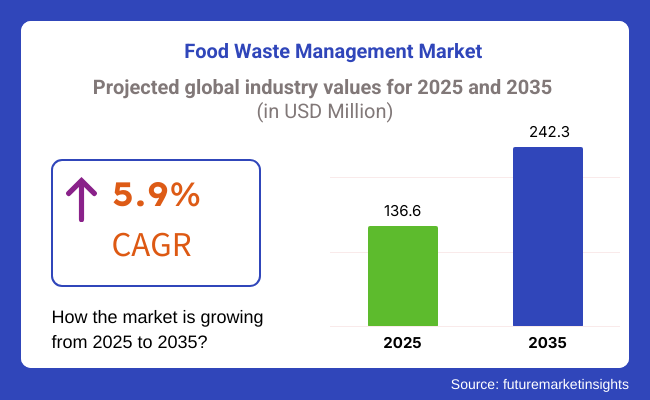
The global food waste management market is projected to grow from USD 136.6 million in 2025 to about USD 242.3 million by 2035 at a 5.9% CAGR. Growth is being propelled by three reinforcing shifts.
Regulation is tightening first. The EU’s Farm-to-Fork strategy, nine USA states, and South Korea now impose progressive landfill bans or organic-diversion quotas, compelling retailers and food-service chains to contract specialised processors. Future Market Insights notes that organics already represent the fastest-growing waste stream, outpacing plastics and paper by two percentage points annually.
A 2024 Journal of Cleaner Production review found avoided-food-loss initiatives can curb scope-3 emissions more cost-effectively than any packaging swap, driving CPG adoption of surplus-capture programmes. Circular economy technology is maturing. Aerobic digesters that produce soil enhancers, and anaerobic co-digestion systems that yield renewable natural gas (RNG), now reach breakeven in under five years, according to ReFED’s 2025 USA Food-Waste Forecast.
North America leads by value thanks to corporate net-zero pledges and methane-fee provisions in the USA Inflation Reduction Act, which subsidises RNG projects at landfills and wastewater plants. Europe benefits from extended-producer-responsibility levies that make “zero-waste to landfill” contracts financially attractive, spurring city-level kerbside organics schemes.
Asia Pacific will record the fastest unit growth as India formalises its 2026 Food Loss Reduction Roadmap and China scales wet-market separation pilots in 36 mega-cities. Optical sorters now achieve 96 percent purity on mixed bakery streams; enzyme cocktails accelerate in-vessel composting by 40 percent; and blockchain certificates verify source-segregated loads for compost buyers. Start-ups such as Winnow, Leanpath, and Orbisk deploy AI-vision bins that quantify cafeteria leftovers in real time, helping hospitality groups cut plate waste by up to 50 percent.
Executive sentiment mirrors the opportunity. Commenting on WM’s USD 3 billion renewable-energy build-out, CEO Jim Fish said in January 2025, “Our organics strategy turns what was once a liability into low-carbon fuel for fleets and grids-proof that food waste is a resource when managed correctly.” as mentioned in Wall Street Journal.
His outlook underscores a sector pivoting from disposal to resource recovery. With policy pressure, carbon economics, and technology converging, food-waste management is set for durable, innovation-led growth through 2035.
The table below presents a comparative assessment of the variation in CAGR over six months for the base year (2025) and the current year (2025) for the global food waste management industry. This analysis highlights crucial performance shifts and revenue realization patterns, providing stakeholders with a clearer outlook on industry growth trends.
| Particular | Value CAGR |
|---|---|
| H1 (2024 to 2034) | 5.6% |
| H2 (2024 to 2034) | 5.9% |
| H1 (2025 to 2035) | 5.7% |
| H2 (2025 to 2035) | 6.0% |
The first half of the year (H1) spans from January to June, while the second half (H2) covers July to December. In the first half (H1) of the decade from 2025 to 2035, the industry is projected to expand at a CAGR of 5.6%, followed by a slightly higher growth rate of 5.9% in the second half (H2).
Moving into the subsequent period, from H1 2025 to H2 2035, the CAGR is anticipated to rise to 6.1% in the first half, while the second half (H2) is expected to sustain a strong growth rate of 5.9%. During H1, the sector experienced an increase of 10 BPS, whereas in H2, the business witnessed a slight increase of 10 BPS.
The recycling segment is projected to dominate the food waste management market, accounting for approximately 35% market share by 2025. This dominance is driven by escalating regulatory pressures, corporate sustainability goals, and growing public awareness around environmental protection.
Companies increasingly prioritize recycling over landfilling to mitigate ecological impact and align with government-imposed waste reduction initiatives. Sophisticated recycling technologies, including anaerobic digestion, composting, and bioconversion, effectively transform food waste into valuable by-products such as biofuels, fertilizers, and compost.
Leading corporations such as Nestlé and Unilever actively employ waste-to-energy methods, converting unsold food into renewable energy, thereby significantly contributing to circular economy efforts. Government support through subsidies and tax incentives further accelerates adoption of recycling programs, compelling manufacturers and retailers to reduce their reliance on landfills, a method responsible for substantial global methane emissions.
Enhanced operational efficiency achieved through AI-driven waste tracking systems, such as Winnow and Leanpath, further strengthens the segment by enabling real-time waste reduction at source. Overall, growing regulatory actions, economic incentives, technological advancements, and consumer demand for sustainability firmly position recycling as the primary growth driver within food waste management.
The food processing waste segment is expected to capture a considerable share of approximately 28% by 2025, primarily due to large-scale waste generation across bakery, dairy, seafood, and meat industries. The inherent nature of food processing, involving rejected ingredients, spoilage, and by-products, necessitates effective waste management solutions.
Emerging valorisation technologies, such as enzyme extraction, fermentation, and bioconversion, increasingly transform food processing waste into valuable nutritional ingredients or protein-rich animal feed. Companies like Cargill and Danone actively invest in upcycling dairy by-products into high-value proteins and nutritional additives.
Nestlé’s strategic partnership with Veolia exemplifies industry collaboration to develop innovative valorisation processes that substantially reduce environmental footprints. Regulatory frameworks such as the FDA’s Food Recovery Hierarchy and the EU's Farm to Fork Strategy further promote sustainable management, driving companies to prioritize waste prevention, recycling, and upcycling over traditional disposal methods.
Additionally, substantial investment by companies like ADM and Bühler in processing agri-produce waste-transforming grains, fruits, and vegetable by-products into plant proteins, antioxidants, and dietary fibers-reinforces the segment’s prominence. These combined factors underscore the food processing waste segment’s critical role in the global shift towards sustainable, circular economy practices in food waste management.
During 2020 to 2024, the industry for food waste management increased steadily due to augmenting food production and consumption, thus increasing the level of waste. Governments and institutions emphasized minimizing food waste through legislation, enhanced segregation of waste, and recycling practices.
AI and big data were utilized to monitor waste patterns, maximize food processing, and minimize spoilage. Companies embraced anaerobic digestion, composting, and waste-to-energy technology to reduce landfill contribution and create renewable energy. Yet, with the high costs of operations, inefficient waste collection infrastructure, and insufficient public education, industry development was hindered.
With IoT and edge AI for real-time monitoring of food production and consumption, automated reduction methods will be enabled. Blockchain-integrated supply chains will enhance traceability and accountability, reducing food loss.
Quantum computing will enhance the efficiency of waste processing, while biodegradable and recyclable packaging will keep the environment to a minimum. AI-powered waste-to-energy technologies will achieve maximum energy recovery from organic waste.
Governments will implement tougher zero-waste regulations, nudging industries toward circular economy activities. Automation and decentralized processing will optimize waste collection and recycling, making food waste management cheaper and more sustainable. Artificial intelligence-based platforms will enable real-time waste tracking and minimization, propelling a more sustainable food system.
A Comparative Market Shift Analysis 2020 to 2024 vs. 2025 to 2035
| 2020 to 2024 | 2025 to 2035 |
|---|---|
| Government-initiated food waste reduction strategies and recycling incentives | Compliance tracking and zero-waste enforcement by AI using blockchain |
| Big data and AI to track waste and develop reduction strategies | Real-time edge AI and IoT for autonomous waste reduction |
| Anaerobic digestion, composting, and waste-to-energy solutions | AI-optimized, quantum-driven waste processing for optimal efficiency |
| Challenges in tracking waste through supply chains | Blockchain-based, transparent waste tracking and accountability |
| Emphasis on lowering landfill contributions and boosting recycling | Circular economy-focused zero-waste approaches using biodegradable substances |
| AI-grounded knowledge for waste management processes optimization | Autonomous, smart waste management systems |
| Exorbitant operation cost and erratic waste collection infrastructure | Decentralized waste collection and recycling with AI-driven infrastructure |
Food waste management industry is a risk where many people are participating in, including regulatory, operational, and financial difficulties. The specific government regulations concerning waste disposal, landfill bans, and carbon emissions are incredibly risky for companies because of compliance requirements.
Should the companies fail to abide by these regulations, they risk incurring heavy fines, facing legal actions, or being forced to shut down operations.One more issue of high concern is high operational expenditures.
Entrenching waste processing technologies, such as anaerobic digestion, composting, and waste-to-energy conversion demands vast amounts of capital investment, including not only the initial price but the ongoing maintenance as well. Such companies as the small ones may face difficulties in terms of cost, advancement, and financial resources required for implementing the solutions of waste management.
Another risk that is equal to the is the inefficiency within the supply chain. The industry is solely dependent on the durable waste pickup, transport, and processing infrastructure. If the logistics do not work due to some labour shortages, fluctuations of fuel prices, or inefficient sorting techniques it will cause waste overflow, dependency on landfills, and consequently, it will cost them more to operate.
Consumer behaviour and awareness also matter considerably. The number of businesses and households that adopt zero-waste techniques is continuously increasing yet, they still do not sort and recycle the waste properly, which leads to contamination of the waste and the processing due to inefficiencies. For the companies to motivate their customers to make the right decisions when it comes to waste disposal, they need to spend money on education and incentives.
| Country | CAGR (2025 to 2035) |
|---|---|
| The USA | 6.6% |
| China | 7.8% |
| The UK | 6.1% |
| Japan | 5.1% |
| India | 5.9% |
The USA holds significant share with USD 28.15 billion in 2025 and a 6.6% CAGR from 2025 to 2035. Sustainability awareness of the environment and effective regulatory policies drive growth. The USA generates an estimated 63 million tons of food waste per annum in the commercial, institutional, and household sectors.
About 32% of these waste materials get recycled as recycling schemes and animal feeds. Funding waste management using intelligent technologies such as anaerobic digestion facilities and commercial compost facilities enhances effectiveness in waste avoidance.
Food-service premises and retail biggies utilize out-of-the-box approaches such as waste-tracking methods with the aid of artificial intelligence and donation-of-surplus-food schemes minimizing waste at sources. All such disparate efforts altogether largely contribute towards growth.
Growth Factors in the USA
| Key Drivers | Details |
|---|---|
| Government Policies | Demanding policies ensure food wastage reduction via recycling and composting in states. |
| Technology Advances | Waste tracking using A.I. technology, anaerobic digestion, and composting works best. |
| Retail & Consumer Actions | Dining restaurants and supermarkets enforce surplus food donation and smart inventory management. |
| Circular Economy Trends | Biz transforms food wastage into biofuel and eco-friendly packaging companies. |
China's industry is expanding at a very rapid rate and will reach a value of USD 20.12 billion in the year 2025, with a growth rate of 7.8% CAGR for the time period of 2035. Industrialization and urbanization are also leading to excessive production and consumption of food, thereby causing wastage.
Chinese government enforces stringent waste segregation programs and policies like "Clean Your Plate," controlling excess consumption from consumers. Advanced waste treatment technologies, like gasification and anaerobic digestion, convert organic waste to energy in sync with sustainability goals.
Smart waste bins and artificial intelligence-driven waste sorters make it more efficient. Increased collaboration between municipalities and private firms accelerates infrastructure construction with sustainable waste management technologies.
Growth Factors in China
| Key Drivers | Details |
|---|---|
| National Policies | "Clean Your Plate" and food wastage segregation rules reduce overconsumption. |
| Waste-to-Energy Conversion | Anaerobic digestion and gasification transform food wastage into energy products. |
| Smart Waste Infrastructure | Artificial Intelligence-based intelligent bins and sorting stations increase the efficiency of waste disposal. |
| Urbanization Impact | Growing food consumption and disposable income result in the need for efficient waste disposal. |
The UK industry is likely to be USD 7.0 billion in 2025, growing at a CAGR of 6.1% during 2025 to 2035. The government has tough policies like landfill taxes and business-to-business waste reporting, encouraging companies to be eco-friendly.
Companies use smart waste monitoring systems that optimize collection and disposal and reduce wasteful landfill input. Excess food redistribution generates new partnerships between charities, food banks, and retailers to reroute surplus food to hungry recipients instead of landfills. New technologies for recycling food waste, like enzymatic breakdown, offer new prospects for recycling organic waste. Enhanced consumer consciousness promotes better consumption habits, which in turn encourages additional strategies for waste reduction.
Growth Factors in the UK
| Key Drivers | Details |
|---|---|
| Regulatory Framework | Landfill tax and mandatory reporting of waste place greater waste minimization obligations. |
| Surplus Redistribution | Food bank-retailer partnerships ensure food availability to vulnerable individuals. |
| Smart Waste Technology | Artificial intelligence monitoring systems enhance waste collection and minimize landfill waste. |
| Recycling Advancements | Enzymatic decomposition of food waste enhances the recycling of organic wastes. |
Industry in Japan is growing at a CAGR of 5.1% for the 2025 to 2035 period, is supported by its advanced technological master plan and strong government policies. The government guarantees the recycling of waste through the Food Recycling Law, which requires businesses to recycle trash efficiently. Greater application of bioconversion processes converts food waste to animal feed and fertilizers.
Japan's cities are densely populated and require compact waste treatment technology, such as city-scale fermentation plants. IoT in waste management enhances efficiency because it records data in real-time regarding the generation of waste and collection routes. The increased application of precision agriculture also reduces the wastage of food at the production level.
Growth Factors in Japan
| Key Drivers | Details |
|---|---|
| Regulatory Recycling Legislation | Food Recycling Law compels firms to treat and recycle food waste. |
| Bioconversion Technologies | The conversion of food waste into animal feed and fertilizer decreases landfill waste. |
| Space-Saving Waste Solutions | Small urban fermentation plants overcome the issue of high population density. |
| IoT Integration | Real-time monitoring of the waste stream optimizes collection and recycling efficiency. |
Indian food waste management industry is likely to grow at 5.9% CAGR from 2025 to 2035 due to rapid population growth and urbanization. India generates over 68 million tons of food waste annually with the help of ineffective chains of storage and distribution.
To promote waste segregation and management, the government has rolled out programs such as the Swachh Bharat Abhiyan. Cold chain logistic innovation reduces post-harvest losses, and decentralization of composting promotes grassroots organic recycling. Niche startups employ blockchain technology to develop transparent supply chains and minimize food wastage. Greater use of food-sharing platforms also dissuades restaurants and parties from wasting surplus food.
Growth Factors in India
| Key Drivers | Details |
|---|---|
| Government Policies | Swachh Bharat Abhiyan and other policies promote waste management solutions. |
| Cold Chain Technologies | Intelligent storage and logistics reduce food wastage after harvesting. |
| Decentralized Composting | Composting programs enhance the organic recycling of waste at the community level. |
| Technology-Based Solutions | Transparency in the supply chain via blockchain technology reduces food wastage. |
The industry is currently booming due to growing environmental concerns that are being manifested in government regulations as well as sustainability initiatives to minimize food loss and optimize resource use. The increased implementation of organic recycling, composting, anaerobic digestion, and waste-to-energy methods has been witnessed in international industries such as food manufacturing, retail, hospitality, and households.
Veolia, Waste Management Inc., SUEZ, Republic Services, and Clean Harbors are top players in that industry scope with an overall waste collection, processing, and recycling solution. Startup entrepreneurs have AI-enabled waste tracking, blockchain-enabled traceability, and on-site food waste processing applications in competition with traditional solutions because they could differentiate their offerings.
The transformation of the industry will largely depend on innovations in technology, such as automated waste separation, improved bioconversion, and smart composting solutions. Similarly, on a very small scale, initiatives devoted to a circular economy create partnerships between waste managers and food producers or retailers to reduce waste at every point in the supply chain.
Strategic factors shaping the competition include compliance with the regulatory frameworks accompanying global sustainability goals, advances in waste valorization techniques, and rising consumer demand for zero-waste and closed-loop food production models.
In this dynamic industry, organizations will gain a competitive edge when data-driven waste analytics, scalable waste diversion strategies, and green processing technologies are integrated into their waste management plans.
Market Share Analysis by Company
| Company Name | Estimated Market Share (%) |
|---|---|
| Veolia Environnement | 18-22% |
| Waste Management, Inc. | 15-18% |
| SUEZ Group | 12-16% |
| Republic Services, Inc. | 10-14% |
| Clean Harbors, Inc. | 8-12% |
| Other Players | 30-40% |
| Company Name | Key Offerings & Market Focus |
|---|---|
| Veolia Environnement | Specializes in integrated waste management, waste-to-energy solutions, and circular economy initiatives. |
| Waste Management, Inc. | Focuses on advanced landfill management, organic waste recycling, and anaerobic digestion technology. |
| SUEZ Group | Offers biogas production from food waste, AI-driven waste tracking, and sustainable waste valorization. |
| Republic Services, Inc. | Strong in municipal solid waste (MSW) processing, composting, and industrial waste recycling. |
| Clean Harbors, Inc. | Expertise in hazardous and non-hazardous waste disposal, with a focus on regulatory compliance. |
Key Company Insights
Veolia Environment (18-22%)
It is a global leader in sustainable waste management solutions, which includes practices of circular economy and innovative recycling technologies.
Waste Management, Inc. (15-18%)
It has a strong market presence in landfill diversion, organics recycling, and waste-to-energy programs.
SUEZ Group (12-16%)
The company specializes in smart waste tracking and biogas generation, concentrating on waste valorization and reducing climate impact.
Republic Services, Inc. (10-14%)
The company places a big emphasis on commercial and industrial food waste solutions and invests in renewable energy projects.
Clean Harbors, Inc. (8-12%)
This company specializes in processing both hazardous and non-hazardous waste according to regulations, assuring safe and sustainable disposal.
Other Key Players (30-40% Combined)
| Report Attributes | Details |
|---|---|
| Current Total Market Size (2025) | USD 136.6 Million |
| Projected Market Size (2035) | USD 242.3 Million |
| CAGR (2025 to 2035) | 5.9% |
| Base Year for Estimation | 2024 |
| Historical Period | 2020 to 2024 |
| Projections Period | 2025 to 2035 |
| Quantitative Units | Revenue in USD Million |
| By Service | Recycling (35%), Composting, Landfilling, Anaerobic Digestion |
| By Waste Type | Food Processing Waste (28%), Agricultural Waste, Retail Waste, Household Waste |
| By End Use | Food Manufacturers, Retailers, Hospitality, Municipalities, Households |
| Regions Covered | North America, Latin America, Western Europe, Eastern Europe, East Asia, South Asia & Pacific, Middle East & Africa |
| Countries Covered | USA, China, UK, Japan, India |
| Key Players influencing the Food Waste Management Market | Veolia Environnement, Waste Management Inc., SUEZ Group, Republic Services Inc., Clean Harbors Inc., GFL Environmental Inc., Covanta Holding Corporation, Biffa PLC, Remondis SE & Co. KG |
| Additional Attributes | Semi-annual update, AI-driven infrastructure trends, circular economy developments |
| Customization and Pricing | Available upon Request |
The market is segmented into prevention, collection, transfer, recycling, and landfill, with recycling gaining traction due to rising sustainability initiatives and waste repurposing efforts.
The industry covers food production waste, agri produce waste, poultry, meat, and seafood waste, food processing waste, agri produce processing waste, dairy food processing waste, and other food waste sources.
The market is divided into animal feed, fertilizer, renewable energy & biofuels, and others, with increasing focus on converting food waste into alternative energy sources.
The global market is segmented into North America, Latin America, Western Europe, Eastern Europe, South Asia & Pacific, East Asia, Central Asia, Balkan and Baltic Countries, Russia and Belarus, and The Middle East & Africa.
The global industry is projected to grow at a CAGR of 5.9% during the forecast period from 2025 to 2035.
By 2035, the global industry is expected to reach a significant valuation, driven by increasing regulatory measures and sustainability initiatives.
Recycling is anticipated to be the fastest-growing segment, as businesses and municipalities increasingly adopt sustainable waste processing technologies to reduce landfill dependency.
Key factors include stringent government regulations on waste disposal, rising consumer awareness, increasing food production waste, advancements in waste-to-energy technology, and the adoption of AI-based waste monitoring systems.
Top companies in the market include Veolia Environment, Waste Management Inc., SUEZ Group, Republic Services Inc., GFL Environmental Inc., and Covanta Holding Corporation.
Table 1: Global Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Region, 2017 to 2033
Table 2: Global Market Volume (Tonnes) Forecast by Region, 2017 to 2033
Table 3: Global Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Service, 2017 to 2033
Table 4: Global Market Volume (Tonnes) Forecast by Service, 2017 to 2033
Table 5: Global Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Waste Type, 2017 to 2033
Table 6: Global Market Volume (Tonnes) Forecast by Waste Type, 2017 to 2033
Table 7: Global Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by End-use, 2017 to 2033
Table 8: Global Market Volume (Tonnes) Forecast by End-use, 2017 to 2033
Table 9: North America Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Country, 2017 to 2033
Table 10: North America Market Volume (Tonnes) Forecast by Country, 2017 to 2033
Table 11: North America Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Service, 2017 to 2033
Table 12: North America Market Volume (Tonnes) Forecast by Service, 2017 to 2033
Table 13: North America Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Waste Type, 2017 to 2033
Table 14: North America Market Volume (Tonnes) Forecast by Waste Type, 2017 to 2033
Table 15: North America Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by End-use, 2017 to 2033
Table 16: North America Market Volume (Tonnes) Forecast by End-use, 2017 to 2033
Table 17: Latin America Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Country, 2017 to 2033
Table 18: Latin America Market Volume (Tonnes) Forecast by Country, 2017 to 2033
Table 19: Latin America Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Service, 2017 to 2033
Table 20: Latin America Market Volume (Tonnes) Forecast by Service, 2017 to 2033
Table 21: Latin America Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Waste Type, 2017 to 2033
Table 22: Latin America Market Volume (Tonnes) Forecast by Waste Type, 2017 to 2033
Table 23: Latin America Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by End-use, 2017 to 2033
Table 24: Latin America Market Volume (Tonnes) Forecast by End-use, 2017 to 2033
Table 25: Western Europe Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Country, 2017 to 2033
Table 26: Western Europe Market Volume (Tonnes) Forecast by Country, 2017 to 2033
Table 27: Western Europe Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Service, 2017 to 2033
Table 28: Western Europe Market Volume (Tonnes) Forecast by Service, 2017 to 2033
Table 29: Western Europe Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Waste Type, 2017 to 2033
Table 30: Western Europe Market Volume (Tonnes) Forecast by Waste Type, 2017 to 2033
Table 31: Western Europe Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by End-use, 2017 to 2033
Table 32: Western Europe Market Volume (Tonnes) Forecast by End-use, 2017 to 2033
Table 33: Eastern Europe Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Country, 2017 to 2033
Table 34: Eastern Europe Market Volume (Tonnes) Forecast by Country, 2017 to 2033
Table 35: Eastern Europe Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Service, 2017 to 2033
Table 36: Eastern Europe Market Volume (Tonnes) Forecast by Service, 2017 to 2033
Table 37: Eastern Europe Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Waste Type, 2017 to 2033
Table 38: Eastern Europe Market Volume (Tonnes) Forecast by Waste Type, 2017 to 2033
Table 39: Eastern Europe Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by End-use, 2017 to 2033
Table 40: Eastern Europe Market Volume (Tonnes) Forecast by End-use, 2017 to 2033
Table 41: Asia Pacific excluding Japan Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Country, 2017 to 2033
Table 42: Asia Pacific excluding Japan Market Volume (Tonnes) Forecast by Country, 2017 to 2033
Table 43: Asia Pacific excluding Japan Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Service, 2017 to 2033
Table 44: Asia Pacific excluding Japan Market Volume (Tonnes) Forecast by Service, 2017 to 2033
Table 45: Asia Pacific excluding Japan Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Waste Type, 2017 to 2033
Table 46: Asia Pacific excluding Japan Market Volume (Tonnes) Forecast by Waste Type, 2017 to 2033
Table 47: Asia Pacific excluding Japan Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by End-use, 2017 to 2033
Table 48: Asia Pacific excluding Japan Market Volume (Tonnes) Forecast by End-use, 2017 to 2033
Table 49: Japan Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Country, 2017 to 2033
Table 50: Japan Market Volume (Tonnes) Forecast by Country, 2017 to 2033
Table 51: Japan Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Service, 2017 to 2033
Table 52: Japan Market Volume (Tonnes) Forecast by Service, 2017 to 2033
Table 53: Japan Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Waste Type, 2017 to 2033
Table 54: Japan Market Volume (Tonnes) Forecast by Waste Type, 2017 to 2033
Table 55: Japan Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by End-use, 2017 to 2033
Table 56: Japan Market Volume (Tonnes) Forecast by End-use, 2017 to 2033
Table 57: MIDDLE EAST AND AFRICA Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Country, 2017 to 2033
Table 58: MIDDLE EAST AND AFRICA Market Volume (Tonnes) Forecast by Country, 2017 to 2033
Table 59: MIDDLE EAST AND AFRICA Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Service, 2017 to 2033
Table 60: MIDDLE EAST AND AFRICA Market Volume (Tonnes) Forecast by Service, 2017 to 2033
Table 61: MIDDLE EAST AND AFRICA Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Waste Type, 2017 to 2033
Table 62: MIDDLE EAST AND AFRICA Market Volume (Tonnes) Forecast by Waste Type, 2017 to 2033
Table 63: MIDDLE EAST AND AFRICA Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by End-use, 2017 to 2033
Table 64: MIDDLE EAST AND AFRICA Market Volume (Tonnes) Forecast by End-use, 2017 to 2033
Figure 1: Global Market Value (US$ Million) by Service, 2023 to 2033
Figure 2: Global Market Value (US$ Million) by Waste Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 3: Global Market Value (US$ Million) by End-use, 2023 to 2033
Figure 4: Global Market Value (US$ Million) by Region, 2023 to 2033
Figure 5: Global Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Region, 2017 to 2033
Figure 6: Global Market Volume (Tonnes) Analysis by Region, 2017 to 2033
Figure 7: Global Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Region, 2023 to 2033
Figure 8: Global Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Region, 2023 to 2033
Figure 9: Global Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Service, 2017 to 2033
Figure 10: Global Market Volume (Tonnes) Analysis by Service, 2017 to 2033
Figure 11: Global Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Service, 2023 to 2033
Figure 12: Global Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Service, 2023 to 2033
Figure 13: Global Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Waste Type, 2017 to 2033
Figure 14: Global Market Volume (Tonnes) Analysis by Waste Type, 2017 to 2033
Figure 15: Global Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Waste Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 16: Global Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Waste Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 17: Global Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by End-use, 2017 to 2033
Figure 18: Global Market Volume (Tonnes) Analysis by End-use, 2017 to 2033
Figure 19: Global Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by End-use, 2023 to 2033
Figure 20: Global Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by End-use, 2023 to 2033
Figure 21: Global Market Attractiveness by Service, 2023 to 2033
Figure 22: Global Market Attractiveness by Waste Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 23: Global Market Attractiveness by End-use, 2023 to 2033
Figure 24: Global Market Attractiveness by Region, 2023 to 2033
Figure 25: North America Market Value (US$ Million) by Service, 2023 to 2033
Figure 26: North America Market Value (US$ Million) by Waste Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 27: North America Market Value (US$ Million) by End-use, 2023 to 2033
Figure 28: North America Market Value (US$ Million) by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 29: North America Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Country, 2017 to 2033
Figure 30: North America Market Volume (Tonnes) Analysis by Country, 2017 to 2033
Figure 31: North America Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 32: North America Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 33: North America Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Service, 2017 to 2033
Figure 34: North America Market Volume (Tonnes) Analysis by Service, 2017 to 2033
Figure 35: North America Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Service, 2023 to 2033
Figure 36: North America Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Service, 2023 to 2033
Figure 37: North America Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Waste Type, 2017 to 2033
Figure 38: North America Market Volume (Tonnes) Analysis by Waste Type, 2017 to 2033
Figure 39: North America Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Waste Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 40: North America Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Waste Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 41: North America Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by End-use, 2017 to 2033
Figure 42: North America Market Volume (Tonnes) Analysis by End-use, 2017 to 2033
Figure 43: North America Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by End-use, 2023 to 2033
Figure 44: North America Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by End-use, 2023 to 2033
Figure 45: North America Market Attractiveness by Service, 2023 to 2033
Figure 46: North America Market Attractiveness by Waste Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 47: North America Market Attractiveness by End-use, 2023 to 2033
Figure 48: North America Market Attractiveness by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 49: Latin America Market Value (US$ Million) by Service, 2023 to 2033
Figure 50: Latin America Market Value (US$ Million) by Waste Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 51: Latin America Market Value (US$ Million) by End-use, 2023 to 2033
Figure 52: Latin America Market Value (US$ Million) by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 53: Latin America Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Country, 2017 to 2033
Figure 54: Latin America Market Volume (Tonnes) Analysis by Country, 2017 to 2033
Figure 55: Latin America Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 56: Latin America Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 57: Latin America Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Service, 2017 to 2033
Figure 58: Latin America Market Volume (Tonnes) Analysis by Service, 2017 to 2033
Figure 59: Latin America Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Service, 2023 to 2033
Figure 60: Latin America Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Service, 2023 to 2033
Figure 61: Latin America Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Waste Type, 2017 to 2033
Figure 62: Latin America Market Volume (Tonnes) Analysis by Waste Type, 2017 to 2033
Figure 63: Latin America Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Waste Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 64: Latin America Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Waste Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 65: Latin America Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by End-use, 2017 to 2033
Figure 66: Latin America Market Volume (Tonnes) Analysis by End-use, 2017 to 2033
Figure 67: Latin America Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by End-use, 2023 to 2033
Figure 68: Latin America Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by End-use, 2023 to 2033
Figure 69: Latin America Market Attractiveness by Service, 2023 to 2033
Figure 70: Latin America Market Attractiveness by Waste Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 71: Latin America Market Attractiveness by End-use, 2023 to 2033
Figure 72: Latin America Market Attractiveness by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 73: Western Europe Market Value (US$ Million) by Service, 2023 to 2033
Figure 74: Western Europe Market Value (US$ Million) by Waste Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 75: Western Europe Market Value (US$ Million) by End-use, 2023 to 2033
Figure 76: Western Europe Market Value (US$ Million) by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 77: Western Europe Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Country, 2017 to 2033
Figure 78: Western Europe Market Volume (Tonnes) Analysis by Country, 2017 to 2033
Figure 79: Western Europe Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 80: Western Europe Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 81: Western Europe Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Service, 2017 to 2033
Figure 82: Western Europe Market Volume (Tonnes) Analysis by Service, 2017 to 2033
Figure 83: Western Europe Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Service, 2023 to 2033
Figure 84: Western Europe Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Service, 2023 to 2033
Figure 85: Western Europe Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Waste Type, 2017 to 2033
Figure 86: Western Europe Market Volume (Tonnes) Analysis by Waste Type, 2017 to 2033
Figure 87: Western Europe Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Waste Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 88: Western Europe Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Waste Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 89: Western Europe Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by End-use, 2017 to 2033
Figure 90: Western Europe Market Volume (Tonnes) Analysis by End-use, 2017 to 2033
Figure 91: Western Europe Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by End-use, 2023 to 2033
Figure 92: Western Europe Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by End-use, 2023 to 2033
Figure 93: Western Europe Market Attractiveness by Service, 2023 to 2033
Figure 94: Western Europe Market Attractiveness by Waste Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 95: Western Europe Market Attractiveness by End-use, 2023 to 2033
Figure 96: Western Europe Market Attractiveness by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 97: Eastern Europe Market Value (US$ Million) by Service, 2023 to 2033
Figure 98: Eastern Europe Market Value (US$ Million) by Waste Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 99: Eastern Europe Market Value (US$ Million) by End-use, 2023 to 2033
Figure 100: Eastern Europe Market Value (US$ Million) by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 101: Eastern Europe Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Country, 2017 to 2033
Figure 102: Eastern Europe Market Volume (Tonnes) Analysis by Country, 2017 to 2033
Figure 103: Eastern Europe Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 104: Eastern Europe Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 105: Eastern Europe Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Service, 2017 to 2033
Figure 106: Eastern Europe Market Volume (Tonnes) Analysis by Service, 2017 to 2033
Figure 107: Eastern Europe Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Service, 2023 to 2033
Figure 108: Eastern Europe Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Service, 2023 to 2033
Figure 109: Eastern Europe Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Waste Type, 2017 to 2033
Figure 110: Eastern Europe Market Volume (Tonnes) Analysis by Waste Type, 2017 to 2033
Figure 111: Eastern Europe Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Waste Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 112: Eastern Europe Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Waste Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 113: Eastern Europe Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by End-use, 2017 to 2033
Figure 114: Eastern Europe Market Volume (Tonnes) Analysis by End-use, 2017 to 2033
Figure 115: Eastern Europe Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by End-use, 2023 to 2033
Figure 116: Eastern Europe Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by End-use, 2023 to 2033
Figure 117: Eastern Europe Market Attractiveness by Service, 2023 to 2033
Figure 118: Eastern Europe Market Attractiveness by Waste Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 119: Eastern Europe Market Attractiveness by End-use, 2023 to 2033
Figure 120: Eastern Europe Market Attractiveness by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 121: Asia Pacific excluding Japan Market Value (US$ Million) by Service, 2023 to 2033
Figure 122: Asia Pacific excluding Japan Market Value (US$ Million) by Waste Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 123: Asia Pacific excluding Japan Market Value (US$ Million) by End-use, 2023 to 2033
Figure 124: Asia Pacific excluding Japan Market Value (US$ Million) by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 125: Asia Pacific excluding Japan Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Country, 2017 to 2033
Figure 126: Asia Pacific excluding Japan Market Volume (Tonnes) Analysis by Country, 2017 to 2033
Figure 127: Asia Pacific excluding Japan Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 128: Asia Pacific excluding Japan Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 129: Asia Pacific excluding Japan Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Service, 2017 to 2033
Figure 130: Asia Pacific excluding Japan Market Volume (Tonnes) Analysis by Service, 2017 to 2033
Figure 131: Asia Pacific excluding Japan Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Service, 2023 to 2033
Figure 132: Asia Pacific excluding Japan Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Service, 2023 to 2033
Figure 133: Asia Pacific excluding Japan Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Waste Type, 2017 to 2033
Figure 134: Asia Pacific excluding Japan Market Volume (Tonnes) Analysis by Waste Type, 2017 to 2033
Figure 135: Asia Pacific excluding Japan Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Waste Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 136: Asia Pacific excluding Japan Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Waste Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 137: Asia Pacific excluding Japan Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by End-use, 2017 to 2033
Figure 138: Asia Pacific excluding Japan Market Volume (Tonnes) Analysis by End-use, 2017 to 2033
Figure 139: Asia Pacific excluding Japan Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by End-use, 2023 to 2033
Figure 140: Asia Pacific excluding Japan Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by End-use, 2023 to 2033
Figure 141: Asia Pacific excluding Japan Market Attractiveness by Service, 2023 to 2033
Figure 142: Asia Pacific excluding Japan Market Attractiveness by Waste Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 143: Asia Pacific excluding Japan Market Attractiveness by End-use, 2023 to 2033
Figure 144: Asia Pacific excluding Japan Market Attractiveness by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 145: Japan Market Value (US$ Million) by Service, 2023 to 2033
Figure 146: Japan Market Value (US$ Million) by Waste Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 147: Japan Market Value (US$ Million) by End-use, 2023 to 2033
Figure 148: Japan Market Value (US$ Million) by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 149: Japan Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Country, 2017 to 2033
Figure 150: Japan Market Volume (Tonnes) Analysis by Country, 2017 to 2033
Figure 151: Japan Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 152: Japan Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 153: Japan Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Service, 2017 to 2033
Figure 154: Japan Market Volume (Tonnes) Analysis by Service, 2017 to 2033
Figure 155: Japan Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Service, 2023 to 2033
Figure 156: Japan Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Service, 2023 to 2033
Figure 157: Japan Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Waste Type, 2017 to 2033
Figure 158: Japan Market Volume (Tonnes) Analysis by Waste Type, 2017 to 2033
Figure 159: Japan Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Waste Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 160: Japan Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Waste Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 161: Japan Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by End-use, 2017 to 2033
Figure 162: Japan Market Volume (Tonnes) Analysis by End-use, 2017 to 2033
Figure 163: Japan Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by End-use, 2023 to 2033
Figure 164: Japan Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by End-use, 2023 to 2033
Figure 165: Japan Market Attractiveness by Service, 2023 to 2033
Figure 166: Japan Market Attractiveness by Waste Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 167: Japan Market Attractiveness by End-use, 2023 to 2033
Figure 168: Japan Market Attractiveness by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 169: MIDDLE EAST AND AFRICA Market Value (US$ Million) by Service, 2023 to 2033
Figure 170: MIDDLE EAST AND AFRICA Market Value (US$ Million) by Waste Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 171: MIDDLE EAST AND AFRICA Market Value (US$ Million) by End-use, 2023 to 2033
Figure 172: MIDDLE EAST AND AFRICA Market Value (US$ Million) by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 173: MIDDLE EAST AND AFRICA Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Country, 2017 to 2033
Figure 174: MIDDLE EAST AND AFRICA Market Volume (Tonnes) Analysis by Country, 2017 to 2033
Figure 175: MIDDLE EAST AND AFRICA Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 176: MIDDLE EAST AND AFRICA Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 177: MIDDLE EAST AND AFRICA Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Service, 2017 to 2033
Figure 178: MIDDLE EAST AND AFRICA Market Volume (Tonnes) Analysis by Service, 2017 to 2033
Figure 179: MIDDLE EAST AND AFRICA Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Service, 2023 to 2033
Figure 180: MIDDLE EAST AND AFRICA Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Service, 2023 to 2033
Figure 181: MIDDLE EAST AND AFRICA Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Waste Type, 2017 to 2033
Figure 182: MIDDLE EAST AND AFRICA Market Volume (Tonnes) Analysis by Waste Type, 2017 to 2033
Figure 183: MIDDLE EAST AND AFRICA Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Waste Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 184: MIDDLE EAST AND AFRICA Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Waste Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 185: MIDDLE EAST AND AFRICA Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by End-use, 2017 to 2033
Figure 186: MIDDLE EAST AND AFRICA Market Volume (Tonnes) Analysis by End-use, 2017 to 2033
Figure 187: MIDDLE EAST AND AFRICA Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by End-use, 2023 to 2033
Figure 188: MIDDLE EAST AND AFRICA Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by End-use, 2023 to 2033
Figure 189: MIDDLE EAST AND AFRICA Market Attractiveness by Service, 2023 to 2033
Figure 190: MIDDLE EAST AND AFRICA Market Attractiveness by Waste Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 191: MIDDLE EAST AND AFRICA Market Attractiveness by End-use, 2023 to 2033
Figure 192: MIDDLE EAST AND AFRICA Market Attractiveness by Country, 2023 to 2033






Our Research Products

The "Full Research Suite" delivers actionable market intel, deep dives on markets or technologies, so clients act faster, cut risk, and unlock growth.

The Leaderboard benchmarks and ranks top vendors, classifying them as Established Leaders, Leading Challengers, or Disruptors & Challengers.

Locates where complements amplify value and substitutes erode it, forecasting net impact by horizon

We deliver granular, decision-grade intel: market sizing, 5-year forecasts, pricing, adoption, usage, revenue, and operational KPIs—plus competitor tracking, regulation, and value chains—across 60 countries broadly.

Spot the shifts before they hit your P&L. We track inflection points, adoption curves, pricing moves, and ecosystem plays to show where demand is heading, why it is changing, and what to do next across high-growth markets and disruptive tech

Real-time reads of user behavior. We track shifting priorities, perceptions of today’s and next-gen services, and provider experience, then pace how fast tech moves from trial to adoption, blending buyer, consumer, and channel inputs with social signals (#WhySwitch, #UX).

Partner with our analyst team to build a custom report designed around your business priorities. From analysing market trends to assessing competitors or crafting bespoke datasets, we tailor insights to your needs.
Supplier Intelligence
Discovery & Profiling
Capacity & Footprint
Performance & Risk
Compliance & Governance
Commercial Readiness
Who Supplies Whom
Scorecards & Shortlists
Playbooks & Docs
Category Intelligence
Definition & Scope
Demand & Use Cases
Cost Drivers
Market Structure
Supply Chain Map
Trade & Policy
Operating Norms
Deliverables
Buyer Intelligence
Account Basics
Spend & Scope
Procurement Model
Vendor Requirements
Terms & Policies
Entry Strategy
Pain Points & Triggers
Outputs
Pricing Analysis
Benchmarks
Trends
Should-Cost
Indexation
Landed Cost
Commercial Terms
Deliverables
Brand Analysis
Positioning & Value Prop
Share & Presence
Customer Evidence
Go-to-Market
Digital & Reputation
Compliance & Trust
KPIs & Gaps
Outputs
Full Research Suite comprises of:
Market outlook & trends analysis
Interviews & case studies
Strategic recommendations
Vendor profiles & capabilities analysis
5-year forecasts
8 regions and 60+ country-level data splits
Market segment data splits
12 months of continuous data updates
DELIVERED AS:
PDF EXCEL ONLINE
Demand for Food Waste Management in EU Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Food Waste Shredder Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Food Waste Disposal Equipment Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Food Waste Composting Machine Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Food Waste-Derived Protein Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Waste Management Carbon Credit Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Waste Management Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
E-Waste Management Market Growth - Trends & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Fish Waste Management Market Analysis by Source and End Use Industry Through 2035
Smart Waste Management Market Growth - Trends & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Liquid Waste Management Market
The Medical Waste Management System Market is segmented by Medical Waste Treatment, and Disposable Medical Waste Management from 2025 to 2035
Weight Management Dog Food Market
Products from Food Waste Industry Analysis in Korea Size, Share and Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Products from Food Waste in Japan - Size, Share, and Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Products from Food Waste Market Analysis - Size, Growth, and Forecast 2025 to 2035
Municipal Solid Waste Management Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Onshore Drilling Waste Management Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
USA Products from Food Waste Market Growth – Trends, Demand & Outlook 2025-2035
Demand for Products From Food Waste in Western Europe - Size, Share and Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035

Thank you!
You will receive an email from our Business Development Manager. Please be sure to check your SPAM/JUNK folder too.
Chat With
MaRIA