The LEO satellite market is set to rise from USD 16.1 billion in 2025 to USD 55.5 billion by 2035, reflecting a CAGR of 13.2%. Inflection point mapping highlights distinct growth shifts where adoption accelerates due to technological readiness, investment momentum, and scaling of satellite constellations. Between 2021 and 2025, the market advances from USD 8.6 billion to USD 16.1 billion. This phase reflects the first inflection point, as early large-scale constellations in broadband internet, Earth observation, and defense applications enter deployment.
Growth accelerates as launch costs decline and satellite miniaturization improves. From 2026 to 2030, the market grows from USD 18.2 billion to USD 29.9 billion. This period marks the second inflection point, driven by expansion of mega-constellations and stronger commercialization of space-based internet services. Private investments and government-backed projects converge, creating rapid adoption in communication, navigation, and data relay applications. The inflection here is sharper, indicating a mass-market transition. Between 2031 and 2035, the market expands from USD 33.8 billion to USD 55.5 billion. This forms the third inflection point, characterized by maturing ecosystems where ground infrastructure, inter-satellite links, and AI-enabled traffic management scale alongside satellite deployments. Growth moderates compared to earlier phases but remains significant as replacement cycles, service bundling, and integration into aviation, maritime, and defense reinforce demand.
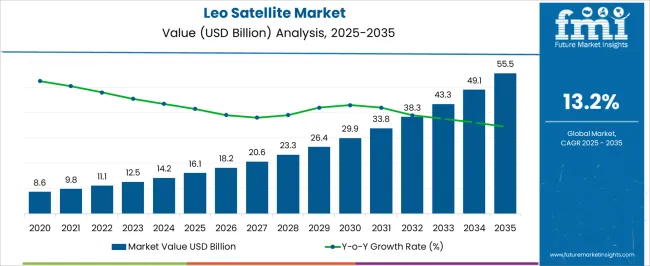
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| LEO Satellite Market Estimated Value in (2025 E) | USD 16.1 billion |
| LEO Satellite Market Forecast Value in (2035 F) | USD 55.5 billion |
| Forecast CAGR (2025 to 2035) | 13.2% |
The LEO satellite market represents a high-growth subset across multiple parent domains, with its share defined by rapid constellation deployment and versatility in both civil and defense applications. Within the satellite communication market, LEO satellites account for nearly 25 to 28%, as companies such as SpaceX, OneWeb, and Amazon Kuiper drive large-scale broadband constellations. In the earth observation and remote sensing market, their share is close to 18 to 20%, since most imaging, mapping, and environmental monitoring missions are now launched into low Earth orbit for higher resolution and quicker revisit times. The space launch services market shows strong dependence, with LEO-related payloads making up nearly 35 to 38%, as the majority of small satellite launches are destined for LEO orbits due to cost and accessibility advantages. Within the global navigation satellite systems (GNSS) market, LEO constellations contribute around 6 to 8%, complementing GEO and MEO systems by enhancing accuracy, resilience, and latency for navigation and timing services. Finally, in the defense and military space systems market, LEO satellites hold close to 15 to 17%, supporting surveillance, reconnaissance, and secure tactical communications.
The LEO Satellite market is undergoing rapid expansion, driven by the increasing need for high-speed, low-latency connectivity across diverse applications. The growing adoption of satellite-based broadband services, earth observation programs, and remote sensing operations has significantly boosted market activity. Advancements in satellite miniaturization, cost-effective launch solutions, and reusable rocket technology have lowered barriers to entry, encouraging participation from both established aerospace players and emerging startups.
Regulatory approvals and spectrum allocations are also enabling faster deployment of constellations, meeting the surging demand for global connectivity. Continuous innovation in payload technology, coupled with the integration of AI and edge computing capabilities, is improving operational efficiency and expanding service potential.
The market is positioned to benefit from strong government investments, commercial contracts, and collaborative ventures aimed at enhancing global communications infrastructure As low Earth orbit constellations mature, their ability to provide scalable and resilient solutions is expected to ensure sustained growth and long-term market viability.
The LEO satellite market is segmented by satellite type, frequency, application, end use, and geographic regions. By satellite type, LEO satellite market is divided into Small satellites, Medium satellites (180 - 1000 Kg), and Large satellite (Above 1000 Kg). In terms of frequency, LEO satellite market is classified into Ka-Band: 26–40 GHz, L-Band: 1–2 GHz, S-Band: 2–4 GHz, C-Band: 4–8 GHz, X-Band: 8–12 GHz, Ku-Band: 12–18 GHz, and Q/V-Band: 33–75 GHz. Based on application, LEO satellite market is segmented into Communication, Earth Observation & remote sensing, Navigation & positioning, and Scientific research. By end use, LEO satellite market is segmented into Commercial, Military & defense, Government (law enforcement & homeland security), and Universities. Regionally, the LEO satellite industry is classified into North America, Latin America, Western Europe, Eastern Europe, Balkan & Baltic Countries, Russia & Belarus, Central Asia, East Asia, South Asia & Pacific, and the Middle East & Africa.
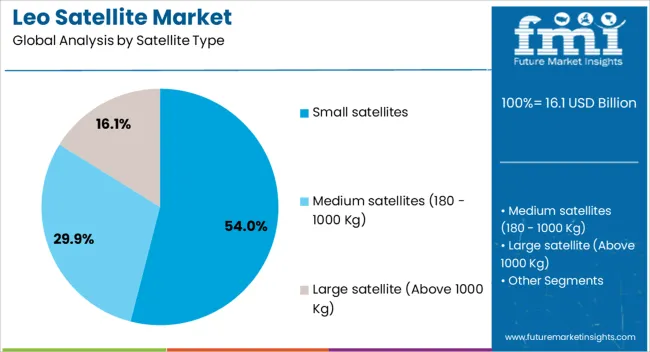
The small satellites segment is projected to account for 54% of the LEO Satellite market revenue share in 2025, making it the leading satellite type. This dominance has been driven by the lower manufacturing and launch costs associated with small satellite platforms, which enable rapid deployment of large constellations.
Their compact size allows for integration of advanced payloads and sensors, supporting diverse missions including communication, earth observation, and scientific research. The flexibility of small satellites to be launched in batches on shared missions has accelerated constellation buildouts, reducing lead times and operational expenses.
Technological advancements in miniaturization, power systems, and onboard processing have expanded the performance capabilities of these satellites, making them suitable for both commercial and governmental use Their adaptability to frequent software updates and modular configurations ensures sustained operational relevance, further solidifying their leadership in the market.
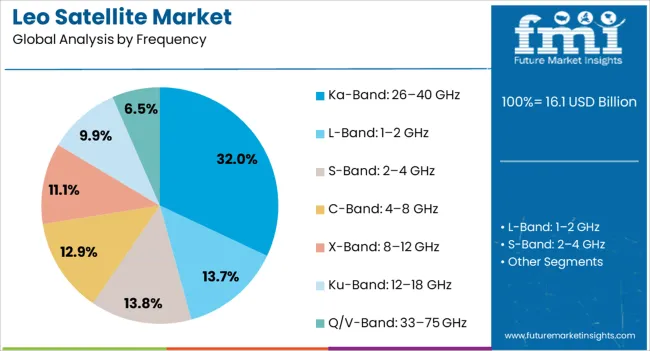
The Ka-Band frequency segment is expected to hold 32% of the LEO Satellite market revenue share in 2025, representing the leading frequency range. Growth in this segment has been propelled by its ability to deliver high-capacity data transmission, making it ideal for broadband internet, streaming services, and high-resolution imagery transfer.
The wider bandwidth offered by the Ka-Band supports greater throughput and more simultaneous connections, catering to the rising global demand for fast, reliable communications. Advancements in ground station technology and adaptive beamforming have improved signal stability and reduced latency, even under challenging weather conditions.
Its suitability for both fixed and mobile applications, including maritime and aviation connectivity, has expanded its adoption across sectors As data-intensive applications continue to grow, the Ka-Band’s balance of speed, capacity, and coverage is expected to maintain its competitive advantage in the frequency segment.
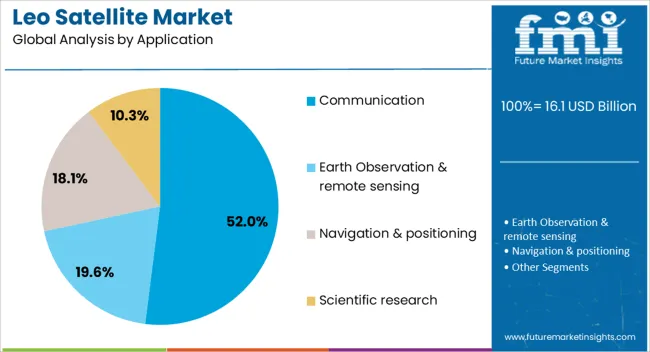
The communication segment is forecasted to command 52% of the LEO Satellite market revenue share in 2025, establishing it as the leading application. This leadership position has been reinforced by the increasing reliance on satellite networks to bridge connectivity gaps in underserved and remote areas.
LEO satellites offer low-latency and high-bandwidth communication capabilities, enabling services such as broadband internet, secure enterprise networking, and emergency response communications. The rise in demand from commercial sectors, defense agencies, and maritime operators has driven substantial investments in communication-focused satellite constellations.
Enhanced interoperability with terrestrial networks and the integration of 5G infrastructure have further expanded the segment’s scope The ability to provide scalable, global communication coverage without dependence on extensive ground infrastructure has positioned LEO satellites as a vital component in the future of connectivity, supporting sustained growth in this segment.
Low earth orbit satellite adoption is rising as low latency connectivity, geospatial monitoring, and mobile backhaul are prioritized across sectors. Demand is supported by mass production, faster launch cadence, and emerging non terrestrial network standards that enable direct to device use. Barriers remain in capital intensity, spectrum coordination, debris management, terminal costs, and competition from terrestrial networks. Opportunities are opening in enterprise backhaul, aviation and maritime links, emergency restoration, and geospatial intelligence. Trends highlight vertical integration, laser links, multi orbit strategies, sovereign programs, and service models built on bundled contracts.
Low earth orbit satellite adoption is being accelerated by demand for low latency broadband, reliable backhaul, and persistent sensing across remote and mobile domains. Enterprises, governments, and households in hard to reach regions value LEO connectivity for maritime, aviation, mining, and energy uses. Shorter build cycles, mass production of small satellites, and frequent ride share launches have reduced time to orbit, supporting faster refresh of on orbit assets. Standardization around non terrestrial networks is improving device interoperability, while direct to device pathways expand the reachable user base without specialized terminals. Earth observation operators benefit from high revisit imaging and RF monitoring that support geospatial analytics and logistics planning. Multi orbit strategies that combine LEO with GEO and MEO are being adopted to balance latency, coverage, and capacity. These factors position LEO platforms as practical tools for closing access gaps and strengthening connectivity worldwide.
Growth remains constrained by high capital requirements, spectrum coordination, and congestion in low earth orbit. Constellation buildouts demand large financing, disciplined manufacturing, and guaranteed launch access, which raises execution risk for newcomers. International filings and frequency coordination extend timelines, while interference management across Ku, Ka, and V bands increases engineering workload. Space debris, conjunction alerts, and deorbit obligations require tracking, propulsion reserves, and ground monitoring that add complexity. Ground segment scaling is not trivial, since gateways need power, fiber, and real estate in difficult locations. Flat panel user terminals remain expensive for mass adoption, and subsidies can strain cash flow if usage patterns are uneven. Insurance, export rules, and sanctions limit certain suppliers and markets. Competition from terrestrial fiber, mobile networks, and fixed wireless offerings keeps pricing pressure intense, reducing room for error in service launches and slowing expansion in cost sensitive regions.
Clear upside is emerging in direct to device messaging, voice, and low rate data, where standardized non terrestrial networks enable roaming with unmodified handsets. Automotive, maritime, and aviation segments seek links for safety services, telemetry, and passenger connectivity, creating channels for capacity leasing and managed offerings. Enterprises adopt LEO for edge backhaul at mines, rail corridors, and offshore assets, while emergency agencies use portable terminals for rapid restoration. Earth observation data is being packaged into geospatial intelligence for agriculture, insurance, shipping, and infrastructure monitoring, which broadens revenue beyond raw imagery. Optical inter satellite links enable global trunks with reduced reliance on terrestrial gateways, supporting secure transport. Partnerships with cloud providers, handset makers, and mobile operators are expanding distribution reach. Vendors that bundle terminals, airtime, analytics, and service level agreements are positioned to capture long term contracts across commercial and government programs.
Industry direction points to tighter vertical integration across satellite manufacturing, launch, terminals, and ground software, aiming to control cost and cadence. Multi orbit architectures that stitch LEO with GEO and MEO are gaining traction, supported by orchestration platforms that steer traffic by latency and throughput targets. Laser inter satellite links, digital payloads, and dynamic beamforming are being deployed to increase flexibility and route traffic around constrained gateways. Flat panel antennas for vehicles and fixed sites are improving reliability, easing enterprise adoption in harsh climates. Sovereign LEO initiatives are proliferating as governments seek assured capacity and control of strategic data flows. Debris mitigation, deorbit plans, and space traffic coordination are receiving heightened scrutiny, making operational discipline a clear differentiator. Commercial models are shifting toward usage based pricing, wholesale partnerships, and cloud peering at gateways, which encourages service bundling and recurring revenue at scale.
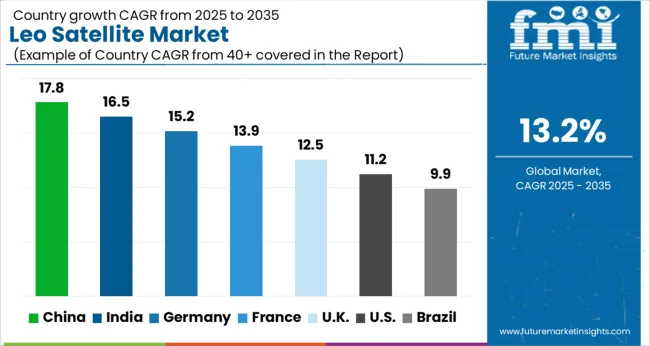
| Country | CAGR |
|---|---|
| China | 17.8% |
| India | 16.5% |
| Germany | 15.2% |
| France | 13.9% |
| UK | 12.5% |
| USA | 11.2% |
| Brazil | 9.9% |
The LEO satellite market is forecasted to grow globally at a CAGR of 13.2% from 2025 to 2035. China leads with 17.8%, followed by India at 16.5% and France at 13.9%, while the UK records 12.5% and the USA posts 11.2%. China and India secure the strongest growth premiums above baseline at +4.6% and +3.3%, fueled by connectivity expansion, defense programs, and growing launch capabilities. France anchors European growth through ESA and CNES-led projects, while the UK contributes through OneWeb and small satellite manufacturing leadership. The USA, though slower in CAGR, remains unmatched in scale due to its mega-constellation projects and private-sector dominance. The analysis includes over 40 countries, with the leading markets shown below.
The LEO satellite market in China is forecasted to grow at a CAGR of 17.8% from 2025 to 2035, making it the fastest among the profiled regions. China is aggressively expanding its LEO satellite constellations for broadband connectivity, earth observation, and military applications. National programs are emphasizing space autonomy, with domestic firms scaling manufacturing to deploy hundreds of small satellites annually. Partnerships between state-owned aerospace companies and private startups are accelerating innovation in satellite miniaturization and launch capacity. China’s focus on developing reusable launch vehicles further supports cost-effective deployment. With rising demand for connectivity in rural and remote areas, LEO satellites are critical to bridging digital divides.
The LEO satellite market in India is expected to expand at a CAGR of 16.5% during 2025–2035. India is investing heavily in LEO satellite networks to enhance connectivity, weather monitoring, and national security. The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) is spearheading multiple missions, while private companies are entering partnerships to deploy satellite-based internet services. India’s growing focus on digital inclusion across rural regions creates strong demand for LEO broadband coverage. Startups are also emerging in the satellite manufacturing and launch service ecosystem, supported by favorable policies and public-private collaborations. Defense and surveillance applications further contribute to adoption.
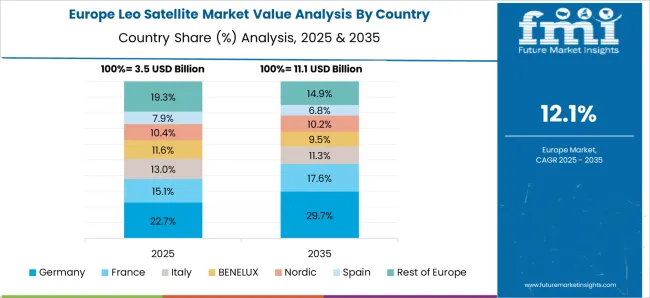
The LEO satellite market in France is projected to grow at a CAGR of 13.9% from 2025 to 2035. France plays a central role in European satellite innovation through CNES (French Space Agency) and leading aerospace firms. The focus is on earth observation, defense surveillance, and broadband connectivity. French companies are also collaborating under European Union and ESA programs to strengthen satellite constellations. Toulouse and Paris continue to act as hubs for satellite R&D, with advancements in satellite miniaturization and propulsion systems. France’s defense sector is driving investment in secure satellite communication networks. Export opportunities are expanding as French manufacturers supply satellites and components to global operators.
The LEO satellite market in the United Kingdom is forecast to grow at a CAGR of 12.5% between 2025 and 2035. The UK is a major player in small satellite manufacturing, with Glasgow recognized as a leading hub for CubeSat and micro-satellite production. Investments in OneWeb and related broadband satellite constellations have positioned the UK as a global force in satellite connectivity. Government-backed programs are supporting satellite R&D, while partnerships with international aerospace companies enhance innovation. LEO satellites are being deployed for broadband internet, climate monitoring, and defense-related surveillance.
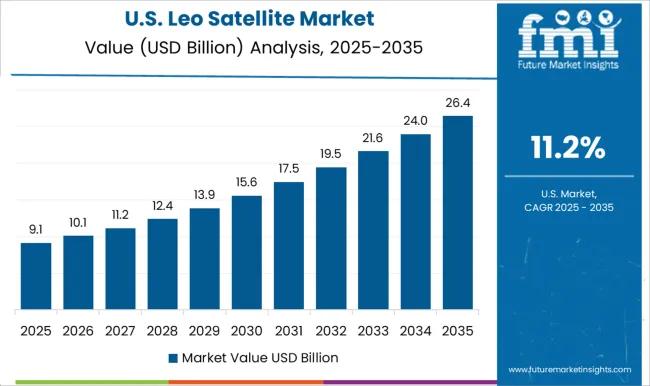
The LEO satellite market in the United States is expected to grow at a CAGR of 11.2%, slower than Asia but highly significant in terms of absolute scale. The USA leads in mega-constellation deployments, with SpaceX’s Starlink and Amazon’s Kuiper projects driving massive satellite launches. Defense and national security applications further underpin adoption, as LEO satellites provide enhanced reconnaissance and communication capabilities. NASA and DARPA programs are fostering innovations in satellite propulsion, miniaturization, and deep-space communication. The USA private sector dominates global launches, with reusable rockets making satellite deployment more economical
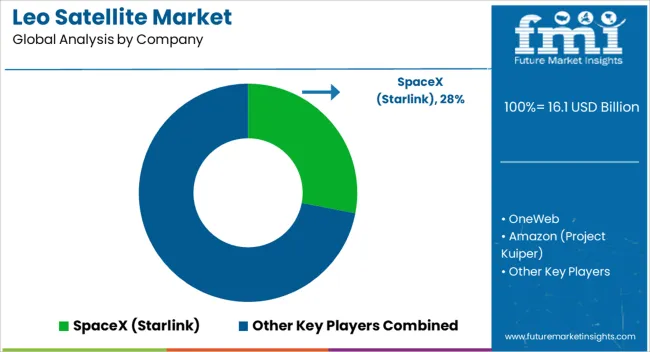
Competition in the low Earth orbit satellite domain has been largely determined by the scale of deployed constellations, launch integration, and advanced ground segment infrastructure. SpaceX, through its Starlink program, has taken a dominant position by combining vertically integrated launch capacity with the largest active satellite fleet. Its strategy has been centered on securing a global broadband subscriber base while maintaining control over critical upstream and downstream operations. OneWeb has adopted a more targeted approach, operating a mid-scale constellation that caters primarily to enterprise, maritime, and government customers, while leveraging European aerospace partnerships to strengthen its service credibility. Amazon, under Project Kuiper, is preparing to enter the market with an ambitious large-scale constellation that will be tied closely to its AWS ecosystem and logistics expertise. The company has emphasized cloud integration and secure data handling as differentiators, while its initial launch programs have been structured to ensure a phased yet aggressive rollout. Airbus Defense & Space has focused on payload manufacturing and assembly capacity, providing expertise for both commercial and government-backed LEO missions in Europe. Lockheed Martin, on the other hand, has reinforced its presence in defense-grade constellations by prioritizing secure communications and resilient network capabilities tailored to military requirements.
Other participants, such as Northrop Grumman and Thales, contribute through niche constellations, subsystem manufacturing, and collaborative projects across defense and commercial segments. Differentiation across the market has been shaped by vertical integration of manufacturing and launch services, the development of phased array terminals, and wide frequency coverage in Ka and Ku bands. Spectrum licensing, long-term government contracts, and resilience against cyber and orbital threats have also become central levers of competition. The strategic interplay of commercial expansion and government-backed security programs continues to define the evolution of the LEO satellite landscape.
| Item | Value |
|---|---|
| Quantitative Units | USD 16.1 Billion |
| Satellite Type | Small satellites, Medium satellites (180 - 1000 Kg), and Large satellite (Above 1000 Kg) |
| Frequency | Ka-Band: 26–40 GHz, L-Band: 1–2 GHz, S-Band: 2–4 GHz, C-Band: 4–8 GHz, X-Band: 8–12 GHz, Ku-Band: 12–18 GHz, and Q/V-Band: 33–75 GHz |
| Application | Communication, Earth Observation & remote sensing, Navigation & positioning, and Scientific research |
| End Use | Commercial, Military & defense, Government (law enforcement & homeland security), and Universities |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America, Middle East & Africa |
| Country Covered | United States, Canada, Germany, France, United Kingdom, China, Japan, India, Brazil, South Africa |
| Key Companies Profiled | SpaceX (Starlink), OneWeb, Amazon (Project Kuiper), Airbus Defence & Space, Lockheed Martin, and [Other players: Northrop Grumman, Thales, etc.] |
| Additional Attributes | Dollar sales by product type include communication satellites, Earth observation platforms, defense surveillance units, and navigation augmentation payloads. Dollar sales by end use cover commercial broadband, enterprise and mobility services, defense and intelligence, and scientific missions. Demand dynamics are driven by the surge in global data consumption, defense need for resilient LEO-based communications, and enterprise requirements for low-latency broadband. Regional trends highlight North America as the anchor with large-scale constellation deployments, Europe advancing with industrial collaborations and government-backed missions, and Asia Pacific scaling with domestic satellite programs and rising commercial broadband adoption. |
The global LEO satellite market is estimated to be valued at USD 16.1 billion in 2025.
The market size for the LEO satellite market is projected to reach USD 55.5 billion by 2035.
The LEO satellite market is expected to grow at a 13.2% CAGR between 2025 and 2035.
The key product types in LEO satellite market are small satellites, _femtosatellite (less than 0.01 kg), _pico-satellite (0.01-1 kg), _nanosats (1–10 kg), _microsats (10–100 kg), _minisats (100-180 kg), medium satellites (180 - 1000 kg) and large satellite (above 1000 kg).
In terms of frequency, ka-band: 26–40 ghz segment to command 32.0% share in the LEO satellite market in 2025.






Our Research Products

The "Full Research Suite" delivers actionable market intel, deep dives on markets or technologies, so clients act faster, cut risk, and unlock growth.

The Leaderboard benchmarks and ranks top vendors, classifying them as Established Leaders, Leading Challengers, or Disruptors & Challengers.

Locates where complements amplify value and substitutes erode it, forecasting net impact by horizon

We deliver granular, decision-grade intel: market sizing, 5-year forecasts, pricing, adoption, usage, revenue, and operational KPIs—plus competitor tracking, regulation, and value chains—across 60 countries broadly.

Spot the shifts before they hit your P&L. We track inflection points, adoption curves, pricing moves, and ecosystem plays to show where demand is heading, why it is changing, and what to do next across high-growth markets and disruptive tech

Real-time reads of user behavior. We track shifting priorities, perceptions of today’s and next-gen services, and provider experience, then pace how fast tech moves from trial to adoption, blending buyer, consumer, and channel inputs with social signals (#WhySwitch, #UX).

Partner with our analyst team to build a custom report designed around your business priorities. From analysing market trends to assessing competitors or crafting bespoke datasets, we tailor insights to your needs.
Supplier Intelligence
Discovery & Profiling
Capacity & Footprint
Performance & Risk
Compliance & Governance
Commercial Readiness
Who Supplies Whom
Scorecards & Shortlists
Playbooks & Docs
Category Intelligence
Definition & Scope
Demand & Use Cases
Cost Drivers
Market Structure
Supply Chain Map
Trade & Policy
Operating Norms
Deliverables
Buyer Intelligence
Account Basics
Spend & Scope
Procurement Model
Vendor Requirements
Terms & Policies
Entry Strategy
Pain Points & Triggers
Outputs
Pricing Analysis
Benchmarks
Trends
Should-Cost
Indexation
Landed Cost
Commercial Terms
Deliverables
Brand Analysis
Positioning & Value Prop
Share & Presence
Customer Evidence
Go-to-Market
Digital & Reputation
Compliance & Trust
KPIs & Gaps
Outputs
Full Research Suite comprises of:
Market outlook & trends analysis
Interviews & case studies
Strategic recommendations
Vendor profiles & capabilities analysis
5-year forecasts
8 regions and 60+ country-level data splits
Market segment data splits
12 months of continuous data updates
DELIVERED AS:
PDF EXCEL ONLINE
LEO Terminal Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Ileostomy Market
Paleo Food Market Trends - Growth & Consumer Demand 2025 to 2035
Nucleotide Market Analysis - Size, Growth, and Forecast 2025 to 2035
Nucleotide Premixes Market Analysis by form, application and region Flavors Through 2035
USA Nucleotide Premixes Market Report – Size, Trends & Industry Forecast 2025-2035
Oligonucleotide API Market Forecast and Outlook 2025 to 2035
Supramalleolar Osteotomy Implants Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Yeast Nucleotides Market Analysis by Product Type, Nature, Form and Application Through 2035
Turmeric Oleoresin Market – Growth & Demand 2025 to 2035
Single Nucleotide Polymorphism (SNP) Genotyping Market
Microbial Nucleotides Market Analysis - Size, Share, and Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Spice Oils and Oleoresins Market Analysis - Size, Share, and Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Antisense Oligonucleotides Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Demand for Spice Oils and Oleoresins in the EU Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Analysis and Growth Projections for Asia Pacific Essential Oil and Oleoresin Business
Satellite Launch Vehicle Market Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Satellite Simulator Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Satellite Communication Components Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035

Thank you!
You will receive an email from our Business Development Manager. Please be sure to check your SPAM/JUNK folder too.
Chat With
MaRIA