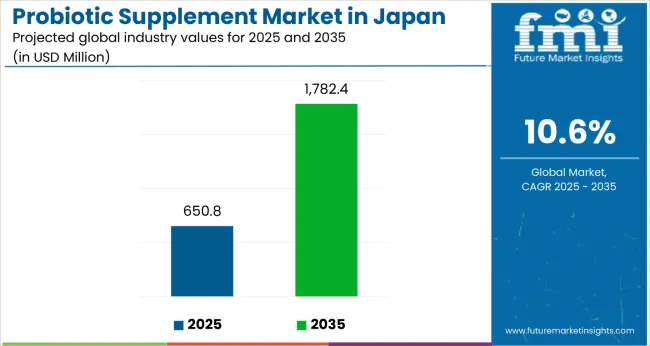
Sales of probiotic supplements in Japan are estimated at USD 650.8 million in 2025, and are projected to reach USD 1,782.4 million by 2035, reflecting a CAGR of 10.6% over the forecast period.
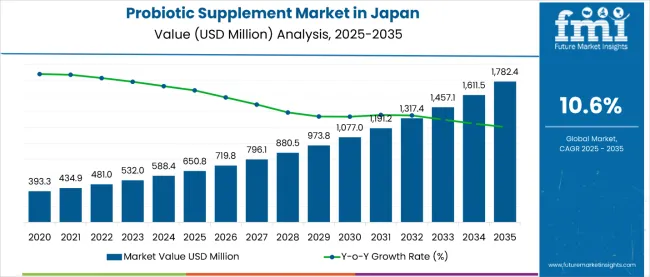
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Estimated Size (2025E) | USD 650.8 million |
| Projected Value (2035F) | USD 1,782. 4 million |
| CAGR (2025-2035) | 10.6% |
This growth reflects both a broadening consumer base and increased per capita consumption in key urban centres. The rise in demand is linked to shifting dietary preferences, growing awareness of gut health benefits, and evolving health consciousness trends. By 2025, per capita consumption in leading Japanese regions such as Kanto, Chubu, and Kinki averages between 2.1 to 2.4 kilograms, with projections reaching 3.2 kilograms by 2035. Tokyo leads among metropolitan areas, expected to generate USD 297 million in probiotic supplement sales by 2035, followed by Osaka (USD 189 million), Nagoya (USD 134 million), Fukuoka (USD 89 million), and Sendai (USD 67 million).
The largest contribution to demand continues to come from women consumers, who are expected to account for 44% of total sales in 2025, owing to strong health consciousness, preventive care focus, and increased awareness of gut health benefits. By bacteria type, lactobacillus represents the dominant formulation, responsible for 38% of all sales, while capsule forms and immunity-focused products are expanding rapidly.
Consumer adoption is particularly concentrated among health-conscious women and aging populations, with income and urban density emerging as significant drivers of demand. While price sensitivity remains a factor, the average price premium over conventional supplements has declined from 28% in 2020 to 19% in 2025. Continued improvements in manufacturing scale and private label offerings are expected to accelerate affordability and access across mid-income households. Regional disparities persist, but per capita demand in emerging regions is narrowing the gap with traditionally strong urban hubs.
The probiotic supplement in Japan is classified across several segments. By bacteria type, the key categories include lactobacillus, streptococcus, bifidobacterium, and emerging probiotic strains. By form, the segment spans tablets, capsules, liquid formulations, powder premixes, gummies/chewables, lozenges, and liquid gels. By function, formulations include immunity & digestive health, urogenital health, vaginal health, urinary tract infections, pregnancy support, and weight management. By end user, the segment covers women, seniors, and kids with growing health consciousness.
By distribution channel, categories include hypermarkets/supermarkets, specialty stores, e-commerce platforms, and pharmacy stores. By region, areas such as Kanto, Chubu, Kinki, Kyushu & Okinawa, Tohoku, and Rest of Japan are included.
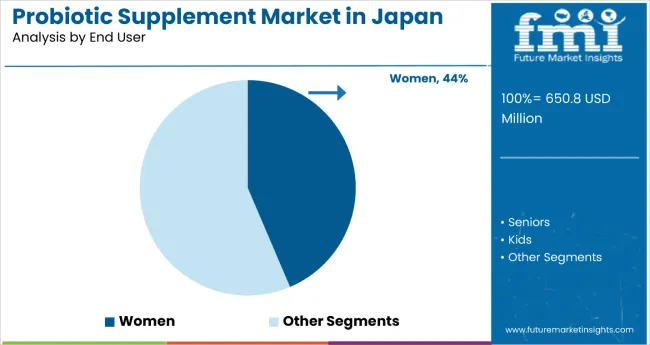
Women are projected to dominate sales in 2025, supported by heightened health awareness, focus on preventive care, and growing understanding of gut health connections to overall wellness. Other demographics such as seniors and kids are growing steadily, each serving distinct health needs.
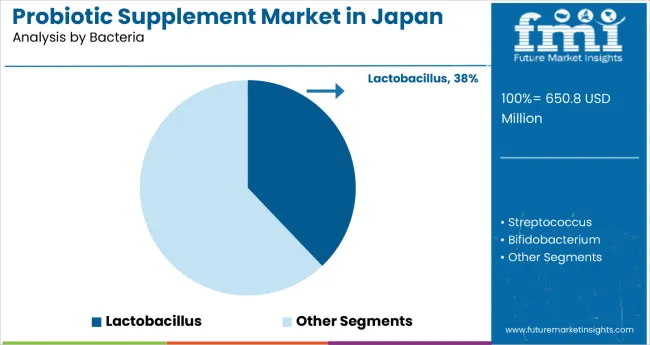
Probiotic supplements in Japan utilize a variety of bacterial strains, selected for efficacy, research backing, consumer familiarity, and health benefits. Lactobacillus is expected to remain the primary bacterial type in 2025, followed by bifidobacterium and streptococcus. Formulation strategies are evolving to match consumer health priorities, with growth coming from both single-strain and multi-strain products.
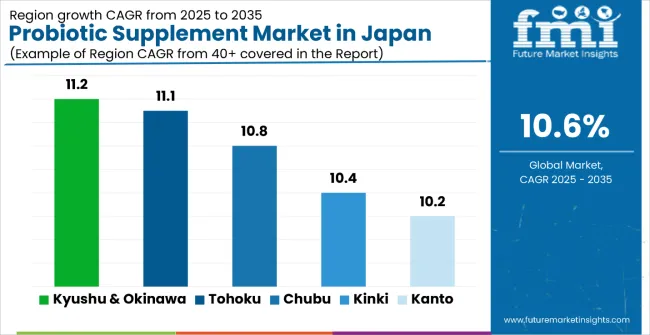
| Region | CAGR (2025 to 2035) |
|---|---|
| Kyushu & Okinawa | 11.2% |
| Tohoku | 11.1% |
| Chubu | 10.8% |
| Kinki | 10.4% |
| Kanto | 10.2% |
Probiotic supplement sales will not grow uniformly across every prefecture. Rising urbanization and faster per-capita adoption in developing regions give Kyushu & Okinawa and Tohoku a measurable edge, while mature metropolitan areas such as Kanto expand more steadily from a higher base. The table below shows the compound annual growth rate (CAGR) which is expected to record between 2025 and 2035.
Between 2025 and 2035, demand for probiotic supplements is projected to expand across all major Japanese regions, but the pace of growth will vary based on demographic shifts, retail penetration, and baseline consumption levels. Among the top five regions analyzed, Kyushu & Okinawa and Tohoku are expected to register the fastest compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 11.2% and 11.1% respectively, outpacing more mature metropolitan hubs.
This acceleration is underpinned by a combination of factors: aging population focus on health, growing wellness awareness, and increasing availability of probiotic products across pharmacy chains and health stores. In both regions, per capita consumption is projected to rise from 1.8 kg in 2025 to 2.9 kg by 2035, closing the gap with higher-consumption regions such as Kanto and Kinki. Retail assortment is also expanding faster in these regions, with new specialized formulations and targeted health applications gaining traction in regional pharmacy networks and wellness stores.
Chubu and Kinki are each forecast to grow at a CAGR of 10.8% and 10.4% respectively over the same period. Both regions already maintain established retail ecosystems, with widespread access to diverse probiotic supplement formulations in pharmacies, health stores, and specialized wellness retailers. In Chubu, growth is supported by a strong health-conscious consumer base, product innovation, and increasing uptake of functional health solutions.
Kinki reflects similar dynamics, particularly among women consumers and households seeking preventive healthcare approaches. In both regions, per capita consumption is projected to increase from 2.2 kg in 2025 to 3.1 kg by 2035, reflecting mainstreaming of probiotic health solutions.
Kanto, while maintaining the highest overall sales in absolute terms, is expected to grow at a CAGR of 10.2%, slightly below its peripheral counterparts. The region already exhibits higher-than-average per capita intake (2.4 kg in 2025), extensive product saturation, and a dense urban retail network. Growth will likely come from repeat purchasing, specialized health applications, and premium product expansion rather than first-time trial.
Collectively, these five regions represent the core of urban demand for probiotic supplements in Japan, but their individual growth paths highlight the importance of regional tailoring in product development, health positioning, and distribution strategy.
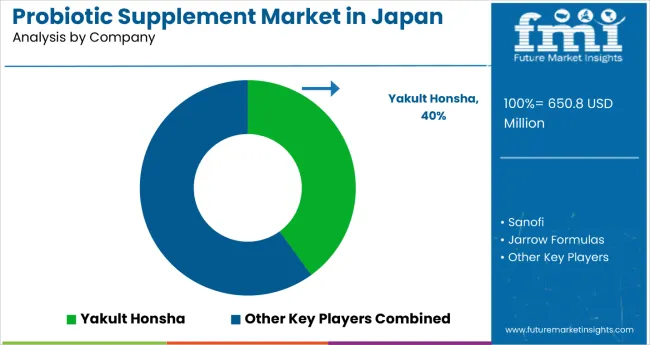
The competitive environment is characterized by a mix of established healthcare manufacturers and specialized probiotic companies. Distribution breadth rather than sheer product count remains the decisive success factor: the five largest suppliers collectively reach more than 15,000 retail outlets nationwide and account for a majority of pharmacy and health store shelf facings in the category.
The next tier comprises diversified healthcare companies. Suntory Holdings Limited focuses on premium wellness products and functional health applications; recent financial reports showed growing supplement segment contributions, signaling national but still developing scale. Eisai Co., Ltd., leveraging pharmaceutical industry expertise, adds specialized probiotic formulations to healthcare product portfolios and is expected to benefit from clinical research credibility and healthcare provider recommendations.
Private-label programs at major pharmacy chains and health retailers are widening assortment at price points 15-20% below branded equivalents, putting margin pressure on smaller suppliers while supporting household adoption. Consolidation is therefore likely to continue as distribution scale and healthcare channel reach become critical for maintaining shelf visibility and promotional frequency in this rapidly evolving category.
| Item | Value |
|---|---|
| Quantitative Units | USD 650.8 Million |
| By Bacteria | Lactobacillus, Streptococcus, and Bifidobacterium |
| By Form | Tablet, Capsules, Liquid, Powder Premixes, Gummies/Chewable, Lozenges a nd Liquid & Gels |
| By Function | Immunity and Digestive Health, Urogenital Health, Vaginal Health, Urinary Tract Infections, Pregnancy, and Weight Management |
| By Distribution Channel | Hypermarket/Supermarket, Specialty Stores, eCommerce, and Pharmacy Stores |
| By End User | Women, Seniors, and Kids |
| Regions Covered | Kanto, Chubu, Kinki, Kyushu & Okinawa, Tohoku, and Rest of Japan |
| Key Companies Profiled | Yakult Honsha, Moringa Milk, Jarrow Formulas, NOVA Probiotics, Lifeway Foods, Inc., Church & Dwight Co. Inc., PharmaCare Laboratories, Total Nutrition, Inc., Sanofi, and Goerlich Pharma |
| Additional Attributes | Dollar sales by application and purity grade, regional demand trends, competitive landscape, consumer preferences for natural versus synthetic alternatives, integration with sustainable sourcing practices, innovations in extraction technology and quality standardization for diverse industrial applications |
The global demand and trend analysis of probiotic supplement in Japan is estimated to be valued at USD 0.7 billion in 2025.
The market size for the demand and trend analysis of probiotic supplement in Japan is projected to reach USD 1.7 billion by 2035.
The demand and trend analysis of probiotic supplement in Japan is expected to grow at a 10.1% CAGR between 2025 and 2035.
The key product types in demand and trend analysis of probiotic supplement in Japan are lactobacillus, streptococcus and bifidobacterium.
In terms of form, capsules segment to command 36.4% share in the demand and trend analysis of probiotic supplement in Japan in 2025.






Our Research Products

The "Full Research Suite" delivers actionable market intel, deep dives on markets or technologies, so clients act faster, cut risk, and unlock growth.

The Leaderboard benchmarks and ranks top vendors, classifying them as Established Leaders, Leading Challengers, or Disruptors & Challengers.

Locates where complements amplify value and substitutes erode it, forecasting net impact by horizon

We deliver granular, decision-grade intel: market sizing, 5-year forecasts, pricing, adoption, usage, revenue, and operational KPIs—plus competitor tracking, regulation, and value chains—across 60 countries broadly.

Spot the shifts before they hit your P&L. We track inflection points, adoption curves, pricing moves, and ecosystem plays to show where demand is heading, why it is changing, and what to do next across high-growth markets and disruptive tech

Real-time reads of user behavior. We track shifting priorities, perceptions of today’s and next-gen services, and provider experience, then pace how fast tech moves from trial to adoption, blending buyer, consumer, and channel inputs with social signals (#WhySwitch, #UX).

Partner with our analyst team to build a custom report designed around your business priorities. From analysing market trends to assessing competitors or crafting bespoke datasets, we tailor insights to your needs.
Supplier Intelligence
Discovery & Profiling
Capacity & Footprint
Performance & Risk
Compliance & Governance
Commercial Readiness
Who Supplies Whom
Scorecards & Shortlists
Playbooks & Docs
Category Intelligence
Definition & Scope
Demand & Use Cases
Cost Drivers
Market Structure
Supply Chain Map
Trade & Policy
Operating Norms
Deliverables
Buyer Intelligence
Account Basics
Spend & Scope
Procurement Model
Vendor Requirements
Terms & Policies
Entry Strategy
Pain Points & Triggers
Outputs
Pricing Analysis
Benchmarks
Trends
Should-Cost
Indexation
Landed Cost
Commercial Terms
Deliverables
Brand Analysis
Positioning & Value Prop
Share & Presence
Customer Evidence
Go-to-Market
Digital & Reputation
Compliance & Trust
KPIs & Gaps
Outputs
Full Research Suite comprises of:
Market outlook & trends analysis
Interviews & case studies
Strategic recommendations
Vendor profiles & capabilities analysis
5-year forecasts
8 regions and 60+ country-level data splits
Market segment data splits
12 months of continuous data updates
DELIVERED AS:
PDF EXCEL ONLINE
Japan Probiotic Yogurt Market is segmented by product type, source type, nature type, flavor type, fat content, sales channel and key city/province through 2025 to 2035.
Probiotic Supplements Market Analysis - Size, Share, and Forecast 2025 to 2035
Probiotic Supplements Market Share Analysis – Key Trends & Forecast 2025-2035
Japan Dietary Supplements Market, By Ingredients, Form, Application, and Region through 2035
Japan Calcium Supplement Market Trends – Growth, Demand & Forecast 2025-2035
UK Probiotic Supplements Market Report – Size, Share & Outlook 2025-2035
USA Probiotic Supplement Market Trends – Growth, Demand & Forecast 2025-2035
Pet Probiotics Supplements Market - Size, Share, and Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Korea Probiotic Supplement Industry – Industry Insights & Demand 2025 to 2035
ASEAN Probiotic Supplements Market Trends – Growth, Demand & Forecast 2025-2035
Postnatal Probiotic Supplements Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Australia Probiotic Supplements Market Trends – Growth, Demand & Forecast 2025–2035
Demand for Probiotic Supplements in EU Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Latin America Probiotic Supplements Market Trends – Growth, Demand & Forecast 2025–2035
Western Europe Probiotic Supplement Market Analysis in – Growth & Market Trends from 2025 to 2035
Demand for Weight Loss Supplements in Japan Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Japan Faith-based Tourism Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Japan Sports Tourism Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Japan Respiratory Inhaler Devices Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Japan Halal Tourism Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035

Thank you!
You will receive an email from our Business Development Manager. Please be sure to check your SPAM/JUNK folder too.
Chat With
MaRIA