The space lander and rover market is estimated to be valued at USD 666.3 million in 2025 and is projected to reach USD 1681.7 million by 2035, registering a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 9.7% over the forecast period.
Growth during this period was driven primarily by government space programs and select private ventures focusing on exploratory missions. Early adopters concentrated on mission-specific projects, demonstrating feasibility and securing interest from investors. This stage emphasized testing capabilities, establishing supply chains, and building confidence in robotic space exploration, laying the foundation for broader market expansion. From 2025 to 2030, the market enters its scaling phase, rising from USD 666.3 million to approximately 1,058.6 million.
Adoption broadens as more countries and commercial entities invest in planetary exploration, lunar missions, and extraterrestrial research projects. Market participants expand production capacity and standardize rover designs to meet increasing demand. By 2030, with the market exceeding USD 1,058.6 million, adoption is widespread within the exploratory space sector. Between 2030 and 2035, the market moves into consolidation, growing to USD 1,681.7 million, where leading players dominate mission contracts, infrastructure matures, and market growth stabilizes around a predictable trajectory of advanced space exploration missions.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Space Lander and Rover Market Estimated Value in (2025 E) | USD 666.3 million |
| Space Lander and Rover Market Forecast Value in (2035 F) | USD 1681.7 million |
| Forecast CAGR (2025 to 2035) | 9.7% |
The market is advancing rapidly, supported by a resurgence in lunar and planetary missions initiated by government agencies and private space enterprises. This growth is being driven by renewed international interest in space exploration, technological miniaturization, and increased funding for deep space missions. Space agencies are prioritizing lunar exploration as a precursor to human settlement, which is fueling demand for advanced landers and rovers capable of performing autonomous navigation, terrain analysis, and in situ scientific research.
Public-private partnerships and commercial space ventures are playing a pivotal role in accelerating mission deployment timelines, enhancing the market's dynamism. Strategic objectives such as resource mapping, infrastructure testing, and long-duration robotic operations are paving the path for future growth.
Ongoing advancements in power systems, AI-based autonomy, and high-efficiency propulsion are also reinforcing the adoption of next-generation exploration vehicles The outlook remains positive, with long-term demand expected to expand as lunar missions transition from demonstration to sustained operation phases.
The space lander and rover market is segmented by mission type, vehicle type, propulsion type, application, end-user, and geographic regions. By mission type, the market is divided into Lunar surface exploration, Mars surface exploration, and Asteroids and comet exploration. In terms of vehicle type, the market is classified into space rovers and space landers. Based on propulsion type, the market is segmented into chemical propulsion, electric/Ion propulsion, and hybrid propulsion systems. By application, the market is segmented into scientific research, resource exploration, technology demonstration, and others. By end-user, the market is segmented into government and defense, space exploration organizations, private aerospace companies, and research institutions. Regionally, the space lander and rover industry is classified into North America, Latin America, Western Europe, Eastern Europe, Balkan & Baltic Countries, Russia & Belarus, Central Asia, East Asia, South Asia & Pacific, and the Middle East & Africa.
The lunar surface exploration segment is anticipated to hold 44.2% of the Space Lander and Rover market revenue share in 2025, positioning it as the leading mission type. This dominance is being driven by a global shift in focus toward establishing a sustainable human presence on the Moon. Lunar missions have been prioritized by space agencies for their potential to test life-support systems, resource extraction techniques, and long-duration operations.
The segment's strength has been reinforced by government-backed programs that aim to establish lunar bases and validate critical technologies before proceeding to Mars exploration. Increased launch frequency, public-private mission collaborations, and scientific interest in the Moon's geology and polar volatiles have contributed to this segment’s growth.
The relative proximity of the Moon and reduced mission risk compared to deep space targets have also made lunar missions more viable for technology demonstration and commercial experimentation These drivers have led to the segment’s leadership position within the market.
The space rovers segment is projected to capture 58.7% of the Space Lander and Rover market revenue share in 2025, emerging as the dominant vehicle type. This growth is being fueled by their critical role in enabling autonomous surface mobility, terrain exploration, and sample collection in challenging extraterrestrial environments.
Space rovers are being increasingly selected for missions due to their capability to navigate complex terrains, support modular payloads, and deliver long-term scientific data. Rovers have been designed with enhanced AI-driven autonomy and real-time obstacle avoidance, aligning with mission requirements for precision, safety, and extended operational periods.
Advancements in miniaturization and power efficiency have made rovers suitable for deployment across various mission sizes, from micro-explorers to heavy-duty robotic systems These capabilities have driven widespread adoption by both national agencies and private mission operators seeking scalable, multifunctional vehicles, ensuring that space rovers remain the most utilized and reliable asset in planetary and lunar surface missions.
The space rovers segment is projected to capture 58.7% of the Space Lander and Rover market revenue share in 2025, emerging as the dominant vehicle type. This growth is being fueled by their critical role in enabling autonomous surface mobility, terrain exploration, and sample collection in challenging extraterrestrial environments.
Space rovers are being increasingly selected for missions due to their capability to navigate complex terrains, support modular payloads, and deliver long-term scientific data. Rovers have been designed with enhanced AI-driven autonomy and real-time obstacle avoidance, aligning with mission requirements for precision, safety, and extended operational periods.
Advancements in miniaturization and power efficiency have made rovers suitable for deployment across various mission sizes, from micro-explorers to heavy-duty robotic systems These capabilities have driven widespread adoption by both national agencies and private mission operators seeking scalable, multifunctional vehicles, ensuring that space rovers remain the most utilized and reliable asset in planetary and lunar surface missions.
The space lander and rover market is expanding as government space agencies, private companies, and research organizations invest in planetary exploration, lunar missions, and asteroid studies. Advancements in autonomous navigation, robotics, and miniaturized payloads are enabling more sophisticated mission capabilities. North America and Europe lead due to established aerospace infrastructure, while Asia-Pacific is emerging rapidly with increased space programs. Market growth is driven by scientific research, commercial exploration opportunities, and international collaborations. Innovation focuses on mobility systems, energy efficiency, AI-driven autonomy, and modular designs to support diverse planetary environments.
Designing and deploying space landers and rovers involves extreme technological complexity. Systems must withstand harsh environments including vacuum, radiation, extreme temperatures, and dust-laden terrains. Autonomous navigation, precise landing, and energy-efficient mobility require advanced robotics, AI algorithms, and sensor integration. Development timelines are long, and testing is costly due to mission-critical reliability requirements. Small errors in hardware or software can compromise multi-million-dollar missions. Companies investing in rigorous testing, simulation, and modular designs improve mission success rates. Until technology maturity and reliability improve further, development complexity remains a significant barrier to rapid market expansion.
Advancements in rover mobility, AI-based navigation, and remote operation technologies are transforming the market. Rovers now feature adaptive suspension systems, solar or nuclear energy solutions, and autonomous decision-making for terrain traversal. Miniaturized scientific payloads enable real-time data collection and environmental analysis. Innovations such as modular and reconfigurable designs allow landers and rovers to support multiple mission objectives simultaneously. Collaboration with research institutions, AI developers, and aerospace technology providers enhances performance and mission versatility. As autonomous and energy-efficient systems advance, space landers and rovers are becoming more capable, cost-effective, and attractive for scientific, commercial, and defense applications.
The space lander and rover market is highly regulated, with mission approvals governed by national space agencies and international treaties. Licensing for planetary exploration, orbital trajectories, and payload transport involves compliance with strict safety, environmental, and international agreements. Approval timelines can be long, affecting project scheduling and cost management. Export control regulations, particularly for sensitive technologies, create additional barriers for cross-border collaborations. Companies aligning development with agency standards, obtaining necessary certifications, and maintaining compliance with ITAR, ESA, or other space regulations gain smoother market access. Until global regulatory frameworks evolve to accommodate private and collaborative missions more efficiently, mission approval constraints will continue to influence market growth.
The space lander and rover market is highly competitive, involving government agencies, aerospace giants, and private startups. Leading players leverage R&D capabilities, mission experience, and proprietary technology, while emerging players focus on niche innovations, cost efficiency, or specific mission payloads. Supply chains for specialized components like robotics actuators, sensors, and energy systems are limited and highly technical, creating procurement challenges. Long lead times and reliance on advanced materials intensify operational risks. Companies investing in vertical integration, strategic partnerships, and supplier diversification achieve enhanced reliability and mission readiness. Until specialized component production and supply chains scale further, competition and supply constraints will remain key factors shaping market dynamics.
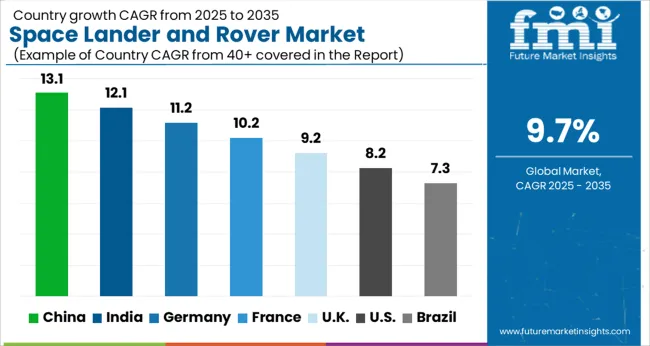
The global space lander and rover market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 9.7% through 2035, supported by increasing applications in planetary exploration, scientific research, and satellite deployment missions. Among BRICS nations, China has been recorded with 13.1% growth, driven by expanded space programs and robotic exploration initiatives, while India has been observed at 12.1%, supported by growing government-funded missions and research projects. In the OECD region, Germany has been measured at 11.2%, where advanced engineering capabilities and industrial collaboration have been steadily applied. The United Kingdom has been noted at 9.2%, reflecting increased development in robotic systems and mission support, while the USA has been recorded at 8.2%, with production and deployment for scientific and defense applications being consistently increased. This report includes insights on 40+ countries; the top five markets are shown here for reference.
The space lander and rover market in China is witnessing significant growth with a CAGR of 13.1%, driven by the country’s ambitious space exploration initiatives. China’s space program is increasingly investing in lunar and planetary missions, including lunar landers, Mars rovers, and related autonomous robotics. Government funding, technological advancements, and collaborations with research institutes are accelerating the development of high-performance space vehicles. Chinese manufacturers are focusing on innovation in propulsion, navigation, and communication systems to ensure mission success. Additionally, private sector participation is expanding, promoting innovation and commercialization of space technologies. Rising interest in lunar resource exploration and Mars missions is increasing demand for landers and rovers capable of long-duration operations. With ongoing investment in satellite infrastructure and autonomous robotics, China is positioned to be a key player in the global space exploration market.
India’s space lander and rover market is growing at a CAGR of 12.1%, supported by the Indian Space Research Organisation’s (ISRO) ambitious exploration programs. India has successfully conducted missions to the Moon and Mars, creating a demand for landers, rovers, and autonomous space vehicles. Advancements in robotics, communication, and propulsion technologies are enabling the development of reliable and cost-effective space exploration vehicles. Private companies in India are increasingly contributing to manufacturing, research, and software development for space missions. With rising government funding, the focus is also on developing modular and reusable rover systems for scientific and exploratory purposes. The Indian space sector’s growing capabilities in miniaturized payloads and mission automation are attracting global attention. As India plans upcoming lunar and interplanetary missions, demand for advanced landers and rovers is expected to rise steadily.
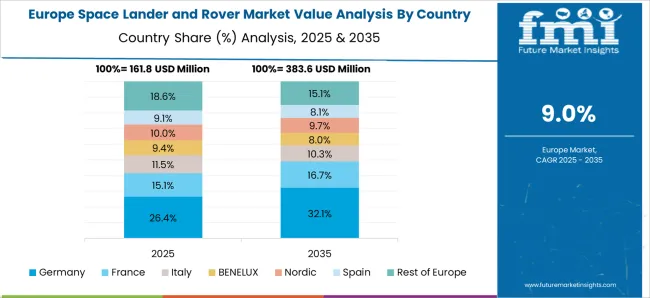
The space lander and rover market in Germany is expanding at a CAGR of 11.2%, driven by the country’s participation in European Space Agency (ESA) projects and strong aerospace research. German manufacturers specialize in high-precision instrumentation, autonomous robotics, and mobility systems for planetary exploration. Advanced engineering capabilities allow Germany to produce reliable rovers and landers capable of operating in extreme conditions. Collaborative initiatives with international space agencies enhance technology sharing and development of specialized payloads. Research institutions are actively engaged in developing sensors, navigation systems, and power-efficient lander components. Growing demand for scientific exploration missions and technological innovation is fueling market growth. Germany’s focus on sustainable space technologies and robotics integration positions the country as a vital contributor to the global space lander and rover ecosystem.
The space lander and rover market in the United Kingdom is projected to grow at a CAGR of 9.2%, supported by strong investments in space research and participation in international exploratory missions. UK companies specialize in advanced robotics, autonomous navigation, and lightweight lander structures. Collaborative projects with ESA and other global agencies promote technological advancements and testing of rover systems. Rising interest in lunar and planetary exploration is increasing the demand for robust landers and rovers equipped with scientific payloads. Universities and private sector players are also developing AI-based navigation and energy-efficient mobility solutions. With growing government support and expanding private sector involvement, the UK is strengthening its position in the global market for space landers and rovers.
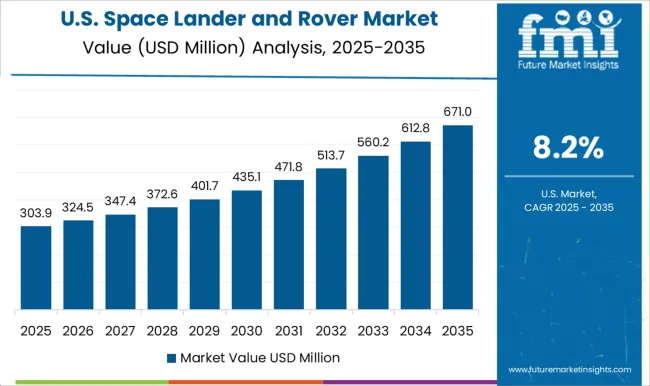
The United States space lander and rover market is growing at a CAGR of 8.2%, reflecting the country’s leadership in space exploration and technological innovation. NASA’s numerous missions to the Moon, Mars, and asteroids drive high demand for sophisticated landers and rovers. US companies are focusing on autonomous operation, advanced instrumentation, and AI-based navigation systems for planetary exploration. Public-private partnerships, such as those with SpaceX and Blue Origin, are accelerating development cycles and reducing costs. The market is also seeing innovations in energy-efficient propulsion, lightweight materials, and long-duration operational capabilities. Increased interest in lunar bases, asteroid mining, and deep-space exploration is boosting demand for advanced landers and rovers. With sustained investment in research and development, the United States remains a global leader in the space lander and rover market.
The space lander and rover market is rapidly expanding, driven by increasing investments in space exploration, lunar and Martian missions, and commercial space initiatives. These robotic platforms are critical for planetary exploration, sample collection, in-situ resource utilization, and scientific research. Both government space agencies and private aerospace companies are advancing technology to improve mobility, autonomy, and payload capacity for rovers and landers. Lockheed Martin Corporation is a major player, providing advanced lander systems, spacecraft, and robotics solutions for lunar and planetary missions. Airbus SE contributes with its expertise in space systems, designing robotic exploration vehicles and mission support technologies. Astrobotic Technology specializes in lunar payload delivery and rover development, enabling commercial and scientific missions to the Moon. Blue Origin is leveraging its aerospace capabilities to support lunar lander missions, while the Canadian Space Agency has contributed robotics expertise, particularly in mobility and manipulator systems. The China Academy of Space Technology develops landers and rovers for lunar and Mars exploration, supporting China’s ambitious planetary programs.
European Space Agency (ESA) and Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) actively design and deploy rovers and landers for collaborative and national exploration missions. ISRO (Indian Space Research Organization) continues to develop lander and rover technologies for lunar and interplanetary missions, complementing NASA’s robotic exploration programs. Northrop Grumman Corporation provides spacecraft and systems engineering for robotic planetary missions. Roscosmos develops robust planetary rovers and landers for scientific exploration of the Moon, Mars, and other celestial bodies. Innovative companies like ispace, Inc., and Spacebit Technologies are pioneering commercial lunar rovers and mobility solutions, supporting the growing private-sector participation in space exploration. The market outlook is strong, driven by technological innovation, international collaborations, and the rising interest in lunar and Mars missions, both from government space agencies and private enterprises.
| Item | Value |
|---|---|
| Quantitative Units | USD 666.3 Million |
| Mission Type | Lunar surface exploration, Mars surface exploration, and Asteroids and comet exploration |
| Vehicle Type | Space rovers and Space landers |
| Propulsion Type | Chemical propulsion, Electric/Ion propulsion, and Hybrid propulsion systems |
| Application | Scientific research, Resource exploration, Technology demonstration, and Others |
| End-user | Government and defense, Space exploration organizations, Private aerospace companies, and Research institutions |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America, Middle East & Africa |
| Country Covered | United States, Canada, Germany, France, United Kingdom, China, Japan, India, Brazil, South Africa |
| Key Companies Profiled | Lockheed Martin Corporation, Airbus SE, Astrobotic Technology, Astrobotic Technology, Inc, Blue Origin, Canadian Space Agency, China Academy of Space Technology, European Space Agency, ispace, inc., ISRO, Japanese Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), National Aeronautics and Space Administration, Northrop Grumman Corporation, Roscosmos, and Spacebit Technologies |
| Additional Attributes | Dollar sales by type including robotic landers, autonomous rovers, and hybrid exploration systems, application across planetary exploration, lunar missions, and asteroid research, and region covering North America, Europe, and Asia-Pacific. Growth is driven by increasing space exploration initiatives, government funding, and advancements in autonomous robotics technology. |
The global space lander and rover market is estimated to be valued at USD 666.3 million in 2025.
The market size for the space lander and rover market is projected to reach USD 1,681.7 million by 2035.
The space lander and rover market is expected to grow at a 9.7% CAGR between 2025 and 2035.
The key product types in space lander and rover market are lunar surface exploration, mars surface exploration and asteroids and comet exploration.
In terms of vehicle type, space rovers segment to command 58.7% share in the space lander and rover market in 2025.






Full Research Suite comprises of:
Market outlook & trends analysis
Interviews & case studies
Strategic recommendations
Vendor profiles & capabilities analysis
5-year forecasts
8 regions and 60+ country-level data splits
Market segment data splits
12 months of continuous data updates
DELIVERED AS:
PDF EXCEL ONLINE
Space-based C4ISR Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Space-Based Solar Power Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Space Frame Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Space Situational Awareness Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Space Robotics Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Space On Board Computing Platform Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Space Militarization Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Space Economy Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Space Power Electronics Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Space Management Solutions Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Industry Share Analysis for Space Tourism Providers
Space Tourism Industry Analysis by Supplier, by Age Group, by Tourism Type, by Demographics, by Nationality, by Booking Channel, by Tour Type, and by Region - Forecast for 2025 to 2035
Spacer Tapes Market Insights & Growth Outlook through 2034
Space DC-DC Converter Market Insights – Growth & Forecast 2024-2034
In Space Manufacturing Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Aerospace Fastener Manufacturing Solution Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Aerospace Fluid Conveyance System Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Aerospace Forging Materials Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Aerospace Cold Forgings Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Aerospace Defense Ducting Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035

Thank you!
You will receive an email from our Business Development Manager. Please be sure to check your SPAM/JUNK folder too.
Chat With
MaRIA