The Marine Variable Frequency Drives Market is estimated to be valued at USD 1.0 billion in 2025 and is projected to reach USD 1.7 billion by 2035, registering a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.0% over the forecast period. Market share gain is expected for manufacturers offering compact, energy-efficient VFDs designed for hybrid propulsion and electric ship systems. These technologies are increasingly preferred by naval architects and vessel operators seeking compliance with emissions and fuel-efficiency regulations.
Vendors capable of integrating smart diagnostics and load-adaptive features are likely to gain share as operational cost savings become a priority in commercial fleets. Conversely, share erosion is projected for suppliers focused solely on legacy AC drive configurations without modular upgrade pathways. These systems are expected to lose competitiveness as shipbuilders move toward optimized onboard energy systems and demand flexibility in retrofitting.
Regional players lacking global certifications or integration with automation control systems may also see reduced share, especially in large-volume contracts for offshore support vessels and cruise segments. The shift from mechanical control to electrical propulsion continues to favor manufacturers aligned with long-term electrification trends. Overall, share redistribution across the forecast period is likely to be shaped by technological alignment, vessel class-specific compliance, and aftersales support infrastructure.
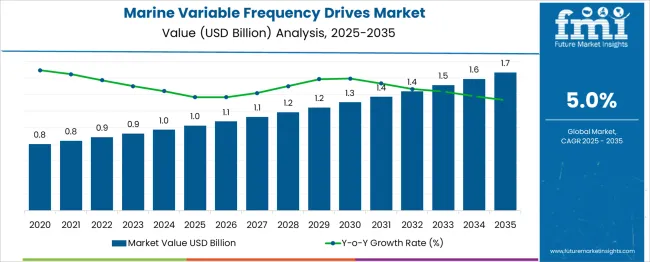
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Marine Variable Frequency Drives Market Estimated Value in (2025 E) | USD 1.0 billion |
| Marine Variable Frequency Drives Market Forecast Value in (2035 F) | USD 1.7 billion |
| Forecast CAGR (2025 to 2035) | 5.0% |
The marine variable frequency drives market comprises roughly 33–35 % of the global marine propulsion and auxiliary control systems segment, enabling speed control in motors powering thrusters, compressors, and pumps. It contributes about 30–34 % to the marine energy efficiency systems market, driven by demand for lower fuel consumption and load optimization. In ship electrification infrastructure, its share is estimated at 25–28 %, where integration into power distribution systems is increasing. Across marine automation and control segments, VFDs hold around 15–18 % as vessel designs shift toward intelligent load management. Retrofitting of older fleets contributes approximately 10–12 %, positioning VFDs as a key enabler for modernization and regulatory compliance. Technical developments are focused on compact, high-efficiency AC VFDs capable of operating in harsh marine conditions and confined engine room spaces. Liquid-cooled units are being adopted in vessels requiring higher power density and thermal stability. Intelligent drive platforms equipped with real-time diagnostics and motor protection features are supporting predictive maintenance strategies. Hybrid-compatible VFD systems are enabling seamless integration with dual-fuel and battery-supported propulsion setups. Key suppliers are enhancing system compatibility with dynamic positioning, azimuth thrusters, and HVAC systems. These advancements reflect a broader shift toward smarter vessel design, where power modulation and energy efficiency have become priorities across both newbuild and retrofit applications.
The Marine Variable Frequency Drives market is undergoing notable transformation as ship operators and marine system integrators adopt energy-efficient technologies to reduce fuel consumption and emissions. Growth in the market is being propelled by global maritime regulations that emphasize energy conservation and carbon footprint reduction, particularly under frameworks like IMO 2020. The increasing demand for precise motor control in propulsion, pumping, and HVAC applications aboard vessels is further driving the adoption of variable frequency drives.
Advancements in drive technologies that support better torque control, overload protection, and energy optimization are providing a competitive edge for system suppliers. Market players are also investing in ruggedized, marine-grade VFD solutions that can withstand high humidity, temperature, and vibration conditions.
These developments are aligning with the marine industry's long-term objectives of achieving operational efficiency, safety, and compliance with environmental standards. The adoption of variable frequency drives is expected to expand across both retrofit and new-build vessel programs, ensuring sustainable growth in the years ahead..
The marine variable frequency drives market is segmented by voltage and drive and geographic regions. By voltage of the marine variable frequency drives market is divided into Low and Medium. In terms of drive of the marine variable frequency drives market is classified into AC, DC, and Servo. Regionally, the marine variable frequency drives industry is classified into North America, Latin America, Western Europe, Eastern Europe, Balkan & Baltic Countries, Russia & Belarus, Central Asia, East Asia, South Asia & Pacific, and the Middle East & Africa.
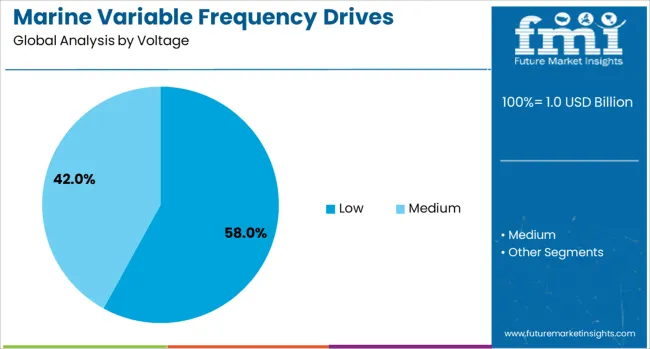
The low voltage segment is anticipated to hold 58% of the Marine Variable Frequency Drives market revenue share in 2025, making it the dominant voltage category. This dominance has been shaped by the growing use of low voltage VFDs in onboard equipment where compact design, operational flexibility, and energy efficiency are critical.
These drives are increasingly being integrated into ventilation systems, cargo pumps, winches, and auxiliary engines, which typically require less than 690 volts. Low voltage drives have been favored for their ease of installation, lower cost of maintenance, and compatibility with standard onboard power systems.
Their ability to deliver precise speed control and energy optimization has led to significant reductions in fuel consumption and mechanical stress, particularly in auxiliary systems. As ship operators focus on reducing emissions and improving vessel performance, the adoption of intelligent low voltage VFDs with condition monitoring and digital interface capabilities is expected to continue its upward trajectory, reinforcing the segment's leading market position..
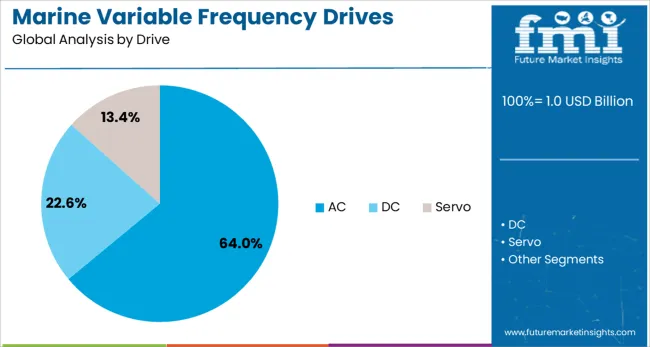
The AC drive segment is projected to account for 64% of the Marine Variable Frequency Drives market revenue share in 2025, establishing its leadership within the drive type category. This growth has been supported by the widespread deployment of AC motors across marine systems, which require effective control solutions for propulsion, thrusters, compressors, and pumps. AC drives have been preferred due to their reliability, scalability, and ability to provide variable torque and speed performance under fluctuating load conditions.
Their higher energy efficiency and reduced harmonic distortion have made them the choice solution for modern vessels aiming to comply with maritime energy regulations. Additionally, AC drives require less maintenance compared to their DC counterparts, offering longer service life and higher operational uptime.
Enhanced software functionality in AC VFDs is enabling better integration with ship automation systems and real-time diagnostics, further improving decision-making and system resilience. As marine vessels continue to evolve toward more electric architectures, the AC drive segment is positioned to remain at the forefront of market demand..
Growth in the marine variable frequency drives market has been supported by increasing demand for energy-efficient propulsion and auxiliary systems aboard ships. Marine VFDs optimize pump, fan, and compressor operation by enabling speed modulation, which reduces fuel consumption and engine wear. Adoption has been driven by new-build vessel orders and retrofit upgrades in tanker, cruise, and offshore sectors. Integration with automation and control systems has further expanded adoption. Demand is rising in regions pursuing emissions control via slower steaming and green ship initiatives, reinforcing marine VFD market traction.
Marine operators have prioritized variable frequency drive systems to optimize vessel energy management and comply with emission control regimes. VFDs allow adjustable speed control for auxiliary systems, leading to energy savings of up to 25% per application. This results in reduced engine load and lower greenhouse gas emissions, especially when vessels operate under slow steaming strategies. Cruise ships, cargo vessels, and offshore platforms are integrating VFDs into propulsion auxiliaries and HVAC systems to meet Tier III and zero‑emission regulations. Retrofit installations are commonly specified during dry‑dock refits, aiming to upgrade efficiency without major hull modifications. These performance benefits have made VFDs standard components in vessel modernization and new construction projects.
Marine VFDs are increasingly deployed within integrated control systems to enhance vessel performance. Real-time monitoring and adaptive control have allowed VFDs to regulate rotational speed based on load demands, minimizing mechanical stress and improving pump/compressor lifespans. Diagnostic interfaces and predictive maintenance features embedded in VFD controllers have enabled seafarer teams to anticipate system faults and schedule service proactively. Integration with bridge automation systems allows seamless coordination of power units with navigation profiles, improving response during port maneuvers and dynamic positioning tasks. Standardization efforts are driving compatibility between marine drives and onboard SCADA or automation protocols. These capabilities have elevated VFDs from simple speed controllers to critical enablers of holistic vessel optimization strategies.
Though long-term operational savings are significant, initial investment in marine VFD systems remains a barrier. Equipment cost is influenced by marine-grade components, certifications, and custom housings suitable for corrosive and vibration-prone environments. Retrofit installations frequently require structural repositioning, control system integration, and alignment with electrical safety modules, which can extend dry dock refit durations. Smaller or older vessels often face budget constraints or limited access to retrofit financing. A shortage of trained marine electrical technicians hinders installation speed and system commissioning. Inconsistent vessel documentation and legacy control architectures add complexity. Unless supported by strategic upgrade planning or incentive programs, VFD adoption may remain deferred in mid-life marine platforms.
Regional regulatory frameworks and green shipping commitments have shaped VFD adoption levels worldwide. In Europe and North America, emission-control zones and slow-steaming guidelines have accelerated integration of VFDs into new and existing fleets. The Asia-Pacific region is witnessing growing retrofit activity driven by expanding cruise and bulk carrier operations prioritizing fuel reduction. Emerging maritime markets in South America and Africa are gradually introducing green vessel upgrade mandates, unlocking retrofit opportunities. Classification societies are increasingly certifying vessels outfitted with variable frequency drives for carbon compliance and marine efficiency labels. As green corridors and low‑carbon shipping lanes form, marine stakeholders are prioritizing VFDs to enhance energy recovery and electrical load control aboard sea‑going assets.
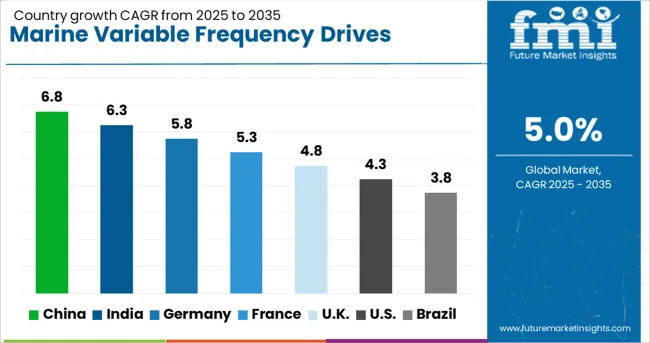
| Country | CAGR |
|---|---|
| China | 6.8% |
| India | 6.3% |
| Germany | 5.8% |
| France | 5.3% |
| UK | 4.8% |
| USA | 4.3% |
| Brazil | 3.8% |
The global marine variable frequency drives market is forecast to grow at a CAGR of 5% between 2025 and 2035. Among the 40+ countries analyzed, China leads with a CAGR of 6.8%, followed by India at 6.3% and Germany at 5.8%. The United Kingdom remains just below the global average at 4.8%, while the United States trails at 4.3%. Growth in China and India is shaped by shipbuilding capacity expansions and propulsion energy efficiency mandates. Germany’s above-baseline performance reflects modernisation in its inland and Baltic marine logistics segments. In contrast, restrained growth in the US and UK is influenced by slower fleet electrification and limited retrofitting of existing vessels. The report includes detailed coverage of 40+ countries, with the top five presented for benchmarking.
China’s marine variable frequency drives market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 6.8% through 2035. Expansion in naval and commercial shipbuilding, particularly in Jiangsu and Guangdong, is supporting high-voltage VFD deployment across propulsion and HVAC systems. Domestic OEMs such as Inovance and Zhuzhou CRRC Times Electric are expanding three-phase AC drive modules tailored for marine power density requirements. Integration of regenerative braking and hybrid-electric drives is increasing in auxiliary systems, enhancing vessel energy profiles. Retrofit subsidies and mandatory adoption in certain vessel classes are reinforcing demand.
India is expected to grow at a CAGR of 6.3% in the marine variable frequency drives market during the forecast period. Domestic shipbuilding policy, including the Shipbuilding Financial Assistance Policy, is facilitating hybrid retrofits in coastal cargo and passenger fleets. Players like ABB India and Schneider Electric are expanding marine-certified low-voltage VFD systems with IP66 enclosures for humid environments. Adoption is concentrated in Tamil Nadu, Gujarat, and Maharashtra, where dockyard upgrades and coastal logistics reforms are driving equipment procurement.
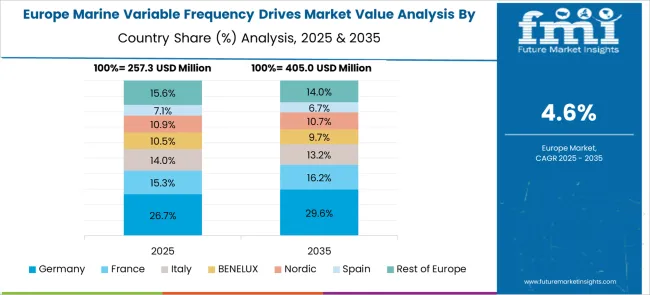
Germany is forecast to register a CAGR of 5.8% in the marine variable frequency drives market from 2025 to 2035. Growth is anchored in decarbonization targets for inland freight and passenger transport. Siemens and Danfoss are advancing VFD systems with low harmonic distortion for maritime grid compatibility. Activity is concentrated around ports in Hamburg and Kiel, where vessels transitioning to electric propulsion are favoring modular drive units. Regulatory push under the National Hydrogen Strategy is also supporting integration of VFDs in hydrogen-electric demonstrators.
The marine variable frequency drives market in the United Kingdom is projected to grow at a CAGR of 4.8% between 2025 and 2035. Growth is led by hybrid retrofit programs in Scotland and Wales, targeting fishing, ferry, and patrol fleets. OEMs such as Parker Hannifin and Control Techniques are introducing marine VFD units compatible with lithium-ion and hydrogen fuel cell systems. Adoption remains limited in large commercial vessels due to low fleet turnover. Technical labor shortages also constrain installation throughput in regional ports.
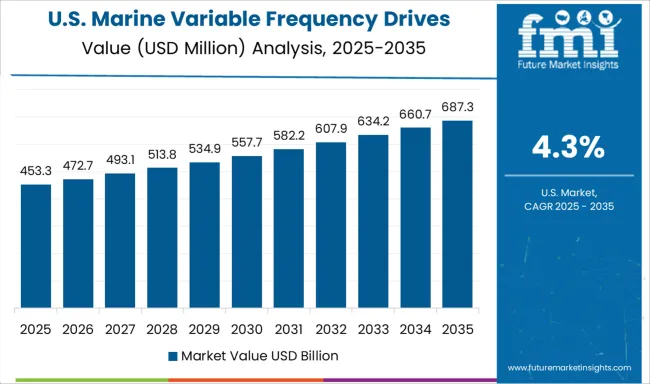
The United States is expected to grow at a CAGR of 4.3% in the marine variable frequency drives market from 2025 to 2035. Growth is focused in the Great Lakes and Gulf Coast regions, where emission controls and propulsion upgrades are mandated in public service and dredging fleets. Eaton and Rockwell Automation are offering UL Marine-listed VFD systems optimized for auxiliary propulsion and cargo handling systems. However, uptake remains restrained by fragmented regulatory enforcement and dependence on legacy diesel setups in key segments.
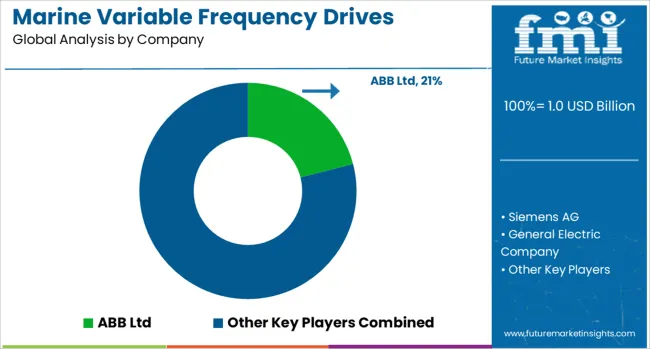
ABB Ltd has expanded its marine VFD portfolio by targeting propulsion and auxiliary systems in commercial vessels and offshore platforms. Its ACS880 series supports flexible torque control and compatibility with marine-class certifications. Focus has been placed on lifecycle services and retrofit solutions for aging fleets, particularly in Europe and Asia. Siemens AG delivers VFDs optimized for marine HVAC, cranes, and thruster applications, with Sinamics drives engineered for harsh marine conditions. Integrated automation capabilities have helped strengthen its position in both new builds and retrofit markets.
General Electric Company offers medium-voltage marine VFDs tailored for propulsion, pump, and winch applications, primarily in defense and merchant shipping. Its emphasis lies in digital monitoring and performance diagnostics to support predictive maintenance. Schneider Electric provides compact marine drives for ventilation, chilled water systems, and deck equipment. Energy efficiency and ease of commissioning are core differentiators. Rockwell Automation has developed scalable VFD systems for marine OEMs and shipbuilders, with its Allen-Bradley drives supporting modular architecture for distributed control. Strategic partnerships with marine integrators and emphasis on class-compliant hardware have helped expand adoption across regional shipbuilding hubs and retrofit service providers.
High-performance VFDs with liquid cooling and modular architecture were deployed to improve energy efficiency in electric tugs and hybrid vessels.
New models focused on optimizing motor torque in low-speed operations, enhancing maneuverability and fuel savings. Retrofit demand increased as operators upgraded legacy systems to comply with emission targets. Advanced VFD systems integrated real-time diagnostics and remote monitoring to support predictive maintenance in maritime environments.
| Item | Value |
|---|---|
| Quantitative Units | USD 1.0 Billion |
| Voltage | Low and Medium |
| Drive | AC, DC, and Servo |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America, Middle East & Africa |
| Country Covered | United States, Canada, Germany, France, United Kingdom, China, Japan, India, Brazil, South Africa |
| Key Companies Profiled | ABB Ltd, Siemens AG, General Electric Company, Schneider Electric, and Rockwell Automation |
The global marine variable frequency drives market is estimated to be valued at USD 1.0 billion in 2025.
The market size for the marine variable frequency drives market is projected to reach USD 1.7 billion by 2035.
The marine variable frequency drives market is expected to grow at a 5.0% CAGR between 2025 and 2035.
The key product types in marine variable frequency drives market are low and medium.
In terms of drive, ac segment to command 64.0% share in the marine variable frequency drives market in 2025.






Our Research Products

The "Full Research Suite" delivers actionable market intel, deep dives on markets or technologies, so clients act faster, cut risk, and unlock growth.

The Leaderboard benchmarks and ranks top vendors, classifying them as Established Leaders, Leading Challengers, or Disruptors & Challengers.

Locates where complements amplify value and substitutes erode it, forecasting net impact by horizon

We deliver granular, decision-grade intel: market sizing, 5-year forecasts, pricing, adoption, usage, revenue, and operational KPIs—plus competitor tracking, regulation, and value chains—across 60 countries broadly.

Spot the shifts before they hit your P&L. We track inflection points, adoption curves, pricing moves, and ecosystem plays to show where demand is heading, why it is changing, and what to do next across high-growth markets and disruptive tech

Real-time reads of user behavior. We track shifting priorities, perceptions of today’s and next-gen services, and provider experience, then pace how fast tech moves from trial to adoption, blending buyer, consumer, and channel inputs with social signals (#WhySwitch, #UX).

Partner with our analyst team to build a custom report designed around your business priorities. From analysing market trends to assessing competitors or crafting bespoke datasets, we tailor insights to your needs.
Supplier Intelligence
Discovery & Profiling
Capacity & Footprint
Performance & Risk
Compliance & Governance
Commercial Readiness
Who Supplies Whom
Scorecards & Shortlists
Playbooks & Docs
Category Intelligence
Definition & Scope
Demand & Use Cases
Cost Drivers
Market Structure
Supply Chain Map
Trade & Policy
Operating Norms
Deliverables
Buyer Intelligence
Account Basics
Spend & Scope
Procurement Model
Vendor Requirements
Terms & Policies
Entry Strategy
Pain Points & Triggers
Outputs
Pricing Analysis
Benchmarks
Trends
Should-Cost
Indexation
Landed Cost
Commercial Terms
Deliverables
Brand Analysis
Positioning & Value Prop
Share & Presence
Customer Evidence
Go-to-Market
Digital & Reputation
Compliance & Trust
KPIs & Gaps
Outputs
Full Research Suite comprises of:
Market outlook & trends analysis
Interviews & case studies
Strategic recommendations
Vendor profiles & capabilities analysis
5-year forecasts
8 regions and 60+ country-level data splits
Market segment data splits
12 months of continuous data updates
DELIVERED AS:
PDF EXCEL ONLINE
Marine Nanocoating Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Marine-grade Polyurethane Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Marine Electronics Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Marine Toxin Market Size and Share Forecast and Outlook 2025 to 2035
Marine Thermal Fluid Heaters Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Marine Nutraceutical Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Marine Power Battery System Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Marine Life Raft Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Marine Trenchers Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Marine Electronics Tester Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Marine Steering Systems Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Marine & Dock Gangways Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Marine HVAC System Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Marine Outboard Engines Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Marine Stabilizers Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Marine Fuel Injection System Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Marine Energy Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Marine Propulsion Engine Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Marine Protein Hydrolysate Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Marine Fin Stabilizer Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035

Thank you!
You will receive an email from our Business Development Manager. Please be sure to check your SPAM/JUNK folder too.
Chat With
MaRIA