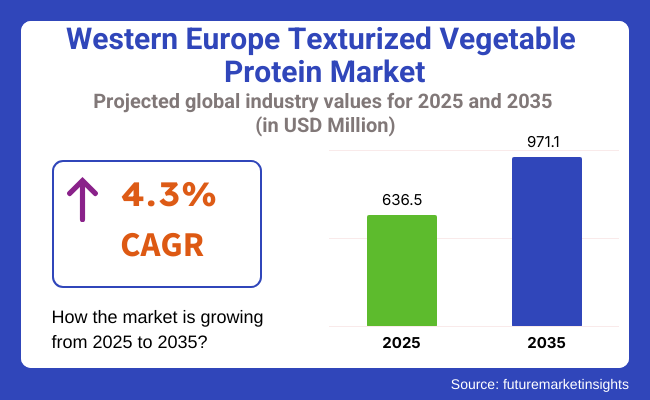
The Western Europe texturized vegetable protein market is poised to register a valuation of USD 636.5 million in 2025. The industry is slated to grow at 4.3% CAGR from 2025 to 2035, witnessing USD 971.1 million by 2035. The expansion of the industry is due to a mix of changing consumer tastes, changing dietary patterns, and increasing environmental consciousness.
One of the main drivers is the growing demand for vegetable-based protein sources as consumers increasingly become health-conscious and look for alternatives to animal products. Texturized vegetable protein, often processed from soy, wheat, or pea, is a cost-effective, flexible, and high-protein alternative that can appeal to vegetarians as well as flexitarians.
With increased concerns over saturated fats, cholesterol, and the correlation of red meat with chronic conditions, individuals are increasingly turning towards plant-based products, particularly in Germany, the UK, and the Netherlands.
Ecological sustainability is yet another main driver that is boosting the growth of TVP markets. In comparison to conventional meat production, plant-based proteins have a much smaller environmental impact, needing less land, water, and energy and producing less greenhouse gas emissions.
As global warming is an increasingly urgent concern, Western European consumers and policymakers alike are emphasizing sustainable food systems. This has resulted in heightened support for plant-based innovations via public campaigns, eco-labeling, and even school and hospital meal recommendations encouraging plant-based eating.
The food technology and culinary diversity have increased the appeal of texturized vegetable proteins. New TVP products closely replicate the texture and mouthfeel of meat, and thus they are perfectly suitable for application in burgers, sausages, sauces, and ready meals.
With food companies developing and diversifying their product lines, consumers can enjoy more delicious and satisfying plant-based meals than ever. Along with the growth of veganism, ethical eating, and allergy-friendly eating (e.g., dairy-free, egg-free), TVP is marketed as a dependable solution that suits many types of diets
The texturized vegetable protein (TVP) industry in Western Europe is witnessing diversified demand patterns among main end-use applications on the back of changing food trends and consumers' priorities. Food producers are prioritizing clean-label ingredients, sustainability, and cost savings.
TVP is preferred for its capability to mix into meat substitutes, ready meals, and convenience foods, particularly as hybrid products (hybrids of meat-TVP) find popularity among flexitarians. Producers value consistent texture, neutral taste, and extended shelf life, which makes TVP an economical bulk commodity. In the foodservice industry, too, versatility and ease of preparation are essential.
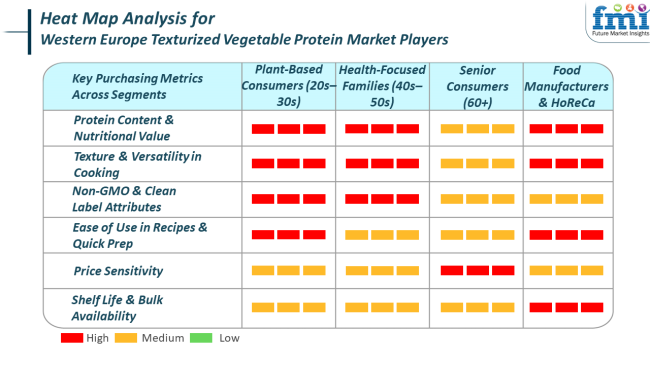
Restaurants, cafes, and institutional foodservice facilities are adding more plant-based items to menus, looking for TVP products that provide good taste, quick prep time, and customer acceptance. Pre-seasoned or half-prepared TVP forms are gaining massive traction in this category because of growing consumers seeking fast, plant-based meals.
Household consumers are embracing TVP on the basis of its health advantage, value for money, and moral worth. With more people turning to vegetarian, vegan, or flexitarian diets, TVP's high protein and fiber content with low fat and zero cholesterol make it an appealing option. Home cooks appreciate it for its ease of use, with transparent labeling (e.g., organic, non-GMO, gluten-free) driving purchasing behavior.
There is also increasing demand for soy-free or allergen-friendly alternatives. Social media, plant-based cooking blogs, and wellness influencers also contribute to driving TVP's popularity at the consumer level. Throughout all segments, the fundamental buying criteria are centered on nutrition, sustainability, product functionality, and clean ingredient profiles, indicative of wider trends in the way that Western Europe thinks about food and health.
From 2020 to 2024, the Western Europe texturized vegetable protein market experienced tremendous change, fueled by a boom in plant-based consumption, supply chain advancements, and heightened consumer concerns regarding health and sustainability. The COVID-19 pandemic was central to changing food habits, with consumers cooking at home more frequently and looking for shelf-stable, healthy, and affordable protein options.
This time also witnessed a visible increase in flexitarianism-where consumers decrease meat consumption but not to zero-increasing demand for TVP even further. Food companies reacted by growing their portfolios with meat alternatives that had TVP as a major ingredient, while supermarkets started carrying more branded and private-label TVP products.
Furthermore, innovation in food tech enabled producers to enhance the flavor, texture, and variety of TVP products to a level that they are now appealing to mainstream consumers.
In the future up to 2025 to 2035, the TVP industry in Western Europe is likely to change with larger trends in sustainable food systems, individualized nutrition, and clean-label consumption. Among the major drivers will be the alignment of alternative protein innovation with climate-sensitive policy systems, as governments promote plant-based diets to achieve climate goals.
Future TVP offerings will increasingly be diversified in origin-beyond soy and wheat to lupin, fava bean, and even fermentation-based proteins to address allergen issues and protein source diversification. Tech-enhanced traceability, such as blockchain-based supply chain tracking and eco-labels, will become increasingly prevalent, as consumers increasingly require transparency and sustainability guarantees.
Comparative Industry Shift Analysis (2020 to 2024 vs. 2025 to 2035)
| 2020 to 2024 | 2025 to 2035 (Projected) |
|---|---|
| Throughout this time, a significant change in diet was seen with an increased number of consumers adopting flexitarian consumption-cutting back on meat without necessarily turning vegetarian or vegan. | By 2025 and beyond, plant-based diets are expected to move from being trend-driven to becoming an integrated part of everyday life, supported by government policies, corporate sustainability goals, and institutional food programs. |
| Innovations at this time were mainly targeted at replicating the experience of consuming meat. TVP found application in offerings like burgers, meatballs, sausages, and nuggets to reach new plant consumers who had a desire for familiar flavors and textures. | In the coming decade, TVP usage will extend beyond meat products. It will be used more and more in various food categories such as protein-based snacks, ethnic foods, ready-to-eat bowls, and even bakery items. |
| Most TVP products during this period were soy and wheat-based, which, although functional, restricted choice for allergy sufferers or those with dietary restrictions. This left a gap in the industry for allergen-friendly and more inclusive protein sources. | The future of TVP will be characterized by a widening range of base ingredients including pea protein, fava beans, lupin, chickpeas, and fermentation-based proteins. |
| TVP retail sales increased vigorously from 2020 to 2024 as consumers searched for affordable and healthy ingredients during times of economic uncertainty. TVP, shelf-stable and long-shelf-life, was a pantry favorite in many households, particularly with the popularity of plant-based cooking on social media. | In the future, TVP will experience significant growth in facilities like schools, hospitals, corporate canteens, and quick-service restaurants. |
Although the Western European TVP market is on the verge of steady growth, a number of risks and challenges may affect its long-term course. Chief among these risks is raw material supply volatility, particularly for soy, wheat, and pea-the three most prevalent protein bases for TVP. These crops are susceptible to disruption by climate change in the form of droughts, floods, and altered growing seasons.
Furthermore, geopolitical considerations, like trade limits or tensions in the major agricultural exporting nations, may continue to interfere with supply chains and increase expenses. This reliance on a small selection of raw materials also creates some hurdles around monoculture techniques and their environmental cost, with the possibility of drawing negative attention from sustainability activists and regulatory authorities.
Another major threat exists in changing consumer tastes and saturation of markets. As the plant protein category gets crowded, with products such as cultured meat, insect protein, and precision-fermented offerings filling the space, TVP will have to deal with strong competition.
Those who first accepted TVP for reasons of health or ethics might be drawn to more recent, cutting-edge offerings considered cleaner, more flavorful, or more sustainable. In addition, unless TVP foods continue to advance in taste, texture, and nutritional content, momentum can be lost-particularly among the mainstream population who have not fully adopted plant-based diets.
In the Western European industry, conventionaltexturized vegetable protein (TVP) is presently more widely available than organic TVP. This is primarily due to cost-effectiveness, accessibility, and scalability. Conventional TVP is made from more conventional agricultural inputs and large-scale farming methods, which enable it to be priced more competitively-a key consideration for food manufacturers as well as price-sensitive consumers.
Since TVP is frequently employed as a functional ingredient in processed food products such as meat analogs, ready meals, and bulk foodservice items, the lower cost of traditional TVP makes it the first choice for mass production. Supply chains for traditional soy, wheat, and pea protein are also more established, which provides easier sourcing and consistent quality.
Conversely, organic TVP, although being more popular, remains a lesser proportion of the industry. The premium price point-attributable to more rigorous farming methods, certification fees, and reduced crop yields-limits its popularity, especially in mass-market foodservice and retail sectors. Nevertheless, there is a growing niche market of health-focused and environmentally conscious consumers who go out of their way to procure organic alternatives.
These shoppers are concerned with non-GMO products, low levels of pesticide usage, and sustainability labels, and so organic TVP is increasingly found in higher-end product lines and specialty health food stores.
Among the different types of texturized vegetable proteins that are found in the Western Europe industry, soy protein is still the most widely marketed, followed by wheat and pea protein. Soy protein dominates because it has been present in the plant food industry for a long time, has well-established supply chains, and has great functional properties.
Soy contains one of the most comprehensive amino acid profiles among all plant proteins and is thus extremely desirable from a nutrition perspective. Additionally, it has no flavor, has a high protein percentage, and superior texturizing properties that enable it to successfully emulate the texture of meat. Soy TVP possesses all these qualities, which result in it becoming a popular ingredient among food makers that manufacture meat substitutes, particularly in cost-driven, high-volume uses.
Wheat protein, in the form of gluten, is also commonly retailed, particularly in traditional European vegetarian foods. Its chewiness and elasticity provide it with application in foods such as plant-based sausages, nuggets, and deli slices. Its application, though, is constrained by the increasing issues with gluten intolerance and dietary limitations, which is creating some movement to gluten-free forms.
In response to this, pea protein has quickly gained popularity and now accounts for one of the fastest-growing segments in the TVP industry.
The Western Europe texturized vegetable protein market is becoming more competitive, spurred by rising consumer demand for plant-based diets, clean-label foods, and environmentally friendly protein sources. The leading players are working to differentiate based on texture, flavor, and protein composition innovation, as well as building distribution through retail and foodservice channels.
Strategic partnerships, vertical integration, and environmentally friendly sourcing practices are crucial as companies aim to align with environmental objectives and changing dietary patterns.
Vestkorn has become a key regional force, concentrating strongly on faba bean and pea protein solutions for allergen-free and gluten-free development. Roquette remains supreme with its vast array of pea-based TVP, underpinned by its commitment to local production and R&D infrastructure within Europe.
Cargill, through its international base, sources soy and pea-based TVP to industry, focusing on scalability, food safety, and usage in retail and industrial channels. Direct Sourcing Ingredients Ltd and The BakeRite Company are gaining traction through B2B channels, providing custom, low-cost blends to medium-sized food manufacturers.
On the specialty and organic side, Indigo Herbs and Forest Whole Foods serve an expanding niche of health-oriented consumers through online and specialty channels. These companies emphasize small-batch, clean-label, and organically grown TVP, driving consumer confidence in the category.
Gericke and Leistritz Extrusion Technology have a supporting role by providing high-performance extrusion equipment to TVP producers, enabling product consistency and innovation. Beneo, which specializes in functional plant ingredients, is investing in diversification of proteins and nutrition-oriented TVP applications for premium markets.
Market Share Analysis by Company
| Company Name | Estimated Market Share (%) |
|---|---|
| Roquette | 18-22% |
| Cargill | 14-18% |
| Vestkorn | 12-15% |
| Beneo | 9-12% |
| Direct Sourcing Ingredients Ltd | 6-9% |
| Forest Whole Foods | 4-6% |
| Indigo Herbs | 3-5% |
| The BakeRite Company | 3-5% |
| Other Players (Combined) | 15-20% |
Roquette dominates the Western Europe TVP industry with a 18-22% estimated share, mainly through its pea protein-based TVP portfolio, supported by robust R&D capabilities and local sourcing initiatives. Its offerings are extensively applied across retail-ready meals as well as industrial quantities of meat alternatives. Cargill, with 14-18%, is aided by its integrated global supply chain and broad product portfolio, emphasizing soy and pea proteins customized for different applications in meat substitutes and high-protein snacks.
Vestkorn, at 12-15%, is also renowned for its allergen-free, locally produced faba bean and pea TVP, appealing immensely to Scandinavian and Central European clean and traceable ingredient-oriented markets. Beneo, at 9-12%, reaches out to the upper-end health food industry with its functional blends of TVP to promote gut well-being and protein enrichment, facilitating differentiation of its portfolio within a highly competitive marketplace.
Direct Sourcing Ingredients Ltd and The BakeRite Company collectively add to the industry by providing tailor-made formulations and blends to small manufacturers. Forest Whole Foods and Indigo Herbs, though niche, are picking up pace with health-conscious consumers through digital platforms, providing organic and minimally processed TVP varieties. Gericke and Leistritz Extrusion Technology, in turn, aid innovation by supplying advanced machinery that allows for uniform quality and scalability in TVP manufacturing.
Collectively, these firms are creating a vibrant and evolving TVP industry within Western Europe where ingredient innovation, processing technology, and strategic procurement will continue to be central to competitive success.
In terms of nature, the industry is classified into organic and conventional.
Based on product type, the industry is divided into soy protein, wheat protein, pea protein, rice protein, faba bean protein, lentil protein, flax protein, chia protein, and corn protein.
With respect to form, the industry is divided into chunks, slices, fakes, and granules.
Based on end-use, the industry is classified into household, industrial, and commercial.
By process type, the industry is categorized into dry TVP and wet TVP.
Based on distribution channel, the industry is divided into direct and indirect.
By country, the industry is segregated into the UK, Germany, Italy, France, Spain, and the rest of Europe.
The industry is expected to reach USD 636.5 million in 2025.
The market is projected to witness USD 971.1 million by 2035.
The industry is slated to capture 4.3% CAGR during the study period.
Soy protein is widely consumed.
Leading companies include Vestkorn, Roquette, Cargill, Direct Sourcing Ingredients Ltd, The BakeRite Company, Forest Whole Foods, Indigo Herbs, Gericke, Leistritz Extrusion Technology, and Beneo.
Table 1: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Country, 2018 to 2033
Table 2: Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (MT) Forecast by Country, 2018 to 2033
Table 3: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Nature, 2018 to 2033
Table 4: Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (MT) Forecast by Nature, 2018 to 2033
Table 5: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Product Type, 2018 to 2033
Table 6: Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (MT) Forecast by Product Type, 2018 to 2033
Table 7: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Form, 2018 to 2033
Table 8: Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (MT) Forecast by Form, 2018 to 2033
Table 9: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Forecast by End-Use, 2018 to 2033
Table 10: Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (MT) Forecast by End-Use, 2018 to 2033
Table 11: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Process Type, 2018 to 2033
Table 12: Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (MT) Forecast by Process Type, 2018 to 2033
Table 13: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Distribution Channel, 2018 to 2033
Table 14: Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (MT) Forecast by Distribution Channel, 2018 to 2033
Table 15: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Forecast By Region, 2018 to 2033
Table 16: Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (MT) Forecast By Region, 2018 to 2033
Table 17: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Nature, 2018 to 2033
Table 18: Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (MT) Forecast by Nature, 2018 to 2033
Table 19: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Product Type, 2018 to 2033
Table 20: Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (MT) Forecast by Product Type, 2018 to 2033
Table 21: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Form, 2018 to 2033
Table 22: Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (MT) Forecast by Form, 2018 to 2033
Table 23: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Forecast by End-Use, 2018 to 2033
Table 24: Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (MT) Forecast by End-Use, 2018 to 2033
Table 25: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Process Type, 2018 to 2033
Table 26: Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (MT) Forecast by Process Type, 2018 to 2033
Table 27: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Distribution Channel, 2018 to 2033
Table 28: Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (MT) Forecast by Distribution Channel, 2018 to 2033
Table 29: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Forecast By Region, 2018 to 2033
Table 30: Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (MT) Forecast By Region, 2018 to 2033
Table 31: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Nature, 2018 to 2033
Table 32: Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (MT) Forecast by Nature, 2018 to 2033
Table 33: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Product Type, 2018 to 2033
Table 34: Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (MT) Forecast by Product Type, 2018 to 2033
Table 35: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Form, 2018 to 2033
Table 36: Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (MT) Forecast by Form, 2018 to 2033
Table 37: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Forecast by End-Use, 2018 to 2033
Table 38: Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (MT) Forecast by End-Use, 2018 to 2033
Table 39: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Process Type, 2018 to 2033
Table 40: Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (MT) Forecast by Process Type, 2018 to 2033
Table 41: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Distribution Channel, 2018 to 2033
Table 42: Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (MT) Forecast by Distribution Channel, 2018 to 2033
Table 43: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Forecast By Region, 2018 to 2033
Table 44: Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (MT) Forecast By Region, 2018 to 2033
Table 45: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Nature, 2018 to 2033
Table 46: Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (MT) Forecast by Nature, 2018 to 2033
Table 47: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Product Type, 2018 to 2033
Table 48: Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (MT) Forecast by Product Type, 2018 to 2033
Table 49: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Form, 2018 to 2033
Table 50: Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (MT) Forecast by Form, 2018 to 2033
Table 51: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Forecast by End-Use, 2018 to 2033
Table 52: Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (MT) Forecast by End-Use, 2018 to 2033
Table 53: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Process Type, 2018 to 2033
Table 54: Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (MT) Forecast by Process Type, 2018 to 2033
Table 55: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Distribution Channel, 2018 to 2033
Table 56: Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (MT) Forecast by Distribution Channel, 2018 to 2033
Table 57: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Forecast By Region, 2018 to 2033
Table 58: Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (MT) Forecast By Region, 2018 to 2033
Table 59: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Nature, 2018 to 2033
Table 60: Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (MT) Forecast by Nature, 2018 to 2033
Table 61: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Product Type, 2018 to 2033
Table 62: Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (MT) Forecast by Product Type, 2018 to 2033
Table 63: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Form, 2018 to 2033
Table 64: Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (MT) Forecast by Form, 2018 to 2033
Table 65: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Forecast by End-Use, 2018 to 2033
Table 66: Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (MT) Forecast by End-Use, 2018 to 2033
Table 67: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Process Type, 2018 to 2033
Table 68: Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (MT) Forecast by Process Type, 2018 to 2033
Table 69: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Distribution Channel, 2018 to 2033
Table 70: Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (MT) Forecast by Distribution Channel, 2018 to 2033
Table 71: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Forecast By Region, 2018 to 2033
Table 72: Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (MT) Forecast By Region, 2018 to 2033
Table 73: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Nature, 2018 to 2033
Table 74: Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (MT) Forecast by Nature, 2018 to 2033
Table 75: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Product Type, 2018 to 2033
Table 76: Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (MT) Forecast by Product Type, 2018 to 2033
Table 77: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Form, 2018 to 2033
Table 78: Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (MT) Forecast by Form, 2018 to 2033
Table 79: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Forecast by End-Use, 2018 to 2033
Table 80: Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (MT) Forecast by End-Use, 2018 to 2033
Table 81: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Process Type, 2018 to 2033
Table 82: Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (MT) Forecast by Process Type, 2018 to 2033
Table 83: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Distribution Channel, 2018 to 2033
Table 84: Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (MT) Forecast by Distribution Channel, 2018 to 2033
Table 85: Rest of Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Nature, 2018 to 2033
Table 86: Rest of Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (MT) Forecast by Nature, 2018 to 2033
Table 87: Rest of Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Product Type, 2018 to 2033
Table 88: Rest of Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (MT) Forecast by Product Type, 2018 to 2033
Table 89: Rest of Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Form, 2018 to 2033
Table 90: Rest of Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (MT) Forecast by Form, 2018 to 2033
Table 91: Rest of Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Forecast by End-Use, 2018 to 2033
Table 92: Rest of Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (MT) Forecast by End-Use, 2018 to 2033
Table 93: Rest of Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Process Type, 2018 to 2033
Table 94: Rest of Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (MT) Forecast by Process Type, 2018 to 2033
Table 95: Rest of Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Distribution Channel, 2018 to 2033
Table 96: Rest of Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (MT) Forecast by Distribution Channel, 2018 to 2033
Figure 1: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) by Nature, 2023 to 2033
Figure 2: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) by Product Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 3: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) by Form, 2023 to 2033
Figure 4: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) by End-Use, 2023 to 2033
Figure 5: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) by Process Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 6: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) by Distribution Channel, 2023 to 2033
Figure 7: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 8: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Country, 2018 to 2033
Figure 9: Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (MT) Analysis by Country, 2018 to 2033
Figure 10: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 11: Industry Analysis and Outlook Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 12: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Nature, 2018 to 2033
Figure 13: Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (MT) Analysis by Nature, 2018 to 2033
Figure 14: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Nature, 2023 to 2033
Figure 15: Industry Analysis and Outlook Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Nature, 2023 to 2033
Figure 16: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Product Type, 2018 to 2033
Figure 17: Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (MT) Analysis by Product Type, 2018 to 2033
Figure 18: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Product Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 19: Industry Analysis and Outlook Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Product Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 20: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Form, 2018 to 2033
Figure 21: Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (MT) Analysis by Form, 2018 to 2033
Figure 22: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Form, 2023 to 2033
Figure 23: Industry Analysis and Outlook Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Form, 2023 to 2033
Figure 24: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Analysis by End-Use, 2018 to 2033
Figure 25: Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (MT) Analysis by End-Use, 2018 to 2033
Figure 26: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by End-Use, 2023 to 2033
Figure 27: Industry Analysis and Outlook Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by End-Use, 2023 to 2033
Figure 28: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Process Type, 2018 to 2033
Figure 29: Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (MT) Analysis by Process Type, 2018 to 2033
Figure 30: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Process Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 31: Industry Analysis and Outlook Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Process Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 32: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Distribution Channel, 2018 to 2033
Figure 33: Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (MT) Analysis by Distribution Channel, 2018 to 2033
Figure 34: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Distribution Channel, 2023 to 2033
Figure 35: Industry Analysis and Outlook Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Distribution Channel, 2023 to 2033
Figure 36: Industry Analysis and Outlook Attractiveness by Nature, 2023 to 2033
Figure 37: Industry Analysis and Outlook Attractiveness by Product Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 38: Industry Analysis and Outlook Attractiveness by Form, 2023 to 2033
Figure 39: Industry Analysis and Outlook Attractiveness by End-Use, 2023 to 2033
Figure 40: Industry Analysis and Outlook Attractiveness by Process Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 41: Industry Analysis and Outlook Attractiveness by Distribution Channel, 2023 to 2033
Figure 42: Industry Analysis and Outlook Attractiveness by Region, 2023 to 2033
Figure 43: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) by Nature, 2023 to 2033
Figure 44: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) by Product Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 45: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) by Form, 2023 to 2033
Figure 46: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) by End-Use, 2023 to 2033
Figure 47: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) by Process Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 48: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) by Distribution Channel, 2023 to 2033
Figure 49: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) By Region, 2023 to 2033
Figure 50: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Analysis By Region, 2018 to 2033
Figure 51: Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (MT) Analysis By Region, 2018 to 2033
Figure 52: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis By Region, 2023 to 2033
Figure 53: Industry Analysis and Outlook Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections By Region, 2023 to 2033
Figure 54: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Nature, 2018 to 2033
Figure 55: Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (MT) Analysis by Nature, 2018 to 2033
Figure 56: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Nature, 2023 to 2033
Figure 57: Industry Analysis and Outlook Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Nature, 2023 to 2033
Figure 58: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Product Type, 2018 to 2033
Figure 59: Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (MT) Analysis by Product Type, 2018 to 2033
Figure 60: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Product Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 61: Industry Analysis and Outlook Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Product Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 62: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Form, 2018 to 2033
Figure 63: Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (MT) Analysis by Form, 2018 to 2033
Figure 64: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Form, 2023 to 2033
Figure 65: Industry Analysis and Outlook Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Form, 2023 to 2033
Figure 66: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Analysis by End-Use, 2018 to 2033
Figure 67: Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (MT) Analysis by End-Use, 2018 to 2033
Figure 68: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by End-Use, 2023 to 2033
Figure 69: Industry Analysis and Outlook Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by End-Use, 2023 to 2033
Figure 70: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Process Type, 2018 to 2033
Figure 71: Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (MT) Analysis by Process Type, 2018 to 2033
Figure 72: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Process Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 73: Industry Analysis and Outlook Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Process Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 74: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Distribution Channel, 2018 to 2033
Figure 75: Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (MT) Analysis by Distribution Channel, 2018 to 2033
Figure 76: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Distribution Channel, 2023 to 2033
Figure 77: Industry Analysis and Outlook Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Distribution Channel, 2023 to 2033
Figure 78: Industry Analysis and Outlook Attractiveness by Nature, 2023 to 2033
Figure 79: Industry Analysis and Outlook Attractiveness by Product Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 80: Industry Analysis and Outlook Attractiveness by Form, 2023 to 2033
Figure 81: Industry Analysis and Outlook Attractiveness by End-Use, 2023 to 2033
Figure 82: Industry Analysis and Outlook Attractiveness by Process Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 83: Industry Analysis and Outlook Attractiveness by Distribution Channel, 2023 to 2033
Figure 84: Industry Analysis and Outlook Attractiveness By Region, 2023 to 2033
Figure 85: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) by Nature, 2023 to 2033
Figure 86: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) by Product Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 87: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) by Form, 2023 to 2033
Figure 88: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) by End-Use, 2023 to 2033
Figure 89: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) by Process Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 90: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) by Distribution Channel, 2023 to 2033
Figure 91: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) By Region, 2023 to 2033
Figure 92: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Analysis By Region, 2018 to 2033
Figure 93: Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (MT) Analysis By Region, 2018 to 2033
Figure 94: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis By Region, 2023 to 2033
Figure 95: Industry Analysis and Outlook Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections By Region, 2023 to 2033
Figure 96: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Nature, 2018 to 2033
Figure 97: Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (MT) Analysis by Nature, 2018 to 2033
Figure 98: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Nature, 2023 to 2033
Figure 99: Industry Analysis and Outlook Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Nature, 2023 to 2033
Figure 100: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Product Type, 2018 to 2033
Figure 101: Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (MT) Analysis by Product Type, 2018 to 2033
Figure 102: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Product Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 103: Industry Analysis and Outlook Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Product Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 104: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Form, 2018 to 2033
Figure 105: Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (MT) Analysis by Form, 2018 to 2033
Figure 106: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Form, 2023 to 2033
Figure 107: Industry Analysis and Outlook Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Form, 2023 to 2033
Figure 108: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Analysis by End-Use, 2018 to 2033
Figure 109: Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (MT) Analysis by End-Use, 2018 to 2033
Figure 110: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by End-Use, 2023 to 2033
Figure 111: Industry Analysis and Outlook Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by End-Use, 2023 to 2033
Figure 112: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Process Type, 2018 to 2033
Figure 113: Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (MT) Analysis by Process Type, 2018 to 2033
Figure 114: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Process Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 115: Industry Analysis and Outlook Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Process Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 116: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Distribution Channel, 2018 to 2033
Figure 117: Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (MT) Analysis by Distribution Channel, 2018 to 2033
Figure 118: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Distribution Channel, 2023 to 2033
Figure 119: Industry Analysis and Outlook Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Distribution Channel, 2023 to 2033
Figure 120: Industry Analysis and Outlook Attractiveness by Nature, 2023 to 2033
Figure 121: Industry Analysis and Outlook Attractiveness by Product Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 122: Industry Analysis and Outlook Attractiveness by Form, 2023 to 2033
Figure 123: Industry Analysis and Outlook Attractiveness by End-Use, 2023 to 2033
Figure 124: Industry Analysis and Outlook Attractiveness by Process Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 125: Industry Analysis and Outlook Attractiveness by Distribution Channel, 2023 to 2033
Figure 126: Industry Analysis and Outlook Attractiveness By Region, 2023 to 2033
Figure 127: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) by Nature, 2023 to 2033
Figure 128: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) by Product Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 129: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) by Form, 2023 to 2033
Figure 130: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) by End-Use, 2023 to 2033
Figure 131: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) by Process Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 132: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) by Distribution Channel, 2023 to 2033
Figure 133: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) By Region, 2023 to 2033
Figure 134: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Analysis By Region, 2018 to 2033
Figure 135: Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (MT) Analysis By Region, 2018 to 2033
Figure 136: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis By Region, 2023 to 2033
Figure 137: Industry Analysis and Outlook Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections By Region, 2023 to 2033
Figure 138: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Nature, 2018 to 2033
Figure 139: Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (MT) Analysis by Nature, 2018 to 2033
Figure 140: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Nature, 2023 to 2033
Figure 141: Industry Analysis and Outlook Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Nature, 2023 to 2033
Figure 142: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Product Type, 2018 to 2033
Figure 143: Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (MT) Analysis by Product Type, 2018 to 2033
Figure 144: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Product Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 145: Industry Analysis and Outlook Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Product Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 146: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Form, 2018 to 2033
Figure 147: Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (MT) Analysis by Form, 2018 to 2033
Figure 148: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Form, 2023 to 2033
Figure 149: Industry Analysis and Outlook Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Form, 2023 to 2033
Figure 150: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Analysis by End-Use, 2018 to 2033
Figure 151: Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (MT) Analysis by End-Use, 2018 to 2033
Figure 152: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by End-Use, 2023 to 2033
Figure 153: Industry Analysis and Outlook Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by End-Use, 2023 to 2033
Figure 154: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Process Type, 2018 to 2033
Figure 155: Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (MT) Analysis by Process Type, 2018 to 2033
Figure 156: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Process Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 157: Industry Analysis and Outlook Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Process Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 158: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Distribution Channel, 2018 to 2033
Figure 159: Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (MT) Analysis by Distribution Channel, 2018 to 2033
Figure 160: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Distribution Channel, 2023 to 2033
Figure 161: Industry Analysis and Outlook Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Distribution Channel, 2023 to 2033
Figure 162: Industry Analysis and Outlook Attractiveness by Nature, 2023 to 2033
Figure 163: Industry Analysis and Outlook Attractiveness by Product Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 164: Industry Analysis and Outlook Attractiveness by Form, 2023 to 2033
Figure 165: Industry Analysis and Outlook Attractiveness by End-Use, 2023 to 2033
Figure 166: Industry Analysis and Outlook Attractiveness by Process Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 167: Industry Analysis and Outlook Attractiveness by Distribution Channel, 2023 to 2033
Figure 168: Industry Analysis and Outlook Attractiveness By Region, 2023 to 2033
Figure 169: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) by Nature, 2023 to 2033
Figure 170: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) by Product Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 171: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) by Form, 2023 to 2033
Figure 172: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) by End-Use, 2023 to 2033
Figure 173: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) by Process Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 174: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) by Distribution Channel, 2023 to 2033
Figure 175: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) By Region, 2023 to 2033
Figure 176: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Analysis By Region, 2018 to 2033
Figure 177: Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (MT) Analysis By Region, 2018 to 2033
Figure 178: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis By Region, 2023 to 2033
Figure 179: Industry Analysis and Outlook Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections By Region, 2023 to 2033
Figure 180: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Nature, 2018 to 2033
Figure 181: Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (MT) Analysis by Nature, 2018 to 2033
Figure 182: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Nature, 2023 to 2033
Figure 183: Industry Analysis and Outlook Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Nature, 2023 to 2033
Figure 184: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Product Type, 2018 to 2033
Figure 185: Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (MT) Analysis by Product Type, 2018 to 2033
Figure 186: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Product Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 187: Industry Analysis and Outlook Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Product Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 188: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Form, 2018 to 2033
Figure 189: Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (MT) Analysis by Form, 2018 to 2033
Figure 190: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Form, 2023 to 2033
Figure 191: Industry Analysis and Outlook Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Form, 2023 to 2033
Figure 192: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Analysis by End-Use, 2018 to 2033
Figure 193: Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (MT) Analysis by End-Use, 2018 to 2033
Figure 194: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by End-Use, 2023 to 2033
Figure 195: Industry Analysis and Outlook Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by End-Use, 2023 to 2033
Figure 196: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Process Type, 2018 to 2033
Figure 197: Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (MT) Analysis by Process Type, 2018 to 2033
Figure 198: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Process Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 199: Industry Analysis and Outlook Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Process Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 200: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Distribution Channel, 2018 to 2033
Figure 201: Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (MT) Analysis by Distribution Channel, 2018 to 2033
Figure 202: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Distribution Channel, 2023 to 2033
Figure 203: Industry Analysis and Outlook Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Distribution Channel, 2023 to 2033
Figure 204: Industry Analysis and Outlook Attractiveness by Nature, 2023 to 2033
Figure 205: Industry Analysis and Outlook Attractiveness by Product Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 206: Industry Analysis and Outlook Attractiveness by Form, 2023 to 2033
Figure 207: Industry Analysis and Outlook Attractiveness by End-Use, 2023 to 2033
Figure 208: Industry Analysis and Outlook Attractiveness by Process Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 209: Industry Analysis and Outlook Attractiveness by Distribution Channel, 2023 to 2033
Figure 210: Industry Analysis and Outlook Attractiveness By Region, 2023 to 2033
Figure 211: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) by Nature, 2023 to 2033
Figure 212: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) by Product Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 213: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) by Form, 2023 to 2033
Figure 214: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) by End-Use, 2023 to 2033
Figure 215: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) by Process Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 216: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) by Distribution Channel, 2023 to 2033
Figure 217: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) By Region, 2023 to 2033
Figure 218: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Analysis By Region, 2018 to 2033
Figure 219: Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (MT) Analysis By Region, 2018 to 2033
Figure 220: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis By Region, 2023 to 2033
Figure 221: Industry Analysis and Outlook Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections By Region, 2023 to 2033
Figure 222: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Nature, 2018 to 2033
Figure 223: Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (MT) Analysis by Nature, 2018 to 2033
Figure 224: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Nature, 2023 to 2033
Figure 225: Industry Analysis and Outlook Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Nature, 2023 to 2033
Figure 226: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Product Type, 2018 to 2033
Figure 227: Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (MT) Analysis by Product Type, 2018 to 2033
Figure 228: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Product Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 229: Industry Analysis and Outlook Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Product Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 230: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Form, 2018 to 2033
Figure 231: Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (MT) Analysis by Form, 2018 to 2033
Figure 232: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Form, 2023 to 2033
Figure 233: Industry Analysis and Outlook Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Form, 2023 to 2033
Figure 234: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Analysis by End-Use, 2018 to 2033
Figure 235: Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (MT) Analysis by End-Use, 2018 to 2033
Figure 236: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by End-Use, 2023 to 2033
Figure 237: Industry Analysis and Outlook Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by End-Use, 2023 to 2033
Figure 238: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Process Type, 2018 to 2033
Figure 239: Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (MT) Analysis by Process Type, 2018 to 2033
Figure 240: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Process Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 241: Industry Analysis and Outlook Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Process Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 242: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Distribution Channel, 2018 to 2033
Figure 243: Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (MT) Analysis by Distribution Channel, 2018 to 2033
Figure 244: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Distribution Channel, 2023 to 2033
Figure 245: Industry Analysis and Outlook Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Distribution Channel, 2023 to 2033
Figure 246: Industry Analysis and Outlook Attractiveness by Nature, 2023 to 2033
Figure 247: Industry Analysis and Outlook Attractiveness by Product Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 248: Industry Analysis and Outlook Attractiveness by Form, 2023 to 2033
Figure 249: Industry Analysis and Outlook Attractiveness by End-Use, 2023 to 2033
Figure 250: Industry Analysis and Outlook Attractiveness by Process Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 251: Industry Analysis and Outlook Attractiveness by Distribution Channel, 2023 to 2033
Figure 252: Industry Analysis and Outlook Attractiveness By Region, 2023 to 2033
Figure 253: Rest of Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) by Nature, 2023 to 2033
Figure 254: Rest of Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) by Product Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 255: Rest of Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) by Form, 2023 to 2033
Figure 256: Rest of Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) by End-Use, 2023 to 2033
Figure 257: Rest of Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) by Process Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 258: Rest of Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) by Distribution Channel, 2023 to 2033
Figure 259: Rest of Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Nature, 2018 to 2033
Figure 260: Rest of Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (MT) Analysis by Nature, 2018 to 2033
Figure 261: Rest of Industry Analysis and Outlook Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Nature, 2023 to 2033
Figure 262: Rest of Industry Analysis and Outlook Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Nature, 2023 to 2033
Figure 263: Rest of Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Product Type, 2018 to 2033
Figure 264: Rest of Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (MT) Analysis by Product Type, 2018 to 2033
Figure 265: Rest of Industry Analysis and Outlook Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Product Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 266: Rest of Industry Analysis and Outlook Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Product Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 267: Rest of Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Form, 2018 to 2033
Figure 268: Rest of Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (MT) Analysis by Form, 2018 to 2033
Figure 269: Rest of Industry Analysis and Outlook Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Form, 2023 to 2033
Figure 270: Rest of Industry Analysis and Outlook Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Form, 2023 to 2033
Figure 271: Rest of Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Analysis by End-Use, 2018 to 2033
Figure 272: Rest of Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (MT) Analysis by End-Use, 2018 to 2033
Figure 273: Rest of Industry Analysis and Outlook Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by End-Use, 2023 to 2033
Figure 274: Rest of Industry Analysis and Outlook Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by End-Use, 2023 to 2033
Figure 275: Rest of Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Process Type, 2018 to 2033
Figure 276: Rest of Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (MT) Analysis by Process Type, 2018 to 2033
Figure 277: Rest of Industry Analysis and Outlook Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Process Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 278: Rest of Industry Analysis and Outlook Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Process Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 279: Rest of Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Distribution Channel, 2018 to 2033
Figure 280: Rest of Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (MT) Analysis by Distribution Channel, 2018 to 2033
Figure 281: Rest of Industry Analysis and Outlook Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Distribution Channel, 2023 to 2033
Figure 282: Rest of Industry Analysis and Outlook Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Distribution Channel, 2023 to 2033
Figure 283: Rest of Industry Analysis and Outlook Attractiveness by Nature, 2023 to 2033
Figure 284: Rest of Industry Analysis and Outlook Attractiveness by Product Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 285: Rest of Industry Analysis and Outlook Attractiveness by Form, 2023 to 2033
Figure 286: Rest of Industry Analysis and Outlook Attractiveness by End-Use, 2023 to 2033
Figure 287: Rest of Industry Analysis and Outlook Attractiveness by Process Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 288: Rest of Industry Analysis and Outlook Attractiveness by Distribution Channel, 2023 to 2033






Full Research Suite comprises of:
Market outlook & trends analysis
Interviews & case studies
Strategic recommendations
Vendor profiles & capabilities analysis
5-year forecasts
8 regions and 60+ country-level data splits
Market segment data splits
12 months of continuous data updates
DELIVERED AS:
PDF EXCEL ONLINE
Western Blotting Processors Market Trends and Forecast 2025 to 2035
Western Blotting Market is segmented by product, application and end user from 2025 to 2035
Western Europe Automotive Performance Tuning & Engine Remapping Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Western Europe Valve Seat Insert Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Western Europe Automated People Mover Industry Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Western Europe Bicycle Component Aftermarket Analysis Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Western Europe Automotive Load Floor IndustryAnalysis in Western Europe Forecast & Analysis 2025 to 2035
Western Europe Probiotic Supplement Market Analysis in – Growth & Market Trends from 2025 to 2035
Western Europe Women’s Intimate Care Market Analysis – Size, Share & Trends 2025 to 2035
Western Europe Non-Dairy Creamer Market Analysis by Growth, Trends and Forecast from 2025 to 2035
Western Europe Last-mile Delivery Software Market – Growth & Outlook through 2035
Western Europe Inkjet Printer Market – Growth & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Western Europe HVDC Transmission System Market – Growth & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Conference Room Solution Market Growth – Trends & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Western Europe Intelligent Enterprise Data Capture Software Market - Growth & Forecast 2025-2035
Communications Platform as a Service (CPaaS) Market Growth - Trends & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Visitor Management System Industry Analysis in Western Europe - Market Outlook 2025 to 2035
Western Europe Base Station Antenna Market - Growth & Demand 2025 to 2035
Western Europe Banking-as-a-Service (BaaS) Platform Market - Growth & Demand 2025 to 2035
Western Europe Event Management Software Market Trends – Growth & Forecast 2025 to 2035

Thank you!
You will receive an email from our Business Development Manager. Please be sure to check your SPAM/JUNK folder too.
Chat With
MaRIA