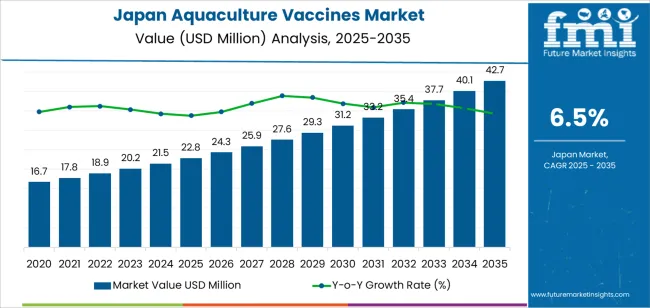
The Japan aquaculture vaccines demand is valued at USD 22.8 million in 2025 and is expected to reach USD 42.7 million by 2035, reflecting a CAGR of 6.5%. Demand is influenced by expanding aquaculture output, higher disease-management requirements, and broader adoption of preventive health programmes in commercial fish farms. Producers are increasing their reliance on vaccination to reduce mortality, limit antimicrobial use, and maintain consistent productivity. Growth is further supported by stricter biosecurity protocols, improved hatchery practices, and rising expectations for pathogen control across coastal and inland aquaculture facilities.
Inactivated vaccines lead the vaccine landscape. These formulations are selected for their safety profile, compatibility with diverse species, and ability to support predictable immune responses under varied culture conditions. Their suitability for salmonids, marine species, and freshwater finfish strengthens utilisation among farms that prioritise stable health performance. Continued investment in multivalent formulations, adjuvant optimisation, and administration techniques supports broader implementation across small- and large-scale producers.
Kyushu & Okinawa, Kanto, and Kinki record the highest utilisation levels due to dense clusters of aquaculture farms, hatchery operations, and seafood-processing activities. These regions also maintain strong cold-chain networks and veterinary-service capacity, allowing consistent deployment of vaccination programmes. Key suppliers include Zoetis Inc., Merck Animal Health, Elanco Animal Health, HIPRA, and Benchmark Holdings. These companies provide inactivated and specialty vaccines used for controlling bacterial and viral pathogens affecting commercial aquaculture production.
Year-on-year growth analysis shows a stable and gradually strengthening pattern shaped by consistent disease-management needs in marine and freshwater production systems. From 2025 to 2029, YoY growth remains steady as fish farms expand preventive-health protocols for species such as salmon, amberjack, and sea bream. Demand is supported by routine vaccination cycles, biosecurity requirements, and incremental adoption of injectable and immersion-based vaccines, producing reliable annual increments without large volatility.
Between 2030 and 2035, YoY gains remain positive but follow a more measured trajectory. Growth becomes anchored in predictable procurement across established hatcheries and grow-out operations, with additional support from improved vaccine-strain matching and stronger regulatory emphasis on antimicrobial-use reduction. Annual expansion is influenced by refinements in autogenous vaccines, better cold-chain management, and broader uptake of multivalent formulations. The YoY pattern shows limited fluctuation due to the sector’s reliance on biological-risk mitigation and consistent farm-level health protocols, resulting in a stable, mid-range annual growth profile across Japan’s aquaculture-vaccine landscape.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Japan Aquaculture Vaccines Sales Value (2025) | USD 22.8 million |
| Japan Aquaculture Vaccines Forecast Value (2035) | USD 42.7 million |
| Japan Aquaculture Vaccines Forecast CAGR (2025-2035) | 6.5% |
The demand for aquaculture vaccines in Japan is increasing because fish farming businesses require reliable disease management strategies to maintain stock health, reduce losses and comply with stricter biosecurity standards. Japanese aquaculture operations, including those farming salmon, sea bass, flounder and other species, face rising threat from viral, bacterial and parasitic diseases. Vaccination helps control outbreaks and supports productivity in high-value aquaculture systems. Manufacturers and service providers respond with vaccines tailored to local species and pathogens, which increases uptake.
Growth is further supported by consumer demand for safer seafood, industry focus on sustainable farming practices and government efforts to enhance aquaculture resilience. Constraints include complex regulatory approval processes for novel vaccines in Japan, high development and production cost of species-specific formulations and limited awareness in some small-scale farms. The relatively modest scale of vaccine adoption compared with terrestrial livestock means growth may be gradual until volume thresholds are met.
Demand for aquaculture vaccines in Japan reflects the needs of salmon farming, disease-prevention programs, and regulated health-management practices across inland and coastal aquaculture systems. Vaccine-type preferences depend on antigen stability, immune-response reliability, and suitability for mass-administration methods used in high-density fish populations. Species-level demand follows the structure of Japan’s aquaculture output, where salmon production dominates. Pathogen-level distribution highlights the disease pressures affecting fish health and farm productivity, particularly bacterial infections that influence mortality and growth performance.
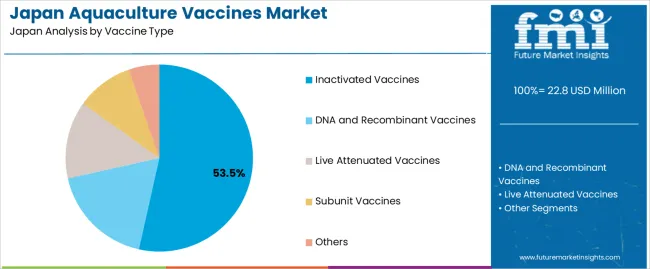
Inactivated vaccines hold 53.5% of national demand and represent the leading vaccine category. These formulations support stable immune responses, controlled safety profiles, and suitability for large-scale injection programs used in salmon aquaculture. DNA and recombinant vaccines account for 18.0%, offering targeted antigen delivery for specific pathogens. Live attenuated vaccines represent 13.4%, supporting robust immune activation where controlled pathogen exposure is appropriate. Subunit vaccines account for 9.8%, providing purified antigen components for species requiring precise immune stimulation. Other vaccine types hold 5.3%, covering emerging and specialised formulations. Vaccine-type adoption reflects immunogenic performance, safety considerations, and operational feasibility in Japanese aquaculture.
Key drivers and attributes:
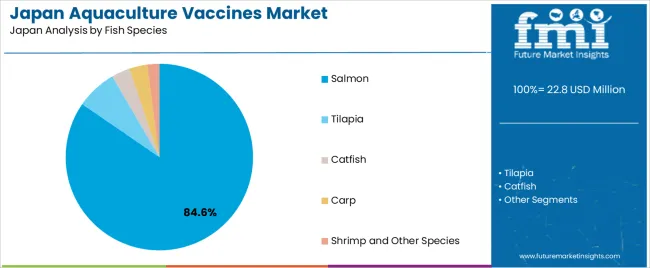
Salmon represents 84.6% of national vaccine demand and is the dominant species category. Salmon farming requires structured vaccination programs due to susceptibility to bacterial and viral pathogens that affect growth and survival. Tilapia holds 7.0%, reflecting smaller-scale but consistent use in inland aquaculture. Catfish and carp represent 3.2% and 3.1%, supporting disease-prevention needs in modest production volumes. Shrimp and other species account for 2.1%, reflecting limited vaccine availability and species-specific constraints. Species-level distribution corresponds to production intensity, disease prevalence, and vaccination feasibility across Japan’s aquaculture systems.
Key drivers and attributes:
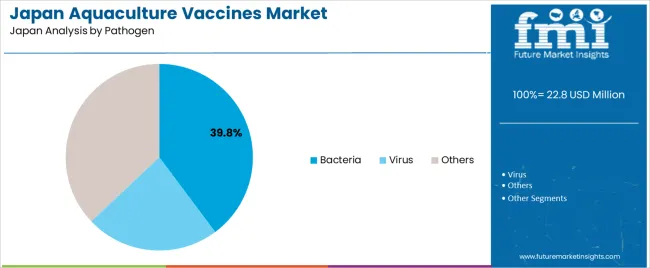
Bacterial pathogens represent 39.8% of national vaccine demand and form the leading pathogen category. Vaccines targeting bacterial infections support the prevention of common conditions affecting salmon, including vibriosis and furunculosis. Viral pathogens account for 23.1%, covering vaccines developed for diseases that cause high mortality in intensive aquaculture. Other pathogen categories represent 37.1%, including parasites and emerging infectious agents requiring specialised vaccine development. Pathogen-level distribution reflects disease prevalence, farm-density conditions, and species-specific susceptibility within Japanese aquaculture operations.
Key drivers and attributes:
Intensifying aquaculture operations and rising disease-management requirements are driving demand.
Demand for aquaculture vaccines in Japan is increasing as producers shift toward more intensive farming systems that heighten the risk of infectious disease outbreaks. Farmers raising species such as salmon, amberjack and eel seek preventive health tools that stabilise production, reduce mortality and improve feed efficiency. Consumer preference for chemical-free seafood encourages operators to replace antibiotics with structured vaccination programmes. The need to maintain consistent supply, support domestic seafood security and meet quality expectations strengthens reliance on vaccines that protect against regionally relevant pathogens and help maintain predictable farm performance across varied coastal and inland aquaculture environments.
Complex regulatory processes and high development cost are restraining broader adoption.
The uptake of aquaculture vaccines is moderated by strict regulatory procedures that require detailed safety and efficacy validation for each vaccine strain. Development costs remain high due to species-specific pathogens, varied water conditions and unique farm practices across Japan’s aquaculture landscape. Smaller farms may avoid vaccination because of cost sensitivity, limited technical capacity or reliance on traditional disease-control methods. Vaccination of small or stress-sensitive fish increases handling challenges, reducing feasibility in certain production stages. Limited availability of vaccines tailored for less common species also restricts uniform adoption, especially among producers with diverse stock or niche cultivation systems.
Advanced vaccine platforms and diversified delivery methods are shaping key industry trends.
Aquaculture vaccine innovation in Japan is expanding through development of DNA based formulations, recombinant antigens and polyvalent products designed to improve immune response and broaden pathogen coverage. Immersion and oral vaccine delivery methods are gaining attention because they reduce labour intensity and minimise physical handling of fish during mass vaccination. The growth of offshore aquaculture and recirculating aquaculture systems increases demand for vaccines suited to controlled, high density farming environments. Companies are integrating health monitoring tools with vaccination programmes to support preventive disease management and improve decision making across the full production cycle, enhancing long term farm resilience.
Demand for aquaculture vaccines in Japan is rising through 2035 as fish-farming operators strengthen disease-prevention programs to protect marine and freshwater species. Growing susceptibility to bacterial and viral infections, stricter biosecurity rules, and rising output from regional aquaculture clusters drive wider adoption of injectable, immersion, and oral vaccines. National focus on stable production of yellowtail, sea bream, salmon, trout, and shellfish supports continued expansion. The Kyushu & Okinawa region leads with 8.1%, followed by Kanto (7.4%), Kinki (6.5%), Chubu (5.7%), Tohoku (5.0%), and the Rest of Japan (4.8%).
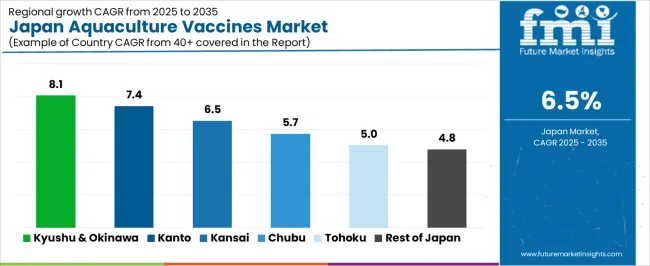
| Region | CAGR (2025-2035) |
|---|---|
| Kyushu & Okinawa | 8.1% |
| Kanto | 7.4% |
| Kinki | 6.5% |
| Chubu | 5.7% |
| Tohoku | 5.0% |
| Rest of Japan | 4.8% |
Kyushu & Okinawa grows at 8.1% CAGR, supported by Japan’s highest concentration of marine aquaculture, including large yellowtail, sea bream, and tuna-farming operations across Kagoshima, Nagasaki, and Miyazaki. High stocking densities increase disease-management requirements, making vaccines essential for reducing mortality and improving feed-conversion performance. Regional farming cooperatives adopt standardized vaccination programs for fingerlings and juvenile fish to limit pathogen spread during seasonal temperature fluctuations. Hatcheries expand vaccine deployment to strengthen early-stage immunity for marine species. Regulatory reviews aimed at reducing antibiotic use also reinforce vaccine adoption across both coastal cages and land-based recirculating aquaculture systems.
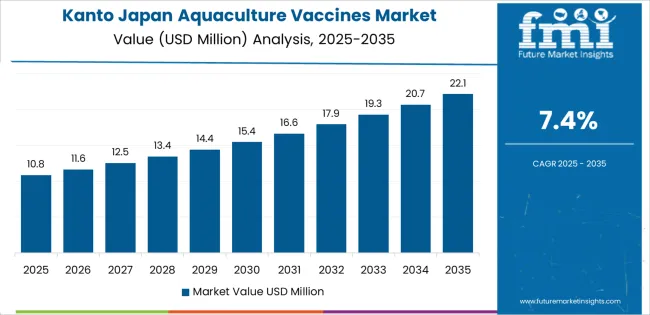
Kanto grows at 7.4% CAGR, supported by hatcheries, research facilities, and distribution networks across Chiba, Kanagawa, and Ibaraki. Although large-scale marine farming is limited, the region’s role in broodstock development, juvenile production, and logistics strengthens demand for consistent vaccination protocols. Research institutes evaluate vaccine performance for new pathogens, accelerating adoption across specialized farms. Seafood-processing companies collaborate with hatcheries to ensure stable supply of vaccinated stock for quality-assurance programs. Inland aquaculture operators producing eel, carp, and trout adopt immune-support vaccines to reduce sensitivity to fluctuating water quality.
Kinki grows at 6.5% CAGR, influenced by significant marine aquaculture activity across Wakayama, Hyogo, and Mie. Sea-bream and yellowtail farms adopt vaccination programs to manage recurring bacterial diseases affecting high-value species. Regional hatcheries standardize vaccine use to improve juvenile survival rates before transfer to offshore cages. Inland trout and ayu farms use vaccines to reduce disease outbreaks during summer temperature spikes. Collaboration between universities and aquaculture associations expands training on vaccination techniques and immunity monitoring, strengthening consistency across farms.
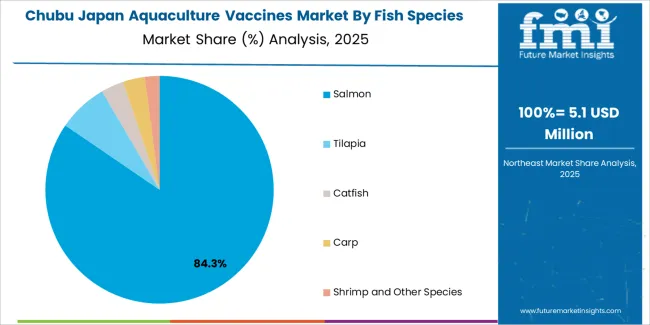
Chubu grows at 5.7% CAGR, supported by inland trout, char, and ayu production across Nagano, Gifu, and Shizuoka. Operators adopt immersion and oral vaccines to prevent diseases linked to temperature stress and variable water conditions. Marine operations along the Shizuoka coast integrate vaccines for high-value species requiring controlled disease-prevention programs. With increasing diversification into recirculating aquaculture systems, farms rely on vaccination to maintain stable biomass levels and reduce antimicrobial usage. Regional technical centers provide diagnostic services that support precise vaccine selection.
Tohoku grows at 5.0% CAGR, supported by cold-water species such as salmon, trout, and scallop farming across Miyagi, Iwate, and Aomori. Farms adopt vaccines to manage diseases intensified by seasonal temperature shifts and long grow-out cycles. Expanded salmon-farming initiatives rely on vaccination to reduce mortality during sea-phase development. Scallop hatcheries use pathogen-management programs that incorporate early-stage immune protection. Regional aquaculture research centers refine disease-monitoring frameworks that guide vaccine deployment.
The Rest of Japan grows at 4.8% CAGR, reflecting stable aquaculture activity in distributed coastal and inland zones. Smaller farms adopt vaccines to reduce disease-related losses in yellowtail, sea bream, trout, and eel production. Operators expanding direct-to-consumer seafood sales rely on vaccinated stock to support quality and continuity. Municipal aquaculture centers provide training on handling, dosage, and seasonal vaccination timing. Increased focus on reducing antibiotic use further incentivizes vaccination across small and mid-scale producers.
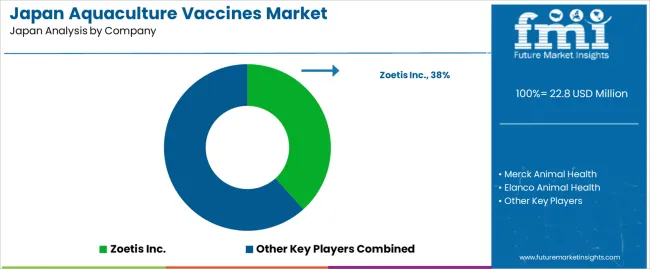
Demand for aquaculture vaccines in Japan is shaped by a concentrated group of animal-health suppliers supporting finfish farms, hatcheries, and marine-species operations across coastal production regions. Zoetis Inc. holds the leading position with an estimated 38.3% share, supported by controlled antigen-production processes, consistent batch quality, and long-standing integration with Japanese aquaculture health-management programmes. Its position is reinforced by predictable immune-response performance and reliable availability for key species including salmon, yellowtail, and seabream.
Merck Animal Health and Elanco Animal Health follow as significant participants. Merck supplies injectable and immersion vaccines characterised by stable potency and verified safety profiles, supporting intensive marine and freshwater production cycles. Elanco maintains a presence through pathogen-specific formulations used in hatcheries and grow-out facilities requiring controlled disease-prevention strategies.
HIPRA contributes capability with targeted vaccines designed for region-specific pathogens, offering consistent antigen stability and dependable field performance. Benchmark Holdings adds further depth through specialised aquaculture-health technologies, including vaccines developed for emerging and persistent marine diseases relevant to Japanese producers.
Competition across this segment centres on antigen stability, species-specific efficacy, cold-chain reliability, withdrawal-time compliance, and performance under varied farming conditions. Demand continues to grow as Japanese aquaculture operators prioritise preventive health measures, reduce antibiotic usage, and adopt vaccines that deliver consistent protection across hatchery and open-water production systems.
| Items | Values |
|---|---|
| Quantitative Units | USD million |
| Vaccine Type | Inactivated Vaccines, DNA and Recombinant Vaccines, Live Attenuated Vaccines, Subunit Vaccines, Others |
| Fish Species | Salmon, Tilapia, Catfish, Carp, Shrimp and Other Species |
| Pathogen | Bacteria, Virus, Others |
| End User | Commercial Aquaculture Farms, Small-Scale Farmers in Emerging Markets, Government and Cooperative Programs, Research Institutions and Diagnostic Labs |
| Regions Covered | Kyushu & Okinawa, Kanto, Kinki, Chubu, Tohoku, Rest of Japan |
| Key Companies Profiled | Zoetis Inc., Merck Animal Health, Elanco Animal Health, HIPRA, Benchmark Holdings |
| Additional Attributes | Dollar sales by vaccine type, fish species, pathogen category, and end-user segments; regional adoption trends across Kyushu & Okinawa, Kanto, Kinki, Chubu, Tohoku, and Rest of Japan; competitive landscape of aquaculture vaccine producers; developments in recombinant and DNA-based immunization, cold-water vs. warm-water species vaccines, and disease-prevention programs in aquaculture; integration with commercial farming operations, hatchery management, fish health monitoring, and government-supported aquaculture initiatives across Japan. |
The demand for aquaculture vaccines in japan is estimated to be valued at USD 22.8 million in 2025.
The market size for the aquaculture vaccines in japan is projected to reach USD 42.7 million by 2035.
The demand for aquaculture vaccines in japan is expected to grow at a 6.5% CAGR between 2025 and 2035.
The key product types in aquaculture vaccines in japan are inactivated vaccines, dna and recombinant vaccines, live attenuated vaccines, subunit vaccines and others.
In terms of fish species, salmon segment is expected to command 84.6% share in the aquaculture vaccines in japan in 2025.






Our Research Products

The "Full Research Suite" delivers actionable market intel, deep dives on markets or technologies, so clients act faster, cut risk, and unlock growth.

The Leaderboard benchmarks and ranks top vendors, classifying them as Established Leaders, Leading Challengers, or Disruptors & Challengers.

Locates where complements amplify value and substitutes erode it, forecasting net impact by horizon

We deliver granular, decision-grade intel: market sizing, 5-year forecasts, pricing, adoption, usage, revenue, and operational KPIs—plus competitor tracking, regulation, and value chains—across 60 countries broadly.

Spot the shifts before they hit your P&L. We track inflection points, adoption curves, pricing moves, and ecosystem plays to show where demand is heading, why it is changing, and what to do next across high-growth markets and disruptive tech

Real-time reads of user behavior. We track shifting priorities, perceptions of today’s and next-gen services, and provider experience, then pace how fast tech moves from trial to adoption, blending buyer, consumer, and channel inputs with social signals (#WhySwitch, #UX).

Partner with our analyst team to build a custom report designed around your business priorities. From analysing market trends to assessing competitors or crafting bespoke datasets, we tailor insights to your needs.
Supplier Intelligence
Discovery & Profiling
Capacity & Footprint
Performance & Risk
Compliance & Governance
Commercial Readiness
Who Supplies Whom
Scorecards & Shortlists
Playbooks & Docs
Category Intelligence
Definition & Scope
Demand & Use Cases
Cost Drivers
Market Structure
Supply Chain Map
Trade & Policy
Operating Norms
Deliverables
Buyer Intelligence
Account Basics
Spend & Scope
Procurement Model
Vendor Requirements
Terms & Policies
Entry Strategy
Pain Points & Triggers
Outputs
Pricing Analysis
Benchmarks
Trends
Should-Cost
Indexation
Landed Cost
Commercial Terms
Deliverables
Brand Analysis
Positioning & Value Prop
Share & Presence
Customer Evidence
Go-to-Market
Digital & Reputation
Compliance & Trust
KPIs & Gaps
Outputs
Full Research Suite comprises of:
Market outlook & trends analysis
Interviews & case studies
Strategic recommendations
Vendor profiles & capabilities analysis
5-year forecasts
8 regions and 60+ country-level data splits
Market segment data splits
12 months of continuous data updates
DELIVERED AS:
PDF EXCEL ONLINE
Aquaculture Vaccines Market Analysis - Size, Share, and Forecast Outlook for 2025 to 2035
Chile Aquaculture Vaccines Market Insights – Size, Demand & Forecast 2025-2035
China Aquaculture Vaccines Market Outlook – Growth & Forecast 2025-2035
Norway Aquaculture Vaccines Market Insights – Size, Demand & Growth 2025-2035
Vietnam Aquaculture Vaccines Market Trends – Growth & Demand 2025-2035
Australia and New Zealand Aquaculture Vaccines Market Report – Key Trends & Forecast 2025-2035
Aquaculture Prebiotics Market Analysis - Size, Share, and Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Japan Faith-based Tourism Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Japan Sports Tourism Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Japan Respiratory Inhaler Devices Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Japan Halal Tourism Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Japan Automated People Mover Industry Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Japan Automotive Load Floor Industry Analysis Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Japan Food Cling Film Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Japan Polypropylene Packaging Films Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Aquaculture Equipment Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Aquaculture Therapeutics Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Vaccines Market Insights - Trends, Growth & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Japan Probiotic Yogurt Market is segmented by product type, source type, nature type, flavor type, fat content, sales channel and key city/province through 2025 to 2035.
japan Tortilla Market - Growth, Trends and Forecast from 2025 to 2035

Thank you!
You will receive an email from our Business Development Manager. Please be sure to check your SPAM/JUNK folder too.
Chat With
MaRIA