The High Voltage Direct Current Power Supply Market is estimated to be valued at USD 4.6 billion in 2025 and is projected to reach USD 10.1 billion by 2035, registering a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 8.2% over the forecast period.
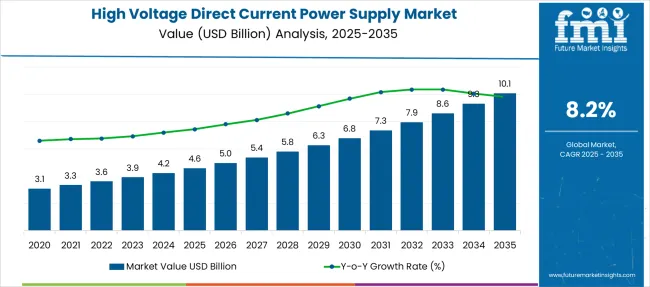
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| High Voltage Direct Current Power Supply Market Estimated Value in (2025 E) | USD 4.6 billion |
| High Voltage Direct Current Power Supply Market Forecast Value in (2035 F) | USD 10.1 billion |
| Forecast CAGR (2025 to 2035) | 8.2% |
The high voltage direct current (HVDC) power supply market is experiencing steady expansion, driven by the global transition toward long-distance power transmission, renewable energy integration, and grid stability enhancement. Increased electrification of rural and remote areas, alongside cross-border power exchange initiatives, is encouraging utility providers and governments to adopt HVDC infrastructure.
Technological advancements in insulation, switching systems, and power electronics have improved system efficiency and operational safety, particularly in high-voltage transmission projects. Regulatory mandates supporting decarbonization and transmission system upgrades are expected to further catalyze HVDC adoption.
Market momentum is also being reinforced by public-private investment in ultra-high-voltage and multi-terminal HVDC projects designed to deliver efficient and loss-minimized power transfer across geographies..
The high voltage direct current power supply market is segmented by installation type, voltage level, technology type, and end-use industry and geographic regions. The high voltage direct current power supply market is divided into Overhead, Underground, and Subsea by installation type. The high voltage direct current power supply market is classified into >4000V, 1000V, and 1000–4000V. Based on the technology type, the high voltage direct current power supply market is segmented into line-commutated converters (LCC), Voltage source converters (VSC), and Ultra-High voltage direct current (UHVDC). The high voltage direct current power supply market is segmented by end-use industry into Industrial, Telecommunication, Medical, Oil & gas, and Others. Regionally, the high voltage direct current power supply industry is classified into North America, Latin America, Western Europe, Eastern Europe, Balkan & Baltic Countries, Russia & Belarus, Central Asia, East Asia, South Asia & Pacific, and the Middle East & Africa.
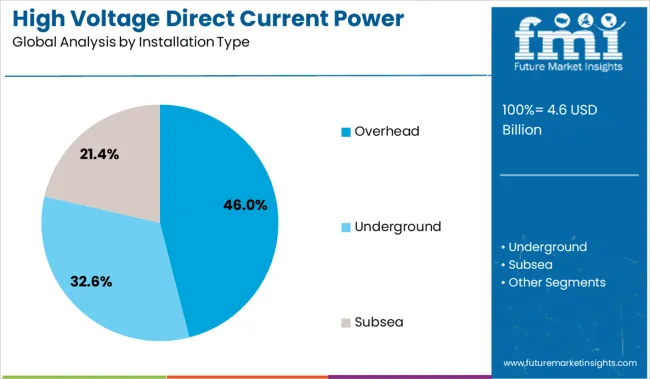
The overhead segment is anticipated to account for 46.0% of the market revenue in 2025, making it the dominant installation type. This leadership is being driven by its cost-efficiency, ease of maintenance, and established deployment frameworks across vast distances.
Overhead installations are preferred in regions with accessible terrain and fewer urban constraints, where long-distance power transfer is necessary. The segment benefits from lower construction timeframes and flexibility in infrastructure expansion compared to underground or submarine alternatives.
Additionally, the scalability of overhead HVDC systems for both point-to-point and multi-terminal configurations enhances their application in high-capacity renewable energy projects and national grid interconnections..
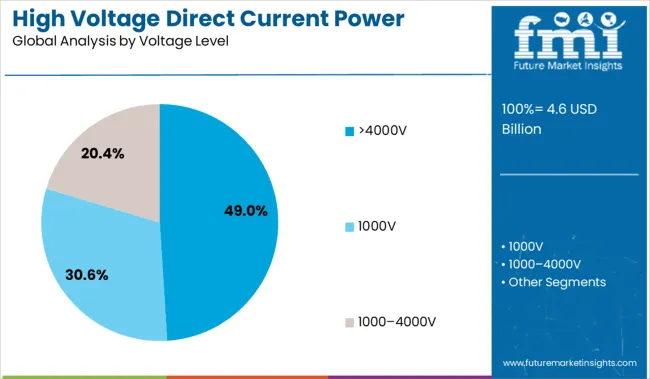
The >4000V segment is projected to hold 49.0% of the market share in 2025, making it the most dominant voltage range in HVDC applications. This is being influenced by the need for bulk power transmission across large distances with minimal energy loss.
Higher voltage levels are enabling the integration of large-scale renewable sources into national grids, particularly from offshore wind, solar deserts, and hydropower hubs. Advances in converter technology and insulation systems have improved the operational reliability of >4000V systems, leading to increased preference in intercontinental and interregional HVDC corridors.
As energy demand grows and transmission complexity increases, utilities are prioritizing ultra-high-voltage DC configurations to ensure efficiency, stability, and grid interoperability..
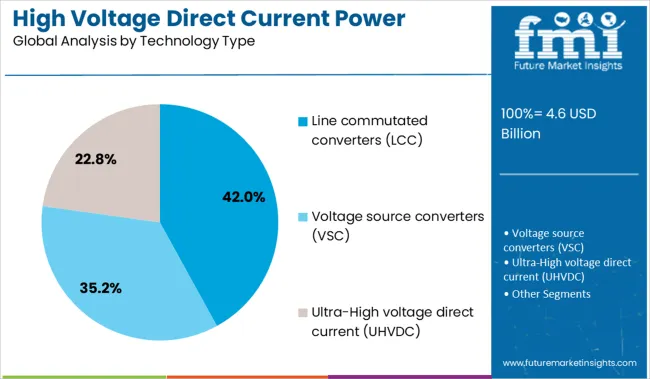
Line commutated converters (LCC) are expected to command 42.0% of the total HVDC power supply market revenue in 2025, securing their position as the leading technology type. LCC systems are widely adopted due to their high power capacity, proven reliability, and long-term cost advantages in large-scale transmission projects.
Their ability to handle high-voltage, high-power loads with minimal harmonic distortion makes them ideal for connecting conventional generation sources and managing grid stability. LCC's operational maturity, robust performance under steady-state conditions, and well-developed technical support ecosystem have reinforced its deployment across legacy HVDC networks.
Despite emerging competition from voltage source converters (VSC), LCC remains the preferred choice for base-load and long-distance transmission due to its lower conduction losses and scalability..
Grid modernization and interregional energy trade are driving HVDC adoption, supported by regulatory shifts and rising demand for transmission stability. Geopolitical energy agendas and cross-border collaborations are further boosting dollar sales and market share.
Grid resilience is being prioritized globally as aging infrastructure and increasing load demand challenge conventional systems. HVDC power supplies are being adopted to stabilize long-distance electricity transmission while minimizing energy losses. Regulatory backing across OECD nations is being observed, with energy transition policies and decarbonization mandates accelerating the shift from AC to HVDC systems. Stakeholders across Asia-Pacific and BRICS nations are also realigning power infrastructure with cross-border energy trade in mind. It is widely believed that HVDC enables not only stable load flow but also facilitates renewables integration, a strategic need in wind-rich or hydropower-dense regions. Dollar sales are being spurred as grid operators, public utilities, and interconnection projects adopt compact, modular HVDC systems.
Cross-border energy flows are being reshaped by geopolitical imperatives and energy security agendas, positioning HVDC as a cornerstone for strategic power exchange. Market share is being increasingly influenced by bilateral energy corridors, especially across Europe, South Asia, and the Middle East, where high-capacity transmission with minimal losses is essential. Partnerships between utilities and transmission system operators are being expanded to deploy voltage-sourced converters (VSC) and line-commutated converters (LCC) in diverse terrain. Global energy consultants suggest that investment is being funneled into HVDC as interconnectivity gains precedence over isolated energy ecosystems. Stakeholder consensus aligns on HVDC’s role in enhancing power availability, export stability, and long-haul energy contracts, all of which are driving long-term dollar sales and adoption.
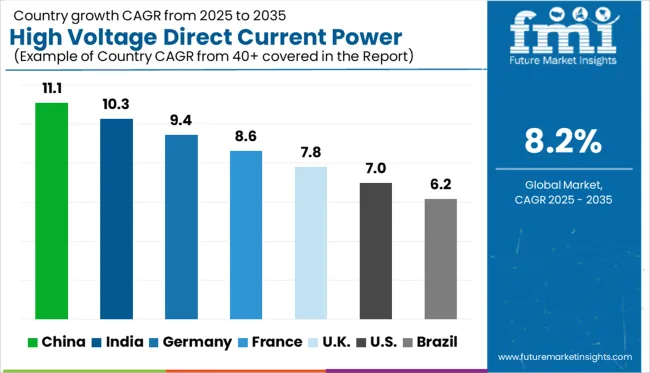
| Country | CAGR |
|---|---|
| China | 11.1% |
| India | 10.3% |
| Germany | 9.4% |
| France | 8.6% |
| UK | 7.8% |
| USA | 7.0% |
| Brazil | 6.2% |
The global high voltage direct current (HVDC) power supply market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 8.2% from 2025 to 2035, yet several BRICS and OECD economies are advancing well beyond this pace. China leads with a CAGR of 11.1%, driven by aggressive investments in long-distance power transmission and integration of renewable energy hubs in western provinces. India follows closely at 10.3%, supported by the expansion of interstate transmission systems and government-led electrification schemes under the National Grid initiative. Germany, a key OECD country, is growing at 9.4%, propelled by grid modernization, offshore wind connectivity, and cross-border interconnectors. The UK trails with 7.8%, reflecting moderate investment in grid resilience and decarbonization. The USA, at 7.0%, remains below the global average, constrained by regulatory fragmentation and aging transmission infrastructure. ASEAN countries show increasing interest in HVDC for regional power pooling, albeit from a smaller base. The report analyzes 40+ countries; the top five are shared here for reference.
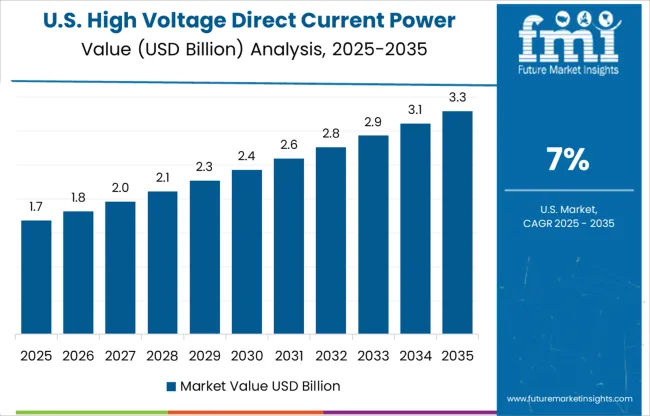
The CAGR of the HVDC power supply market in the United States rose from approximately 3.8% during 2020–2024 to 7.0% for 2025–2035, reflecting increased demand for grid modernization and federal support for interregional energy transmission. During the early 2020s, growth remained limited by policy fragmentation and the absence of large-scale projects. However, with the Inflation Reduction Act and Federal Transmission Acceleration plans rolled out post-2025, transmission infrastructure received renewed attention. Utilities are investing in next-generation voltage source converter (VSC) systems to interconnect renewable energy sources, especially in wind and solar-abundant states. Multi-state HVDC corridors are gaining approval, driven by resilience needs, wildfire threats, and cross-state power balancing.
The CAGR in the United Kingdom increased from just 3.4% in 2020–2024 to 7.8% during 2025–2035, as offshore wind integration, decarbonization mandates, and EU interconnection efforts became more prominent. Between 2020 and 2024, HVDC growth was modest due to project delays and the prioritization of other low-carbon initiatives. Post-Brexit energy independence and National Grid reforms are reshaping transmission priorities. Projects like the Eastern Green Link and North Sea offshore connectors are accelerating the deployment of compact, long-distance HVDC lines. The UK’s strategy to reduce curtailment and connect energy islands is also promoting converter station adoption.
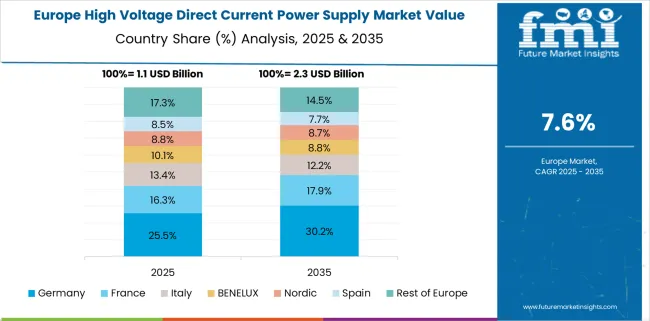
Germany’s HVDC market CAGR rose from 4.6% during 2020–2024 to 9.4% in the 2025–2035 forecast period, backed by the country’s Energiewende transition and accelerated phaseout of coal and nuclear energy. During the earlier period, delays in grid expansion hindered stronger growth. Post-2024, multiple SuedLink and SuedOstLink HVDC projects moved into advanced phases, aimed at transmitting renewable energy from the north to the industrial south. Regulatory simplifications and digital permitting are expediting infrastructure rollout. Germany’s industrial base is also driving HVDC component demand, especially in transformer and converter stations.
The CAGR for China's HVDC power supply market advanced from 6.2% during 2020–2024 to 11.1% over 2025–2035, fueled by the need to transmit power from inland hydropower bases to urban coastal regions. Early growth was shaped by the construction of multiple UHVDC (ultra-high-voltage direct current) lines. However, the real scale-up is forecasted post-2025 with investments in digital substation upgrades, regional interconnections, and decarbonization of western provinces. China’s "West-to-East Power Transmission" strategy and global Belt and Road energy projects are pushing major exports of HVDC equipment and services.
The CAGR for India's HVDC power supply market climbed from 5.9% during 2020–2024 to 10.3% in the 2025–2035 period, driven by government-backed interregional transmission upgrades and renewable energy integration. Earlier market growth was restrained by financing constraints and procurement delays. After 2025, central transmission utility Power Grid Corporation expanded capacity via multi-terminal HVDC corridors to connect solar parks across Rajasthan, Gujarat, and Tamil Nadu. Indigenous manufacturing of transformers, thyristors, and converter systems is gaining momentum under “Make in India.” The Green Energy Corridor project is being scaled to accommodate hybrid renewable transmission.
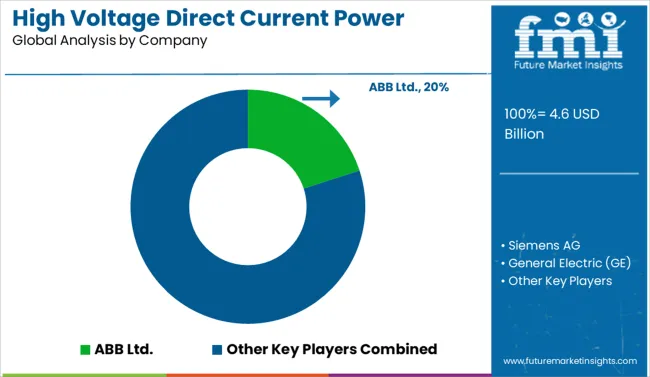
In the HVDC power supply market, global leaders are focusing on grid resilience, interregional power transmission, and integration of renewable sources through modular and ultra-high-voltage solutions. Companies like ABB Ltd., Siemens AG, and Hitachi Energy are driving large-scale deployments of voltage source converters (VSC), multi-terminal links, and offshore HVDC platforms to support long-distance and low-loss power transfer. ABB has strengthened its footprint in North America through capacity expansion, while Siemens continues to lead in European offshore grid integration with flagship projects like BorWin5. Hitachi Energy, leveraging its rebranded expertise, has introduced advanced HVDC Light technologies to support compact transmission and grid stabilization. Toshiba Corporation and Mitsubishi Electric Corporation are scaling domestic and Asian markets with energy-efficient HVDC modules and converter innovations, supported by smart grid initiatives. General Electric (GE) is consolidating its position through infrastructure-linked partnerships and component-level innovations aligned with next-gen transmission corridors.
In May 2024, ABB announced the acquisition of Siemens’s wiring accessories business in China, strengthening ABB’s product distribution network across 230 Chinese cities.
| Item | Value |
|---|---|
| Quantitative Units | USD 4.6 Billion |
| Installation Type | Overhead, Underground, and Subsea |
| Voltage Level | >4000V, 1000V, and 1000–4000V |
| Technology Type | Line commutated converters (LCC), Voltage source converters (VSC), and Ultra-High voltage direct current (UHVDC) |
| End-use Industry | Industrial, Telecommunication, Medical, Oil & gas, and Others |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America, Middle East & Africa |
| Country Covered | United States, Canada, Germany, France, United Kingdom, China, Japan, India, Brazil, South Africa |
| Key Companies Profiled | ABB Ltd., Siemens AG, General Electric (GE), Hitachi Energy (formerly Hitachi ABB Power Grids), Toshiba Corporation, and Mitsubishi Electric Corporation |
| Additional Attributes | Dollar sales, project pipeline by region, converter technology demand, key buyers, competitive share, regulatory shifts, forecasted dollar sales, and CAPEX opportunities. |
The global high voltage direct current power supply market is estimated to be valued at USD 4.6 billion in 2025.
The market size for the high voltage direct current power supply market is projected to reach USD 10.1 billion by 2035.
The high voltage direct current power supply market is expected to grow at a 8.2% CAGR between 2025 and 2035.
The key product types in high voltage direct current power supply market are overhead, underground and subsea.
In terms of voltage level, >4000v segment to command 49.0% share in the high voltage direct current power supply market in 2025.






Our Research Products

The "Full Research Suite" delivers actionable market intel, deep dives on markets or technologies, so clients act faster, cut risk, and unlock growth.

The Leaderboard benchmarks and ranks top vendors, classifying them as Established Leaders, Leading Challengers, or Disruptors & Challengers.

Locates where complements amplify value and substitutes erode it, forecasting net impact by horizon

We deliver granular, decision-grade intel: market sizing, 5-year forecasts, pricing, adoption, usage, revenue, and operational KPIs—plus competitor tracking, regulation, and value chains—across 60 countries broadly.

Spot the shifts before they hit your P&L. We track inflection points, adoption curves, pricing moves, and ecosystem plays to show where demand is heading, why it is changing, and what to do next across high-growth markets and disruptive tech

Real-time reads of user behavior. We track shifting priorities, perceptions of today’s and next-gen services, and provider experience, then pace how fast tech moves from trial to adoption, blending buyer, consumer, and channel inputs with social signals (#WhySwitch, #UX).

Partner with our analyst team to build a custom report designed around your business priorities. From analysing market trends to assessing competitors or crafting bespoke datasets, we tailor insights to your needs.
Supplier Intelligence
Discovery & Profiling
Capacity & Footprint
Performance & Risk
Compliance & Governance
Commercial Readiness
Who Supplies Whom
Scorecards & Shortlists
Playbooks & Docs
Category Intelligence
Definition & Scope
Demand & Use Cases
Cost Drivers
Market Structure
Supply Chain Map
Trade & Policy
Operating Norms
Deliverables
Buyer Intelligence
Account Basics
Spend & Scope
Procurement Model
Vendor Requirements
Terms & Policies
Entry Strategy
Pain Points & Triggers
Outputs
Pricing Analysis
Benchmarks
Trends
Should-Cost
Indexation
Landed Cost
Commercial Terms
Deliverables
Brand Analysis
Positioning & Value Prop
Share & Presence
Customer Evidence
Go-to-Market
Digital & Reputation
Compliance & Trust
KPIs & Gaps
Outputs
Full Research Suite comprises of:
Market outlook & trends analysis
Interviews & case studies
Strategic recommendations
Vendor profiles & capabilities analysis
5-year forecasts
8 regions and 60+ country-level data splits
Market segment data splits
12 months of continuous data updates
DELIVERED AS:
PDF EXCEL ONLINE
High Current Power Supply for Electrophoresis Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
High Voltage Direct Current (HVDC) Capacitor Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
High Voltage Power Transformer Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Utility Scale High Voltage Power Transformer Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
High Voltage Porcelain Bushing Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
High Voltage Air-cooled Battery Compartment Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
High Voltage Cable Termination Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
High Voltage Ionising Air Gun Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
High Voltage Equipment Market Forecast and Outlook 2025 to 2035
High Voltage Ceramic Zinc Oxide Surge Arrester Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
High-Power Microwave Source Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
High Voltage PTC Heater Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
High Current Ion Implanter Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
High Voltage Distribution Substation Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
High-power Objective Lens Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
High Voltage Capacitors Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
High Power Double-Clad Fiber Bragg Grating Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
High Voltage Electric Capacitor Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
High Voltage Circuit Breaker Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
High Voltage Substation Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035

Thank you!
You will receive an email from our Business Development Manager. Please be sure to check your SPAM/JUNK folder too.
Chat With
MaRIA