The Space Economy Market is estimated to be valued at USD 449.8 billion in 2025 and is projected to reach USD 935.6 billion by 2035, registering a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.6% over the forecast period. Analyzing the growth curve reveals a compound upward trajectory with mild acceleration in the second half of the period. From 2025 to 2028, the market moves from USD 449.8 billion to 560.3 billion, contributing USD 110.5 billion, or 22.7% of total growth, driven by increased satellite launches and commercial space services. Between 2029 and 2032, values surge from USD 602.9 billion to 751.1 billion, adding USD 148.2 billion, fueled by private-sector investments, reusable launch systems, and rapid scaling of Earth observation applications. The steepest rise occurs post-2032, as the market jumps from USD 808.1 billion in 2033 to 935.6 billion by 2035, representing 27.3% of overall incremental expansion, linked to deep-space exploration, lunar commercialization projects, and mega-constellation deployments for broadband connectivity.
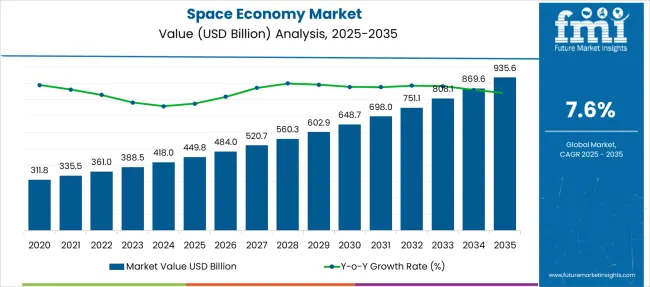
This expansion demonstrates a sharp upward curve, indicating accelerated investment in commercial and government-driven space initiatives. The trajectory is not linear but displays increasing steepness after 2028 as satellite constellations, reusable launch systems, and lunar missions gain momentum.
The satellite industry accounts for 61.0% of the 2025 market, supported by demand for communication networks, Earth observation, and broadband internet solutions in underserved regions. North America remains dominant due to strong private sector engagement and public funding for deep space missions. Asia-Pacific is the fastest-growing region, propelled by China and India’s investments in low-orbit constellations and national space programs. Europe sustains growth through collaboration in scientific research and defense-related space infrastructure.
The growth curve suggests a transition from government-centric operations to a diversified ecosystem where private enterprises lead innovation in launch services, space tourism, and in-orbit servicing. Future acceleration is tied to reusable propulsion technology, space mining, and commercialization of low Earth orbit stations. With strategic alliances forming between aerospace manufacturers and telecom operators, the market outlook positions space as a critical pillar of global economic infrastructure.
The Space Economy Market is estimated to be valued at USD 449.8 billion in 2025 and is projected to reach USD 935.6 billion by 2035, registering a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.6% over the forecast period. Analyzing the growth curve reveals a compound upward trajectory with mild acceleration in the second half of the period. From 2025 to 2028, the market moves from USD 449.8 billion to 560.3 billion, contributing USD 110.5 billion, or 22.7% of total growth, driven by increased satellite launches and commercial space services. Between 2029 and 2032, values surge from USD 602.9 billion to 751.1 billion, adding USD 148.2 billion, fueled by private-sector investments, reusable launch systems, and rapid scaling of Earth observation applications. The steepest rise occurs post-2032, as the market jumps from USD 808.1 billion in 2033 to 935.6 billion by 2035, representing 27.3% of overall incremental expansion, linked to deep-space exploration, lunar commercialization projects, and mega-constellation deployments for broadband connectivity.

This expansion demonstrates a sharp upward curve, indicating accelerated investment in commercial and government-driven space initiatives. The trajectory is not linear but displays increasing steepness after 2028 as satellite constellations, reusable launch systems, and lunar missions gain momentum.
The satellite industry accounts for 61.0% of the 2025 market, supported by demand for communication networks, Earth observation, and broadband internet solutions in underserved regions. North America remains dominant due to strong private sector engagement and public funding for deep space missions. Asia-Pacific is the fastest-growing region, propelled by China and India’s investments in low-orbit constellations and national space programs. Europe sustains growth through collaboration in scientific research and defense-related space infrastructure.
The growth curve suggests a transition from government-centric operations to a diversified ecosystem where private enterprises lead innovation in launch services, space tourism, and in-orbit servicing. Future acceleration is tied to reusable propulsion technology, space mining, and commercialization of low Earth orbit stations. With strategic alliances forming between aerospace manufacturers and telecom operators, the market outlook positions space as a critical pillar of global economic infrastructure.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Space Economy Market Estimated Value in (2025 E) | USD 449.8 billion |
| Space Economy Market Forecast Value in (2035 F) | USD 935.6 billion |
| Forecast CAGR (2025 to 2035) | 7.6% |
The space economy market is undergoing accelerated expansion, fueled by a convergence of advancements in satellite technologies, private sector participation, and increasing commercial demand for space-based services. Governments and space agencies are prioritizing collaborative models with startups and established aerospace firms to boost innovation, reduce mission costs, and commercialize low-Earth orbit opportunities.
The integration of AI, edge computing, and quantum communications is redefining satellite utility across Earth observation, telecom, navigation, and defense sectors. Meanwhile, the growing interest in space tourism, debris management, and lunar exploration is broadening the economic scope of space infrastructure.
With space now recognized as a strategic economic domain, public-private investments, defense-backed R&D, and supportive regulatory pathways are expected to sustain long-term market momentum.
The space economy market is segmented by type, end-user, and region. By type, it includes satellite industry components such as satellite launch, satellite services, satellite manufacturing, and satellite ground equipment, along with non-satellite segments including government space budgets, commercial human spaceflight, and space sustainability activities. In terms of end-users, the market is classified into commercial and government and defense sectors, reflecting a mix of private and public investments in space activities. Regionally, the market spans North America, Latin America, Western and Eastern Europe, Balkan and Baltic countries, Russia and Belarus, Central Asia, East Asia, South Asia and Pacific, and the Middle East and Africa.
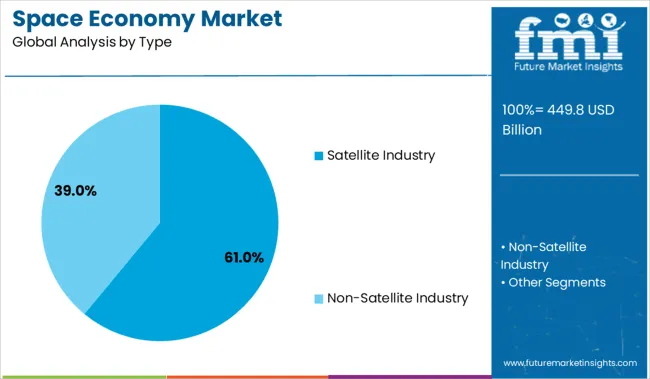
The satellite industry is projected to contribute 61.0% of the total revenue in the space economy market by 2025, making it the leading market type. This dominance is being driven by the surge in small satellite deployments, mega-constellation programs, and increased demand for real-time data transmission, remote sensing, and connectivity across rural and urban geographies.
Advancements in miniaturization, propulsion, and payload flexibility have reduced launch costs and extended satellite lifespans, further enhancing return on investment. The sector’s strategic importance in defense surveillance, climate monitoring, agriculture, and disaster management has also strengthened its economic and geopolitical value.
As new use cases emerge across broadband access and IoT enablement, the satellite industry remains central to the evolving architecture of the global space economy..
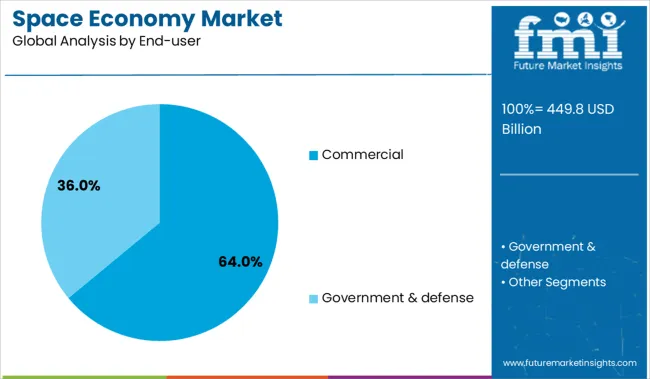
Commercial end users are expected to account for 64.0% of the market’s total revenue in 2025, positioning this segment as the primary driver of space economy demand. This growth is being shaped by increased private investments in satellite broadband, Earth analytics, space tourism, and launch services.
Enterprises across telecom, transportation, agriculture, and finance are integrating satellite data into their operational workflows to enhance decision-making, efficiency, and customer services. The rise of space-based SaaS models and commercialization of orbital platforms has unlocked new business models that appeal to a broader corporate base.
Additionally, the expanding involvement of venture capital and institutional investors in space tech startups has provided the financial momentum necessary for scaling commercial applications. As reliance on space-enabled infrastructure intensifies across sectors, commercial participation is set to remain the cornerstone of the space economy's next growth phase..
The space economy is being propelled by rising commercial participation, strategic public-private alliances, and supportive regulatory reforms. Surging demand for real-time data, global connectivity, and defense applications is expanding market scope across civilian and military sectors.
The growth of the space economy is increasingly driven by expanding private sector participation and government facilitation through strategic partnerships. Dollar sales from satellite services, launch infrastructure, and in-orbit servicing are being fueled by defense collaborations, telecom expansion, and space tourism ambitions. As national agencies open more space programs to private bids, market share is shifting toward commercial players, notably in North America, Europe, and emerging BRICS nations. Commercial satellite constellations, especially for broadband and Earth observation, are reshaping industry economics. Share is also being influenced by regulatory liberalization and licensing reforms. With venture funding increasing for space-tech startups, investor sentiment continues to shape the pace of innovation and deployment, making private-led missions more viable.
A growing demand for low-latency connectivity, real-time Earth data, and advanced reconnaissance capabilities is redefining the functional scope of the space economy. Mega-constellations for internet access and satellite imagery solutions are being rapidly scaled, particularly in remote and underserved regions. Earth observation data is gaining share across sectors like agriculture, insurance, mining, and climate monitoring, prompting broader institutional adoption. Geopolitical risks and national security concerns are prompting increased space-based defense spending across OECD and non-OECD markets. Surveillance satellites, missile-warning systems, and navigation technologies are being prioritized. As satellite payloads become more compact and affordable, the deployment of multi-use assets is growing, strengthening the market’s momentum across both civilian and military domains.
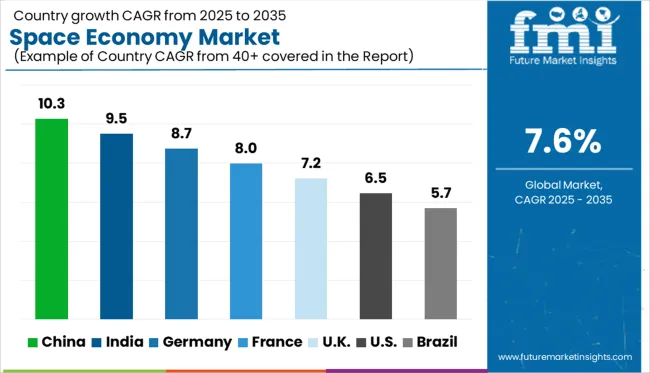
| Country | CAGR |
|---|---|
| China | 10.3% |
| India | 9.5% |
| Germany | 8.7% |
| France | 8.0% |
| UK | 7.2% |
| USA | 6.5% |
| Brazil | 5.7% |
The global space economy market is growing at a CAGR of 7.6% from 2025 to 2035, yet several BRICS and OECD nations are exceeding this pace, driven by a combination of sovereign investment, private sector expansion, and space-tech commercialization. China leads with a robust 10.3% CAGR, propelled by state-backed satellite constellations, space station operations, and an expanding ecosystem of commercial launch providers.
India follows at 9.5%, boosted by ISRO’s cost-effective mission model and increasing private participation under the space sector liberalization policy. Germany, representing the OECD bloc, is expanding at 8.7%, leveraging advanced aerospace manufacturing capabilities and growing demand for Earth observation technologies.The UK and USA are growing at 7.2% and 6.5%, respectively, lagging behind the global average due to market maturity and regulatory inertia in commercial satellite and launch services. ASEAN countries, while not listed, are emerging with niche capabilities in space-based analytics and IoT infrastructure. The report provides insights into 40+ nations, with the top five highlighted above.
The CAGR in the United Kingdom increased from 3.4% during 2020 to 2024 to approximately 7.2% in 2025 to 2035, indicating a shift toward higher commercial traction and defense-backed investments. The rise is attributed to the UK Space Agency’s increasing engagement with private launch providers and the growing utility of satellite data for national infrastructure and climate resilience projects.
The low CAGR in the earlier phase reflected conservative public spending, slower commercial rollouts, and Brexit-linked uncertainties in collaborative missions. Post to 2025, streamlined licensing, support for Earth observation startups, and national interest in sovereign satellite navigation systems led to renewed growth. Connectivity programs like OneWeb’s LEO rollout and satellite-backed emergency networks saw strong backing from the government and private players, enhancing market depth.
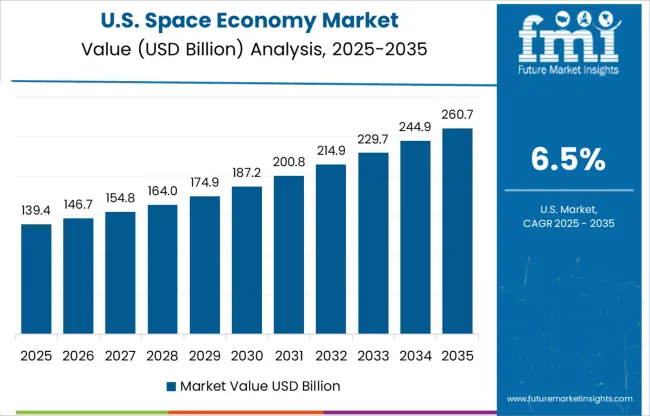
The CAGR in the United States was about 4.8% during 2020 to 2024 and is projected to increase to 6.5% between 2025 and 2035, bolstered by intensified Department of Defense (DoD) collaborations and expanding commercial launches. During the earlier phase, the market saw steady but mature growth due to saturation in traditional segments like geostationary satellites and restricted budget allocations.
Post to 2025, the emergence of space tourism, in-orbit servicing, and private cargo resupply missions drove incremental dollar sales. NASA’s Artemis missions, combined with private contracts under CLPS and ISS replacement programs, created new revenue streams. LEO constellations for broadband access and advanced reconnaissance satellites are further broadening the domestic ecosystem and export potential.
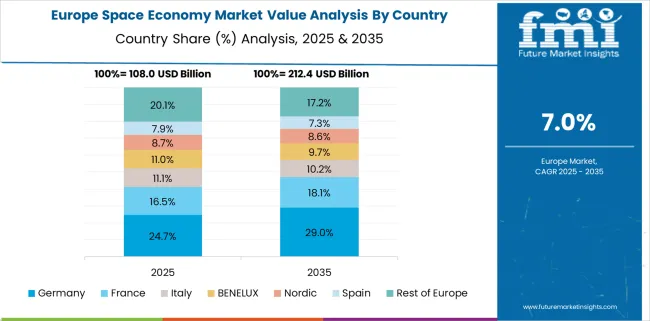
Germany's CAGR increased from 5.1% in 2020 to 2024 to 8.7% during 2025 to 2035, driven by federal support for dual-use satellite applications and stronger ESA-led coordination. Early growth was hindered by limited commercialization and lower private investment in launch capabilities. After 2025, the German Aerospace Center (DLR) promoted market-linked R&D, while public procurement started prioritizing local Earth intelligence providers.
The demand for high-resolution imagery, satellite-based climate risk analysis, and industrial IoT connectivity gave domestic players a strong foothold. Strategic cooperation with EU and NATO defense mandates also expanded Germany’s stake in secure communication and observation networks.
The CAGR in China advanced from about 7.9% in 2020 to 2024 to 10.3% over 2025 to 2035, growth backed by aggressive state investment and technology localization. The early period focused heavily on national infrastructure, lunar missions, and the development of the BeiDou navigation system. Post to 2025, commercial satellite manufacturers, reusable launch systems, and private players like CAS Space and Galaxy Space received stronger regulatory and financial support.
China’s Belt and Road partners increased demand for space-based navigation, climate, and broadband services. Space science and crewed spaceflight programs expanded under national innovation plans, aligning with long-term strategic goals.
India’s CAGR improved from nearly 6.3% in 2020 to 2024 to 9.5% during the 2025 to 2035 period, largely due to rising commercial satellite missions and ISRO’s strategic reforms. Earlier, growth was moderate due to state monopoly in most space segments and restricted commercial integration. After 2025, initiatives like IN-SPACe and NSIL opened access to launch pads and satellite capabilities for private firms.
NewSpace startups focusing on small satellites, launch services, and remote sensing have received increased venture capital, with exports gaining traction. India’s strategic interest in defense satellites and rural connectivity via LEO networks also lifted the demand trajectory.
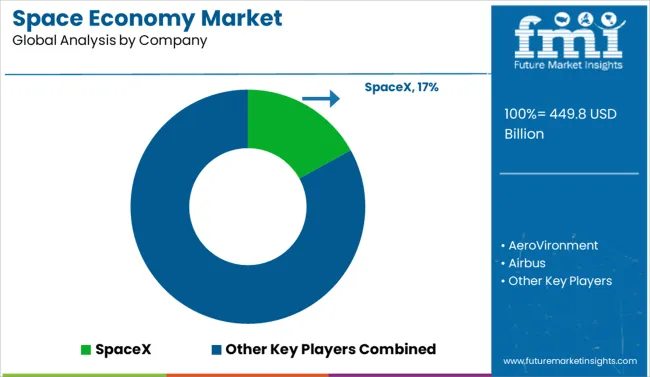
In the rapidly expanding space economy, key players are intensifying their roles across launch systems, satellite services, and defense-linked space capabilities. SpaceX and Blue Origin are revolutionizing reusable launch technologies, while Boeing, Airbus, and Lockheed Martin remain central to satellite manufacturing and crewed missions.
Defense leaders like BAE Systems, Northrop Grumman, Raytheon Technologies, and General Dynamics are advancing orbital surveillance and secure communication systems. Maxar Technologies and Viasat are critical to Earth observation and broadband infrastructure.
Government-linked organizations such as the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) and Israel Aerospace Industries are scaling international collaborations and low-cost mission success. Elbit Systems and Thales continue to expand in defense payloads and dual-use assets, while AeroVironment pioneers satellite-linked drones and atmospheric data systems.
In July 2025, Starlink successfully launched 24 satellites on July 18 with Falcon 9.
| Item | Value |
|---|---|
| Quantitative Units | USD 449.8 Billion |
| Type | Satellite Industry, Satellite launch, Satellite services, Satellite manufacturing, Satellite ground equipment, Non-Satellite Industry, Government space budgets, Commercial human spaceflight, and Space sustainability activities |
| End-user | Commercial and Government & defense |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America, Middle East & Africa |
| Country Covered | United States, Canada, Germany, France, United Kingdom, China, Japan, India, Brazil, South Africa |
| Key Companies Profiled | SpaceX, AeroVironment, Airbus, BAE Systems, Blue Origin, Boeing, Elbit Systems, General Dynamics, Indian Space Research Organisation, Israel Aerospace Industries, Lockheed Martin, Maxar Technologies, Northrop Grumman, Raytheon Technologies, Thales, and Viasat |
| Additional Attributes | Dollar sales by segment, share by satellite type, launch systems, and geography, emerging private-public contracts, defense spending shifts, LEO demand drivers, and tech export potential. |
The global space economy market is estimated to be valued at USD 449.8 billion in 2025.
The market size for the space economy market is projected to reach USD 935.6 billion by 2035.
The space economy market is expected to grow at a 7.6% CAGR between 2025 and 2035.
The key product types in space economy market are satellite industry, satellite launch, satellite services, satellite manufacturing, satellite ground equipment, non-satellite industry, government space budgets, commercial human spaceflight and space sustainability activities.
In terms of end-user, commercial segment to command 64.0% share in the space economy market in 2025.






Full Research Suite comprises of:
Market outlook & trends analysis
Interviews & case studies
Strategic recommendations
Vendor profiles & capabilities analysis
5-year forecasts
8 regions and 60+ country-level data splits
Market segment data splits
12 months of continuous data updates
DELIVERED AS:
PDF EXCEL ONLINE
Space-based C4ISR Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Space Lander and Rover Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Space-Based Solar Power Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Space Frame Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Space Situational Awareness Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Space Robotics Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Space On Board Computing Platform Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Space Militarization Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Space Power Electronics Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Space Management Solutions Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Industry Share Analysis for Space Tourism Providers
Space Tourism Industry Analysis by Supplier, by Age Group, by Tourism Type, by Demographics, by Nationality, by Booking Channel, by Tour Type, and by Region - Forecast for 2025 to 2035
Spacer Tapes Market Insights & Growth Outlook through 2034
Space DC-DC Converter Market Insights – Growth & Forecast 2024-2034
In Space Manufacturing Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Aerospace Fastener Manufacturing Solution Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Aerospace Fluid Conveyance System Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Aerospace Adhesives and Sealants Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Aerospace Forging Materials Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Aerospace and Defense Cyber Security Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035

Thank you!
You will receive an email from our Business Development Manager. Please be sure to check your SPAM/JUNK folder too.
Chat With
MaRIA