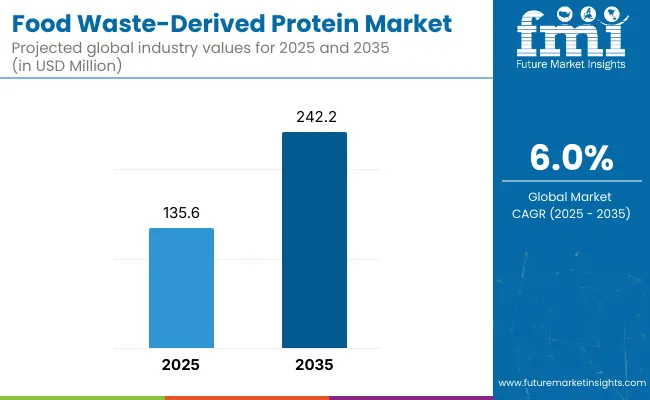
The food-waste derived protein market is expected to be valued at USD 135.6 million in 2025 and is projected to reach USD 242.2 million by 2035. This anticipated increase of USD 106.6 million reflects a market expansion of over 78.6% during the decade. A steady compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.0% is forecasted, suggesting that the market is likely to achieve nearly a 2X size increase within ten years.
Food Waste-Derived Protein Key Takeaways
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Estimated Value in (2025E) | USD 135.6 million |
| Forecast Value in (2035F) | USD 242.2 million |
| Forecast CAGR (2025 to 2035) | 6.0% |
Between 2025 and 2030, the market is projected to rise from USD 135.6 million to approximately USD 180.8 million, contributing USD 45.2 million or about 42.4% of the decade's total growth. During this period, demand is expected to be fueled by circular economy mandates, food industry waste valorization programs, and increasing functional food innovation. Fruit, vegetable, and cereal waste streams are anticipated to dominate volume adoption due to their high nutrient retention and availability across food supply chains.
The second phase from 2030 to 2035 is expected to contribute an additional USD 61.4 million in revenue, equivalent to 57.6% of the total growth, as the market grows from USD 180.8 million to USD 242.2 million. This phase will likely be driven by advancements in precision fermentation, enzymatic hydrolysis, and biorefinery integration.
A shift toward localized bioprocessing units and traceability-compliant protein ingredients is expected to accelerate commercialization across both developed and emerging economies. The market’s maturity will be supported by regulatory standardization, nutritional validation, and improved downstream scalability.
From 2020 to 2024, the Food-Waste Derived Protein Market expanded from ~USD 125.5 million to USD 135.6 million, driven largely by regulatory support and ESG-aligned reformulations in food and feed sectors. During this period, protein manufacturers converting high-volume waste streams particularly insect-based players captured nearly 30-35% of global revenue. Companies such as InnovaFeed, Ynsect, and Better Origin led the field through vertical integration and scalable bioconversion infrastructure.
Competitive advantage was anchored in volume capacity, regulatory compliance, and alignment with zero-waste and circular economy frameworks. Functional protein inclusion in sports, elderly, and animal nutrition products surged, while industrial and cosmetic applications remained nascent. As the market heads toward USD 242.2 million by 2035, growth is expected to be reshaped by subscription-based ingredient supply models, biorefinery integrations, and functional performance standards.
Legacy players must pivot beyond bulk protein delivery toward ingredient traceability, clean-label compliance, and functional differentiation. Competitive strength is now expected to depend on ecosystem partnerships, traceability platforms, and product customization aligned with end-use precision and nutritional integrity.
Significant growth in the food-waste derived protein market has been driven by the rising urgency to reduce food system inefficiencies and enhance resource circularity. Regulatory mandates on organic waste reduction and sustainable sourcing have been enacted across major economies, creating a strong policy tailwind.
As traditional protein inputs face environmental scrutiny, food-waste streams are being repositioned as viable, nutrient-dense alternatives. Advances in enzymatic hydrolysis and fermentation-based recovery have enabled greater extraction efficiency and consistency in amino acid profiles.
Demand has been further supported by heightened consumer interest in clean-label, upcycled, and environmentally responsible ingredients. Applications in functional foods, nutraceuticals, and animal feed have been prioritized by manufacturers seeking to meet sustainability targets.
Integration into B2B ingredient platforms and closed-loop processing systems is expected to scale adoption across industries. Growth is anticipated to be led by plant-based proteins, fermentation-based extraction technologies, and food & beverage applications, owing to their scalability, versatility, and growing mainstream acceptance.
The food-waste derived protein market has been segmented across six key categories: protein source, protein type, processing technology, product form, application, and sales channel. These segments define the upstream availability, technological pathway, and commercial integration of food-waste valorization.
The protein source segment classifies inputs such as fruit, vegetable, grain, dairy, and meat waste, reflecting the diversity of feedstock supply. Protein type segmentation distinguishes between animal-based, plant-based, and mixed proteins, which are processed and positioned differently in functional food and feed applications.
Processing technology segmentation, including enzymatic hydrolysis and fermentation-based recovery, outlines the core methods enabling waste-to-protein conversion. Each segment offers unique drivers of scale, nutritional performance, and end-market alignment providing a multidimensional framework for competitive and operational analysis.
| Protein Source Segment | Market Value Share, 2025 |
|---|---|
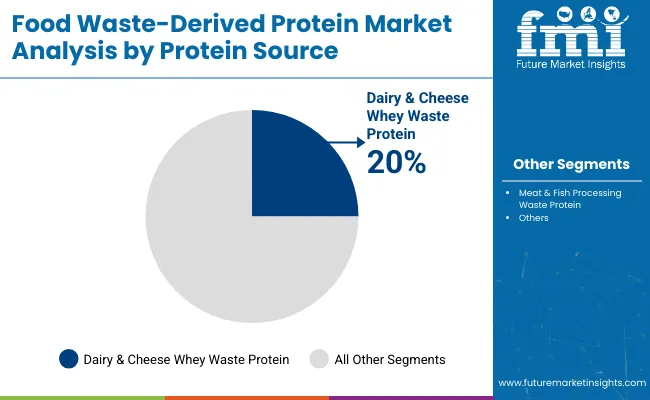
| Dairy & Cheese Whey Waste Protein | 20.0% |
| Meat & Fish Processing Waste Protein | 18.0% |
In 2025, dairy and cheese whey waste protein has been projected to hold the largest share at 20%, driven by its proven nutritional density, high protein yield, and integration with ultrafiltration and enzymatic systems. These proteins have been increasingly adopted for infant nutrition, performance foods, and nutraceuticals where complete amino acid profiles are prioritized. Meat and fish processing waste protein has emerged as the second-leading source, especially in animal feed and functional hydrolysates.
Meanwhile, plant-based waste proteins from fruits, vegetables, legumes, and grains have been gaining ground as sustainable, allergen-friendly options for clean-label foods. Growth across these segments has been supported by global zero-waste policies, rising ingredient traceability standards, and investments in local biomass valorization platforms. Going forward, protein sourcing strategies are expected to be guided by cost-efficiency, carbon reduction metrics, and compatibility with decentralized bioprocessing models.
| Protein Type | 2025 Share % |
|---|---|
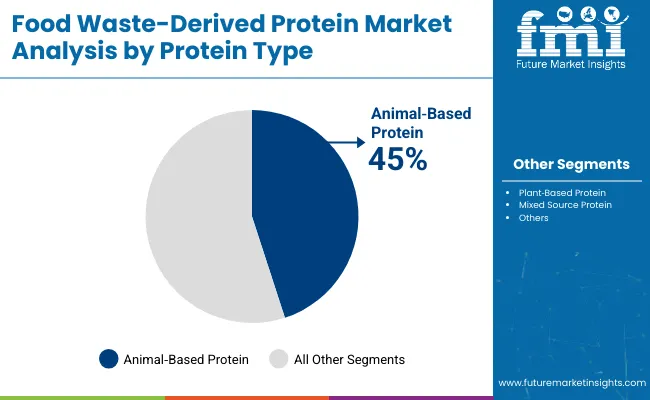
| Animal Based Protein | 45.0% |
| Plant Based Protein | 40.0% |
| Mixed Source Protein | 15.0% |
Animal-based protein is expected to maintain a dominant share of 45% in 2025, attributed to the high protein content and functionality derived from dairy whey, meat, and fish waste. These proteins have been widely adopted in technical food, pet nutrition, and sports formulations where amino acid completeness and functional stability are required. However, the fastest growth is expected to come from plant-based protein, driven by the rising shift toward vegan diets, allergen-free nutrition, and environmentally-conscious formulations.
Waste streams from legumes, grains, and vegetables have been increasingly harnessed for protein extraction through enzymatic and microbial methods. Mixed-source proteins, typically created through blending or co-processing, have found utility in feed and aquaculture segments where cost and volume efficiency are prioritized. Over the coming years, market share dynamics are anticipated to shift in favor of plant-based proteins as novel extraction methods, flavor masking, and texturization technologies continue to mature.
| Processing Technology | 2025 Share % |
|---|---|
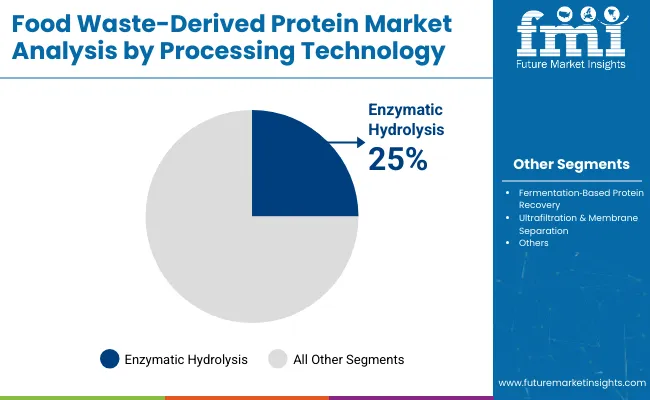
| Enzymatic Hydrolysis | 25.0% |
| Fermentation Based Protein Recovery | 22.0% |
| Ultrafiltration & Membrane Separation | 20.0% |
Enzymatic hydrolysis has been identified as the leading technology, expected to capture 25% of the market in 2025. Its prominence has been secured through its ability to convert complex proteins into bioavailable peptides with minimal nutrient loss and clean-label positioning. This method has been particularly favored in the production of hypoallergenic formulas and protein hydrolysates for dietary supplements. Fermentation-based recovery, close behind at 22%, has seen rapid adoption due to its capacity to improve digestibility and enhance protein stability.
The method has also aligned well with probiotic-infused formulations and circular fermentation ecosystems. Ultrafiltration and membrane separation have gained attention for their precision in fractionating protein concentrates, especially in dairy and plant applications. Drying and concentration technologies continue to support volume scalability, while chemical extraction has retained a niche presence for industrial-grade proteins. As cost-efficiency, bioactivity, and sustainability become critical selection criteria, enzymatic and fermentation platforms are projected to drive innovation leadership.
Rising processing costs and regulatory uncertainty continue to challenge scalability in the food-waste derived protein market, even as demand surges across nutrition, feed, and wellness sectors for upcycled, sustainable proteins aligned with zero-waste goals and circular ingredient innovation.
Policy-Driven Valorization of Food Waste
Mandatory food waste reduction policies and landfill diversion laws have been enacted across major economies, driving the valorization of waste streams into high-value protein ingredients. Government initiatives promoting upcycled food and fiscal incentives for waste-to-value projects have been introduced to accelerate adoption.
Sustainability-linked procurement standards have been integrated into institutional food programs, further increasing demand for traceable, circular-sourced protein inputs. The market has been supported by cross-sector partnerships between municipalities, agri-processors, and food manufacturers. As regulatory pressure intensifies and reporting becomes mandatory, food companies are expected to integrate food-waste derived proteins as a core component of their sustainability and ESG disclosures.
Shift Toward Functional Protein Ingredients in Clean-Label Nutrition
Functional proteins derived from food waste are being positioned beyond commodity markets and are increasingly incorporated into specialized clean-label, plant-based, and performance nutrition applications. Market traction has been observed in fortified beverages, meal replacements, and gut-health-enhancing powders, where bioactive peptides and fiber-rich matrices are valued. Advanced extraction methods are enabling the preservation of functional compounds such as polyphenols and prebiotics alongside protein content. As consumer demand pivots toward multi-functional, transparent ingredients with environmental claims, food-waste proteins are being reformulated into high-margin, value-added offerings. The clean-label trend is expected to expand protein use cases and redefine quality benchmarks within this segment.
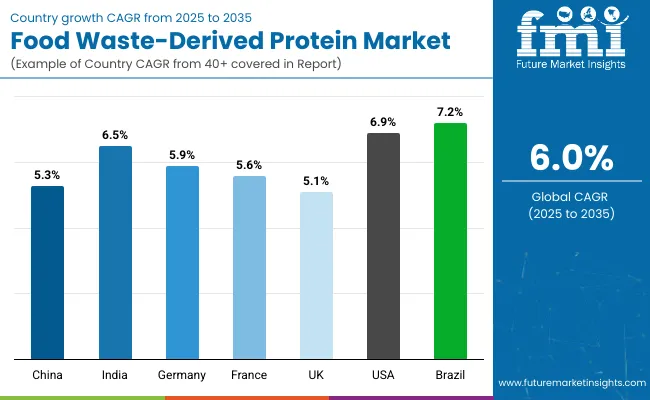
| Countries | CAGR (2025 to 2035) |
|---|---|
| China | 5.3% |
| India | 6.5% |
| Germany | 5.9% |
| France | 5.6% |
| UK | 5.1% |
| USA | 6.9% |
| Brazil | 7.2% |
The global food-waste derived protein market has exhibited significant cross-country divergence in adoption patterns, largely shaped by food system modernization, waste recovery infrastructure, and sustainability legislation. North America has been positioned as a key growth driver, with the United States forecasted to expand at a 6.9% CAGR.
This momentum has been supported by rising consumer demand for upcycled protein ingredients and corporate net-zero targets influencing ingredient procurement strategies. Brazil, with a projected CAGR of 7.2%, is expected to lead Latin America, driven by biomass-rich supply chains and government-backed circular economy frameworks encouraging agro-industrial waste valorization.
In Asia-Pacific, India is projected to grow at 6.5%, propelled by national food processing policies, capacity-building for municipal waste recovery, and private investments in functional protein start-ups. China, despite a slightly lower CAGR of 5.3%, remains strategically important due to its scale of food waste generation and growing regulatory pressure on food manufacturers to reduce organic waste volumes.
Europe continues to reflect a structured yet slower-paced growth curve, with Germany (5.9%), France (5.6%), and the UK (5.1%) advancing under EU waste reduction directives and retailer-led sustainability programs. Future growth across these markets is expected to be influenced by policy alignment, infrastructure funding, and the scalability of low-emission protein extraction technologies.
| Years | 2025 | 2026 | 2027 | 2028 | 2029 | 2030 | 2031 | 2032 | 2033 | 2034 | 2035 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| USA Food Waste-Derived Protein | 32.5 | 34.6 | 36.5 | 39.0 | 41.2 | 43.7 | 46.2 | 48.6 | 51.5 | 54.6 | 57.8 |
The food-waste derived protein market in the United States is projected to expand at a CAGR of 6.0% from 2025 to 2035, underpinned by government-backed waste reduction policies, ESG-driven reformulations by food manufacturers, and growing consumer alignment with clean-label and upcycled nutrition. Increased attention has been placed on valorizing organic residues from food service, brewery, and dairy sectors leading to strong demand for both plant- and animal-based functional protein ingredients.
Innovations in enzymatic and membrane separation technologies have been adopted by mid-size ingredient producers, enabling cost-effective recovery at scale. Greater traction has been observed in performance nutrition and pet food sectors, where digestibility and traceability are prioritized. USA universities and startups have also introduced pilot-scale systems integrating waste capture and protein extraction, supporting regionalized protein production.
As sustainability-linked sourcing becomes institutionalized in procurement frameworks, demand for USA-produced food-waste derived protein is expected to experience continued acceleration.
The food-waste derived protein market in the UK is projected to grow moderately from 19.6% share in 2025 to 20.7% by 2035. Growth has been supported by strict landfill diversion mandates and post-Brexit sustainability commitments across the food sector. Upcycled proteins have been integrated into reformulated ready meals, bakery products, and sports nutrition lines as UK retailers adopt aggressive zero-waste targets. Local food manufacturers have partnered with municipal waste aggregators and academic institutions to develop closed-loop protein recovery systems.
India’s food-waste derived protein market is forecasted to register strong growth through 2035, supported by government initiatives under the Food Processing and Swachh Bharat missions. Decentralized bioprocessing units have been promoted to convert agri-waste, pulse husks, and fruit pulp into protein-rich inputs for domestic food, feed, and supplement sectors. The market has been shaped by demand for affordable, high-volume functional ingredients aligned with nutrition security goals.
China’s share in the food-waste derived protein market is projected to grow steadily, anchored by strong state-led waste management reforms and rising demand for sustainable domestic ingredients. Circular economy targets have been embedded in the Five-Year Plan, prompting large food manufacturers to invest in high-volume protein extraction from fruit pomace, cereal residues, and dairy waste. National R&D programs have prioritized scalable recovery technologies and traceability infrastructure.
| Countries | 2025 | 2035 |
|---|---|---|
| UK | 19.6% | 20.7% |
| Germany | 20.3% | 21.7% |
| Italy | 10.0% | 9.6% |
| France | 13.4% | 13.6% |
| Spain | 9.1% | 9.0% |
| BENELUX | 6.8% | 5.0% |
| Nordic | 6.0% | 5.1% |
| Rest of Europe | 14.8% | 15.4% |
Germany is expected to remain a frontrunner in Europe’s food-waste derived protein landscape, with its market share increasing from 20.3% in 2025 to 21.7% by 2035. The country’s advanced recycling infrastructure, strong regulatory frameworks, and innovation-led food processing sector have enabled rapid adoption of protein extraction technologies. Functional proteins from bread waste, dairy by-products, and brewery residues have been integrated into premium food and nutraceutical applications.
| Protein Source | Market Value Share, 2025 |
|---|---|
| Fruit & Vegetable Waste Protein | 11.0% |
| Cereal & Grain Waste Protein | 9.0% |
| Dairy & Cheese Whey Waste Protein | 22.0% |
| Legume & Pulse Waste Protein | 12.0% |
| Meat & Fish Processing Waste Protein | 20.0% |
| Brewery & Distillery Waste Protein | 9.0% |
| Bakery Waste Protein | 7.0% |
| Other Agro Industrial Waste Protein | 10.0% |
The food-waste derived protein market in Japan is projected to reach a valuation of USD 5.7 million in 2025, with dairy and cheese whey waste protein leading at 22%, followed closely by meat and fish processing waste protein at 20%. These shares reflect Japan’s emphasis on high-purity, nutritionally complete protein inputs for medical, elderly, and functional food segments. The preference for animal-based waste inputs is underpinned by their strong amino acid profiles and compatibility with existing dairy and seafood processing infrastructure.
Innovation has been steered by Japan’s long-standing expertise in fermentation, driving advancements in probiotic-infused upcycled proteins. Local manufacturers have prioritized ultra-clean extraction and traceability systems, aligning with national standards for food safety and low environmental impact.
| Processing Technology | Market Value Share, 2025 |
|---|---|
| Enzymatic Hydrolysis | 26.0% |
| Fermentation Based Protein Recovery | 23.0% |
| Ultrafiltration & Membrane Separation | 21.0% |
| Drying & Concentration Technologies | 17.0% |
| Chemical Extraction & Purification | 13.0% |
The food-waste derived protein market in South Korea is projected to advance steadily by 2035, with enzymatic hydrolysis leading at 26% share in 2025, closely followed by fermentation-based recovery at 23%. This dominance has been supported by South Korea’s strong biochemical processing base and consumer demand for bioavailable, functional proteins. Proteins derived from food waste are being integrated into fortified beverages, functional foods, and elderly nutrition sectors in which enzymatic hydrolysis offers superior solubility and digestibility.
Fermentation-based processes have been championed for their compatibility with Korea’s traditional food biotech ecosystems, particularly in kombucha-style drinks and soy-ferment blends. Meanwhile, ultrafiltration methods have been increasingly deployed by ingredient manufacturers targeting purity and concentration without thermal degradation.
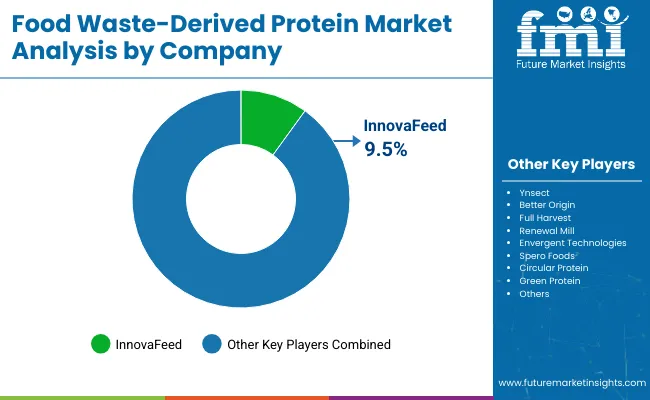
The food-waste derived protein market is moderately fragmented, with global pioneers, mid-sized disruptors, and niche sustainability specialists competing across food, feed, and nutraceutical applications. Circular economy leaders such as InnovaFeed, Ynsect, and Better Origin have secured substantial market share by building vertically integrated platforms that convert agri-food waste into high-performance proteins for aquaculture, poultry, and pet nutrition. Their strategic advantage has been reinforced through investments in insect-based bioconversion systems, supported by favorable European regulations and zero-waste certification schemes.
Mid-sized innovators such as Spero Foods, Full Harvest, and Renewal Mill have focused on food-grade, plant-based protein ingredients derived from upcycled fruits, vegetables, and pulses. These companies have accelerated commercial traction through co-branding partnerships with CPG brands and by emphasizing functional nutrition, clean-label credentials, and traceable sourcing.
Specialized players, including Green Protein, Circular Protein, and Envergent Technologies, are targeting industrial food sectors with application-specific solutions in enzymatic hydrolysates and fiber-rich protein concentrates. Their strength lies in modular processing models and alignment with local biomass availability.
Competitive advantage in this market is increasingly defined by end-to-end sustainability, ingredient transparency, and functional performance, rather than volume scale alone. Strategic focus is expected to shift further toward subscription-based ingredient supply, upcycling-as-a-service models, and integration with regenerative agriculture systems.
| Item | Value |
|---|---|
| Quantitative Units | USD 135.6 million |
| Protein Source | Fruit & Vegetable Waste Protein, Cereal & Grain Waste Protein, Dairy & Cheese Whey Waste Protein, Legume & Pulse Waste Protein, Meat & Fish Processing Waste Protein, Brewery & Distillery Waste Protein, Bakery Waste Protein, Other Agro-Industrial Waste Protein |
| Protein Type | Animal-Based Protein, Plant-Based Protein, Mixed Source Protein |
| Processing Technology | Enzymatic Hydrolysis, Fermentation-Based Protein Recovery, Ultrafiltration & Membrane Separation, Drying & Concentration Technologies, Chemical Extraction & Purification |
| Product Form | Protein Concentrates, Protein Isolates, Protein Hydrolysates, Functional Protein Ingredients |
| Application | Food & Beverage Ingredients, Animal Feed & Aquafeed, Nutraceuticals & Dietary Supplements, Cosmetics & Personal Care, Industrial Uses |
| Sales Channel | B2B Ingredient Suppliers, Food & Beverage Manufacturers, Animal Feed Producers, Nutraceutical Companies, Online Ingredient Marketplaces |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America, Middle East & Africa |
| Country Covered | United States, Canada, Germany, France, United Kingdom, China, Japan, India, Brazil, South Africa |
| Key Companies Profiled | InnovaFeed, Ynsect, Better Origin, Full Harvest, Renewal Mill, Envergent Technologies, Spero Foods, Circular Protein, Green Protein |
| Additional Attributes | Dollar sales by protein source, technology, and application; demand shift toward clean-label and upcycled proteins; innovations in fermentation and enzymatic hydrolysis; regional mandates on food waste reduction; bioconversion platform scale-ups; functional protein inclusion in sports, wellness, and senior nutrition; B2B supplier integration; traceability and ESG-aligned sourcing; vertical integratio n in insect protein ecosystems. |
The global Food Waste-Derived Protein is estimated to be valued at USD 135.6 million in 2025.
The market size for the Food Waste-Derived Protein is projected to reach USD 242.2 million by 2035.
The Food Waste-Derived Protein is expected to grow at a 6.0% CAGR between 2025 and 2035.
The key protein sources in the Food Waste-Derived Protein Market are fruit & vegetable waste protein, cereal & grain waste protein, dairy & cheese whey waste protein, legume & pulse waste protein, meat & fish processing waste protein, brewery & distillery waste protein, bakery waste protein, and other agro-industrial waste protein.
In terms of processing technology, Enzymatic Hydrolysis is projected to command the highest share at 25% in the Food-Waste Derived Protein Market in 2025.






Our Research Products

The "Full Research Suite" delivers actionable market intel, deep dives on markets or technologies, so clients act faster, cut risk, and unlock growth.

The Leaderboard benchmarks and ranks top vendors, classifying them as Established Leaders, Leading Challengers, or Disruptors & Challengers.

Locates where complements amplify value and substitutes erode it, forecasting net impact by horizon

We deliver granular, decision-grade intel: market sizing, 5-year forecasts, pricing, adoption, usage, revenue, and operational KPIs—plus competitor tracking, regulation, and value chains—across 60 countries broadly.

Spot the shifts before they hit your P&L. We track inflection points, adoption curves, pricing moves, and ecosystem plays to show where demand is heading, why it is changing, and what to do next across high-growth markets and disruptive tech

Real-time reads of user behavior. We track shifting priorities, perceptions of today’s and next-gen services, and provider experience, then pace how fast tech moves from trial to adoption, blending buyer, consumer, and channel inputs with social signals (#WhySwitch, #UX).

Partner with our analyst team to build a custom report designed around your business priorities. From analysing market trends to assessing competitors or crafting bespoke datasets, we tailor insights to your needs.
Supplier Intelligence
Discovery & Profiling
Capacity & Footprint
Performance & Risk
Compliance & Governance
Commercial Readiness
Who Supplies Whom
Scorecards & Shortlists
Playbooks & Docs
Category Intelligence
Definition & Scope
Demand & Use Cases
Cost Drivers
Market Structure
Supply Chain Map
Trade & Policy
Operating Norms
Deliverables
Buyer Intelligence
Account Basics
Spend & Scope
Procurement Model
Vendor Requirements
Terms & Policies
Entry Strategy
Pain Points & Triggers
Outputs
Pricing Analysis
Benchmarks
Trends
Should-Cost
Indexation
Landed Cost
Commercial Terms
Deliverables
Brand Analysis
Positioning & Value Prop
Share & Presence
Customer Evidence
Go-to-Market
Digital & Reputation
Compliance & Trust
KPIs & Gaps
Outputs
Full Research Suite comprises of:
Market outlook & trends analysis
Interviews & case studies
Strategic recommendations
Vendor profiles & capabilities analysis
5-year forecasts
8 regions and 60+ country-level data splits
Market segment data splits
12 months of continuous data updates
DELIVERED AS:
PDF EXCEL ONLINE
Food & Beverage OEE Software Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Food Grade Crosslinked Polyvinylpolypyrrolidone (PVPP) Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Food Grade Cassia Gum Powder Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Food Grade Dry Film Lubricant Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Foodservice Equipment Market Analysis - Size, Share, and Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Food Basket Market Forecast and Outlook 2025 to 2035
Food Grade Tremella Polysaccharide Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Food Sorting Machine Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Foodservice Paper Bag Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Food Stabilizers Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Food Packaging Film Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Food Certification Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Food Tray Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Food & Beverage Industrial Disinfection and Cleaning Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Food Technology Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Food Tourism Sector Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Food Processing Boiler Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Food Packaging Machines Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Food Minerals Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Food And Beverage Chemicals Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035

Thank you!
You will receive an email from our Business Development Manager. Please be sure to check your SPAM/JUNK folder too.
Chat With
MaRIA