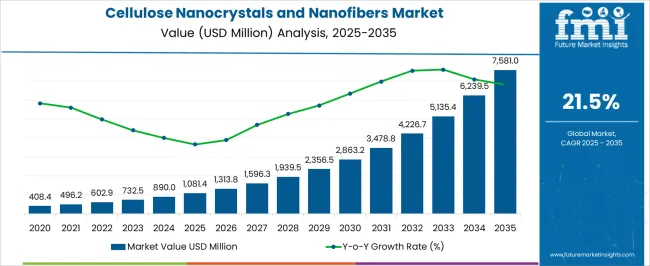
The cellulose nanocrystals and nanofibers market is estimated to be valued at USD 1081.4 million in 2025 and is projected to reach USD 7581.0 million by 2035, registering a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 21.5% over the forecast period.
Between 2021 and 2025, the market rises from USD 408.4 million to USD 1,081.4 million, reflecting strong early-stage growth driven by rising adoption across packaging, biomedical, electronics, and composite material applications. Incremental growth is observed with values reaching USD 496.2 million in 2022, USD 602.9 million in 2023, USD 732.5 million in 2024, and USD 890.0 million prior to attaining USD 1,081.4 million in 2025, demonstrating a rolling increase as adoption scales. From 2026 to 2030, the market continues an accelerated trajectory, growing from USD 1,081.4 million to USD 2,863.2 million. Annual increments indicate strong momentum, with market values of USD 1,313.8 million in 2026, USD 1,596.3 million in 2027, USD 1,939.5 million in 2028, USD 2,356.5 million in 2029, and USD 2,863.2 million in 2030.
Growth during this phase is fueled by the increasing use of cellulose nanocrystals and nanofibers as lightweight reinforcement in composites, biomedical scaffolds, barrier films, and conductive materials, alongside technological improvements in extraction and production efficiency. Between 2031 and 2035, the market accelerates further to USD 7,581.0 million. Values rise from USD 3,478.8 million in 2031 to USD 4,226.7 million in 2032, USD 5,135.4 million in 2033, USD 6,239.5 million in 2034, culminating at USD 7,581.0 million.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Cellulose Nanocrystals and Nanofibers Market Estimated Value in (2025 E) | USD 1081.4 million |
| Cellulose Nanocrystals and Nanofibers Market Forecast Value in (2035 F) | USD 7581.0 million |
| Forecast CAGR (2025 to 2035) | 21.5% |
The cellulose nanocrystals and nanofibers market is shaped by several parent markets that define its scope and applications across advanced materials and industrial sectors. The nanomaterials market provides a broad base, with cellulose nanocrystals (CNCs) and nanofibers (CNFs) contributing nearly 12-15% of its share. Their nanoscale structure, high strength, and biodegradability position them as renewable alternatives to synthetic nanomaterials. The biomaterials market is another key driver, accounting for around 10-12%, as CNCs and CNFs are being adopted in biomedical, pharmaceutical, and eco-friendly material applications due to their renewable origin and biocompatibility. The paper and pulp market contributes about 8-10%, where cellulose nanofibers are used to reinforce packaging, improve durability, and enhance barrier properties in specialty paper products.
The polymer and composites market also plays a major role, holding nearly 9-11% of the share, as CNCs and CNFs are integrated into plastics, automotive components, and construction composites to strengthen mechanical performance while reducing reliance on non-renewable fillers. Lastly, the coatings and adhesives market represents approximately 6-8% of the demand. Here, cellulose nanomaterials are applied to enhance viscosity, adhesion, and barrier properties, finding applications in paints, packaging, and electronics. Together, these parent markets emphasize the versatility of cellulose nanocrystals and nanofibers, reflecting their rising role in industries seeking high-performance, lightweight, and renewable materials.
The market is experiencing accelerated growth driven by the rising demand for sustainable, high-performance materials in diverse industrial applications. The unique mechanical strength, lightweight nature, and biodegradability of these nanocellulose products are making them an attractive alternative to petroleum-based materials. Increasing environmental regulations, coupled with corporate sustainability goals, are encouraging the adoption of cellulose-based solutions across packaging, composites, and specialty chemical industries.
Technological advancements in extraction and processing methods are improving production efficiency and scalability, further supporting market expansion. Additionally, research and innovation in nanocellulose applications are opening opportunities in electronics, biomedical devices, and barrier materials.
Strategic collaborations between raw material suppliers, research institutions, and end-user industries are strengthening the commercialization pathway As industries shift towards renewable feedstocks and eco-friendly materials, cellulose nanocrystals and nanofibers are positioned as key enablers of the transition, ensuring their sustained relevance in the global materials landscape.
The cellulose nanocrystals and nanofibers market is segmented by product type, source, application, end use industry, and geographic regions. By product type, cellulose nanocrystals and nanofibers market is divided into cellulose nanofibers (CNFs), cellulose nanocrystals (CNCs), bacterial nanocellulose (BNC), cellulose nanofibrils (CNF), and other nanocellulose products. In terms of source, cellulose nanocrystals and nanofibers market is classified into wood, non-wood plant sources, bacterial synthesis, algae and tunicates, and recycled sources. Based on application, cellulose nanocrystals and nanofibers market is segmented into composites, paper and packaging, coatings and films, biomedical and pharmaceutical, electronics and sensors, rheology modifiers, filtration and separation, aerogels and foams, and other applications. By end use industry, cellulose nanocrystals and nanofibers market is segmented into packaging, pulp and paper, food and beverage, healthcare and pharmaceuticals, electronics and optoelectronics, automotive and transportation, construction and building materials, textiles and apparel, personal care and cosmetics, oil and gas, paints, coatings, and adhesives, and others. Regionally, the cellulose nanocrystals and nanofibers industry is classified into North America, Latin America, Western Europe, Eastern Europe, Balkan & Baltic Countries, Russia & Belarus, Central Asia, East Asia, South Asia & Pacific, and the Middle East & Africa.
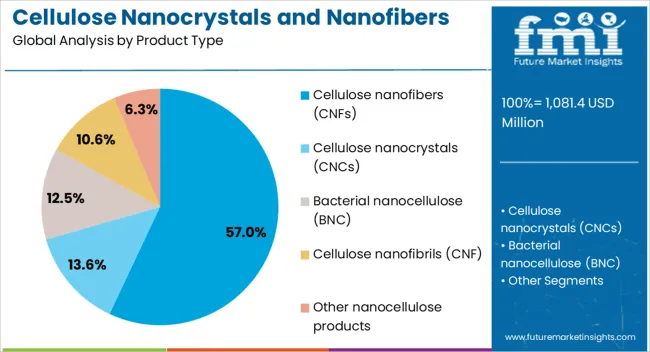
The cellulose nanofibers segment is projected to hold 57% of the cellulose nanocrystals and nanofibers market revenue share in 2025, making it the leading product type. This dominance has been driven by their exceptional tensile strength, flexibility, and ability to improve the mechanical properties of composite materials. Their compatibility with various polymers and resins has enabled wide adoption in applications requiring lightweight yet durable components. In industries such as automotive, construction, and packaging, cellulose nanofibers are being increasingly used to enhance performance while reducing reliance on synthetic fibers. The sustainable nature of these fibers, derived from renewable biomass, aligns with growing environmental priorities. Cost-effectiveness achieved through advancements in processing technology has further contributed to their popularity Moreover, the capability to tailor surface chemistry for specific end-use requirements has widened their application potential, reinforcing their market-leading position.
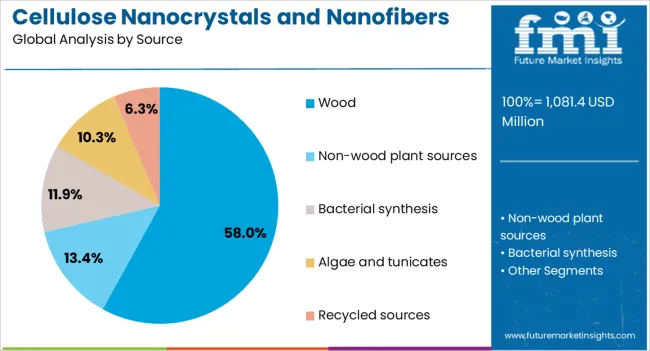
The wood source segment is expected to command 58% of the market revenue share in 2025, emerging as the dominant raw material source. This leadership position is supported by the abundant availability of wood biomass and its well-established supply chain infrastructure. The high cellulose content in wood, combined with cost-efficient extraction processes, has made it a preferred choice for large-scale production. Consistency in quality and performance has been a critical factor in securing long-term adoption across industries. The use of wood as a feedstock also supports circular economy principles, as it enables the conversion of forestry by-products into high-value nanomaterials. Technological advancements in pulping and nanofibrillation processes have enhanced yield and reduced production costs, further strengthening its competitiveness As sustainability becomes a core requirement in material sourcing, wood-derived nanocellulose is expected to maintain its leading role in meeting both performance and environmental targets.
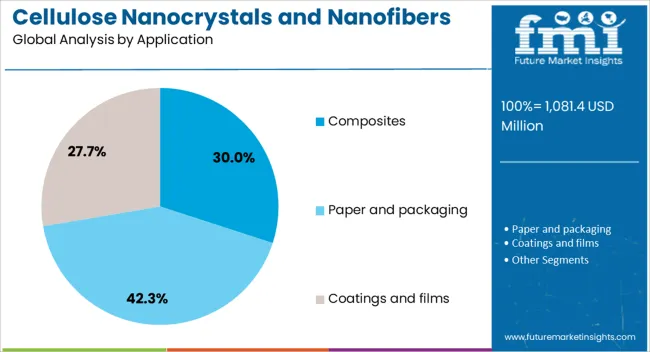
The composites segment is forecasted to hold 30% of the market revenue share in 2025, representing the largest application area. Growth in this segment has been propelled by the increasing need for high-strength, lightweight materials in sectors such as automotive, aerospace, and construction. Incorporation of cellulose nanocrystals and nanofibers into composite matrices has been shown to significantly enhance mechanical, thermal, and barrier properties. This has driven their adoption in applications where performance, durability, and sustainability are equally critical. The ability to integrate these nanomaterials into both thermoset and thermoplastic systems has expanded their versatility. As manufacturers seek to reduce carbon footprints and improve material recyclability, nanocellulose-reinforced composites have gained traction as an environmentally responsible alternative to traditional composites Ongoing advancements in dispersion techniques and surface modification are further enhancing compatibility with various polymer systems, ensuring sustained demand in this segment.
The cellulose nanocrystals and nanofibers market is expanding, driven by rising use in packaging, automotive, and medical applications. Their strength, transparency, and biodegradability make them attractive for high-performance composites and coatings. However, high production costs, limited scalability, and processing complexities remain barriers to wider adoption. Opportunities are increasing in biocomposites, drug delivery, and flexible electronics, supported by active research collaborations. With pilot projects advancing toward commercialization and regional adoption gaining momentum, cellulose nanocrystals and nanofibers are emerging as versatile materials with growing importance across multiple industries.
The cellulose nanocrystals and nanofibers market is gaining traction as industries seek lightweight, high-strength, and renewable alternatives to traditional materials. Their superior mechanical properties, biodegradability, and optical transparency make them attractive for packaging, automotive, and electronics applications. In packaging, they are used to improve barrier properties of films, enhancing protection against moisture and gases. Automotive manufacturers are incorporating nanocellulose into composites to reduce weight while maintaining durability, contributing to improved efficiency. Electronics and medical devices are also exploring these materials for coatings and reinforcement purposes. Their versatility across multiple industries, coupled with increasing interest in bio-based feedstocks, has positioned cellulose nanocrystals and nanofibers as advanced materials with strong potential. The growing demand for innovative, high-performance solutions is expected to continue supporting their adoption in both developed and emerging economies.
Cellulose nanocrystals and nanofibers face significant challenges that limit widespread commercialization. The production process requires advanced chemical treatments and mechanical refining, both of which are costly and energy-intensive. Maintaining consistency in quality across batches remains difficult, as properties can vary depending on the feedstock and processing methods used. Limited large-scale production infrastructure further restricts supply and makes pricing less competitive compared to conventional polymers and composites. The storage stability and sensitivity to moisture complicate logistics and end-use performance. Intellectual property barriers, coupled with fragmented research efforts, also slow down technology transfer to industries that could benefit most. These limitations result in higher costs for end users, discouraging adoption in cost-sensitive applications. Addressing these challenges through technological improvements and scaled-up production is critical for expanding the reach of cellulose nanocrystals and nanofibers.
Emerging applications are creating promising opportunities for cellulose nanocrystals and nanofibers. Their reinforcement ability in polymers is driving the growth of lightweight biocomposites used in construction, packaging, and consumer goods. In medical applications, their biocompatibility makes them suitable for drug delivery systems, wound dressings, and tissue engineering scaffolds, opening new growth areas. Researchers are also exploring their potential in electronics, where they can serve as substrates for flexible devices or as additives for improved conductivity. Their ability to form transparent films with excellent strength-to-weight ratios is attracting attention in optical applications as well. Strategic collaborations between universities, research institutions, and industrial players are accelerating progress in tailoring nanocellulose properties for specific uses. These advancements are paving the way for greater integration across industries, where performance improvements and versatility create a compelling case for adoption in high-value applications.
A defining trend in the cellulose nanocrystals and nanofibers market is the emphasis on research-driven innovation and early commercialization. Companies are investing in pilot-scale facilities to address the gap between laboratory discoveries and industrial-scale applications. Governments and research institutes are supporting programs that encourage commercialization through funding, joint ventures, and industrial partnerships. The focus is shifting toward developing standardized processing methods that ensure consistent performance and reduce costs, making the materials more accessible. Regional adoption varies, with North America and Europe advancing through industrial trials, while Asia shows growing interest due to its strong pulp and paper base. Industry leaders are also collaborating across sectors, combining nanocellulose with advanced polymers, coatings, and electronics, thereby broadening the market’s scope. These trends highlight a shift from experimental development toward structured commercialization, setting the foundation for future growth.
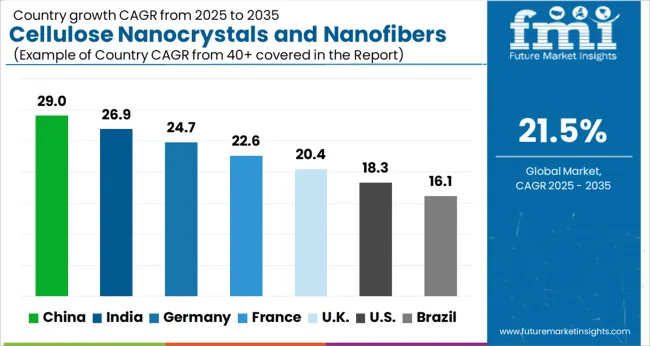
| Country | CAGR |
|---|---|
| China | 29.0% |
| India | 26.9% |
| Germany | 24.7% |
| France | 22.6% |
| UK | 20.4% |
| USA | 18.3% |
| Brazil | 16.1% |
The cellulose nanocrystals and nanofibers market is projected to grow at a global CAGR of 21.5% from 2025 to 2035, with China leading at 29.0%, followed by India at 26.9% and France at 22.6%, while the UK records 20.4% and the USA posts 18.3%. Asia dominates expansion due to strong agricultural resources, cost-efficient production, and government-backed R&D, with China and India setting the pace. Europe demonstrates steady growth with industrial innovation in France and research-oriented activity in the UK The USA, although slower, maintains strategic momentum through aerospace, defense, and healthcare applications. The analysis spans over 40+ countries, with the leading markets shown below.
China is expected to lead the cellulose nanocrystals and nanofibers market with a CAGR of 29.0% from 2025 to 2035. The rapid expansion is tied to large-scale research programs, industrial applications, and government-backed initiatives for advanced material science. The use of nanocellulose in packaging, electronics, biomedical devices, and construction is receiving strong support from both domestic enterprises and academic institutions. Collaborations between global companies and local players are also fostering technological exchange, enhancing the commercial viability of cellulose nanocrystals and nanofibers in multiple sectors.
India is forecast to record a CAGR of 26.9% during 2025–2035 in the cellulose nanocrystals and nanofibers market. The growth is being shaped by strong academic research, rising demand in packaging and textiles, and increasing focus on biopolymer-based industrial materials. Indian institutes and start-ups are driving innovation in extraction methods, making cellulose nanocrystals more cost-efficient for local industries. Applications in pharmaceuticals and food-grade materials are also gaining momentum. With a large agricultural base providing abundant raw material sources, India is positioning itself as a key supplier in global markets.
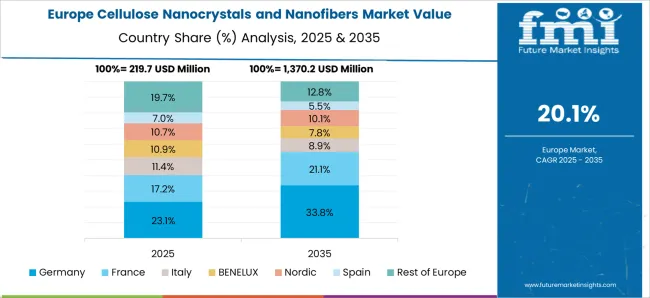
France is anticipated to expand at a CAGR of 22.6% between 2025 and 2035 in the cellulose nanocrystals and nanofibers market. Demand is being driven by the country’s advanced chemical and material industries, supported by research institutions focusing on nanomaterials. French companies are channeling resources into packaging, electronics, and biomedical sectors, with cellulose nanofibers increasingly viewed as high-value additives. Government-backed innovation programs are accelerating industrial adoption, particularly in composites and performance-enhancing coatings. Cross-industry collaboration between academic institutions and manufacturing enterprises ensures faster commercialization of research outputs.
The United Kingdom is projected to achieve a CAGR of 20.4% between 2025 and 2035 in the cellulose nanocrystals and nanofibers market. Industrial players are exploring applications in electronics, medical devices, and coatings. The research sector, supported by universities, plays a critical role in advancing nanocellulose technologies, particularly in precision medicine and advanced packaging. British firms are entering partnerships with European and Asian companies to accelerate the scaling of production processes. Governmental interest in advanced material science further supports funding for pilot projects, enhancing commercialization.
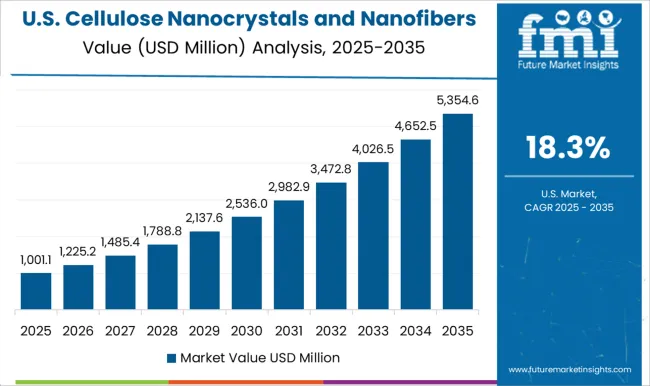
The United States is forecast to record a CAGR of 18.3% from 2025 to 2035 in the cellulose nanocrystals and nanofibers market. Growth is largely influenced by the strong industrial base, advanced R&D, and increasing focus on applications in aerospace, defense, and healthcare. Research institutions and leading chemical companies are driving innovation in nanocellulose extraction and functionalization techniques. Adoption is spreading across diverse sectors such as packaging, construction, and automotive, supported by large-scale pilot projects. Federal programs and grants are encouraging companies to advance production technologies, while partnerships with global firms are facilitating cross-border application expansion..
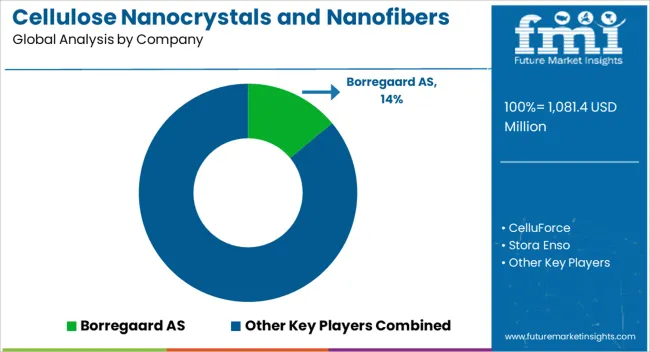
In the cellulose nanocrystals and nanofibers market, competition is defined by product differentiation, scalable production, and application development across packaging, composites, coatings, and specialty chemicals. Borregaard AS leverages its expertise in biorefined products, offering cellulose nanomaterials designed for rheology control, barrier properties, and reinforcement in industrial applications. CelluForce, one of the earliest producers of cellulose nanocrystals (CNCs), emphasizes proprietary processing and partnerships with industrial users, supplying materials for advanced composites, coatings, and performance additives. Stora Enso invests heavily in nanocellulose as part of its broader bio-based materials strategy, focusing on applications in sustainable packaging and advanced fiber composites. Nippon Paper Industries promotes cellulose nanofibers (CNFs) targeted at automotive parts, electronics, and functional coatings, supported by large-scale production capacity.
FiberLean Technologies competes with its mineral–nanofibrillated cellulose composites, offering cost-effective reinforcement solutions in paper, packaging, and specialty industrial sectors. Smaller innovators such as CelluComp and Melodea highlight unique formulations, with CelluComp advancing CNF-based additives for paints, coatings, and concrete, while Melodea develops barrier films and coatings for sustainable packaging. Kruger Inc. focuses on CNFs for papermaking and specialty applications, leveraging its established pulp and paper infrastructure. Sappi and UPM pursue broader bio-innovation strategies, integrating nanocellulose into packaging, textiles, and performance chemicals while investing in pilot projects to scale adoption. Product brochures showcase versatile properties: Borregaard emphasizes rheology modifiers and dispersants; CelluForce highlights CNCs for strength and barrier applications; Stora Enso and Nippon Paper detail CNFs for packaging and coatings; FiberLean presents composites combining minerals and nanocellulose; CelluComp and Melodea emphasize specialty uses in paints, coatings, and packaging; Kruger, Sappi, and UPM underline scalable CNF solutions integrated into pulp and bio-based material chains. These brochures reinforce nanocellulose as a multifunctional, renewable material with wide industrial applicability.
| Item | Value |
|---|---|
| Quantitative Units | USD 1081.4 million |
| Product Type | Cellulose nanofibers (CNFs), Cellulose nanocrystals (CNCs), Bacterial nanocellulose (BNC), Cellulose nanofibrils (CNF), and Other nanocellulose products |
| Source | Wood, Non-wood plant sources, Bacterial synthesis, Algae and tunicates, and Recycled sources |
| Application | Composites, Paper and packaging, Coatings and films, Biomedical and pharmaceutical, Electronics and sensors, Rheology modifiers, Filtration and separation, Aerogels and foams, and Other applications |
| End Use Industry | Packaging, Pulp and paper, Food and beverage, Healthcare and pharmaceuticals, Electronics and optoelectronics, Automotive and transportation, Construction and building materials, Textiles and apparel, Personal care and cosmetics, Oil and gas, Paints, coatings, and adhesives, and Others |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America, Middle East & Africa |
| Country Covered | United States, Canada, Germany, France, United Kingdom, China, Japan, India, Brazil, South Africa |
| Key Companies Profiled | Borregaard AS, CelluForce, Stora Enso, Nippon Paper Industries, FiberLean Technologies, CelluComp, Melodea, Kruger Inc., Sappi, and UPM |
| Additional Attributes | Dollar sales by product type (cellulose nanocrystals, cellulose nanofibers), source material (wood pulp, recycled fibers, agricultural residues), and application (packaging, composites, coatings, biomedical, construction). Demand is driven by increased adoption of lightweight, high-strength, and biodegradable materials. Regional trends indicate strong growth in North America, Europe, and Asia-Pacific, supported by industrial innovation, green material initiatives, and investment in advanced manufacturing processes. |
The global cellulose nanocrystals and nanofibers market is estimated to be valued at USD 1,081.4 million in 2025.
The market size for the cellulose nanocrystals and nanofibers market is projected to reach USD 7,581.0 million by 2035.
The cellulose nanocrystals and nanofibers market is expected to grow at a 21.5% CAGR between 2025 and 2035.
The key product types in cellulose nanocrystals and nanofibers market are cellulose nanofibers (cnfs), mechanically fibrillated cnfs, tempo-oxidized cnfs, enzymatically pretreated cnfs, and others.
In terms of source, wood segment to command 58.0% share in the cellulose nanocrystals and nanofibers market in 2025.






Full Research Suite comprises of:
Market outlook & trends analysis
Interviews & case studies
Strategic recommendations
Vendor profiles & capabilities analysis
5-year forecasts
8 regions and 60+ country-level data splits
Market segment data splits
12 months of continuous data updates
DELIVERED AS:
PDF EXCEL ONLINE
Cellulose Derivative Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Cellulose Film Packaging Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Cellulose Esters Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Cellulose Gel Market Growth, Forecast, and Analysis 2025 to 2035
Market Share Insights for Cellulose Fiber Providers
Key Players & Market Share in Cellulose Film Packaging Market
Cellulose Fiber Market by Material Source from 2024 to 2034
Cellulose Ether and Derivatives Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Nanocellulose Coating Market Analysis - Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Nanocellulose Barrier Coating Market Analysis - Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Nanocellulose Market Report - Demand, Growth & Industry Outlook 2025 to 2035
Ethyl Cellulose Market
Methyl Cellulose Market
Powdered Cellulose Market Analysis - Size, Share, and Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Ethyl Methyl Cellulose Market
Carboxymethyl Cellulose Market 2024-2034
Japan Powdered Cellulose Market, By Type, By Application, By Region, and Forecast, 2025 to 2035
Korea Powdered Cellulose Market Analysis by Source, End-use, Functionality, and Region Through 2035
Nanocrystalline cellulose Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Microcrystalline Cellulose Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035

Thank you!
You will receive an email from our Business Development Manager. Please be sure to check your SPAM/JUNK folder too.
Chat With
MaRIA