The severe hypertriglyceridemia (SHTG) treatment industry is valued at USD 950 million in 2025. As per FMI's analysis, the market will grow at a CAGR of 14.3% and reach USD 3.61 billion by 2035.
The treatment market for severe hypertriglyceridemia (SHTG) saw significant growth in 2024, fuelled by regulatory clearances, increased patient access, and growing clinical trial activity.
According to research by FMI, big drug companies sped up late-stage clinical trials for new triglyceride-lowering drugs, and some of them were given FDA fast-track designations. Reimbursement systems in North America and Europe were also strengthened, enhancing the accessibility of treatments.
FMI thinks that the acceptance of RNA-based treatments sped up because a number of biotech companies entered the SHTG Treatment market. Continued innovation in gene-based therapeutics and combination lipid-lowering therapies will fuel industry expansion through 2025 and in the future years.
FMI research predicts a surge in demand in Asia-Pacific markets due to the increasing incidence of metabolic disorders and healthcare spending. Competition will also increase as entrants bring with them cost-competitive substitutes.
Industry Forecast Table
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Industry Size (2025E) | USD 950 Million |
| Industry Value (2035F) | USD 3.61 Billion |
| CAGR (2025 to 2035) | 14.3% |
The market for treating severe hypertriglyceridemia (SHTG) is growing quickly. This is because the disease is becoming more common, drug approvals are being sped up, and new RNA-based and gene-targeted therapies are being developed.
According to the FMI study, pharmaceutical companies that come up with new lipid-lowering therapies will benefit the most. Conversely, generic drug companies will face significant challenges in competing in a market increasingly dominated by high-efficacy biologics. According to FMI, the industry will continue to grow until 2035 because more investments will be made in healthcare in emerging markets and reimbursement policies will be made stricter.
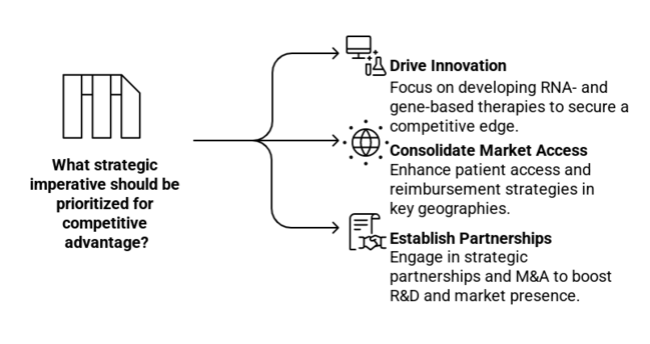
Drive innovation in RNA- and gene-based therapies.
Executive leaders must lead investments in innovative lipid-lowering therapies, RNA-based, and gene-editing technologies to secure a competitive advantage and address the mounting demand for highly effective solutions.
Consolidate Market Access and Reimbursement Strategies
The adoption and enhancement of patient access to high-end SHTG Treatment will be fuelled by changing healthcare policies and increasing reimbursement coverage in priority geographies, particularly North America and Asia-Pacific.
Establish Strategic Partnerships and M&A for Competitive Advantage
The pharmaceutical and biotechnology industries need to make strategic partnerships, license agreements, and acquisitions to stay ahead of the competition for a long time. This will help them do better research and development (R&D), speed up their clinical pipelines, and strengthen their presence in markets with a lot of growth.
| Risk | Probability & Impact |
|---|---|
| Regulatory Delays in Drug Approvals | High Probability-High Impact |
| Pricing Pressures and Reimbursement Challenges | Medium Probability-High Impact |
| Competition from Cost-Effective Generics | High Probability-Medium Impact |
1-Year Executive Watch-list
| Priority | Immediate Action |
|---|---|
| Expansion of RNA-Based Therapies | Accelerate clinical trials and secure regulatory fast-track designations |
| Market Access Optimization | Strengthen payer negotiations and expand reimbursement frameworks in key regions |
| Competitive Positioning | Pursue strategic M&A or licensing deals to enhance pipeline and global footprint |
To stay ahead of the competition, businesses need to quickly invest in RNA-based and gene-targeted therapies and get fast-track approvals from regulators. FMI Research highlights that optimising reimbursement strategies and strengthening market access will be critical for long-term adoption in high-growth regions. FMI believes that strategic M&A and licensing deals should be prioritised to expand therapeutic pipelines and establish dominance in an increasingly competitive landscape shift towards high-efficacy biologics.
Global Consensus
Regional Variance
Innovation Leaders
Diverging ROI Perspectives
72% of stakeholders in North America think that new treatments should be more expensive because they work better, but only 39% of stakeholders in Asia agree. They prefer models that are based on affordability.
Global Concerns
Regional Differences
Policy-Driven Market Shifts
Reimbursement Bottlenecks
Industry Alignment
73% of pharmaceutical manufacturers aim to invest in next-generation RNA-based and gene therapies.
Regional Priorities
Pharmaceutical Manufacturers
Health Care Professionals & End Users
Global Agreement
Industrywide, high efficacy, affordability, and regulatory clarity continue to be priorities.
Key Variances
Strategic Insight
There is no universally effective approach to commercialisation. They are trained on how to adapt product positioning, pricing, and market access strategies to each region’s problematic access points, which have unique affordability constraints, regulatory domains, and treatment preference ecosystems.
| Country | Regulatory Impact & Mandatory Certifications |
|---|---|
| United States | Biologics License Applications (BLA) and New Drug Applications (NDA) are the two ways that the FDA controls SHTG Treatment. The new polar priority tests prioritise fast-track and breakthrough therapy designations for novel lipid- designation medicines. The medical transparency law's new rules on prices and Medicare's ability to negotiate drug prices are both putting more pressure on prices. |
| United Kingdom | After Brexit, the drugs regulator, the Medicines and Healthcare Products Regulatory Agency (MHRA), will only have a slimmer regulatory alignment with the EU for authorisation. The National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) wants detailed cost-effectiveness analyses, so getting approval for reimbursement ahead of time can make it harder to get into the market. |
| France | The French National Agency for Medicines and Health Products Safety (ANSM) requires very strict approvals for clinical trials. The Economical Committee for Health Products (CESP) is in charge of reimbursement, and the Haute Autorité de Santé (HAS) does pharmacoeconomic analyses. This system makes it take longer for people to get expensive medicines. |
| Germany | The BfArM demands strict clinical evidence for innovative therapies. AMNOG: The Act to Restructure the Pharmaceutical Market requires cost-effectiveness analyses after the drug has been on the market. This is usually done with price cuts within 12 months of launch. |
| Italy | AIFA, the Italian Medicines Agency that oversees the drug market, strictly controls drug pricing and reimbursement. Therapeutic positioning reports (RPTs) lead market access, subjecting biologics' prices to intense scrutiny. The approval process presents obstacles for new SHTG treatments. |
| South Korea | The revised Drug Approval System is used by the Ministry of Food and Drug Safety (MFDS) to oversee SHTG treatments. HIRA plays a significant role in determining the reimbursement of a drug, favouring affordable generics over costly biologics. |
| Japan | Medicines and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA) and the Ministry of Health, Labour, and Welfare (MHLW) are in charge of giving approvals. The National Health Insurance (NHI) price list sets prices, and drugs with high prices find it hard to stay profitable in the long term when prices keep going down. |
| China | National Medical Products Administration (NMPA) simplifies approval of new treatments via priority review channels. China's National Reimbursement Drug List (NRDL) requires market access, but price negotiation can lead to margin depletion. |
| Australia & New Zealand | The Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA) and Medsafe NZ conduct stringent evidence-based assessments to approve drugs. Globally, medication reimbursement is decided by agencies such as the Pharmaceutical Benefits Scheme (PBS) in Australia and Pharmac in New Zealand, which make their recommendations on the basis of cost-effectiveness. |
| India | Approvals from the Central Drug Standard Control Organisation (CDSCO) govern it, and these standards are becoming more and more similar to global ones. The National Pharmaceutical Pricing Authority (NPPA) sets price caps on essential drugs that make it harder for people to use high-end biologics. |
The United States market for the treatment of severe hypertriglyceridemia is projected to grow at a CAGR of 15.1% during 2025 to 2035. Robust R&D activity, early uptake of new lipid-lowering therapies, and a sophisticated healthcare infrastructure support the nation as the leading market.
The FDA fast-track and breakthrough therapy designations help new drugs get approved more quickly, which makes it easier for new products to hit the market.
But the Inflation Reduction Act and Medicare drug price negotiations are exerting downward pressure on drug prices. Regardless of that, the USA dominates the use of RNA-based treatments and biologics due to high healthcare spending and favourable reimbursement policies.
Projections indicate that the market for treating severe hypertriglyceridemia in the United Kingdom will grow at a CAGR of 11.4% between 2025 and 2035. Although the post-Brexit regulatory reforms have streamlined the MHRA approval process, NICE appraisals, which apply strict cost-effectiveness checks, still dominate the market.
Demand for combined therapy is increasing, particularly among elderly patients, but high drug prices are a limiting factor. Government-sponsored research programmes and the growing recognition of lipid disorders support the UK market. Reimbursement approval from the NHS, however, is key to entering the market.
Between 2025 and 2035, the market for treating severe hypertriglyceridemia is expected to grow at a rate of 9.8% CAGR in France. Because ANSM and HAS regulations are out there, strict clinical trials and price negotiations must happen before a drug is approved.
France boasts a well-developed universal healthcare system, but the CEPS price controls render high-end biologics challenging to market. In spite of this, demand for new SHTG Treatment is on the rise with the growth in obesity and cardiovascular disease incidence. Pharmaceutical companies need to balance strict cost-effectiveness measures with the pursuit of advantageous reimbursement agreements to thrive in this market.
From 2025 to 2035, the market for treating severe hypertriglyceridemia is expected to grow at a rate of 10.2% per year in Germany. One of the most organised pharmaceutical markets in Europe, Germany's market is controlled by BfArM and AMNOG price reforms.
Cost-benefit analyses are mandatory for new therapies, often leading to price reductions in the first year. The country’s focus on precision medicine and lipid management is fuelling demand for RNA-based therapies and biologics.
To get their treatments covered by the public health insurance system (GKV), which covers more than 85% of the population, companies must make sure that their treatments meet AMNOG's cost-effectiveness assessments.
Between 2025 and 2035, the market for treating severe hypertriglyceridemia in Italy is expected to grow at a rate of 8.9% per year. The AIFA has strict rules about drug prices and reimbursement, which makes it hard for expensive therapies to break into the market. Even though everyone in Italy is covered by the public system, new therapies aren't used as quickly as they could be because of long regulatory approval delays and price caps put in place by the government.
Still, more people are becoming aware of lipid disorders and efforts to prevent heart disease are increasing the need for affordable treatments that lower lipids. To gain momentum, companies have to emphasise price negotiations and value-based reimbursement schemes.
The market for treating severe hypertriglyceridemia in South Korea is expected to grow at a CAGR of 12.7% from 2025 to 2035. The MFDS regulatory system and the HIRA reimbursement system in South Korea have big effects on keeping drug prices low and making sure everyone can get them.
Prices are tightly controlled, but the country is investing more and more in biopharmaceutical innovation and precision medicine. Demand for advanced lipid-lowering therapies is growing because more people are becoming aware of metabolic disorders and more people are getting them. However, companies must navigate complex reimbursement negotiations because HIRA favours generics over high-cost biologics, making cost-effective formulations and domestic partnerships essential for market entry.
From 2025 to 2035, projections indicate a CAGR of 9.5% for the treatment market for severe hypertriglyceridemia in Japan. The PMDA and MHLW regulate approvals, while the NHI pricing system determines drug prices. While there is a high affinity for evidence-based medicine in Japan, expensive biologics are subject to periodic price reductions under the system for reviewing drug prices every two years.
Notwithstanding this, the growing incidence of metabolic diseases and government programs to mitigate cardiovascular risk are creating increasing demand for new treatments. Japan-focused companies need to maximise their pricing approaches and partner with local pharmaceutical companies to cope with the convoluted reimbursement process.
The projections indicate that the severe hypertriglyceridemia treatment market in China will grow at a CAGR of 14.6% from 2025 to 2035. The NMPA's sped-up approval processes in the country have made it easier for people to get new treatments that lower lipids, but premium biologics are still having trouble with pricing negotiations in the NRDL. China has the most people with hypertriglyceridemia in the world, so there is a lot of room for growth, especially for cheaper formulations.
Greater government spending on local pharmaceutical research and development and increased private health expenditures are fuelling demand. Foreign drug companies have to ally with domestic companies to overcome regulatory hurdles and widen distribution networks, though.
In Australia and New Zealand, the treatment market for severe hypertriglyceridemia is projected to grow at a CAGR of 10.8% during 2025 to 2035. The TGA and Medsafe NZ decide which drugs can be sold, while PBS (Australia) and Pharmac (NZ) decide how much drugs cost and who pays for them. These organisations are cost-conscious, preferring generics and low-cost formulations over high-priced biologics.
Yet, rising cardiovascular disease incidence and a growing government emphasis on preventive care are fuelling demand for sophisticated SHTG treatments. To get into the market, companies have to work within strict reimbursement structures and show proof of their effectiveness in the real world.
The treatment market for severe hypertriglyceridemia in India is forecast to grow at a CAGR of 13.2% from 2025 to 2035. CDSCO governs drug approvals, while NPPA oversees drug pricing, implementing an effective cost-containment strategy.
Even though price is very important, there is a lot of demand for cheap lipid-lowering drugs because India's middle-class population is growing and metabolic disorders are becoming more common. Generic drugs dominate the market, but health awareness is fuelling interest in new biologics and RNA therapies. Companies need to ride cost-effective models of production and price strategies to succeed in the Indian market.
When it comes to treating severe hypertriglyceridemia (SHTG), olezarsen is the market leader because it works so well at lowering triglyceride levels through RNA-based mechanisms. Since tests are still going on and approvals from regulators are expected, we think Olezarsen will grow at a CAGR of 16.2% from 2025 to 2035.
Pegozafermin, which is another FGF21 analogue, is also becoming more popular, especially among people with metabolic syndrome. This is a sign of a high-growth market. Pegozafermin is anticipated to grow at a CAGR of 14.8% during the period under forecast. Epeleuton, a sophisticated fatty acid-based treatment, is emerging as a viable alternative for non-invasive patients, with its market projected to grow at a CAGR of 13.5%.
However, Lomitapide, a proven therapy, is facing side effects and competition from newer therapies, limiting its growth to a CAGR of 9.4%. Lomitapide is still very important for high-risk patients who don't get better with newer treatments.
At the moment, injectables are the most popular way to treat severe hypertriglyceridemia because biologics and RNA-based medicines, like Olezarsen and Pegozafermin, need to be given under the skin. Physician-supervised drug delivery and precision-based therapies are driving expansion in this segment.
The injectable route will grow at a CAGR of 15.7% in 2025 to 2035. On the other hand, the oral route is the preferred choice for Lomitapide and Epeleuton, with the need to maintain patient convenience and compliance.
Even so, the segment will grow at a CAGR of 11.3% because newer oral products can't compete with how well advanced injectables work. Notwithstanding this, attempts to improve oral bioavailability and patient compliance could underpin steady demand.
Hospital pharmacies continue to be the leading distribution channel, fuelled by the delivery of high-cost biologics and physician-supervised treatments. Hospital pharmacies are expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 14.9% from 2025 to 2035. This is because more people will be hospitalised and pay for their medicines, which will help the market. Retail pharmacies are increasing gradually, providing convenience for oral drugs and repeat prescriptions.
The expansion of treatment guidelines for lipid disorders is driving the growth of retail pharmacies at a CAGR of 12.5%. However, expanding digital healthcare consumption and direct-to-patient strategies are driving the fastest growth in the online pharmacy segment.
The market for online pharmacies is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 16.5%. This is because more people are getting online, telemedicine is becoming more common, and people want home delivery.
The big players in the market for treating severe hypertriglyceridemia (SHTG) are competing on price, new biologics, partnerships, and the number of places they can reach. Companies are significantly investing in RNA therapies and FGF21 analogues, and Olezarsen and Pegozafermin are fuelling competition.
Price strategies prioritise premium biologics over affordable oral drugs, ensuring accessibility while maintaining profitability. Players are making alliances with contract manufacturers and research centres to hasten drug development.
Companies are getting regulatory approval and setting up regional distribution networks in order to grow in emerging markets. Mergers and acquisitions are also mounting as companies integrate expertise to cement market leadership.
Industry Share Analysis
Amarin Corporation
Ionis Pharmaceuticals & Akcea Therapeutics
Novo Nordisk
HLS Therapeutics
Other Companies (Kowa Pharmaceuticals, Mochida Pharmaceutical, etc.)
Key Developments in 2024
The industry is segmented into olezarsen, pegozafermin, epeleuton and lomitapide
It is segmented into oral route and injectable route
It is fragmented among hospital pharmacy, retail pharmacy and online pharmacy
The industry is studied across North America, Latin America, Europe, South Asia, East Asia, Oceania, Middle East & Africa
More people with hypertriglyceridemia, more people who are open to RNA-based treatments, and new developments in biologics are the main things that are driving demand.
The market will grow considerably because of new lipid-lowering drugs, strong clinical pipeline progress, and more regulatory approvals.
Major players are Ionis Pharmaceuticals, Arrowhead Pharmaceuticals, 89bio, Amgen, Novartis, Pfizer, Sanofi, and AstraZeneca.
Olezarsen is likely to take the lead because it lowers triglycerides more effectively. Pegozafermin, which is a therapy that is growing quickly, will likely come in second.
By 2035, the market should have reached USD 3.61 billion, thanks to more patients wanting to be treated and more treatment options becoming available.
Table 1: Global Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Region, 2018 to 2033
Table 2: Global Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Drug Class, 2018 to 2033
Table 3: Global Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Drug Delivery Method, 2018 to 2033
Table 4: Global Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Distribution Channel , 2018 to 2033
Table 5: North America Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Country, 2018 to 2033
Table 6: North America Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Drug Class, 2018 to 2033
Table 7: North America Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Drug Delivery Method, 2018 to 2033
Table 8: North America Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Distribution Channel , 2018 to 2033
Table 9: Latin America Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Country, 2018 to 2033
Table 10: Latin America Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Drug Class, 2018 to 2033
Table 11: Latin America Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Drug Delivery Method, 2018 to 2033
Table 12: Latin America Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Distribution Channel , 2018 to 2033
Table 13: Europe Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Country, 2018 to 2033
Table 14: Europe Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Drug Class, 2018 to 2033
Table 15: Europe Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Drug Delivery Method, 2018 to 2033
Table 16: Europe Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Distribution Channel , 2018 to 2033
Table 17: South Asia Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Country, 2018 to 2033
Table 18: South Asia Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Drug Class, 2018 to 2033
Table 19: South Asia Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Drug Delivery Method, 2018 to 2033
Table 20: South Asia Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Distribution Channel , 2018 to 2033
Table 21: East Asia Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Country, 2018 to 2033
Table 22: East Asia Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Drug Class, 2018 to 2033
Table 23: East Asia Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Drug Delivery Method, 2018 to 2033
Table 24: East Asia Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Distribution Channel , 2018 to 2033
Table 25: Oceania Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Country, 2018 to 2033
Table 26: Oceania Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Drug Class, 2018 to 2033
Table 27: Oceania Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Drug Delivery Method, 2018 to 2033
Table 28: Oceania Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Distribution Channel , 2018 to 2033
Table 29: MEA Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Country, 2018 to 2033
Table 30: MEA Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Drug Class, 2018 to 2033
Table 31: MEA Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Drug Delivery Method, 2018 to 2033
Table 32: MEA Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Distribution Channel , 2018 to 2033
Figure 1: Global Market Value (US$ Million) by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 2: Global Market Value (US$ Million) by Drug Delivery Method, 2023 to 2033
Figure 3: Global Market Value (US$ Million) by Distribution Channel , 2023 to 2033
Figure 4: Global Market Value (US$ Million) by Region, 2023 to 2033
Figure 5: Global Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Region, 2018 to 2033
Figure 6: Global Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Region, 2023 to 2033
Figure 7: Global Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Region, 2023 to 2033
Figure 8: Global Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Drug Class, 2018 to 2033
Figure 9: Global Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 10: Global Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 11: Global Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Drug Delivery Method, 2018 to 2033
Figure 12: Global Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Drug Delivery Method, 2023 to 2033
Figure 13: Global Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Drug Delivery Method, 2023 to 2033
Figure 14: Global Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Distribution Channel , 2018 to 2033
Figure 15: Global Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Distribution Channel , 2023 to 2033
Figure 16: Global Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Distribution Channel , 2023 to 2033
Figure 17: Global Market Attractiveness by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 18: Global Market Attractiveness by Drug Delivery Method, 2023 to 2033
Figure 19: Global Market Attractiveness by Distribution Channel , 2023 to 2033
Figure 20: Global Market Attractiveness by Region, 2023 to 2033
Figure 21: North America Market Value (US$ Million) by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 22: North America Market Value (US$ Million) by Drug Delivery Method, 2023 to 2033
Figure 23: North America Market Value (US$ Million) by Distribution Channel , 2023 to 2033
Figure 24: North America Market Value (US$ Million) by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 25: North America Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Country, 2018 to 2033
Figure 26: North America Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 27: North America Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 28: North America Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Drug Class, 2018 to 2033
Figure 29: North America Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 30: North America Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 31: North America Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Drug Delivery Method, 2018 to 2033
Figure 32: North America Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Drug Delivery Method, 2023 to 2033
Figure 33: North America Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Drug Delivery Method, 2023 to 2033
Figure 34: North America Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Distribution Channel , 2018 to 2033
Figure 35: North America Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Distribution Channel , 2023 to 2033
Figure 36: North America Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Distribution Channel , 2023 to 2033
Figure 37: North America Market Attractiveness by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 38: North America Market Attractiveness by Drug Delivery Method, 2023 to 2033
Figure 39: North America Market Attractiveness by Distribution Channel , 2023 to 2033
Figure 40: North America Market Attractiveness by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 41: Latin America Market Value (US$ Million) by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 42: Latin America Market Value (US$ Million) by Drug Delivery Method, 2023 to 2033
Figure 43: Latin America Market Value (US$ Million) by Distribution Channel , 2023 to 2033
Figure 44: Latin America Market Value (US$ Million) by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 45: Latin America Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Country, 2018 to 2033
Figure 46: Latin America Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 47: Latin America Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 48: Latin America Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Drug Class, 2018 to 2033
Figure 49: Latin America Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 50: Latin America Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 51: Latin America Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Drug Delivery Method, 2018 to 2033
Figure 52: Latin America Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Drug Delivery Method, 2023 to 2033
Figure 53: Latin America Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Drug Delivery Method, 2023 to 2033
Figure 54: Latin America Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Distribution Channel , 2018 to 2033
Figure 55: Latin America Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Distribution Channel , 2023 to 2033
Figure 56: Latin America Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Distribution Channel , 2023 to 2033
Figure 57: Latin America Market Attractiveness by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 58: Latin America Market Attractiveness by Drug Delivery Method, 2023 to 2033
Figure 59: Latin America Market Attractiveness by Distribution Channel , 2023 to 2033
Figure 60: Latin America Market Attractiveness by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 61: Europe Market Value (US$ Million) by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 62: Europe Market Value (US$ Million) by Drug Delivery Method, 2023 to 2033
Figure 63: Europe Market Value (US$ Million) by Distribution Channel , 2023 to 2033
Figure 64: Europe Market Value (US$ Million) by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 65: Europe Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Country, 2018 to 2033
Figure 66: Europe Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 67: Europe Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 68: Europe Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Drug Class, 2018 to 2033
Figure 69: Europe Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 70: Europe Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 71: Europe Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Drug Delivery Method, 2018 to 2033
Figure 72: Europe Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Drug Delivery Method, 2023 to 2033
Figure 73: Europe Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Drug Delivery Method, 2023 to 2033
Figure 74: Europe Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Distribution Channel , 2018 to 2033
Figure 75: Europe Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Distribution Channel , 2023 to 2033
Figure 76: Europe Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Distribution Channel , 2023 to 2033
Figure 77: Europe Market Attractiveness by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 78: Europe Market Attractiveness by Drug Delivery Method, 2023 to 2033
Figure 79: Europe Market Attractiveness by Distribution Channel , 2023 to 2033
Figure 80: Europe Market Attractiveness by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 81: South Asia Market Value (US$ Million) by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 82: South Asia Market Value (US$ Million) by Drug Delivery Method, 2023 to 2033
Figure 83: South Asia Market Value (US$ Million) by Distribution Channel , 2023 to 2033
Figure 84: South Asia Market Value (US$ Million) by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 85: South Asia Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Country, 2018 to 2033
Figure 86: South Asia Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 87: South Asia Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 88: South Asia Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Drug Class, 2018 to 2033
Figure 89: South Asia Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 90: South Asia Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 91: South Asia Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Drug Delivery Method, 2018 to 2033
Figure 92: South Asia Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Drug Delivery Method, 2023 to 2033
Figure 93: South Asia Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Drug Delivery Method, 2023 to 2033
Figure 94: South Asia Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Distribution Channel , 2018 to 2033
Figure 95: South Asia Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Distribution Channel , 2023 to 2033
Figure 96: South Asia Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Distribution Channel , 2023 to 2033
Figure 97: South Asia Market Attractiveness by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 98: South Asia Market Attractiveness by Drug Delivery Method, 2023 to 2033
Figure 99: South Asia Market Attractiveness by Distribution Channel , 2023 to 2033
Figure 100: South Asia Market Attractiveness by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 101: East Asia Market Value (US$ Million) by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 102: East Asia Market Value (US$ Million) by Drug Delivery Method, 2023 to 2033
Figure 103: East Asia Market Value (US$ Million) by Distribution Channel , 2023 to 2033
Figure 104: East Asia Market Value (US$ Million) by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 105: East Asia Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Country, 2018 to 2033
Figure 106: East Asia Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 107: East Asia Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 108: East Asia Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Drug Class, 2018 to 2033
Figure 109: East Asia Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 110: East Asia Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 111: East Asia Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Drug Delivery Method, 2018 to 2033
Figure 112: East Asia Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Drug Delivery Method, 2023 to 2033
Figure 113: East Asia Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Drug Delivery Method, 2023 to 2033
Figure 114: East Asia Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Distribution Channel , 2018 to 2033
Figure 115: East Asia Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Distribution Channel , 2023 to 2033
Figure 116: East Asia Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Distribution Channel , 2023 to 2033
Figure 117: East Asia Market Attractiveness by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 118: East Asia Market Attractiveness by Drug Delivery Method, 2023 to 2033
Figure 119: East Asia Market Attractiveness by Distribution Channel , 2023 to 2033
Figure 120: East Asia Market Attractiveness by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 121: Oceania Market Value (US$ Million) by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 122: Oceania Market Value (US$ Million) by Drug Delivery Method, 2023 to 2033
Figure 123: Oceania Market Value (US$ Million) by Distribution Channel , 2023 to 2033
Figure 124: Oceania Market Value (US$ Million) by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 125: Oceania Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Country, 2018 to 2033
Figure 126: Oceania Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 127: Oceania Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 128: Oceania Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Drug Class, 2018 to 2033
Figure 129: Oceania Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 130: Oceania Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 131: Oceania Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Drug Delivery Method, 2018 to 2033
Figure 132: Oceania Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Drug Delivery Method, 2023 to 2033
Figure 133: Oceania Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Drug Delivery Method, 2023 to 2033
Figure 134: Oceania Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Distribution Channel , 2018 to 2033
Figure 135: Oceania Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Distribution Channel , 2023 to 2033
Figure 136: Oceania Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Distribution Channel , 2023 to 2033
Figure 137: Oceania Market Attractiveness by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 138: Oceania Market Attractiveness by Drug Delivery Method, 2023 to 2033
Figure 139: Oceania Market Attractiveness by Distribution Channel , 2023 to 2033
Figure 140: Oceania Market Attractiveness by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 141: MEA Market Value (US$ Million) by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 142: MEA Market Value (US$ Million) by Drug Delivery Method, 2023 to 2033
Figure 143: MEA Market Value (US$ Million) by Distribution Channel , 2023 to 2033
Figure 144: MEA Market Value (US$ Million) by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 145: MEA Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Country, 2018 to 2033
Figure 146: MEA Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 147: MEA Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 148: MEA Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Drug Class, 2018 to 2033
Figure 149: MEA Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 150: MEA Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 151: MEA Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Drug Delivery Method, 2018 to 2033
Figure 152: MEA Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Drug Delivery Method, 2023 to 2033
Figure 153: MEA Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Drug Delivery Method, 2023 to 2033
Figure 154: MEA Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Distribution Channel , 2018 to 2033
Figure 155: MEA Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Distribution Channel , 2023 to 2033
Figure 156: MEA Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Distribution Channel , 2023 to 2033
Figure 157: MEA Market Attractiveness by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 158: MEA Market Attractiveness by Drug Delivery Method, 2023 to 2033
Figure 159: MEA Market Attractiveness by Distribution Channel , 2023 to 2033
Figure 160: MEA Market Attractiveness by Country, 2023 to 2033






Our Research Products

The "Full Research Suite" delivers actionable market intel, deep dives on markets or technologies, so clients act faster, cut risk, and unlock growth.

The Leaderboard benchmarks and ranks top vendors, classifying them as Established Leaders, Leading Challengers, or Disruptors & Challengers.

Locates where complements amplify value and substitutes erode it, forecasting net impact by horizon

We deliver granular, decision-grade intel: market sizing, 5-year forecasts, pricing, adoption, usage, revenue, and operational KPIs—plus competitor tracking, regulation, and value chains—across 60 countries broadly.

Spot the shifts before they hit your P&L. We track inflection points, adoption curves, pricing moves, and ecosystem plays to show where demand is heading, why it is changing, and what to do next across high-growth markets and disruptive tech

Real-time reads of user behavior. We track shifting priorities, perceptions of today’s and next-gen services, and provider experience, then pace how fast tech moves from trial to adoption, blending buyer, consumer, and channel inputs with social signals (#WhySwitch, #UX).

Partner with our analyst team to build a custom report designed around your business priorities. From analysing market trends to assessing competitors or crafting bespoke datasets, we tailor insights to your needs.
Supplier Intelligence
Discovery & Profiling
Capacity & Footprint
Performance & Risk
Compliance & Governance
Commercial Readiness
Who Supplies Whom
Scorecards & Shortlists
Playbooks & Docs
Category Intelligence
Definition & Scope
Demand & Use Cases
Cost Drivers
Market Structure
Supply Chain Map
Trade & Policy
Operating Norms
Deliverables
Buyer Intelligence
Account Basics
Spend & Scope
Procurement Model
Vendor Requirements
Terms & Policies
Entry Strategy
Pain Points & Triggers
Outputs
Pricing Analysis
Benchmarks
Trends
Should-Cost
Indexation
Landed Cost
Commercial Terms
Deliverables
Brand Analysis
Positioning & Value Prop
Share & Presence
Customer Evidence
Go-to-Market
Digital & Reputation
Compliance & Trust
KPIs & Gaps
Outputs
Full Research Suite comprises of:
Market outlook & trends analysis
Interviews & case studies
Strategic recommendations
Vendor profiles & capabilities analysis
5-year forecasts
8 regions and 60+ country-level data splits
Market segment data splits
12 months of continuous data updates
DELIVERED AS:
PDF EXCEL ONLINE
Severe Asthma Treatment Market Analysis by Drug Class, Route of Administration, Device Type, and Region through 2035
Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Treatment Market
Moderate-to-Severe Acne Treatment Market Trends and Forecast 2025 to 2035
Treatment-Resistant Hypertension Management Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Treatment-Resistant Depression Treatment Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Treatment Pumps Market Insights Growth & Demand Forecast 2025 to 2035
Pretreatment Coatings Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Air Treatment Ozone Generator Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
CNS Treatment and Therapy Market Insights - Trends & Growth Forecast 2025 to 2035
Seed Treatment Materials Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Acne Treatment Solutions Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Scar Treatment Market Overview - Growth & Demand Forecast 2025 to 2035
Soil Treatment Chemicals Market
Water Treatment System Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Water Treatment Chemical Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Algae Treatment Chemical Market Forecast and Outlook 2025 to 2035
Water Treatment Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Water Treatment Ozone Generator Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Water Treatment Equipment Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Burns Treatment Market Overview – Growth, Demand & Forecast 2025 to 2035

Thank you!
You will receive an email from our Business Development Manager. Please be sure to check your SPAM/JUNK folder too.
Chat With
MaRIA