The Maritime Patrol Aircraft Market is estimated to be valued at USD 8.4 billion in 2025 and is projected to reach USD 24.8 billion by 2035, registering a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 11.5% over the forecast period.
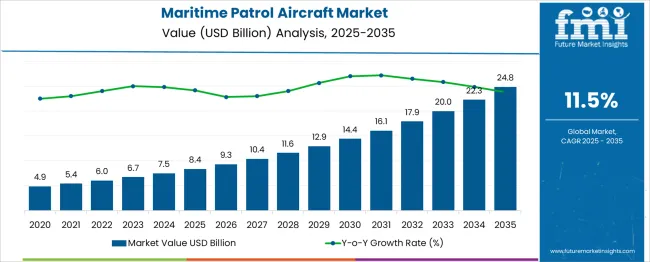
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Maritime Patrol Aircraft Market Estimated Value in (2025 E) | USD 8.4 billion |
| Maritime Patrol Aircraft Market Forecast Value in (2035 F) | USD 24.8 billion |
| Forecast CAGR (2025 to 2035) | 11.5% |
The maritime patrol aircraft market is advancing steadily as maritime security threats, territorial disputes, and demand for surveillance of exclusive economic zones intensify. Naval modernization programs and growing emphasis on integrated coastal defense have accelerated procurement of advanced aircraft designed for reconnaissance, anti-submarine warfare, and search and rescue missions.
The integration of multi-role capabilities, improved endurance, and sophisticated sensors is driving adoption among defense forces seeking cost-effective yet highly capable platforms. Future growth is expected to be underpinned by technological innovations in radar, communications, and weapons systems alongside strategic collaborations between aircraft manufacturers and defense ministries.
Rising operational demands in contested waters and expanding responsibilities for monitoring shipping lanes are paving the path for further investment and deployment of modern maritime patrol fleets.
The maritime patrol aircraft market is segmented by type, engine, component, platform, application, mode of operation, and geographic regions. By type, the maritime patrol aircraft market is divided into Armoured and Unarmoured. In terms of engine, the maritime patrol aircraft market is classified into turboprop and jet engines. Based on component, the maritime patrol aircraft market is segmented into Radar, Camera, Sensors, and Others. By platform, the maritime patrol aircraft market is segmented into fixed-wing and rotary-wing. By application, the maritime patrol aircraft market is segmented into Surveillance and reconnaissance, Combat support, Search and rescue, Coastal patrolling, and Others. By mode of operation, the maritime patrol aircraft market is segmented into Manned and Unmanned. Regionally, the maritime patrol aircraft industry is classified into North America, Latin America, Western Europe, Eastern Europe, Balkan & Baltic Countries, Russia & Belarus, Central Asia, East Asia, South Asia & Pacific, and the Middle East & Africa.
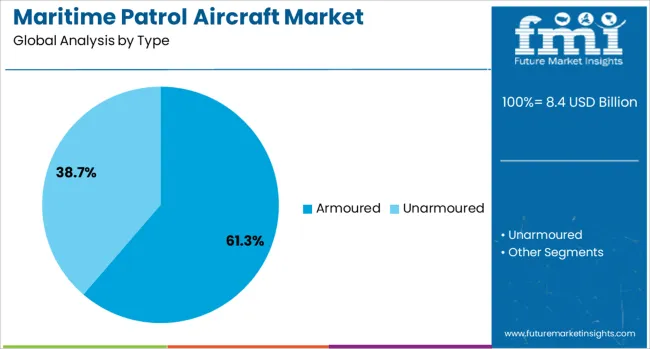
When segmented by type, the armoured segment is projected to hold 61.3% of the total market revenue in 2025, positioning it as the leading type. This dominance is attributed to the increasing operational need for enhanced protection against hostile threats while conducting missions over contested or high-risk maritime zones.
The ability of armoured configurations to withstand small arms fire and debris impact has reinforced confidence in deploying these aircraft for extended missions near conflict-prone areas. Additionally, armoured designs have enabled longer mission durations by improving survivability, which has been a critical factor in meeting the rigorous demands of modern naval operations.
The sustained emphasis on crew safety and mission assurance in volatile environments has further solidified the armoured segment’s leadership within the market.
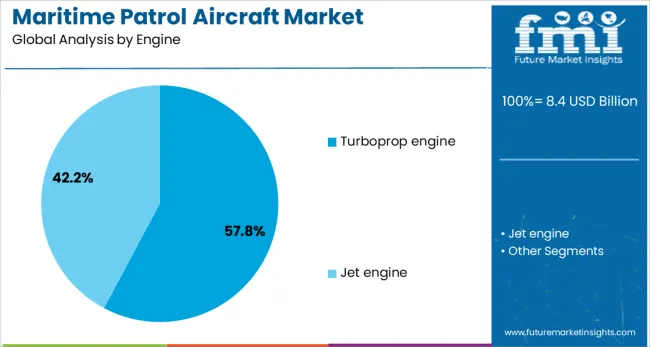
Segmented by engine type, the turboprop engine segment is expected to account for 57.8% of the market revenue in 2025, maintaining its position as the dominant engine category. This leadership has been driven by the operational efficiency and reliability of turboprop engines, which offer optimal fuel consumption for long-duration, low-altitude maritime missions.
The ability to sustain lower speeds for extended surveillance without compromising maneuverability has made turboprops particularly suited for maritime patrol duties. Their proven track record in diverse environmental conditions and lower maintenance costs compared to jet engines have further strengthened their preference in procurement decisions.
The combination of durability, cost-effectiveness, and mission suitability has enabled the turboprop engine segment to remain at the forefront of market adoption.
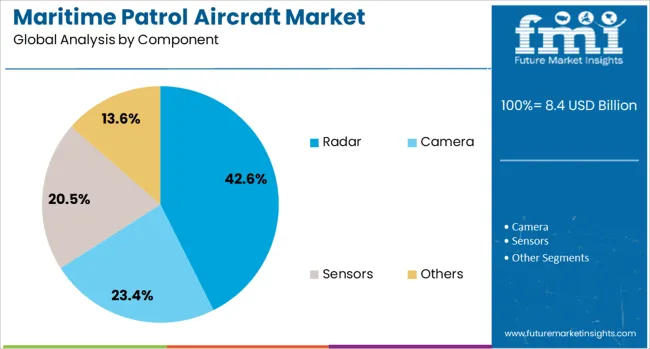
When segmented by component, the radar segment is projected to capture 42.6% of the market revenue in 2025, affirming its status as the leading component. This prominence is underpinned by the indispensable role of radar systems in detecting, tracking, and identifying surface and sub-surface threats across vast maritime territories.
Continuous advancements in radar technology have enhanced detection ranges, resolution, and multi-target tracking capabilities, which are critical for effective surveillance and reconnaissance missions. The integration of modern phased-array and over-the-horizon radars has improved situational awareness and response times, strengthening the overall operational effectiveness of maritime patrol missions.
As mission requirements evolve to address complex maritime security challenges, the radar component has remained a cornerstone of aircraft capability, securing its leadership position in the market.
Maritime patrol aircraft demand is expanding due to heightened maritime security needs, modernization programs, and multi-role mission capabilities. Strategic partnerships and technology-sharing agreements are further enhancing operational readiness and fleet sustainability.
Rising maritime threats, including piracy, smuggling, and illegal fishing, have driven the need for advanced patrol aircraft capable of conducting long-endurance missions. Governments are prioritizing coastal and offshore monitoring to secure economic zones and safeguard shipping lanes. Modern maritime patrol aircraft are being equipped with multi-mode radars, infrared sensors, and electronic intelligence suites to detect and track surface and subsurface activities. The emphasis on interoperability between naval and air forces is increasing to improve mission efficiency. Regional conflicts and disputes over territorial waters have intensified the procurement of upgraded aircraft with anti-submarine and anti-ship warfare capabilities. These trends are expected to maintain steady procurement cycles in both developed and emerging defense markets.
Many nations are replacing aging maritime patrol fleets with modern platforms that offer enhanced range, payload capacity, and mission flexibility. Aircraft such as the P-8 Poseidon and modernized turboprop variants are becoming popular for their adaptability to diverse maritime roles. Investments are focusing on integrating mission systems that support data fusion, satellite communications, and real-time intelligence sharing. Modular designs allow operators to upgrade sensors and weapons without replacing the entire platform, reducing life-cycle costs. Naval and air force collaborations are improving operational readiness. These modernization programs are often backed by long-term procurement contracts, ensuring continuous upgrades and sustained service availability across the fleet.
Maritime patrol aircraft are increasingly being configured for multi-role operations beyond traditional surveillance, including search and rescue, disaster response, and environmental monitoring. This versatility allows operators to justify procurement costs while enhancing operational value. Aircraft are being fitted with flexible mission bays, advanced avionics, and quick-change systems to transition between roles. The inclusion of electronic warfare suites and maritime strike weapons further expands mission scope. Governments are seeking aircraft that can operate effectively in both peacetime patrols and combat situations. The demand for platforms that can integrate with unmanned systems is growing, creating hybrid operational strategies for wider area coverage. This multi-role approach strengthens both peacetime utility and combat readiness.
Joint development initiatives between defense manufacturers and governments are accelerating technology transfer and reducing procurement timelines. Partnerships enable shared research, joint production, and localized assembly to meet regional defense requirements. Offset agreements are helping countries develop domestic aerospace capabilities while acquiring advanced maritime patrol platforms. Global defense contractors are collaborating with local firms to integrate indigenous mission systems, creating customized solutions for specific operational environments. Such partnerships improve supply chain resilience and maintenance support throughout the aircraft’s service life. Strategic collaborations also facilitate upgrades over time, allowing fleets to remain competitive against evolving threats and operational demands without requiring complete platform replacement.
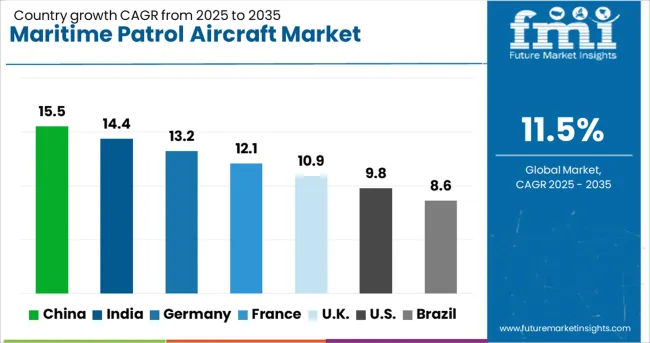
| Country | CAGR |
|---|---|
| China | 15.5% |
| India | 14.4% |
| Germany | 13.2% |
| France | 12.1% |
| UK | 10.9% |
| USA | 9.8% |
| Brazil | 8.6% |
The maritime patrol aircraft sector is expected to expand globally at a CAGR of 11.5% between 2025 and 2035, driven by heightened maritime security requirements, coastal surveillance programs, and modernization of naval aviation fleets. China leads with a CAGR of 15.5%, propelled by large-scale fleet procurement, regional power projection objectives, and integration of advanced anti-submarine warfare capabilities. India follows at 14.4%, supported by indigenous aircraft development, coastal defense initiatives, and expanded naval cooperation agreements. France posts 12.1%, driven by defense modernization programs and strategic overseas territorial monitoring. The United Kingdom grows at 10.9%, reflecting investments in next-generation maritime surveillance platforms and enhanced anti-ship warfare capabilities, while the United States records 9.8% as a mature market maintaining steady replacement and upgrade cycles for long-standing maritime patrol fleets. The analysis spans over 40 countries, with these six representing the primary drivers of procurement strategies, technological upgrades, and multi-role capability integration shaping the global maritime patrol aircraft landscape.
China is expected to register a 15.5% CAGR for 2025–2035, outpacing the global 11.5% baseline as long-range anti-submarine patrols, wide-area ISR coverage, and blue-water deployments receive priority funding. Fleet expansion has been supported by localized mission system supply, sonar buoy manufacturing, and airframe assembly that compress procurement cycles. Training pipelines and basing infrastructure have been scaled to improve sortie rates and endurance management across contested sea lanes. Maritime strike readiness has been elevated through integrated weapon carriage, data-linked targeting, and coordinated surface tasking. In this view, China’s trajectory appears durable, with multi-year orders, depot partnerships, and iterative avionics refreshes likely to keep upgrade momentum intact and life-cycle availability high relative to peer fleets.
India is projected to post a 14.4% CAGR for 2025–2035, above the global average, as coastal surveillance networks, anti-submarine operations, and SAR roles are prioritized. Procurement has been supported by indigenous content mandates and licensed assembly that reduce spares exposure and shorten maintenance downtimes. Multi-role tasking across fisheries protection, HADR, and deterrent patrols has been adopted to raise utilization and justify payload upgrades. The operating model increasingly favors modular bays, roll-on sensors, and quick reconfiguration, which limits aircraft downtime and increases mission availability. With stronger logistics chains and improved crew conversion pipelines, India’s fleet outlook appears resilient and positioned to scale through staggered tranches that balance capability with budget pacing.
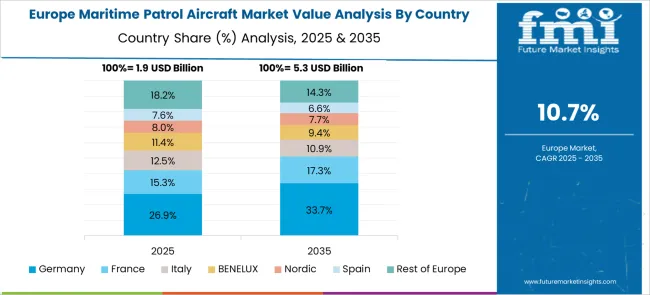
France is anticipated to achieve a 12.1% CAGR for 2025–2035, slightly above the global curve’s middle band, as overseas territories, Atlantic patrols, and Mediterranean missions anchor demand. Replacement of legacy types with longer-leg airframes and enhanced acoustic suites has been prioritized to maintain contact endurance against quiet subs. Enterprise planning favors mid-life upgrades and cockpit standardization that streamline training and improve fleet interchangeability across squadrons. Networked operations with surface groups and allied assets have been emphasized to lift detection probability and response timing. Budget discipline has been paired with predictable tranche ordering that secures supplier capacity and protects delivery slots, creating a credible path to sustained availability and mission readiness.
The United Kingdom is set to grow at a 10.9% CAGR for 2025–2035, slightly below the global 11.5% benchmark, as North Atlantic patrols, deterrence support, and multi-agency surveillance shape budgets. A distinct 3.4% CAGR characterized 2020–2024, when capability recapitalization was in early ramp with deliveries, crew conversion, and infrastructure commissioning pacing growth. The rise from 3.4% to 10.9% is attributed to transition from initial operational capability to stable multi-aircraft availability, maturing acoustic tactics, and deeper integration with surface and submarine forces. Sensor suites have been standardized, mission data flows have been tightened, and depot capacity has been expanded, which raises utilization and reduces time-to-task. As training pipelines stabilize and sustainment contracts mature, sortie density and on-station endurance improve, translating into higher procurement confidence, clearer upgrade timetables, and more assertive budgeting across the 2025–2035 window.
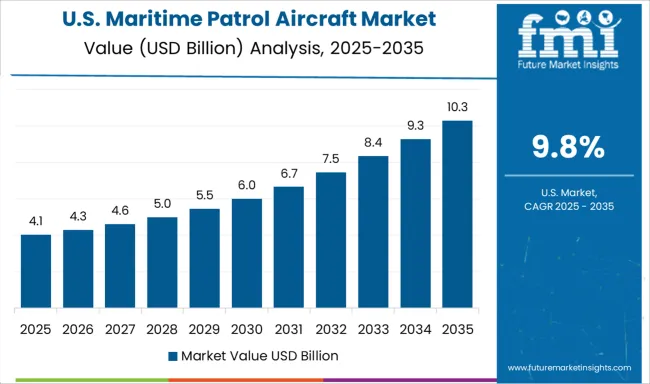
The United States is expected to record a 9.8% CAGR for 2025–2035, below the global 11.5% rate, as a mature replacement cycle progresses with emphasis on reliability, interoperability, and life-cycle cost control. Capability has been concentrated on incremental avionics refreshes, acoustic processing advances, and weapons carriage certification that sustain deterrence while avoiding disruptive fleet churn. Training, depot throughput, and spares pooling have been optimized to maintain high availability across multiple theaters. Strategic posture has favored predictable upgrade spirals and software-led improvements that reduce integration risk and preserve mission continuity. With standardized mission kits and broad logistics depth, the outlook suggests durable readiness supported by steady funding and measured capacity growth across priority maritime corridors.
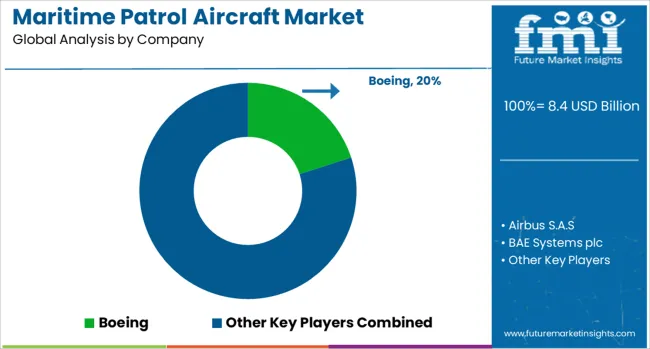
The maritime patrol aircraft market is led by established defense OEMs that provide integrated platforms, mission systems, and long-term support solutions. Lockheed Martin commands a strong position with its legacy P-3 Orion and modern P-8 Poseidon, adopted by the U.S. Navy, India, Australia, and the United Kingdom. Its advantage stems from extensive service contracts, global training programs, and integration of advanced sensors such as surveillance radars and electronic warfare suites.
Boeing maintains a competitive edge through the P-8 Poseidon platform, focusing on multi-mission versatility, interoperability with allied naval fleets, and exportable solutions that meet complex defense requirements. Saab Group occupies a niche segment with the Swordfish and GlobalEye maritime variants, offering high-end surveillance capabilities and cost-efficient operations, attracting regional navies with limited budgets. Kawasaki Heavy Industries and Tupolev serve domestic and regional markets with platforms like the P-1 and Tu-142, optimized for long-endurance missions and national procurement policies.
Emerging players such as Embraer and Leonardo provide modified maritime surveillance derivatives and ATR-based MPAs, addressing coastal security, short-range patrols, and budget-conscious naval requirements. Market competition is heavily shaped by platform endurance, advanced sensor integration, network-centric capabilities, and after-sales support, making long-term government contracts and system reliability critical factors for maintaining leadership in the global MPA landscape.
| Item | Value |
|---|---|
| Quantitative Units | USD 8.4 Billion |
| Type | Armoured and Unarmoured |
| Engine | Turboprop engine and Jet engine |
| Component | Radar, Camera, Sensors, and Others |
| Platform | Fixed wing and Rotary wing |
| Application | Surveillance and reconnaissance, Combat support, Search and rescue, Coastal patrolling, and Others |
| Mode of Operation | Manned and Unmanned |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America, Middle East & Africa |
| Country Covered | United States, Canada, Germany, France, United Kingdom, China, Japan, India, Brazil, South Africa |
| Key Companies Profiled | Boeing, Airbus S.A.S, BAE Systems plc, Dassault Aviation, EMBRAER, GENERAL ATOMICS AERONAUTICAL SYSTEMS INC., Kawasaki Heavy Industries, L, Leonardo S.p.A., Lockheed Martin Corporation, RUAG Group, Saab AB, SHINMAYWA INDUSTRIES, LTD., Textron Inc., and Thales Group |
| Additional Attributes | Dollar sales, share, regional demand trends, fleet replacement cycles, procurement budgets, competitor capabilities, technology adoption rates, and long-term defense spending outlook. |
The global maritime patrol aircraft market is estimated to be valued at USD 8.4 billion in 2025.
The market size for the maritime patrol aircraft market is projected to reach USD 24.8 billion by 2035.
The maritime patrol aircraft market is expected to grow at a 11.5% CAGR between 2025 and 2035.
The key product types in maritime patrol aircraft market are armoured and unarmoured.
In terms of engine, turboprop engine segment to command 57.8% share in the maritime patrol aircraft market in 2025.






Our Research Products

The "Full Research Suite" delivers actionable market intel, deep dives on markets or technologies, so clients act faster, cut risk, and unlock growth.

The Leaderboard benchmarks and ranks top vendors, classifying them as Established Leaders, Leading Challengers, or Disruptors & Challengers.

Locates where complements amplify value and substitutes erode it, forecasting net impact by horizon

We deliver granular, decision-grade intel: market sizing, 5-year forecasts, pricing, adoption, usage, revenue, and operational KPIs—plus competitor tracking, regulation, and value chains—across 60 countries broadly.

Spot the shifts before they hit your P&L. We track inflection points, adoption curves, pricing moves, and ecosystem plays to show where demand is heading, why it is changing, and what to do next across high-growth markets and disruptive tech

Real-time reads of user behavior. We track shifting priorities, perceptions of today’s and next-gen services, and provider experience, then pace how fast tech moves from trial to adoption, blending buyer, consumer, and channel inputs with social signals (#WhySwitch, #UX).

Partner with our analyst team to build a custom report designed around your business priorities. From analysing market trends to assessing competitors or crafting bespoke datasets, we tailor insights to your needs.
Supplier Intelligence
Discovery & Profiling
Capacity & Footprint
Performance & Risk
Compliance & Governance
Commercial Readiness
Who Supplies Whom
Scorecards & Shortlists
Playbooks & Docs
Category Intelligence
Definition & Scope
Demand & Use Cases
Cost Drivers
Market Structure
Supply Chain Map
Trade & Policy
Operating Norms
Deliverables
Buyer Intelligence
Account Basics
Spend & Scope
Procurement Model
Vendor Requirements
Terms & Policies
Entry Strategy
Pain Points & Triggers
Outputs
Pricing Analysis
Benchmarks
Trends
Should-Cost
Indexation
Landed Cost
Commercial Terms
Deliverables
Brand Analysis
Positioning & Value Prop
Share & Presence
Customer Evidence
Go-to-Market
Digital & Reputation
Compliance & Trust
KPIs & Gaps
Outputs
Full Research Suite comprises of:
Market outlook & trends analysis
Interviews & case studies
Strategic recommendations
Vendor profiles & capabilities analysis
5-year forecasts
8 regions and 60+ country-level data splits
Market segment data splits
12 months of continuous data updates
DELIVERED AS:
PDF EXCEL ONLINE
Maritime Patrol Naval Vessels Market Growth - Trends & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Aircraft Cabin Environment Sensor Market Forecast and Outlook 2025 to 2035
Aircraft Flight Control System Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Aircraft Electric Motor Market Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Aircraft Cooling Turbines Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Aircraft Smoke Detection and Fire Extinguishing System Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Aircraft Hose Fittings Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Aircraft Cabin Interior Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Aircraft Galley Systems Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Aircraft Interior Lighting Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Aircraft Battery Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Aircraft Floor Panels Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Aircraft Fuel Systems Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Aircraft Lubricant Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Aircraft Seat Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Aircraft Ground Support Equipment Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Maritime Satellite Communication Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Aircraft Maintenance, Repair and Overhaul Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Aircraft Actuators Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Aircraft Elevator Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035

Thank you!
You will receive an email from our Business Development Manager. Please be sure to check your SPAM/JUNK folder too.
Chat With
MaRIA