The feed enzymes market is projected to grow from USD 1.3 billion in 2025 to USD 2 billion by 2035, at a CAGR of 4.4% during the forecast period. Demand is rising as producers aim to improve feed conversion ratios while reducing reliance on antibiotic growth promoters.
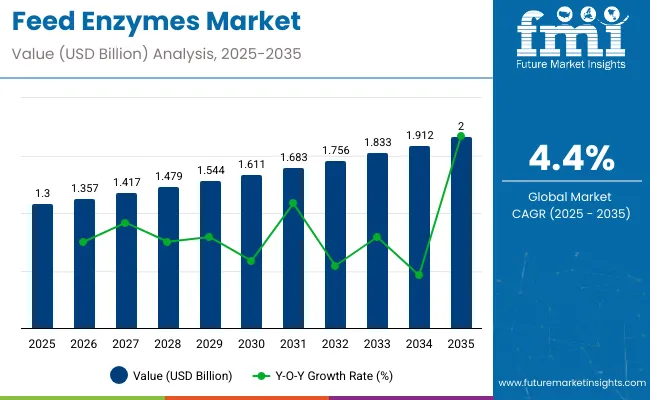
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Industry Size (2025E) | USD 1.3 billion |
| Industry Value (2035F) | USD 2 billion |
| CAGR (2025 to 2035) | 4.4% |
Enzyme manufacturers are optimizing microbial fermentation for higher yields of phytase, protease, and xylanase to match species-specific digestion profiles. Blenders incorporate these enzymes into pre-mixes or directly into pelleted and mash feeds using precision coating technologies to ensure heat stability.
Feed producers in Asia and Latin America are adopting multi-enzyme blends to manage raw material variability, particularly in corn-soy and DDGS-heavy formulations. Large integrators are leveraging in-house testing tools to monitor nutrient digestibility, aligning enzyme use with genetic improvements in broiler and swine herds. Regulatory pressure in the EU and rising phosphate costs globally are also accelerating enzyme adoption in aquaculture and ruminant segments.
As of 2025, the feed enzymes market is being positioned as a strategic segment within its broader agricultural and animal nutrition industries. Within the global animal feed additives market, approximately 8-10% of value is driven by feed enzymes, as they enhance nutrient absorption and reduce feed costs. In the animal nutrition market, feed enzymes account for about 5-7% of total ingredient sales, supported by rising demand for performance-driven diets.
Within the livestock feed sector, around 4-6% of formulations are enzyme-enhanced, particularly in swine and poultry production. In the aquaculture feed market, 3-5% of diets leverage enzymes to improve protein and phosphorus utilization. Finally, in the broader specialty enzymes market, feed enzymes represent 6-8%, reflecting their importance among tailored enzyme solutions for industrial applications.
Labeling certifications in the feed enzymes market are essential to ensure product safety, traceability, and regulatory compliance across international markets. These certifications validate the quality, composition, and functional claims of enzyme-based additives used in animal nutrition and are often mandatory for cross-border trade.
The feed enzymes market experiences dynamic international trade between countries with advanced biotechnology and animal nutrition industries and those with expanding livestock sectors but limited local enzyme production. High-quality feed enzymes are exported worldwide to improve feed efficiency, animal health, and sustainability in the livestock industry.
The market is expanding steadily with strong investments in dry-form solutions, phytase-based formulations, plant-derived enzyme sources, and poultry-specific applications. Growth is driven by the need for improved feed efficiency, nutrient absorption, and cost-effective animal nutrition.
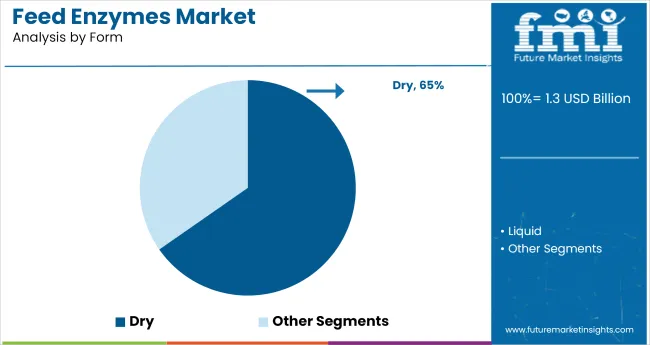
Dry-form feed enzymes are expected to dominate the format category, accounting for 65% of the global market by 2025. Their ease of handling, extended shelf life, and high compatibility with bulk feed processing have made them the preferred format for large-scale livestock and poultry farms.
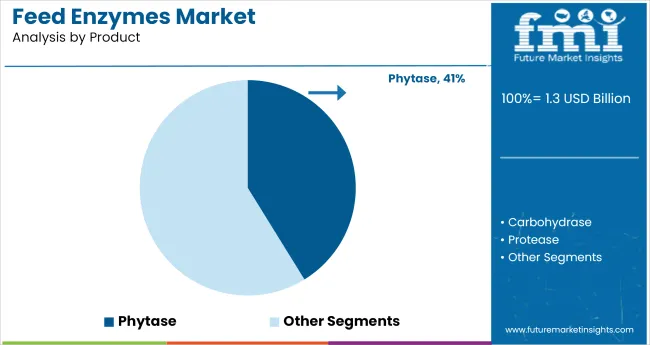
Phytase enzymes are projected to lead the product segment, securing a 41% share by 2025. They enhance phosphorus bioavailability in animal feed by breaking down phytate compounds, lowering feed costs and reducing environmental phosphate discharge.
Plant-Based Enzymes Gain Ground with 26% Market Share
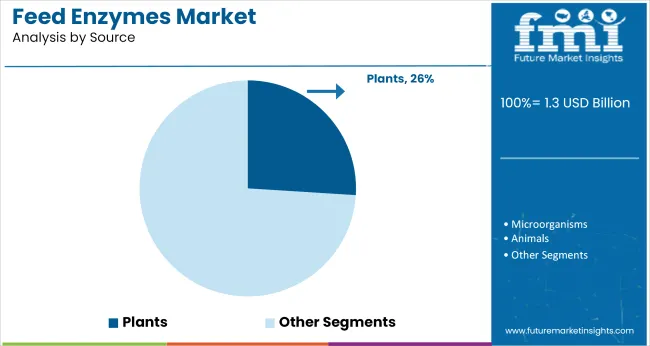
Plant-based feed enzymes are forecasted to account for 26% of the market by 2025. These natural enzyme sources appeal to sustainability-focused producers and regions looking to reduce reliance on synthetic or microbial enzyme origins.
Poultry Segment to Dominate Animal Category with 48% Share
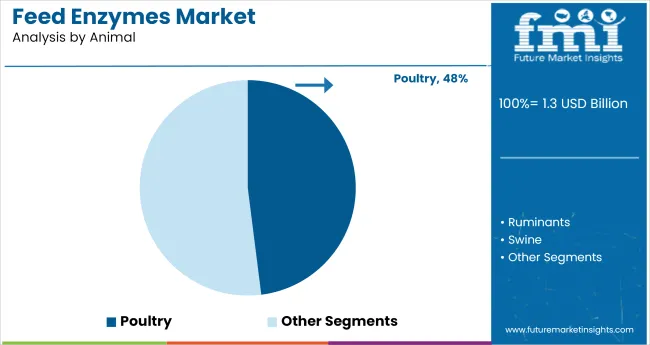
Poultry is anticipated to lead the animal type segment, capturing 48% of the global market by 2025. Rising global demand for poultry meat and eggs, combined with intensive farming systems, drives the need for efficient enzyme supplementation.
The market is expanding due to rising pressure to improve animal nutrition efficiency while lowering feed costs. Global demand reached 370 kilotons in 2024, led by poultry and swine segments. Phytase, xylanase, and protease enzymes are being widely adopted to enhance nutrient absorption and reduce feed wastage.
As AGP bans spread across Asia and Europe, enzymes are being positioned as alternatives to antibiotics for gut health and productivity. In 2024, over 61% of EU livestock feed enzymes were used in antibiotic-free systems. Enzyme blends with probiotic and prebiotic compatibility are being promoted to support immunity and digestion.
Feedstock differences across geographies are shaping enzyme development. In India and Southeast Asia, multi-enzyme complexes are used to process rice bran, DDGS, and palm kernel meal. Customized blends are being offered by global suppliers to match local raw material profiles and reduce undigested energy losses.
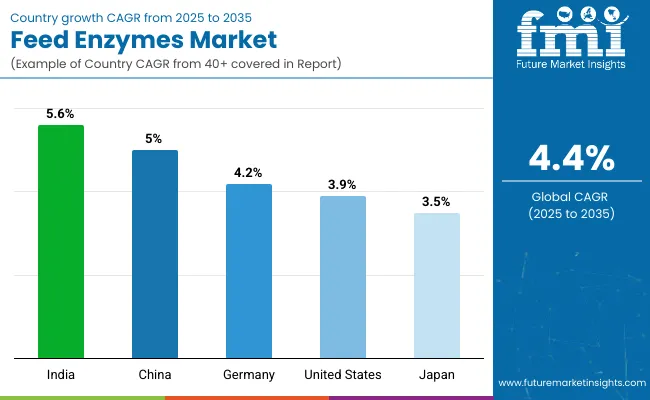
| Country | CAGR (2025 to 2035) |
|---|---|
| India | 5.6% |
| China | 5.0% |
| Germany | 4.2% |
| United States | 3.9% |
| Japan | 3.5% |
Global demand for feed enzymes is expected to increase at a 4.4% CAGR from 2025 to 2035. India leads with a growth rate of 5.6%, exceeding the global average by +27%, driven by greater adoption of performance-enhancing feed additives across poultry and dairy sectors. China follows at 5.0% (+14%), where rising industrial livestock operations are driving consistent demand for enzyme-enriched formulations.
Germany posts 4.2% (-5%), showing stable use within its well-regulated animal nutrition systems. The United States grows at 3.9% (-11%), reflecting steady but plateauing adoption in a mature feed market. Japan lags at 3.5% (-20%), held back by slower innovation uptake and lower livestock volumes. This divergence in growth reveals expanding enzyme use across key BRICS economies while several OECD countries post moderate or below-average gains.
The report provides insights across 40+ countries. The five below are highlighted for their strategic influence and growth trajectory.
India is forecast to expand at a CAGR of 5.6% from 2025 to 2035. Rapid livestock population growth and evolving animal nutrition practices are accelerating the need for enzyme-based feed additives. Rising awareness among farmers about feed efficiency and improved animal health outcomes is increasing the adoption of phytase and protease products.
Domestic manufacturers are expanding enzyme portfolios to cater to poultry, swine, and aquaculture sectors. Government support for safe and sustainable animal protein production further boosts demand.
China’s market for feed enzymes is projected to register a CAGR of 5.0% between 2025 and 2035. Shifts in livestock production methods and higher demand for quality meat have intensified the use of functional feed inputs. Feed enzyme usage is growing in swine and poultry sectors to address digestion and nutrient absorption issues.
China’s move away from antibiotic-based growth promoters has encouraged enzyme-based alternatives. Regional feed mills are increasingly customizing formulations using xylanase and beta-glucanase.
Sales of feed enzymes in Germany are expanding at a CAGR of 4.2% from 2025 to 2035. Environmental compliance and pressure to reduce phosphorus discharge are motivating livestock producers to adopt enzyme-enhanced feeds. Enzymes such as phytase help reduce nutrient waste, aligning with EU sustainability targets.
German feed manufacturers are innovating enzyme blends for ruminants and poultry, improving nutrient utilization. Germany’s advanced animal farming systems create high demand for precision-formulated feed supplements.
The U.S. market is estimated to grow at a CAGR of 3.9% from 2025 to 2035. As producers seek alternatives to antibiotics and chemical additives, demand for enzyme-based feed solutions continues to rise. The poultry and swine industries are driving innovation in feed formulation, particularly in the Midwest and Southeast regions.
Enzyme blends are being integrated to enhance fiber digestibility and boost feed efficiency. Regulatory support for safer animal health products is also creating a favorable environment.
Japan’s market is anticipated to grow at a CAGR of 3.5% from 2025 to 2035. Declining domestic livestock numbers are pushing producers to optimize feed conversion and animal health using enzyme additives. Imports of high-quality enzymes are rising, particularly for use in pig and broiler production.
Japanese feed integrators prefer precision dosing and multi-enzyme blends for efficient nutrient uptake. Sustainability concerns and waste reduction goals are also influencing enzyme selection in feed production.
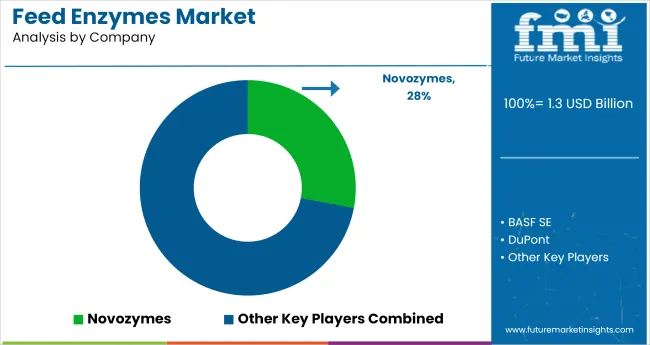
The industry is moderately consolidated, dominated by a mix of global chemical majors and specialized biotech firms. BASF, DuPont, and DSM hold strong positions due to extensive R&D capabilities and integrated supply chains across monogastric and ruminant nutrition. Novozymes and Chr. Hansen drive enzyme innovation with patented formulations targeting gut health and feed efficiency.
Adisseo and Alltech focus on tailored enzyme blends for poultry and swine, strengthening their presence in Asia and Latin America. Emerging players like BIO-CAT, Rossari, and Karyotica Biologicals are gaining traction through region-specific enzyme solutions and pricing flexibility. BEHN MEYER and BEC Feed Solutions serve as key distributors across Southeast Asia and Oceania, fostering localized growth and customization.
| Report Attributes | Details |
|---|---|
| Market Size (2025) | USD 1.3 billion |
| Projected Market Size (2035) | USD 2.0 billion |
| CAGR (2025 to 2035) | 4.4% |
| Base Year for Estimation | 2024 |
| Historical Period | 2020 to 2024 |
| Projections Period | 2025 to 2035 |
| Quantitative Units | USD billion for market value |
| Forms Analyzed (Segment 1) | Dry, Liquid |
| Products Analyzed (Segment 2) | Phytase, Carbohydrase, Protease |
| Sources Analyzed (Segment 3) | Microorganisms, Plants, Animals |
| Animals Analyzed (Segment 4) | Poultry, Ruminants, Swine, Aquatic Animals, Others (Equine, Pet Food) |
| Regions Covered | North America, Latin America, Eastern Europe, Western Europe, East Asia, South Asia & Pacific, Central Asia, Balkan & Baltic Countries, Russia & Belarus, Middle East & Africa |
| Countries Covered | United States, Canada, Germany, United Kingdom, France, Italy, Spain, China, India, Japan, South Korea, Australia, Brazil, Mexico, Argentina, Saudi Arabia, UAE, South Africa |
| Key Players | Novozymes, BASF SE, DuPont, Associated British Foods Plc, BEHN MEYER, DSM, Azelis S.A., Rossari, BIO-CAT, BEC Feed Solutions, Others |
| Additional Attributes | Dollar sales by form and animal segment, increased enzyme inclusion in poultry and swine diets, growing shift toward sustainable feed formulations, and innovations in microbially-derived enzyme technologies. |
Based on form, the market is segmented into dry and liquid variants, each tailored to meet specific feed processing and mixing requirements.
In terms of product type, the market includes phytase, carbohydrase, and protease, each serving a distinct role in enhancing nutrient absorption and digestion efficiency in animals.
The enzymes used in feed formulations are derived from three primary sources: microorganisms, plants, and animals, depending on the desired enzymatic activity and application.
Based on end-use species, the market covers poultry, ruminants, swine, aquatic animals, and others, which include equine and pet food applications.
Geographical analysis spans North America, Latin America, Eastern Europe, Western Europe, East Asia, South Asia & Pacific, Central Asia, Balkan and Baltic Countries, Russia & Belarus, and the Middle East & Africa.
The market is valued at USD 1.3 billion in 2025.
The market is expected to reach USD 2.0 billion by 2035.
The market is projected to expand at a CAGR of 4.4% between 2025 and 2035.
Dry form dominates the market with a 65% share in 2025.
India is the fastest-growing country, recording a CAGR of 5.6% from 2025 to 2035.






Our Research Products

The "Full Research Suite" delivers actionable market intel, deep dives on markets or technologies, so clients act faster, cut risk, and unlock growth.

The Leaderboard benchmarks and ranks top vendors, classifying them as Established Leaders, Leading Challengers, or Disruptors & Challengers.

Locates where complements amplify value and substitutes erode it, forecasting net impact by horizon

We deliver granular, decision-grade intel: market sizing, 5-year forecasts, pricing, adoption, usage, revenue, and operational KPIs—plus competitor tracking, regulation, and value chains—across 60 countries broadly.

Spot the shifts before they hit your P&L. We track inflection points, adoption curves, pricing moves, and ecosystem plays to show where demand is heading, why it is changing, and what to do next across high-growth markets and disruptive tech

Real-time reads of user behavior. We track shifting priorities, perceptions of today’s and next-gen services, and provider experience, then pace how fast tech moves from trial to adoption, blending buyer, consumer, and channel inputs with social signals (#WhySwitch, #UX).

Partner with our analyst team to build a custom report designed around your business priorities. From analysing market trends to assessing competitors or crafting bespoke datasets, we tailor insights to your needs.
Supplier Intelligence
Discovery & Profiling
Capacity & Footprint
Performance & Risk
Compliance & Governance
Commercial Readiness
Who Supplies Whom
Scorecards & Shortlists
Playbooks & Docs
Category Intelligence
Definition & Scope
Demand & Use Cases
Cost Drivers
Market Structure
Supply Chain Map
Trade & Policy
Operating Norms
Deliverables
Buyer Intelligence
Account Basics
Spend & Scope
Procurement Model
Vendor Requirements
Terms & Policies
Entry Strategy
Pain Points & Triggers
Outputs
Pricing Analysis
Benchmarks
Trends
Should-Cost
Indexation
Landed Cost
Commercial Terms
Deliverables
Brand Analysis
Positioning & Value Prop
Share & Presence
Customer Evidence
Go-to-Market
Digital & Reputation
Compliance & Trust
KPIs & Gaps
Outputs
Full Research Suite comprises of:
Market outlook & trends analysis
Interviews & case studies
Strategic recommendations
Vendor profiles & capabilities analysis
5-year forecasts
8 regions and 60+ country-level data splits
Market segment data splits
12 months of continuous data updates
DELIVERED AS:
PDF EXCEL ONLINE
Aquafeed Enzyme Market Analysis - Size, Share, & Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Feed Mixer for Livestock Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Feed Preparation Machine Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Feed Additive Nosiheptide Premix Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Feeder Container Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Feed Machine Market Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Feed Pigment Market Forecast and Outlook 2025 to 2035
Feed Mixer Market Forecast and Outlook 2025 to 2035
Feed Grade Spray-dried Animal Plasma (SDAP) Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Feed Electrolytes Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Feed Micronutrients Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Feed Acidifier Market Analysis Size Share and Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Feed Flavors Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Feed Mycotoxin Binders Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Feed Phytogenics Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Feed Carbohydrase Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Feed Grade Oils Market Analysis - Size, Share, and Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Feed Packaging Market Size, Share & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Feed Mycotoxin Detoxifiers Market Analysis - Size, Share, and Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Feed Premix Market Analysis - Size, Share, & Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035

Thank you!
You will receive an email from our Business Development Manager. Please be sure to check your SPAM/JUNK folder too.
Chat With
MaRIA