce eosinophilic specific subtypes and alleviate clinical expressions of eosinophil related disorders.
Eosins are one of the key drivers of adoption as they are broad-spectrum, treating not just asthma, but also eosinophilic esophagitis (EOE) and hyper eosinophilic syndromes (HES) as well. Corticosteroids (both oral, inhaled, and topical)-prednisone, budesonide, and fluticasone-are often used to suppress airway, GI, and dermatologic eosinophilic disease manifestations.
Corticosteroid may be used on a short-term basis to quickly suppress eosinophil-mediated inflammation for symptomatic relief. In low-resource settings, in which novel biologics and targeted therapies may not be as readily available, they remain an important option terape for therapy.
Corticosteroid long-term distribution finds a problem due to steroid resistance and side effects in many programs (weight gain, osteoporosis, and hypertension) and adrenal suppression, making it less effective. Consequently, researchers and pharmaceutical companies are working toward low-dose corticosteroid regimens, inhaled formulations and other combination therapies that minimize dependence upon systemic steroids to reduce these risks.
As the lack of effective treatment became clearer, immunosuppressants offered an important treatment choice for patients with eosinophilic diseases unresponsive to steroids, quelling immune responses that controlled excess eosinophil activation. Methotrexate, azathioprine and cyclosporine are given by physicians to reduce eosinophils in chronic inflammation and tissue damage.
Initiation of immunosuppressants is more common in the chronic-eosinophilia due to connective tissue disease associated eosinophilia and other eosinophilic syndromes in settings of recurrent relapses, autoimmune eosinophilic syndromes, and also corticosteroid-dependent patients. These drugs decrease tissue infiltration by eosinophils, as well as fibrosis, organ dysfunction and disease progression.
Immunosuppressants, for example, can be used with biologics or corticosteroids as combination therapy to optimize treatment output and minimize adverse effects of related steroids. The increased interest toward the study of precision immunotherapy in eosinophilic disorders is associated with the push for the development of new-generation immunosuppressant agents that specifically target eosinophilic signalling pathways and critically, with less toxicity.
When eosinophils in the peripheral blood are elevated above the normal limit by allergy, parasite infection, autoimmune diseases or drug hypersensitivity reaction, is defined as blood eosinophilia. Underlying Conditions Eosinophilia is frequently identified incidentally on routine blood tests and can be subdivided into mild, moderate, or severe eosinophilia.
Market drivers include increasing incidence of allergic asthma, atopic dermatitis and food allergies acts as strong market drivers for eosinophilia-targeted therapy market; primary treatment options available in the market include monoclonal antibodies and corticosteroids. The majority of patients with eosinophilic asthma have elevated blood eosinophils, which makes them ideal candidates for biologic therapies that significantly deplete eosinophils.
Furthermore, parasitic infection-induced blood eosinophilia remains a serious problem seen in tropical and developing countries. Albenzadole and ivermectin (and often an antiinflammatory agent) are commonly employed in syndromes of eosinophilia due to parasites.
Numerous chronic inflammatory disorders with episodic blood eosinophilia can be very difficult to manage long-term given that most are treatable. Biomarker-based treatment algorithms and reporting of and treatment according to personalized medicine have been investigated for individualized treatment of patients with specific eosinophilic disease phenotypes.
In addition, blood eosinophilia secondary to parasitic infections remains an essential concern in tropical and developing regions. Anti-inflammatory medications, in association with treatment against the parasite itself (albendazole and ivermectin) are generally used under the term parasite-induced eosinophilia syndromes.
Although treatable, chronic inflammatory processes leading to recurrent blood eosinophilia may become challenging to control over time. Further biomarker-driven treatment algorithms and personalized medicine-based studies are under investigation to select potentially more effective targeted therapies based on the eosinophilic disease subtype.
Eosinophilia can be restricted to a single organ (organotopic eosinophilia), resulting in persistent localised eosinophilic inflammation, fibrosis and organ malfunction. It is usually observed in eosinophilic esophagitis (EOE) and eosinophilic gastroenteritis and eosinophilic myocarditis which has a tissue damage as a clinical manifestation.
Localized therapy (topical corticosteroids [budesonide, fluticasone], proton pump inhibitors [PPIs], and newer biologics) is in demand for eosinophilic gastrointestinal disorders (EGIDs) with suspected high prevalence. The improvements are mediated by reduced eosinophilic infiltration; restoration of structure and integrity of the damaged tissue; and relief of associated symptoms such as dysphagia, abdominal pain, and intestinal dysfunction.
Moreover, disease-specific tissue eosinophilia in airway diseases, for example in eosinophilic chronic rhino sinusitis (ECRS) and eosinophilic pneumonitis, has to be addressed by more targeted anti-inflammatory therapy. New evolving therapies that offer more systematic control, improved remission rates, include guided nasal sprays, inhaled corticosteroids, IL-5 targeted.
Although tissue eosinophilia management has made headlines as a solution to these problems, limitations such as ascertainment delay, lack of animal model to find sensible biomarkers or lead therapeutic compounds, and acute eosinophilia circumstance treatment remain. New diagnostic innovation and precision therapeutics will make the difference for access with better patient outcomes.
The eosinophilia therapeutics market is witnessing steady growth due to the increasing prevalence of eosinophilic disorders, including eosinophilic esophagitis (EOE), eosinophilic asthma, hyper eosinophilic syndrome (HES), and eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis (EGPA). The demand for targeted biologics, corticosteroids, and immunosuppressants is rising as more patients require long-term treatment solutions.
The monoclonal antibody market (most successful biologic of this type of biologics) is an innovative space where novel mAb therapies & personalized medicine are being explored to develop additional target specific therapies as the regulatory approvals for novel biologics continue to rule the market.
Market Share Analysis by Key Players
| Company/Organization Name | Estimated Market Share (%) |
|---|---|
| GlaxoSmithKline plc | 18-22% |
| AstraZeneca plc | 14-18% |
| Sanofi S.A. | 12-16% |
| Teva Pharmaceuticals | 10-14% |
| Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | 8-12% |
| Others | 26-32% |
| Company/Organization Name | Key Offerings/Activities |
|---|---|
| GlaxoSmithKline plc | Develops Nucala (Mepolizumab), a biologic therapy for eosinophilic asthma, HES, and EGPA. |
| AstraZeneca plc | Offers Fasenra (Benralizumab), an IL-5 receptor-targeting monoclonal antibody for eosinophilic asthma. |
| Sanofi S.A. | Provides Dupixent (Dupilumab), an IL-4/IL-13 inhibitor for eosinophilic esophagitis and type 2 inflammation. |
| Teva Pharmaceuticals | Manufactures Cinqair (Reslizumab), a biologic therapy targeting IL-5 for severe eosinophilic asthma. |
| Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Specializes in targeted immunotherapy solutions, including pipeline drugs for eosinophilic disorders. |
Key Market Insights
GlaxoSmithKline plc (18-22%)
GSK leads the eosinophilia therapeutics market with Nucala (Mepolizumab), a first-in-class IL-5 inhibitor approved for eosinophilic asthma, EGPA, and hyper eosinophilic syndrome (HES). The company continues to expand its biologic treatment portfolio.
AstraZeneca plc (14-18%)
AstraZeneca’s Fasenra (Benralizumab) is one of the market leaders for IL-5 receptor monoclonal antibodies for severe eosinophilic asthma. The study is one of several trials the company is investigating for eosinophilic-driven indications.
Sanofi S.A. (12-16%)
Dupixent (Dupilumab) by Sanofi, and its partner Regeneron, is an IL-4/IL-13 inhibitor and agent has been approved for FDA eosinophilic esophagitis (EOE), and in clinical development for other eosinophilic diseases.
Teva Pharmaceuticals (10-14%)
Teva's Cinqair (Reslizumab) is a monoclonal antibody targeting IL-5, widely used for severe eosinophilic asthma. The company is expanding its biologic respiratory portfolio.
Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc. (8-12%)
Regeneron is working with Sanofi to create biologics targeted at eosinophilic conditions, with an emphasis on next-generation immune therapy solutions.
Other Key Players (26-32% Combined)
Several emerging and regional players are developing innovative eosinophilia treatments, including:
The overall market size for eosinophilia therapeutics market was USD 464.0 million in 2025.
The eosinophilia therapeutics market is expected to reach USD 800.2 million in 2035.
Increasing prevalence of eosinophilic disorders, rising advancements in targeted biologics, and growing awareness of early diagnosis and treatment will fuel market expansion.
The top 5 countries which drives the development of eosinophilia therapeutics market are USA, European Union, Japan, South Korea and UK.
Tissue eosinophilia command significant share over the assessment period.
Table 1: Global Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Region, 2018 to 2033
Table 2: Global Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Drug Class, 2018 to 2033
Table 3: Global Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Type, 2018 to 2033
Table 4: Global Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Route of Administration , 2018 to 2033
Table 5: Global Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Distribution Channel, 2018 to 2033
Table 6: North America Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Country, 2018 to 2033
Table 7: North America Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Drug Class, 2018 to 2033
Table 8: North America Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Type, 2018 to 2033
Table 9: North America Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Route of Administration , 2018 to 2033
Table 10: North America Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Distribution Channel, 2018 to 2033
Table 11: Latin America Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Country, 2018 to 2033
Table 12: Latin America Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Drug Class, 2018 to 2033
Table 13: Latin America Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Type, 2018 to 2033
Table 14: Latin America Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Route of Administration , 2018 to 2033
Table 15: Latin America Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Distribution Channel, 2018 to 2033
Table 16: Europe Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Country, 2018 to 2033
Table 17: Europe Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Drug Class, 2018 to 2033
Table 18: Europe Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Type, 2018 to 2033
Table 19: Europe Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Route of Administration , 2018 to 2033
Table 20: Europe Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Distribution Channel, 2018 to 2033
Table 21: South Asia Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Country, 2018 to 2033
Table 22: South Asia Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Drug Class, 2018 to 2033
Table 23: South Asia Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Type, 2018 to 2033
Table 24: South Asia Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Route of Administration , 2018 to 2033
Table 25: South Asia Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Distribution Channel, 2018 to 2033
Table 26: East Asia Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Country, 2018 to 2033
Table 27: East Asia Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Drug Class, 2018 to 2033
Table 28: East Asia Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Type, 2018 to 2033
Table 29: East Asia Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Route of Administration , 2018 to 2033
Table 30: East Asia Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Distribution Channel, 2018 to 2033
Table 31: Oceania Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Country, 2018 to 2033
Table 32: Oceania Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Drug Class, 2018 to 2033
Table 33: Oceania Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Type, 2018 to 2033
Table 34: Oceania Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Route of Administration , 2018 to 2033
Table 35: Oceania Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Distribution Channel, 2018 to 2033
Table 36: MEA Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Country, 2018 to 2033
Table 37: MEA Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Drug Class, 2018 to 2033
Table 38: MEA Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Type, 2018 to 2033
Table 39: MEA Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Route of Administration , 2018 to 2033
Table 40: MEA Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Distribution Channel, 2018 to 2033
Figure 1: Global Market Value (US$ Million) by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 2: Global Market Value (US$ Million) by Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 3: Global Market Value (US$ Million) by Route of Administration , 2023 to 2033
Figure 4: Global Market Value (US$ Million) by Distribution Channel, 2023 to 2033
Figure 5: Global Market Value (US$ Million) by Region, 2023 to 2033
Figure 6: Global Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Region, 2018 to 2033
Figure 7: Global Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Region, 2023 to 2033
Figure 8: Global Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Region, 2023 to 2033
Figure 9: Global Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Drug Class, 2018 to 2033
Figure 10: Global Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 11: Global Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 12: Global Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Type, 2018 to 2033
Figure 13: Global Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 14: Global Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 15: Global Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Route of Administration , 2018 to 2033
Figure 16: Global Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Route of Administration , 2023 to 2033
Figure 17: Global Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Route of Administration , 2023 to 2033
Figure 18: Global Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Distribution Channel, 2018 to 2033
Figure 19: Global Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Distribution Channel, 2023 to 2033
Figure 20: Global Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Distribution Channel, 2023 to 2033
Figure 21: Global Market Attractiveness by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 22: Global Market Attractiveness by Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 23: Global Market Attractiveness by Route of Administration , 2023 to 2033
Figure 24: Global Market Attractiveness by Distribution Channel, 2023 to 2033
Figure 25: Global Market Attractiveness by Region, 2023 to 2033
Figure 26: North America Market Value (US$ Million) by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 27: North America Market Value (US$ Million) by Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 28: North America Market Value (US$ Million) by Route of Administration , 2023 to 2033
Figure 29: North America Market Value (US$ Million) by Distribution Channel, 2023 to 2033
Figure 30: North America Market Value (US$ Million) by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 31: North America Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Country, 2018 to 2033
Figure 32: North America Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 33: North America Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 34: North America Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Drug Class, 2018 to 2033
Figure 35: North America Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 36: North America Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 37: North America Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Type, 2018 to 2033
Figure 38: North America Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 39: North America Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 40: North America Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Route of Administration , 2018 to 2033
Figure 41: North America Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Route of Administration , 2023 to 2033
Figure 42: North America Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Route of Administration , 2023 to 2033
Figure 43: North America Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Distribution Channel, 2018 to 2033
Figure 44: North America Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Distribution Channel, 2023 to 2033
Figure 45: North America Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Distribution Channel, 2023 to 2033
Figure 46: North America Market Attractiveness by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 47: North America Market Attractiveness by Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 48: North America Market Attractiveness by Route of Administration , 2023 to 2033
Figure 49: North America Market Attractiveness by Distribution Channel, 2023 to 2033
Figure 50: North America Market Attractiveness by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 51: Latin America Market Value (US$ Million) by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 52: Latin America Market Value (US$ Million) by Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 53: Latin America Market Value (US$ Million) by Route of Administration , 2023 to 2033
Figure 54: Latin America Market Value (US$ Million) by Distribution Channel, 2023 to 2033
Figure 55: Latin America Market Value (US$ Million) by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 56: Latin America Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Country, 2018 to 2033
Figure 57: Latin America Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 58: Latin America Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 59: Latin America Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Drug Class, 2018 to 2033
Figure 60: Latin America Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 61: Latin America Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 62: Latin America Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Type, 2018 to 2033
Figure 63: Latin America Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 64: Latin America Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 65: Latin America Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Route of Administration , 2018 to 2033
Figure 66: Latin America Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Route of Administration , 2023 to 2033
Figure 67: Latin America Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Route of Administration , 2023 to 2033
Figure 68: Latin America Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Distribution Channel, 2018 to 2033
Figure 69: Latin America Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Distribution Channel, 2023 to 2033
Figure 70: Latin America Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Distribution Channel, 2023 to 2033
Figure 71: Latin America Market Attractiveness by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 72: Latin America Market Attractiveness by Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 73: Latin America Market Attractiveness by Route of Administration , 2023 to 2033
Figure 74: Latin America Market Attractiveness by Distribution Channel, 2023 to 2033
Figure 75: Latin America Market Attractiveness by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 76: Europe Market Value (US$ Million) by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 77: Europe Market Value (US$ Million) by Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 78: Europe Market Value (US$ Million) by Route of Administration , 2023 to 2033
Figure 79: Europe Market Value (US$ Million) by Distribution Channel, 2023 to 2033
Figure 80: Europe Market Value (US$ Million) by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 81: Europe Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Country, 2018 to 2033
Figure 82: Europe Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 83: Europe Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 84: Europe Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Drug Class, 2018 to 2033
Figure 85: Europe Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 86: Europe Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 87: Europe Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Type, 2018 to 2033
Figure 88: Europe Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 89: Europe Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 90: Europe Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Route of Administration , 2018 to 2033
Figure 91: Europe Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Route of Administration , 2023 to 2033
Figure 92: Europe Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Route of Administration , 2023 to 2033
Figure 93: Europe Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Distribution Channel, 2018 to 2033
Figure 94: Europe Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Distribution Channel, 2023 to 2033
Figure 95: Europe Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Distribution Channel, 2023 to 2033
Figure 96: Europe Market Attractiveness by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 97: Europe Market Attractiveness by Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 98: Europe Market Attractiveness by Route of Administration , 2023 to 2033
Figure 99: Europe Market Attractiveness by Distribution Channel, 2023 to 2033
Figure 100: Europe Market Attractiveness by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 101: South Asia Market Value (US$ Million) by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 102: South Asia Market Value (US$ Million) by Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 103: South Asia Market Value (US$ Million) by Route of Administration , 2023 to 2033
Figure 104: South Asia Market Value (US$ Million) by Distribution Channel, 2023 to 2033
Figure 105: South Asia Market Value (US$ Million) by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 106: South Asia Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Country, 2018 to 2033
Figure 107: South Asia Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 108: South Asia Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 109: South Asia Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Drug Class, 2018 to 2033
Figure 110: South Asia Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 111: South Asia Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 112: South Asia Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Type, 2018 to 2033
Figure 113: South Asia Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 114: South Asia Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 115: South Asia Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Route of Administration , 2018 to 2033
Figure 116: South Asia Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Route of Administration , 2023 to 2033
Figure 117: South Asia Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Route of Administration , 2023 to 2033
Figure 118: South Asia Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Distribution Channel, 2018 to 2033
Figure 119: South Asia Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Distribution Channel, 2023 to 2033
Figure 120: South Asia Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Distribution Channel, 2023 to 2033
Figure 121: South Asia Market Attractiveness by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 122: South Asia Market Attractiveness by Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 123: South Asia Market Attractiveness by Route of Administration , 2023 to 2033
Figure 124: South Asia Market Attractiveness by Distribution Channel, 2023 to 2033
Figure 125: South Asia Market Attractiveness by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 126: East Asia Market Value (US$ Million) by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 127: East Asia Market Value (US$ Million) by Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 128: East Asia Market Value (US$ Million) by Route of Administration , 2023 to 2033
Figure 129: East Asia Market Value (US$ Million) by Distribution Channel, 2023 to 2033
Figure 130: East Asia Market Value (US$ Million) by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 131: East Asia Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Country, 2018 to 2033
Figure 132: East Asia Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 133: East Asia Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 134: East Asia Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Drug Class, 2018 to 2033
Figure 135: East Asia Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 136: East Asia Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 137: East Asia Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Type, 2018 to 2033
Figure 138: East Asia Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 139: East Asia Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 140: East Asia Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Route of Administration , 2018 to 2033
Figure 141: East Asia Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Route of Administration , 2023 to 2033
Figure 142: East Asia Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Route of Administration , 2023 to 2033
Figure 143: East Asia Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Distribution Channel, 2018 to 2033
Figure 144: East Asia Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Distribution Channel, 2023 to 2033
Figure 145: East Asia Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Distribution Channel, 2023 to 2033
Figure 146: East Asia Market Attractiveness by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 147: East Asia Market Attractiveness by Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 148: East Asia Market Attractiveness by Route of Administration , 2023 to 2033
Figure 149: East Asia Market Attractiveness by Distribution Channel, 2023 to 2033
Figure 150: East Asia Market Attractiveness by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 151: Oceania Market Value (US$ Million) by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 152: Oceania Market Value (US$ Million) by Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 153: Oceania Market Value (US$ Million) by Route of Administration , 2023 to 2033
Figure 154: Oceania Market Value (US$ Million) by Distribution Channel, 2023 to 2033
Figure 155: Oceania Market Value (US$ Million) by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 156: Oceania Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Country, 2018 to 2033
Figure 157: Oceania Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 158: Oceania Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 159: Oceania Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Drug Class, 2018 to 2033
Figure 160: Oceania Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 161: Oceania Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 162: Oceania Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Type, 2018 to 2033
Figure 163: Oceania Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 164: Oceania Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 165: Oceania Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Route of Administration , 2018 to 2033
Figure 166: Oceania Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Route of Administration , 2023 to 2033
Figure 167: Oceania Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Route of Administration , 2023 to 2033
Figure 168: Oceania Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Distribution Channel, 2018 to 2033
Figure 169: Oceania Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Distribution Channel, 2023 to 2033
Figure 170: Oceania Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Distribution Channel, 2023 to 2033
Figure 171: Oceania Market Attractiveness by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 172: Oceania Market Attractiveness by Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 173: Oceania Market Attractiveness by Route of Administration , 2023 to 2033
Figure 174: Oceania Market Attractiveness by Distribution Channel, 2023 to 2033
Figure 175: Oceania Market Attractiveness by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 176: MEA Market Value (US$ Million) by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 177: MEA Market Value (US$ Million) by Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 178: MEA Market Value (US$ Million) by Route of Administration , 2023 to 2033
Figure 179: MEA Market Value (US$ Million) by Distribution Channel, 2023 to 2033
Figure 180: MEA Market Value (US$ Million) by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 181: MEA Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Country, 2018 to 2033
Figure 182: MEA Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 183: MEA Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 184: MEA Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Drug Class, 2018 to 2033
Figure 185: MEA Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 186: MEA Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 187: MEA Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Type, 2018 to 2033
Figure 188: MEA Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 189: MEA Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 190: MEA Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Route of Administration , 2018 to 2033
Figure 191: MEA Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Route of Administration , 2023 to 2033
Figure 192: MEA Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Route of Administration , 2023 to 2033
Figure 193: MEA Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Distribution Channel, 2018 to 2033
Figure 194: MEA Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Distribution Channel, 2023 to 2033
Figure 195: MEA Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Distribution Channel, 2023 to 2033
Figure 196: MEA Market Attractiveness by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 197: MEA Market Attractiveness by Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 198: MEA Market Attractiveness by Route of Administration , 2023 to 2033
Figure 199: MEA Market Attractiveness by Distribution Channel, 2023 to 2033
Figure 200: MEA Market Attractiveness by Country, 2023 to 2033






Full Research Suite comprises of:
Market outlook & trends analysis
Interviews & case studies
Strategic recommendations
Vendor profiles & capabilities analysis
5-year forecasts
8 regions and 60+ country-level data splits
Market segment data splits
12 months of continuous data updates
DELIVERED AS:
PDF EXCEL ONLINE
Biotherapeutics Virus Removal Filters Market Trends – Growth & Forecast 2025 to 2035
COPD Therapeutics Market Report – Growth, Demand & Industry Forecast 2023-2033
Digital Therapeutics and Wellness Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Digital Therapeutics Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Peptide Therapeutics Market Analysis - Growth & Forecast 2024 to 2034
Advanced Therapeutics Pharmaceutical Outsourcing Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Glaucoma Therapeutics Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Leukemia Therapeutics Treatment Market Analysis - Growth & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Microbiome Therapeutics Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
The Canine Flu Therapeutics Market is segmented by product, and end user from 2025 to 2035
Stuttering Therapeutics Market Trends, Analysis & Forecast by Treatment, Type, End-Use and Region through 2035
Pet Cancer Therapeutics Market Insights - Growth & Forecast 2024 to 2034
Candidiasis Therapeutics Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Lung Cancer Therapeutics Market Analysis – Size, Share, and Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Heart Block Therapeutics Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Aquaculture Therapeutics Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Fucosidosis Therapeutics Market - Growth & Innovations 2025 to 2035
Market Leaders & Share in Alzheimer’s Therapeutics
Alzheimer’s Therapeutics Market Analysis by Disease Class into Cholinesterase Inhibitors, NMDA Receptor Antagonists and Combinations Through 2035.
Sarcoidosis Therapeutics Market

Thank you!
You will receive an email from our Business Development Manager. Please be sure to check your SPAM/JUNK folder too.
Chat With
MaRIA