The Low Voltage Disconnect Switch Market is estimated to be valued at USD 4.0 billion in 2025 and is projected to reach USD 6.2 billion by 2035, registering a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4.5% over the forecast period. The low voltage disconnect switch market is projected to expand steadily from USD 3.2 billion in 2024 to approximately USD 6.2 billion by 2035, resulting in an overall increase of USD 3.0 billion over the 16-year period. From 2024 to 2029, the market is set to grow from USD 3.2 billion to USD 4.2 billion, delivering an incremental gain of USD 1.0 billion, driven by rising investments in power distribution infrastructure, modernization of electrical grids, and the replacement of aging mechanical switches with advanced, safety-compliant disconnect solutions. This phase benefits from demand in industrial facilities, commercial complexes, and renewable energy installations requiring reliable circuit isolation.
Between 2030 and 2034, the market advances from USD 4.4 billion to USD 5.4 billion, adding USD 1.0 billion in value as automation in switching systems gains traction, and adoption of arc-flash protection and remote operation features becomes standard practice. Growth during this period is also supported by stricter electrical safety regulations and increased demand in data centers and critical power applications.
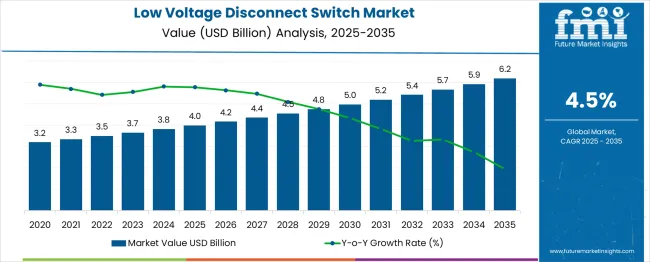
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Low Voltage Disconnect Switch Market Estimated Value in (2025 E) | USD 4.0 billion |
| Low Voltage Disconnect Switch Market Forecast Value in (2035 F) | USD 6.2 billion |
| Forecast CAGR (2025 to 2035) | 4.5% |
The low voltage disconnect switch market is experiencing consistent growth driven by increasing requirements for safe electrical isolation, fault protection, and maintenance efficiency across modern infrastructure. As industries pursue higher uptime and equipment reliability, the demand for reliable switching mechanisms that can isolate circuits without interrupting system integrity has surged.
Growth is being further supported by developments in compact switchgear systems, retrofitting capabilities, and enhanced thermal endurance of low voltage equipment. A shift toward decentralized energy systems, combined with expanded manufacturing and utility sector activities in both developed and emerging regions, has prompted greater adoption of low voltage disconnect switches for machine protection and control.
Regulatory mandates for safety compliance and fault prevention have also contributed to the uptake of these switches in critical operations such as HVAC systems, control panels, and distribution networks. As energy management solutions become more integrated with digital monitoring systems, low voltage disconnect switches are expected to play an increasingly pivotal role in ensuring system efficiency, equipment safety, and power reliability.
The low voltage disconnect switch market is segmented by type, installation, voltage range, application, and geographic regions. By type, the low voltage disconnect switch market is divided into Non-fused low voltage disconnect switches and fused low voltage disconnect switches. In terms of installation of the low voltage disconnect switch, the market is classified into panel-mounted, DIN rail-mounted, base-mounted, and others. Based on the voltage range, the low voltage disconnect switch market is segmented into 0-240V, 240- 480V, and above 480V. By application, the low voltage disconnect switch market is segmented into Automotive, Chemicals, Food & beverage, Healthcare, Mining, Oil & gas, Pharmaceuticals, Utilities, Commercial, Residential, and others. Regionally, the low voltage disconnect switch industry is classified into North America, Latin America, Western Europe, Eastern Europe, Balkan & Baltic Countries, Russia & Belarus, Central Asia, East Asia, South Asia & Pacific, and the Middle East & Africa.
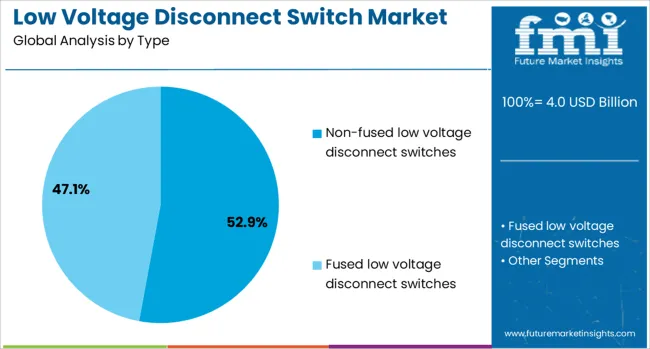
The nonfused low voltage disconnect switch segment is projected to capture 52.9% of the overall market revenue in 2025, positioning it as the leading product type. This dominance is attributed to its cost-effectiveness, simplified design, and suitability for systems where overcurrent protection is managed separately. Nonfused variants are widely preferred in applications requiring only a reliable disconnection mechanism, especially in configurations where circuit breakers or upstream fuses are already installed.
Their compact structure and lower maintenance requirements have increased deployment across industrial control panels and switchboards. The adaptability of these switches to modern electrical systems, along with streamlined installation and reduced downtime during maintenance, has reinforced their demand in environments where operational efficiency is a priority.
Advancements in arc suppression and contact durability have further strengthened their usage in low voltage setups. Their growing incorporation into standardized modular enclosures and intelligent control systems continues to drive their widespread adoption across both legacy systems and new installations.
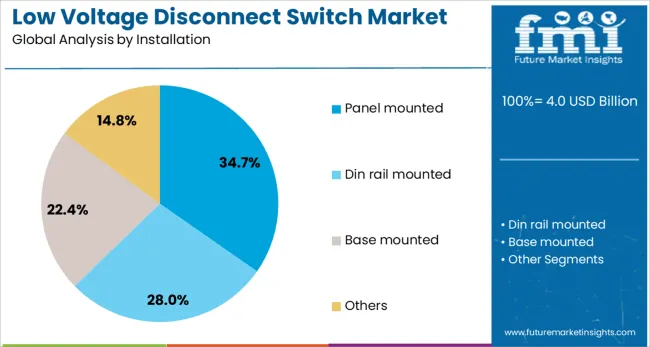
The panel mounted installation segment is expected to contribute 34.7% of the total market share in 2025, reflecting its strong foothold across control cabinets and industrial panels. This segment's growth is being supported by the demand for space-efficient electrical components that can be seamlessly integrated into existing switchgear assemblies. Panel mounted disconnect switches are often chosen for their secure fixing mechanism, simplified wiring access, and compatibility with a range of enclosure designs.
These attributes enable safer handling and more organized electrical layouts in power distribution units and automation panels. The segment's advancement is also tied to increased customization requirements in power management, where panel integration facilitates centralized control and visual status indication.
Enhanced mechanical endurance and the growing availability of smart-ready panel solutions are further enhancing the utility of panel mounted variants in sectors such as manufacturing, utilities, and building automation. Their deployment is increasingly aligned with standardized installation protocols and safety regulations across industrial settings.
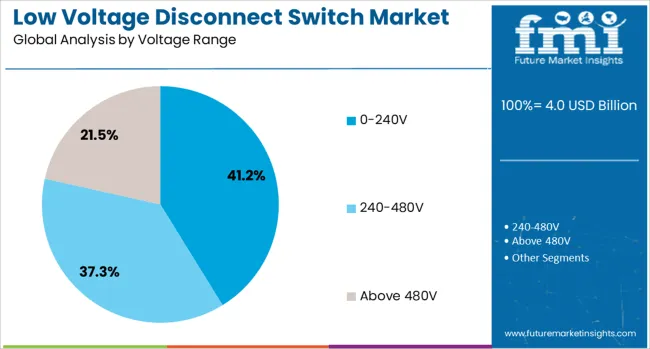
The 0 to 240V voltage range segment is projected to hold 41.2% of the market revenue share in 2025, making it the most significant range in low voltage disconnect switch applications. This is largely due to its widespread usage in residential, light commercial, and compact industrial environments where low voltage systems dominate. The segment's strength is underpinned by rising adoption in HVAC systems, lighting circuits, and auxiliary equipment that require quick and safe disconnection options.
The adaptability of switches operating within this range has aligned with trends in smart building infrastructure, solar inverters, and distributed energy systems. Their compatibility with standard circuit designs and existing electrical codes has made them a preferred choice for OEMs and facility managers.
Ongoing advancements in contact materials, thermal performance, and load handling capabilities have further expanded their applicability in diverse electrical ecosystems. As safety and energy efficiency remain central to low voltage infrastructure, the demand for disconnect switches in the 0 to 240V range is expected to maintain steady growth across global markets.
Low voltage disconnect switches are seeing rising adoption due to industrial expansion, regulatory enforcement, and improved product capabilities. Competitive differentiation and integration with smart systems are expected to sustain long-term demand growth.
Expansion in manufacturing, infrastructure, and commercial facilities has elevated the demand for low voltage disconnect switches. These devices are used to safely isolate electrical circuits, allowing for maintenance, repairs, or upgrades without interrupting broader operations. Industrial plants require reliable disconnection solutions to comply with safety codes and to protect sensitive equipment from electrical faults. Infrastructure projects, particularly in transportation, utilities, and public buildings, increasingly specify advanced disconnect switches for operational reliability. Growth in smart factories and automation-driven production lines has further strengthened their role in maintaining uninterrupted operations. The combination of safety requirements, operational efficiency, and compliance with electrical installation standards drives their adoption across industries and regions.
Stringent safety regulations and compliance frameworks in multiple regions are shaping the market for low voltage disconnect switches. Governments and regulatory bodies mandate the installation of certified disconnection devices in commercial, industrial, and residential projects to mitigate risks of electrical hazards. Standards such as IEC and UL influence manufacturing designs, ensuring that switches meet specific mechanical and electrical endurance criteria. Regulatory pressure in high-growth markets like Asia-Pacific, North America, and Europe is encouraging modernization of outdated systems. This is prompting end users to replace older units with advanced designs that offer improved arc suppression, compact form factors, and longer operational lifespans, directly benefiting suppliers with certified product portfolios.
Integration of advanced monitoring features, such as remote status indicators and smart connectivity options, is enhancing the operational value of low voltage disconnect switches. Industrial facilities are adopting models that can be incorporated into automated control systems for improved safety and real-time fault detection. This technological evolution supports predictive maintenance strategies, reducing downtime and repair costs. Compact modular designs are also enabling easier installation in space-constrained environments, increasing their appeal to contractors and facility managers. Enhanced materials, corrosion resistance, and better arc extinguishing mechanisms are improving reliability in harsh environments. These features are expanding the application scope beyond traditional industrial settings into renewable energy, marine, and specialized commercial applications.
The competitive environment for low voltage disconnect switches is shaped by multinational electrical equipment manufacturers and specialized component suppliers. Differentiation strategies include innovations in switch design, enhanced durability, and improved ease of operation. Strategic partnerships with distributors and system integrators are helping brands strengthen market reach. Companies are also focusing on product lines compatible with diverse voltage ranges and mounting configurations to cater to varied installation needs. Price competitiveness, coupled with value-added services like technical support and installation assistance, is influencing purchasing decisions. Manufacturers that offer compliance-certified, customizable solutions are better positioned to capture demand in projects requiring specialized configurations for industrial and commercial facilities.
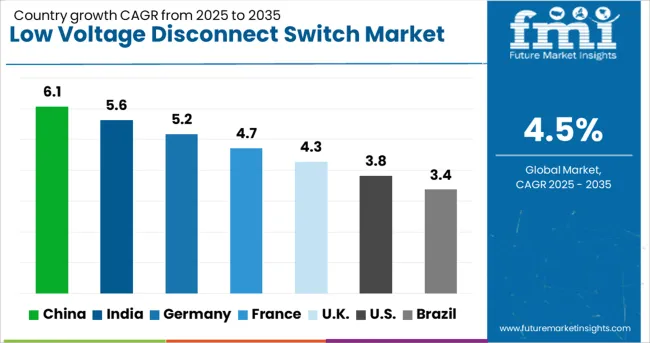
| Country | CAGR |
|---|---|
| China | 6.1% |
| India | 5.6% |
| Germany | 5.2% |
| France | 4.7% |
| UK | 4.3% |
| USA | 3.8% |
| Brazil | 3.4% |
The low voltage disconnect switch sector is projected to grow at a global CAGR of 4.5% from 2025 to 2035, supported by rising demand for electrical safety compliance, infrastructure expansion, and modernization of industrial facilities. China leads with a CAGR of 6.1%, driven by large-scale manufacturing growth, rapid power distribution upgrades, and increased adoption of advanced switchgear solutions. India follows at 5.6%, benefiting from expanding commercial real estate, industrial automation, and strong investments in grid modernization. France records a CAGR of 4.7%, supported by stringent safety regulations and upgrades in public infrastructure. The United Kingdom achieves 4.3% growth, aided by renewable energy integration and retrofitting needs in older facilities. The United States posts a CAGR of 3.8%, reflecting a mature environment where replacement cycles, compliance upgrades, and niche industrial applications sustain demand. This analysis includes over 40 countries, with these markets serving as prime indicators for investment strategies, competitive positioning, and innovation priorities in the global low voltage disconnect switch industry.
China is positioned to outpace the world average as low voltage disconnect switches see widespread specification in factories, public infrastructure, and commercial buildings. A 6.1% CAGR in 2025-2035 is expected, set against continuous power distribution upgrades and dense contractor networks that prefer certified isolation hardware. High-volume industrial parks, metro extensions, and warehousing projects keep panelboard and switchboard orders elevated, with isolation devices mandated for safe maintenance and downtime control. Project bundling by EPC firms encourages multi-site procurement, lifting unit throughput for leading brands. Localized assembly, shorter lead times, and service coverage improve replacement cycles in coastal and inland provinces. Integration with monitoring relays and arc-mitigation features is being prioritized by facility managers aiming for predictable O&M.
India enters a capacity-building phase in which low voltage disconnect switches are specified across commercial real estate, electronics manufacturing clusters, and data center corridors. A 5.6% CAGR during 2025-2035 is anticipated as state utilities, metro projects, and private developers standardize isolation devices for maintenance-safe panels. PLI-backed manufacturing and warehouse networks spur MV to LV downstep investments, increasing placements of load-break and fused isolators. Contractors value compact footprints and higher mechanical endurance, improving panel layout density. Tiered procurement frameworks in industrial townships encourage approved-vendor lists, strengthening branded portfolios. Secondary adoption in solar rooftops, cold chains, and institutional campuses expands the addressable base. Distributor financing and site-commissioning support improve conversion from design intent to installed base.
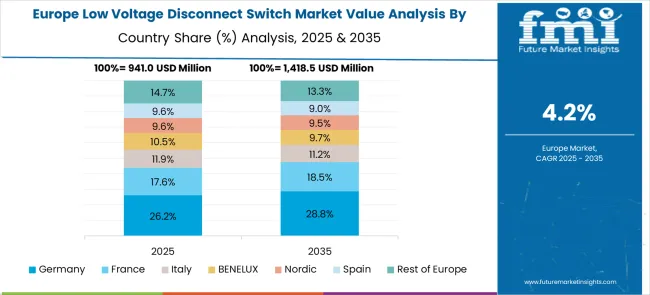
France maintains a rules-driven environment where safety conformity and lifecycle performance guide purchasing. A 4.7% CAGR for 2025-2035 is projected as public buildings, transit assets, and health facilities prioritize certified isolation devices for safe interventions. Replacement of aging panels accelerates in municipal programs, while private commercial upgrades seek better arc containment, clear position indication, and lockout capability. Hospital and pharma campuses emphasize disconnection reliability to protect sensitive loads, lifting demand for premium mechanisms and ingress protection. National retrofit schemes for energy systems translate into steady orders for DIN-rail and door-mounted isolators. Local engineering firms prefer harmonized IEC-certified ranges to simplify documentation and inspection. Distributor training and stocked spares enable fast MTTR in mission-critical sites.
The United Kingdom shows a measured recovery path, with modernizations in commercial estates, logistics hubs, and rail-related infrastructure supporting steady orders. The forward view points to a 4.3% CAGR during 2025-2035, marginally below the 4.5% global path yet notably stronger than the early-post-pandemic phase. For 2020-2024, the UK low voltage disconnect switch CAGR is estimated at about 3.1%, derived from muted capex, elongated project approvals, and supply chain friction relative to global normalization. The step-up toward 4.3% in 2025-2035 is explained by renewed refurbishment cycles in Grade-A offices, safety compliance tightening across facilities, and retrofit programs in older estates where clear isolation is mandated. Data center builds outside London, warehouse automation in the Midlands, and rail electrification works contribute incremental volumes and better mix.
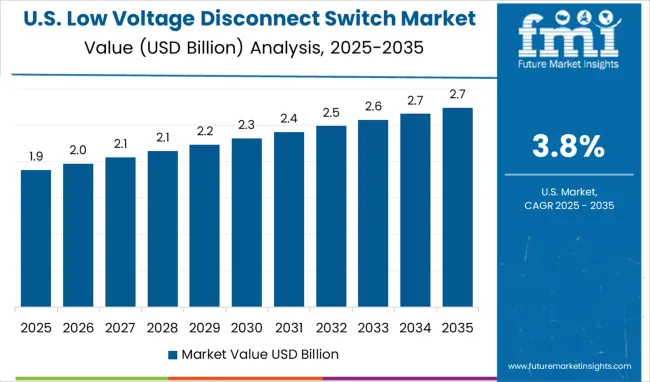
The United States presents a mature installed base where replacements, safety upgrades, and selective greenfield projects sustain demand. A 3.8% CAGR in 2025-2035 is expected as national contractors standardize on proven isolation families with strong mechanical life and visible break features. Healthcare, food processing, and semiconductors maintain elevated standards for safe isolation during maintenance, supporting higher-spec models. Warehouse automation and cold storage add steady panelboard orders, while educational and municipal retrofits keep public tenders active. Buyers emphasize UL-listed designs, clear lockout provisions, and serviceable accessories to reduce mean time to repair. Distributors with strong technical support and field start-up services gain preference in contractor bidding.
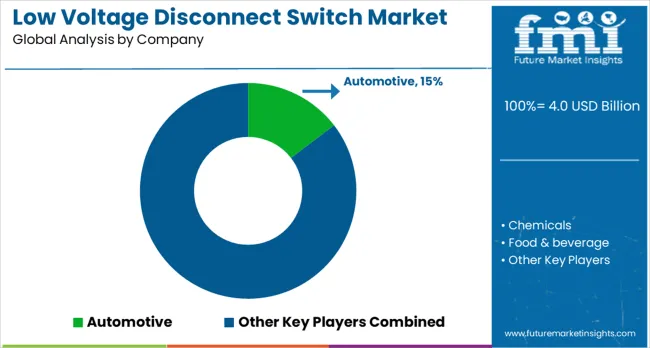
Dominant players, such as Schneider Electric, Siemens, ABB, Eaton, and General Electric, have historically pursued global acquisitions, product portfolio diversification, and compliance certifications (UL, IEC) to strengthen their market positioning. Emphasis was placed on industrial and commercial applications, integration with electrical panels, and collaboration with system integrators. Key players, including Legrand, Mitsubishi Electric, and Chint Group, focused on regional penetration, partnerships with distributors, and retrofitting solutions for legacy installations. Emerging companies leveraged niche innovation, including compact, IoT-enabled switches and enhanced safety features.
Forecast strategies indicate accelerated adoption of digital monitoring, predictive maintenance, and integration with renewable energy systems. Companies aim to provide energy-efficient, modular solutions adaptable to residential, commercial, and industrial microgrids. Differentiation levers include thermal and arc-fault protection, compact form factors, smart panel compatibility, and compliance with local and international safety standards. Growth opportunities are strongest in the APAC and North America regions, driven by the adoption of renewable energy, industrial automation, and infrastructure modernization. OEM collaborations, contract manufacturing, and targeted retrofit solutions remain key avenues for capturing market share and strengthening first-mover advantage in emerging applications.
| Item | Value |
|---|---|
| Quantitative Units | USD 4.0 Billion |
| Type | Non-fused low voltage disconnect switches and Fused low voltage disconnect switches |
| Installation | Panel mounted, Din rail mounted, Base mounted, and Others |
| Voltage Range | 0-240V, 240-480V, and Above 480V |
| Application | Automotive, Chemicals, Food & beverage, Healthcare, Mining, Oil & gas, Pharmaceuticals, Utilities, Commercial, Residential, and Others |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America, Middle East & Africa |
| Country Covered | United States, Canada, Germany, France, United Kingdom, China, Japan, India, Brazil, South Africa |
| Key Companies Profiled | Automotive, Chemicals, Food & beverage, Healthcare, Mining, Oil & gas, Pharmaceuticals, Utilities, Commercial, Data centers, Infrastructure, Residential, and Others |
| Additional Attributes | Dollar sales, share, competitive positioning, regional demand trends, regulatory impacts, technology preferences, pricing benchmarks, supply chain risks, end-user adoption rates, and growth opportunities by sector. |
The global low voltage disconnect switch market is estimated to be valued at USD 4.0 billion in 2025.
The market size for the low voltage disconnect switch market is projected to reach USD 6.2 billion by 2035.
The low voltage disconnect switch market is expected to grow at a 4.5% CAGR between 2025 and 2035.
The key product types in low voltage disconnect switch market are non-fused low voltage disconnect switches and fused low voltage disconnect switches.
In terms of installation, panel mounted segment to command 34.7% share in the low voltage disconnect switch market in 2025.






Our Research Products

The "Full Research Suite" delivers actionable market intel, deep dives on markets or technologies, so clients act faster, cut risk, and unlock growth.

The Leaderboard benchmarks and ranks top vendors, classifying them as Established Leaders, Leading Challengers, or Disruptors & Challengers.

Locates where complements amplify value and substitutes erode it, forecasting net impact by horizon

We deliver granular, decision-grade intel: market sizing, 5-year forecasts, pricing, adoption, usage, revenue, and operational KPIs—plus competitor tracking, regulation, and value chains—across 60 countries broadly.

Spot the shifts before they hit your P&L. We track inflection points, adoption curves, pricing moves, and ecosystem plays to show where demand is heading, why it is changing, and what to do next across high-growth markets and disruptive tech

Real-time reads of user behavior. We track shifting priorities, perceptions of today’s and next-gen services, and provider experience, then pace how fast tech moves from trial to adoption, blending buyer, consumer, and channel inputs with social signals (#WhySwitch, #UX).

Partner with our analyst team to build a custom report designed around your business priorities. From analysing market trends to assessing competitors or crafting bespoke datasets, we tailor insights to your needs.
Supplier Intelligence
Discovery & Profiling
Capacity & Footprint
Performance & Risk
Compliance & Governance
Commercial Readiness
Who Supplies Whom
Scorecards & Shortlists
Playbooks & Docs
Category Intelligence
Definition & Scope
Demand & Use Cases
Cost Drivers
Market Structure
Supply Chain Map
Trade & Policy
Operating Norms
Deliverables
Buyer Intelligence
Account Basics
Spend & Scope
Procurement Model
Vendor Requirements
Terms & Policies
Entry Strategy
Pain Points & Triggers
Outputs
Pricing Analysis
Benchmarks
Trends
Should-Cost
Indexation
Landed Cost
Commercial Terms
Deliverables
Brand Analysis
Positioning & Value Prop
Share & Presence
Customer Evidence
Go-to-Market
Digital & Reputation
Compliance & Trust
KPIs & Gaps
Outputs
Full Research Suite comprises of:
Market outlook & trends analysis
Interviews & case studies
Strategic recommendations
Vendor profiles & capabilities analysis
5-year forecasts
8 regions and 60+ country-level data splits
Market segment data splits
12 months of continuous data updates
DELIVERED AS:
PDF EXCEL ONLINE
Low Voltage Commercial Switchgear Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Low Voltage Residential Switchgear Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Vacuum Insulated Low Voltage Commercial Switchgear Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Indoor Rotary High Voltage Disconnect Switch Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Low Voltage Components Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Low Voltage Substation Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Low Voltage Distribution Panel Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Low Voltage Surge Arrester Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Low Voltage Transmission Substation Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Low Voltage Commercial Electric Boiler Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Low Voltage Composite Insulators Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Low Voltage Digital Substation Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Low Voltage Drives Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Low Voltage Electric Boiler Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Low Voltage Electric Capacitor Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Low Voltage Wire And Cable Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Low Voltage Cable Market Size, Growth, and Forecast 2025 to 2035
Low Voltage Motor Market Growth – Trends & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Low Voltage Motor Control Center Market Growth – Trends & Forecast (2024-2034)
Low Voltage Protection and Control Market Growth – Trends & Forecast 2024-2034

Thank you!
You will receive an email from our Business Development Manager. Please be sure to check your SPAM/JUNK folder too.
Chat With
MaRIA