The global industrial rubber products market is estimated at USD 129.0 billion in 2025 and is forecast to expand to USD 243.8 billion by 2035, advancing at a 6.6% CAGR.
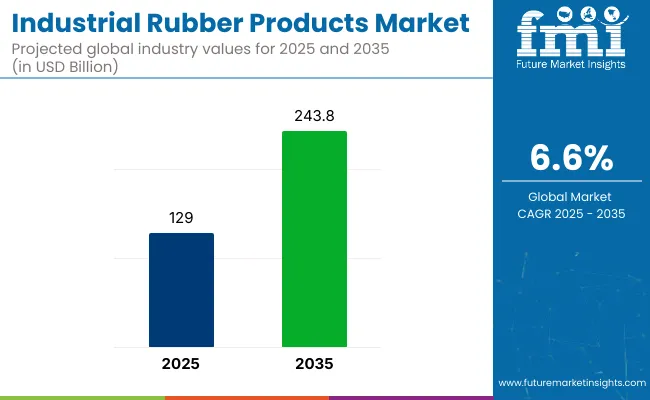
| Attribute | Values |
|---|---|
| Estimated Industry Size (2025E) | USD 129.0 billion |
| Projected Industry Value (2035F) | USD 243.8 billion |
| CAGR (2025 to 2035) | 6.6% |
Growth is driven by industrial recovery, expansion in automotive production, especially electric vehicles requiring specialized hoses and seals, and infrastructure development across regions like Southeast Asia and Central Europe.
The industrial rubber products market observed a recovery across end-use sectors. One of the significant drivers was the global rebound in manufacturing, especially in Central Europe and Southeast Asia, which increased the demand for conveyor belts, moulded rubber goods, and vibration isolation systems.
In automotive, the rising production of electric vehicles led to higher consumption of rubber hoses and thermal-resistant seals. For example, Yokohama Rubber announced a USD 380 million investment to expand manufacturing capacity in India to cater to EV and infrastructure segments.
In the oil and gas sector, a rise in offshore exploration, particularly in West Africa and the North Sea, created demand for rubber linings and tubing with endurance properties. Continental AG responded by launching a new conveyor belt line tailored for the mining sector, aimed at heavy-duty operations in 2024. This reflected a trend where product specifications were adapted to align with operational performance requirements in niche energy and resource industries.
Material advancement focused on synthetics such as EPDM and nitrile, which gained preference for their chemical and thermal resistance. Manufacturers integrated these compounds into hoses, seals, and dampers across EV and industrial use cases. Supply chain stabilisation post-COVID enabled better raw material access, and companies improved delivery schedules and inventory control systems.
Strategic partnerships gained momentum. In January 2024, Bridgestone partnered with Shell to co-develop sustainable rubber materials. This collaboration focused on renewable feedstock and process efficiency to meet regulatory and OEM compliance. Michelin acquired a German rubber components firm in April 2024 to strengthen its position in the European industrial market, particularly in the automotive and machinery sectors.
Looking forward, the sector is set to align with predictive maintenance trends. Integration of wear monitoring systems using sensors in rubber components is under evaluation in manufacturing and logistics. This would shift procurement strategies from reactive to condition-based sourcing.
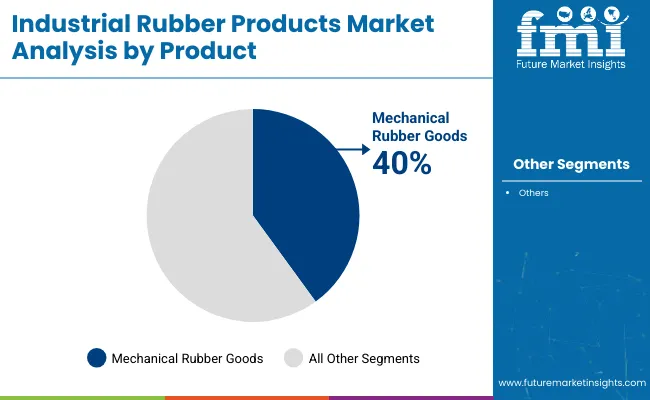
Mechanical rubber goods are projected to hold the largest share in 2025, accounting for 40% of the global market, and are expected to grow at a CAGR of 6.7% through 2035. These products include seals, gaskets, vibration isolators, and other molded items that play a vital role in machinery and automotive systems. Their demand is driven by the need for sealing, shock absorption, and insulation in applications ranging from hydraulic cylinders to automotive engines and industrial compressors.
Growth is further supported by rising investments in automation, electric vehicles, and machinery upgrades across manufacturing and processing sectors. In regions like Southeast Asia and Central Europe, robust industrial growth and rising vehicle production are sustaining the uptake of mechanical rubber components. Additionally, increasing preference for lightweight and durable elastomeric materials over metal parts in OEM applications is positively impacting this segment.
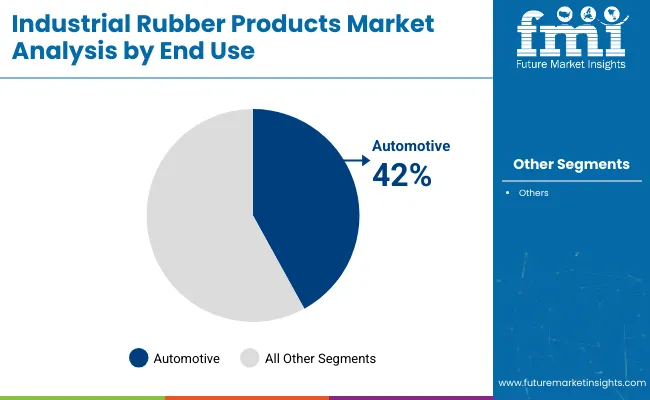
The automotive industry is estimated to be the leading end-use sector, commanding 42% share of the industrial rubber products market in 2025, and is anticipated to grow at a CAGR of 6.8% through 2035. Industrial rubber components are used extensively in vehicle manufacturing, including hoses for fluid systems, belts for power transmission, and seals for engine and drivetrain assemblies, and bushings for suspension systems.
With the global shift toward electrification and light weighting, there is a rising demand for specialized rubber formulations that withstand high temperatures, chemicals, and vibration. EPDM and NBR are commonly used materials in electric vehicle applications due to their flexibility and resistance characteristics.
OEMs are partnering with rubber product manufacturers to integrate noise-dampening and emission-reducing technologies in vehicles. Growing automotive production in Asia and Eastern Europe, combined with stringent regulatory norms for safety and efficiency, supports continued investment in rubber-based automotive components.
The industrial rubber products industry will grow steadily over the period to 2035, driven by growing demand from the automotive, construction, and energy industries. Demand will be boosted by the rising consumption of high-performance synthetic rubber parts in electric cars and industrial equipment. Players with sophisticated material expertise and robust global supply chains will gain the most, while those dependent on the traditional way of production will lose out on industry share.
Push Synthetic Rubber Capabilities Forward
Invest in R&D to create next-generation synthetic rubber compounds with improved thermal, chemical, and mechanical durability to address increasing demand from electric vehicles and offshore energy applications.
Ride Electrification and Green Infrastructure Waves
Redirect product development and go-to-industry efforts toward EV manufacturing, renewable energy installations, and green construction applications, where demand for vibration isolation and sealing systems is gaining momentum.
Expand Strategic Partnerships and Vertical Integration
Seek regional distribution partnerships and contemplate M&A strategies to obtain upstream raw materials and downstream channels and lower supply chain risks, and improve industry access within high-growth economies.
| Risk | Probability - Impact |
|---|---|
| Supply chain disruptions due to geopolitical instability or trade barriers | Medium - High |
| Volatility in raw material prices, especially synthetic rubber inputs | High - Medium |
| Technological obsolescence from advanced material substitutes | Low - High |
| Priority | Immediate Action |
|---|---|
| Strengthen raw material sourcing. | Run feasibility on nickel-based insert sourcing. |
| Adapt to EV and hybrid applications. | Initiate OEM feedback loop on hybrid insert demand. |
| Expand after-industry opportunities | Launch after-industry channel partner incentive pilot. |
Leadership will need to focus on speeding up innovation in synthetic rubber technologies and creating resilience in supply chains through regional diversification and vertical integration. This insight heralds a structural change in patterns of demand-particularly from EVS, offshore energy, and green infrastructure-that necessitates a product portfolio and capital reallocation.
During the ensuing 12 months, aggressive R&D and M&A strategic investment will be paramount in keeping ahead of the pack among aggressively scaling mid-tier players across Asia. The roadmap now must show a twofold orientation: harvesting near-term OEM gains in high-growth applications and preparing core operations against raw material uncertainty and material substitute innovation threats.
| Country | Impact of Policies and Regulations |
|---|---|
| United States | The industry is significantly impacted by environmental regulations, including those imposed by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) on hazardous waste disposal and air quality. Products also have to comply with Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) safety standards. California Proposition 65 requires warning labels on products that contain toxic chemicals. Businesses also have to adhere to ASTM (American Society for Testing and Materials) standards for rubber products. |
| United Kingdom | In the UK, the CE Marking is mandatory for specific industrial rubber products, certifying compliance with EU health, safety, and environmental protection requirements. Business firms also need to adhere to the REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation, and Restriction of Chemicals) regulations in order to prohibit harmful chemicals in products. The UK has now introduced more stringent regulations regarding the sustainable sourcing of materials and waste management. |
| France | France follows EU-wide legislation like REACH and CE Marking. AFNOR (Association Française de Normalisation) also establishes national standards for industrial rubber goods. France is also enforcing extended producer responsibility (EPR) legislation, which mandates producers to take care of recycling and disposal of their products. Tougher environmental laws are compelling businesses to emphasise sustainability and minimise carbon emissions. |
| Germany | Germany is aligned with EU REACH regulation and requires CE Marking on rubber products employed in construction and automotive industries. Germany's WEEE Directive also applies to rubber products employed in electronic equipment. There is great emphasis on carbon neutrality, and there are regulations requiring companies to disclose emissions. Moreover, German regulation also enforces high levels of sustainability in the materials used, particularly in manufacturing industries such as automotive and industrial machinery. |
| Italy | Italy is compliant with REACH, CE Marking, and other EU legislation. ASSORETIPI, which represents the Italian Rubber and Plastics Industry, oversees national specifications for rubber items. Italy has placed increasing efforts in the field of circular economy, with an emphasis placed on recycling and waste. There is increasing regulation in the rubber industry toward lowering environmental influence and ensuring the encouragement of sustainability within product manufacture. |
| South Korea | South Korea follows REACH regulations for chemical substances and requires KCS (Korean Certification System) for rubber products in certain industries. Environmental policies, including recycling and waste reduction standards, are increasingly stringent. The country is promoting eco-friendly materials in manufacturing, and companies are expected to comply with green building certifications for products used in construction. |
| Japan | Japan has JIS (Japanese Industrial Standards) for rubber products, which companies must meet for industrial applications. Environmental regulations are stringent, particularly for chemical substances under the Pollution Control Act. Japan is increasingly focusing on sustainability, mandating eco-labelling for products. Companies also face recycling obligations and are encouraged to comply with standards set by the Japan Rubber Manufacturers Association (JRMA). |
| China | China’s National Standards (GB) regulate industrial rubber products, with a focus on product quality and environmental safety. The country is also increasing regulatory pressure regarding sustainability and emission reduction. Certification under CCC (China Compulsory Certification) is mandatory for certain rubber products in sectors such as automotive and electronics. Companies must adhere to China’s Green Product Certification standards to meet growing demands for eco-friendly materials. |
| Australia-NZ | In Australia, rubber products must comply with AS (Australian Standards) for industrial applications. The National Industrial Chemicals Notification and Assessment Scheme (NICNAS) regulates chemical substances used in rubber production. Companies are subject to waste management regulations, and there are growing expectations for eco-friendly products under Australia’s National Waste Policy. In New Zealand, the Environmental Protection Authority (EPA) enforces strict emissions standards for manufacturers. |
| India | India follows BIS (Bureau of Indian Standards) for rubber product certification. Environmental policies, including EPR and waste disposal regulations, are being strengthened, especially in the rubber recycling sector. Manufacturers must comply with BIS 3400, which includes specific guidelines for rubber used in automotive and industrial products. India is moving towards promoting sustainable manufacturing practices, with policies incentivising green technology adoption and recycling. |
The USA industry for industrial rubber plastics is among the biggest and most profitable for industrial rubber products, with high demand coming from the automotive, construction, and manufacturing industries.
ssThe nation is also concentrating on making the rubber production process more sustainable, encouraging the use of environmentally friendly materials. With strict regulations like EPA standards and OSHA guidelines, businesses are investing in automation and enhancing environmental performance. The USA will likely dominate high-tech rubber innovations and product diversification.
FMI opines that theUS industrial rubber products sales is poised to grow at a CAGR of 6.6% from 2025 to 2035.
The UK industrial rubber products industry is increasing steadily, led by the automotive and construction sectors, which are major consumers of rubber products. The UK has strict regulatory systems, such as REACH and CE Marking, to maintain environmental compliance and product safety.
The nation's focus on sustainability and carbon footprint reduction in production processes is compelling firms to use more environmentally friendly materials. There is also an increasing demand for products that are green building-compliant.
FMI opines that the United Kingdom industrial rubber products sales are projected to grow at a CAGR of 5.3% during the period of 2025 to 2035.
The industrial rubber industry in France is dominated by the automotive, manufacturing, and construction industries. The French manufacturers are emphasising recyclability and sustainable raw materials as part of the EU's drive towards environmentally friendly products. France also adheres to strict EU laws like REACH and CE Marking, guaranteeing that industrial rubber items meet superior environmental standards.
The environmental policy of the country is pushing the intake of emerging technologies to minimise the environmental footprint of rubber products across different industries.
FMI opines that France's industrial rubber products salesare predicted to grow at a CAGR of 5.8% during the period of 2025 to 2035.
The rubber industry in Germany is strong due to the presence of the world's leading automobile and manufacturing sectors. The nation's stringent green regulations and sustainable focus are principal drivers.
Germany's green production focus is inducing the adoption of renewable and recyclable materials as inputs in the rubber industry. With its strong rates of take-up of sophisticated automation technologies, the German industry will continue to be in the vanguard of industrial rubber product innovation, notably in the use of environmentally friendly materials and processing methods.
FMI opines that the industrial rubber products salesin Germany are predicted to grow at a CAGR of 6.0% during the period 2025 to 2035.
The Italian industry is driven by the automotive, machinery, and construction industries, and there is an increasing need for high-performance rubber products. Italian support for sustainable manufacturing is evident in the use of carbon-neutral production technologies and green certification schemes.
The nation follows EU regulations such as REACH and CE Marking, with particular emphasis on environmental compliance and waste reduction. Italy's emphasis on recyclable materials is helping to drive the rubber products industry.
FMI opines that Italy’s industrial rubber products salesare projected to grow at a CAGR of 5.1% from 2025 to 2035.
South Korea's industrial rubber industry is driven by demand from the automotive and electronics industries, keeping in mind sustainable materials and environment-friendly technology. The nation is making great strides in automated manufacturing procedures and recycling technologies.
South Korea also adheres to REACH regulations and maintains strict material safety standards. While there is a growing demand for high-end rubber technologies like robotics and smart materials, there is also a move towards affordable solutions for small businesses.
FMI opines that South Korea's industrial rubber products salesare likely to grow at a CAGR of 5.4% from 2025 to 2035.
The industrial rubber industry in Japan is dominated by the automotive and electronics sectors, with increasing demand for high-technology rubber products. The nation has strict regulations regarding material safety and emissions through bodies such as the Pollution Control Act.
Japan is investing in recyclable materials and sustainability programs as part of its drive for green manufacturing. In addition to the emphasis on cutting-edge technology, there remains a strong preference for cost-efficient and dependable solutions in some segments of the industry.
FMI opines that Japan's industrial rubber products sales are projected to grow at a CAGR of 5.2% during the period of 2025 to 2035.
China is still the largest production centre for industrial rubber products, driven by the automotive, construction, and electronics sectors. The nation is emphasising green certifications and sustainable manufacturing to be on par with international standards.
There are requirements for compliance with CCC (China Compulsory Certification) for product safety, and companies are under increasing pressure to switch to eco-materials. Regulations on chemicals and waste control are also getting tighter from the Chinese government, driving companies in the direction of greener material.
FMI opines that industrial rubber product sales in China are projected to grow at a CAGR of 6.3% from 2025 to 2035.
Australia and New Zealand are witnessing constant growth in the construction and automotive industries, mainly due to growing demands for eco-friendly products. Both nations follow Australian Standards (AS) and New Zealand Standards (NZS) for industrial rubber products, which require adherence to safety and environmental standards.
Australia is also emphasising green technology and environmentally friendly manufacturing processes, with recycling efforts gaining momentum in both industries. Firms are investing in automation and sustainability as differentiators.
FMI opines that New Zealand and Australia’s industrial rubber product salesare forecasted to grow at a CAGR of 5.5% from 2025 to 2035.
The Growth of the industrial rubber industry of India is catalysed by expansion in the automotive, manufacturing, and construction industries. Local manufacturing and affordable solutions are a focus area in India as part of its Make in India mission. Indian businesses are required to follow BIS (Bureau of Indian Standards) guidelines, which mandate the manufacturing and quality of rubber products.
There is also an increasing emphasis on recycling and environment-friendly materials by environmental policies. India is embracing global standards like REACH in order to improve product safety and sustainability.
The FMI opines that the industrial rubber products sales in India are anticipated to grow at a CAGR of 6.2% during the period of 2025 to 2035.
The industrial rubber products market is undergoing structural shifts driven by changes in raw material sourcing and end-user demand across automotive, construction, and energy sectors. Key players are consolidating operations to improve manufacturing efficiency and reduce overhead costs. Investment in automation and digital monitoring is increasing to meet volume and quality requirements.
Companies are forming joint ventures and partnerships to secure regional market access and reduce lead times. Fluctuating prices of synthetic and natural rubber are influencing procurement strategies and contract structures. Mid-sized firms are focusing on specialized applications to maintain competitiveness against large multinationals. Regulatory requirements related to emissions and safety standards are shaping product development and pushing manufacturers toward material innovations and recyclability initiatives.
Mechanical Rubber Goods, Rubber Hose & Belting, Others.
Natural, Styrene Butadiene, Polybutadiene, Ethylene-Propylene, Nitrile Butadiene, Others.
Automotive, Construction & Infrastructure, Energy, Aerospace, and Others.
North America, Latin America, Europe, East Asia, South Asia, Oceania, the Middle East, and Africa.
The demand is fueled by the growing automotive and construction industries, advancements in aerospace technology, and the expanding energy sector, all of which rely heavily on durable and high-performance rubber components.
The sector is poised for steady growth, with increasing demand for high-quality products across various end-use industries like automotive, aerospace, and construction, driven by innovation in material technologies and global infrastructure development.
Top players include Bridgestone Corporation, Michelin Group, Goodyear Tire & Rubber Company, Continental AG, and Hankook Tire & Technology Co., Ltd., among others, who dominate the supply of rubber products globally.
The automotive segment is projected to experience the highest growth, driven by the increasing production of electric vehicles and the demand for advanced rubber components in automotive systems.
The demand is expected to continue expanding significantly, reaching new heights as industries across automotive, aerospace, construction, and energy continue to rely on these essential components, with a projected value of USD 243.8 billion by 2035.






Full Research Suite comprises of:
Market outlook & trends analysis
Interviews & case studies
Strategic recommendations
Vendor profiles & capabilities analysis
5-year forecasts
8 regions and 60+ country-level data splits
Market segment data splits
12 months of continuous data updates
DELIVERED AS:
PDF EXCEL ONLINE
Industrial Precision Oven Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Industrial Water Chiller for PCB Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Industrial & Commercial HVLS Fans Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Industrial Robot Controller Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Industrial Wired Routers Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Industrial Evaporative Condensers Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Industrial Energy Management System Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Industrial Insulation Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Industrial Safety Gloves Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Industrial Cleaner Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Industrial Dust Treatment System Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Industrial Vertical Washing Tower Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Industrial Pepper Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Industrial Electronics Packaging Market Forecast and Outlook 2025 to 2035
Industrial Absorbent Market Forecast and Outlook 2025 to 2035
Industrial Furnace Industry Analysis in Europe Forecast and Outlook 2025 to 2035
Industrial Denox System Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Industrial Electronic Pressure Switch Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Industrial WiFi Module Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Industrial Security System Market Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035

Thank you!
You will receive an email from our Business Development Manager. Please be sure to check your SPAM/JUNK folder too.
Chat With
MaRIA