The Offshore Wind Turbine Market is estimated to be valued at USD 16.6 billion in 2025 and is projected to reach USD 61.7 billion by 2035, registering a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 14.0% over the forecast period. The Growth Contribution Index highlights a heavily back-weighted expansion pattern across the forecast period. From 2025 to 2030, the market advances from USD 16.6 billion to USD 28.1 billion, contributing USD 11.5 billion, which accounts for only 25.5% of the total growth, despite steady installations driven by early adoption in Europe and emerging projects in Asia-Pacific.
Annual values during this phase include USD 19.0 billion in 2026, USD 21.6 billion in 2027, USD 24.7 billion in 2028, and USD 28.1 billion in 2030, showing progressive acceleration. The second half (2030–2035) dominates growth, adding USD 33.6 billion, or 74.5% of cumulative gains, as the market climbs through USD 32.0 billion in 2031, USD 36.5 billion in 2032, USD 41.6 billion in 2033, USD 47.5 billion in 2034, and USD 61.7 billion by 2035. This surge is linked to large-scale offshore wind farm developments, floating turbine deployments, and grid integration projects across North America, China, and Europe. Manufacturers investing in high-capacity turbines, digital monitoring, and supply chain localization will capture maximum value during this accelerating growth phase.
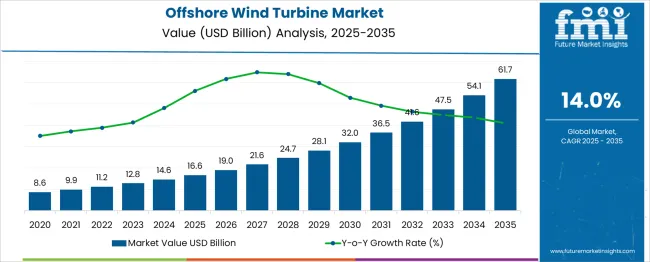
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Offshore Wind Turbine Market Estimated Value in (2025 E) | USD 16.6 billion |
| Offshore Wind Turbine Market Forecast Value in (2035 F) | USD 61.7 billion |
| Forecast CAGR (2025 to 2035) | 14.0% |
The offshore wind turbine market holds a crucial role across several renewable energy and infrastructure segments. In the marine renewable energy market, offshore wind turbines represent 65–70%, as they dominate compared to tidal and wave energy technologies. Within the wind power generation equipment market, their share stands at 18–20%, since onshore wind still accounts for the majority of installations globally. For the offshore infrastructure and electrical systems market, offshore turbines contribute 25–28%, given the inclusion of substations, cables, and foundations in overall project costs.
In the green hydrogen and power-to-X production market, the share is relatively small at 5–6%, as most hydrogen production remains pilot-scale, though offshore wind is emerging as a preferred renewable source for electrolysis. In the grid interconnection and transmission systems market, offshore wind accounts for 8–10%, reflecting its growing influence on HVDC links and substation upgrades.
Demand is being propelled by increasing global investments in renewable energy targets, expansion of floating turbine technology, and regulatory mandates for decarbonization in Europe, Asia Pacific, and North America. Rising turbine capacities beyond 15 MW, integration with hybrid power hubs, and digital monitoring for predictive maintenance are driving cost efficiencies, making offshore wind turbines a cornerstone of future clean energy systems worldwide.
The offshore wind turbine market is advancing rapidly, fueled by the transition toward renewable energy, increasing investments in clean power infrastructure, and favorable government policies. Rising energy demand and the urgent need to decarbonize electricity generation have positioned offshore wind as a key pillar of global energy strategies.
Advancements in turbine technology, cost reductions through economies of scale, and improved supply chain capabilities are further driving adoption. Regulatory support in the form of subsidies, auctions, and long-term power purchase agreements is enabling developers to commit to larger and more complex projects.
Future growth is expected to be shaped by innovations in floating foundations, digital monitoring systems, and larger turbine ratings that enhance efficiency and reduce levelized costs. Strategic collaborations between developers, utilities, and equipment manufacturers are paving the way for broader deployment and higher capacity factors across emerging markets.
The offshore wind turbine market is segmented by rating, installation, and geographic regions. The offshore wind turbine market is rated into > 8 to ≤ 10 MW, ≤ 2 MW, > 2 to ≤ 5 MW, > 5 to ≤ 8 MW, > 10 to ≤ 12 MW, and > 12 MW. In terms of installation, the offshore wind turbine market is classified into Fixed and Floating. Regionally, the offshore wind turbine industry is classified into North America, Latin America, Western Europe, Eastern Europe, Balkan & Baltic Countries, Russia & Belarus, Central Asia, East Asia, South Asia & Pacific, and the Middle East & Africa.
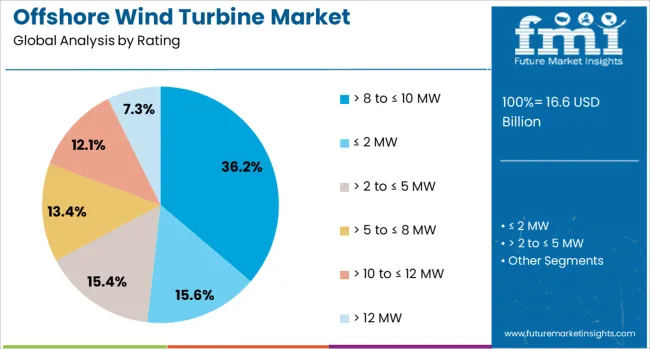
When segmented by rating, the 8 to ≤ 10 MW segment is projected to command 36.20% of the total market revenue in 2025, making it the leading rating category. This leadership has been supported by the balance this segment offers between power output, reliability, and cost effectiveness.
Turbines within this range have been widely adopted as they align with the current capabilities of offshore infrastructure and installation vessels, enabling efficient deployment without requiring extensive upgrades to existing grids or foundations. Their proven performance in diverse marine environments has increased developer confidence, while maintenance and operational costs remain manageable compared to higher-rated turbines.
The segment’s maturity and availability in the global supply chain have also contributed to its prominence, as manufacturers optimize production lines and deliver competitive solutions at scale. This combination of technical feasibility, cost control, and dependable output has solidified the 8 to ≤ 10 MW segment’s leadership in the offshore wind turbine market.
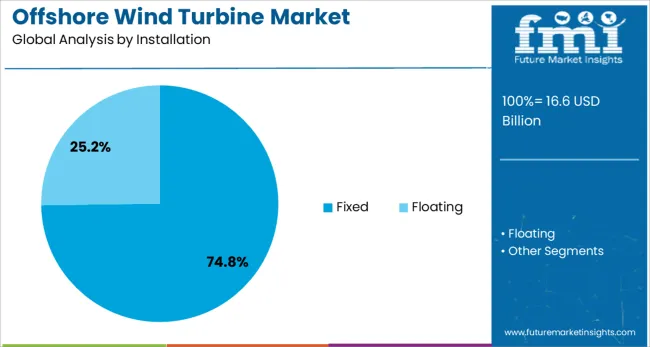
When segmented by installation, the fixed segment is forecast to hold 74.8% of the market revenue in 2025, maintaining its dominant position. This prominence has been driven by the widespread suitability of fixed-bottom technology in shallow and mid-depth waters, which represent the majority of currently exploitable offshore sites.
The well-established engineering practices, lower capital expenditure, and operational predictability of fixed installations have strengthened their appeal among developers and investors. Technological advancements in monopile and jacket foundation designs have further improved efficiency and reduced installation timelines, reinforcing this segment’s competitiveness.
The robust track record of fixed installations in delivering reliable and cost-effective energy has made it the preferred choice for near-shore projects, where water depths and seabed conditions are conducive. The scalability of fixed solutions and the ability to leverage existing port and vessel infrastructure have ensured their continued dominance as the offshore wind industry expands globally.
Offshore wind turbines are large energy generation systems installed in marine environments to harness wind power. These turbines are deployed on fixed foundations in shallow waters and increasingly on floating platforms in deep-water zones. They are applied in coastal regions to support electricity generation at scale. Demand is influenced by the need for reliable renewable energy, supportive policy frameworks, and advancements in turbine engineering. Manufacturers providing robust designs, enhanced efficiency, and simplified maintenance processes are positioned to meet the rising requirements of operators seeking cost-effective and long-lasting offshore installations.
Adoption of offshore wind turbines has been supported by favorable regulatory frameworks and government-backed initiatives that encourage renewable energy integration. Increasing electricity demand in coastal and urban regions has led to higher investments in offshore wind projects. Advancements in turbine design, combined with optimized installation techniques, have improved energy output and operational stability. Expansion of transmission infrastructure and enhanced grid integration have supported large-scale deployments. Developers have focused on efficient foundations and rotor designs to maximize energy capture in variable wind conditions. Growing emphasis on diversifying energy portfolios has further reinforced the deployment of offshore wind solutions across multiple regions.
Expansion in offshore wind turbine installations has been constrained by high capital requirements associated with manufacturing, installation, and maintenance. The need for specialized vessels, heavy-lift equipment, and advanced foundations has increased project complexity. Logistics challenges in transporting oversized components to remote offshore locations have added operational constraints. Harsh marine conditions, including saltwater corrosion and strong currents, have increased design and maintenance demands. Extended lead times for project approvals, combined with regulatory compliance requirements, have slowed execution timelines. Variability in seabed conditions and the requirement for bespoke engineering solutions have further increased overall costs and technical risks for developers.
Opportunities are being created through the adoption of floating wind platforms, which enable deployment in deeper waters where wind resources are stronger and more consistent. Development of modular turbines and prefabricated components is improving installation flexibility. Integration of advanced digital tools for remote condition monitoring and predictive maintenance offers potential to enhance operational efficiency and reduce lifecycle costs. Strategic partnerships between technology providers, energy companies, and maritime contractors are facilitating large-scale deployments. Demand for supply chain localization and investments in port upgrades present additional areas for growth. Offshore wind farms supporting hybrid energy solutions such as storage integration also represent emerging opportunities for innovation.
The trend toward larger-capacity turbines with extended rotor diameters is accelerating to achieve higher power output per unit and reduce project-level costs. Digital control systems equipped with real-time performance monitoring and automated fault detection are gaining adoption to improve reliability. Increased use of corrosion-resistant materials and innovative blade designs is enhancing durability in harsh marine environments. Floating platform technology is advancing, enabling installation in deep-sea zones beyond traditional fixed foundation limits. Project developers are emphasizing modular approaches to reduce assembly time and improve scalability. Collaborative initiatives aimed at optimizing offshore construction techniques and operational automation continue to influence the competitive landscape.
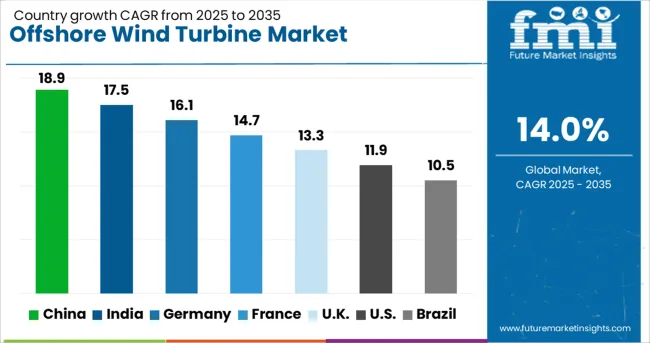
| Country | CAGR |
|---|---|
| China | 18.9% |
| India | 17.5% |
| Germany | 16.1% |
| France | 14.7% |
| UK | 13.3% |
| USA | 11.9% |
| Brazil | 10.5% |
The offshore wind turbine market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 14.0% between 2025 and 2035, driven by large-scale renewable energy projects, advanced turbine technology, and rising demand for green power. China leads with 18.9% CAGR, supported by strong investments in large-capacity turbines and deep-water projects. India follows at 17.5%, with rapid deployment in coastal regions and partnerships for floating wind solutions. Among OECD nations, Germany records 16.1%, driven by offshore expansions in the North and Baltic Seas. France posts 14.7%, emphasizing innovation in floating platforms, while the United Kingdom grows at 13.3%, supported by large-scale projects and grid integration strategies. The report covers over 40 countries, with detailed insights for five profiled below.
China is projected to achieve 18.9% CAGR, the highest among major markets, supported by massive investments in offshore wind infrastructure. The government’s focus on clean energy transition is accelerating turbine installations in the East China Sea and coastal regions. Developers are deploying next-generation turbines exceeding 15 MW capacity to maximize energy yield. Strong manufacturing capabilities allow domestic suppliers to deliver advanced nacelles, blades, and floating foundation systems at competitive costs. Export opportunities are expanding across Asia-Pacific as Chinese firms secure EPC contracts for international projects, strengthening global leadership.
India is forecasted to grow at a 17.5% CAGR, driven by government-backed offshore projects along the Gujarat and Tamil Nadu coastlines. International partnerships with European turbine manufacturers are introducing high-capacity turbines suitable for deep-water conditions. Growing power demand in industrial clusters near coastal areas supports commercial viability for large projects. Floating wind solutions are gaining traction as developers explore installations in high-depth zones. Investments in grid integration and undersea cabling infrastructure are improving transmission reliability for offshore power. The presence of domestic fabrication hubs for towers and blades ensures cost efficiency for large projects.
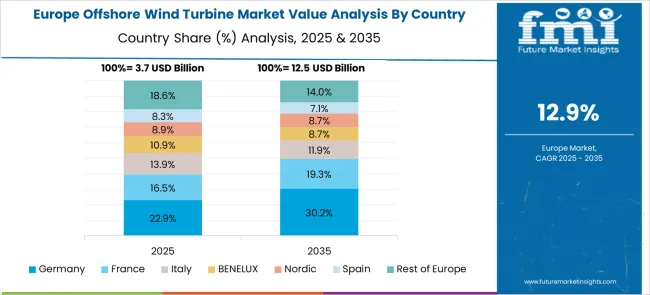
Germany is expected to post a 16.1% CAGR, supported by extensive offshore wind farms in the North Sea and Baltic Sea regions. Developers are installing hybrid foundation systems designed for deeper water installations. The integration of digital monitoring platforms with turbines ensures improved performance and reduced maintenance downtime. Corporate power purchase agreements (PPAs) are stimulating demand for offshore projects dedicated to industrial decarbonization. Domestic manufacturers are introducing recyclable blade technology and high-capacity nacelles for energy-efficient turbines. Investments in port upgrades and specialized installation vessels are accelerating offshore deployment schedules.
France is projected to grow at a 14.7% CAGR, driven by investments in floating wind technology for deep-sea projects. Pilot farms along the Atlantic coast are paving the way for large-scale commercial projects. French developers are prioritizing modular foundation systems and lightweight turbine designs to optimize installation and maintenance. Partnerships with global offshore engineering firms are accelerating innovation in floating platforms. Government-backed auctions and attractive feed-in tariffs are encouraging private investment in long-term projects. Offshore hydrogen production integrated with wind farms is being explored to support decarbonization goals for energy and industrial sectors.
The United Kingdom is forecasted to grow at 13.3% CAGR, supported by ambitious offshore capacity targets in the North Sea. Large-scale projects like Dogger Bank and Hornsea are deploying turbines with rated capacities exceeding 14 MW. The UK offshore wind sector is benefiting from strong developer participation and competitive auction pricing. Investments in high-voltage direct current (HVDC) transmission links are improving energy delivery from distant offshore sites. Efforts to localize component manufacturing, including blades and foundations, are strengthening the domestic supply chain and reducing project costs.
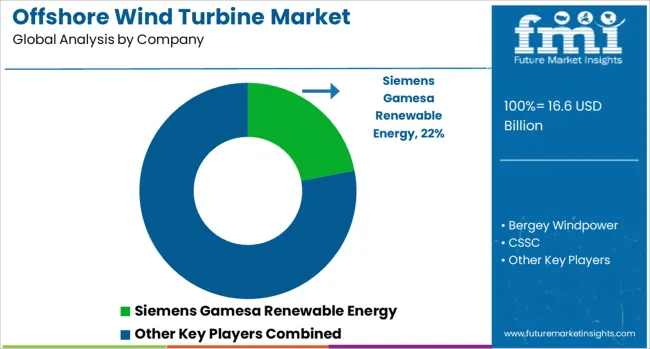
The offshore wind turbine market is dominated by global leaders such as Siemens Gamesa Renewable Energy, General Electric (GE), Vestas, and Goldwind, supported by key regional and niche players including Mingyang Smart Energy Group, NORDEX, Suzlon Energy Limited, Doosan Corporation, ENERCON, and Envision Group. Siemens Gamesa holds a strong leadership position with its advanced direct-drive offshore turbine technology and a significant installed base across Europe and Asia.
GE continues to strengthen its market position with the Haliade-X platform, one of the largest and most powerful offshore wind turbines in the industry, driving efficiency improvements and cost competitiveness. Vestas leverages its expertise in onshore wind to expand offshore capabilities, focusing on modular turbine design and digital optimization. Asian players such as Goldwind, Mingyang, and CSSC are rapidly gaining traction in the Asia-Pacific region through cost-competitive offerings and localized manufacturing strategies. Market rivalry is intense due to the capital-intensive nature of offshore projects, complex regulatory requirements, and the need for long-term service agreements.
Competitive differentiation is driven by turbine capacity scaling (12 MW and above), blade design innovation, predictive maintenance capabilities, and integration of digital twin technology for performance monitoring. Strategic partnerships between turbine OEMs and energy developers such as Ørsted and Vattenfall play a critical role in securing large-scale offshore projects. Future growth will hinge on floating offshore wind technology development, hybrid power systems, and grid integration solutions as nations accelerate renewable energy adoption. High entry barriers persist due to supply chain complexity, installation challenges, and heavy investment in R&D and marine logistics.
| Item | Value |
|---|---|
| Quantitative Units | USD 16.6 Billion |
| Rating | > 8 to ≤ 10 MW, ≤ 2 MW, > 2 to ≤ 5 MW, > 5 to ≤ 8 MW, > 10 to ≤ 12 MW, and > 12 MW |
| Installation | Fixed and Floating |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America, Middle East & Africa |
| Country Covered | United States, Canada, Germany, France, United Kingdom, China, Japan, India, Brazil, South Africa |
| Key Companies Profiled | Siemens Gamesa Renewable Energy, Bergey Windpower, CSSC, Doosan Corporation, ENERCON, ENESSERE, Envision Group, EOLINK, General Electric, Goldwind, Mingyang Smart Energy Group, NORDEX, Orsted, Senvion, Suzlon Energy Limited, Vattenfall, Vestas, and WEG |
| Additional Attributes | Dollar sales by turbine capacity segment (≤5 MW, 6–10 MW, >10 MW) and deployment type (fixed-bottom and floating), with demand driven by global decarbonization policies, offshore project auctions, and utility-scale investments. Regional trends show Europe leading in installed capacity, while Asia-Pacific experiences rapid growth with large-scale developments in China, Japan, and South Korea. Innovation focuses on high-capacity turbines, floating platforms for deepwater projects, and AI-enabled predictive analytics for real-time monitoring and improved energy output efficiency. |
The global offshore wind turbine market is estimated to be valued at USD 16.6 billion in 2025.
The market size for the offshore wind turbine market is projected to reach USD 61.7 billion by 2035.
The offshore wind turbine market is expected to grow at a 14.0% CAGR between 2025 and 2035.
The key product types in offshore wind turbine market are > 8 to ≤ 10 mw, ≤ 2 mw, > 2 to ≤ 5 mw, > 5 to ≤ 8 mw, > 10 to ≤ 12 mw and > 12 mw.
In terms of installation, fixed segment to command 74.8% share in the offshore wind turbine market in 2025.






Our Research Products

The "Full Research Suite" delivers actionable market intel, deep dives on markets or technologies, so clients act faster, cut risk, and unlock growth.

The Leaderboard benchmarks and ranks top vendors, classifying them as Established Leaders, Leading Challengers, or Disruptors & Challengers.

Locates where complements amplify value and substitutes erode it, forecasting net impact by horizon

We deliver granular, decision-grade intel: market sizing, 5-year forecasts, pricing, adoption, usage, revenue, and operational KPIs—plus competitor tracking, regulation, and value chains—across 60 countries broadly.

Spot the shifts before they hit your P&L. We track inflection points, adoption curves, pricing moves, and ecosystem plays to show where demand is heading, why it is changing, and what to do next across high-growth markets and disruptive tech

Real-time reads of user behavior. We track shifting priorities, perceptions of today’s and next-gen services, and provider experience, then pace how fast tech moves from trial to adoption, blending buyer, consumer, and channel inputs with social signals (#WhySwitch, #UX).

Partner with our analyst team to build a custom report designed around your business priorities. From analysing market trends to assessing competitors or crafting bespoke datasets, we tailor insights to your needs.
Supplier Intelligence
Discovery & Profiling
Capacity & Footprint
Performance & Risk
Compliance & Governance
Commercial Readiness
Who Supplies Whom
Scorecards & Shortlists
Playbooks & Docs
Category Intelligence
Definition & Scope
Demand & Use Cases
Cost Drivers
Market Structure
Supply Chain Map
Trade & Policy
Operating Norms
Deliverables
Buyer Intelligence
Account Basics
Spend & Scope
Procurement Model
Vendor Requirements
Terms & Policies
Entry Strategy
Pain Points & Triggers
Outputs
Pricing Analysis
Benchmarks
Trends
Should-Cost
Indexation
Landed Cost
Commercial Terms
Deliverables
Brand Analysis
Positioning & Value Prop
Share & Presence
Customer Evidence
Go-to-Market
Digital & Reputation
Compliance & Trust
KPIs & Gaps
Outputs
Full Research Suite comprises of:
Market outlook & trends analysis
Interviews & case studies
Strategic recommendations
Vendor profiles & capabilities analysis
5-year forecasts
8 regions and 60+ country-level data splits
Market segment data splits
12 months of continuous data updates
DELIVERED AS:
PDF EXCEL ONLINE
Offshore Wind Turbine Bearing Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Offshore Wind Turbine Blade Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Offshore Fibre Optic Cable Lay Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Offshore Platform Electrification Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Offshore Drilling Riser Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Offshore Crane Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Offshore Pipeline Infrastructure Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Offshore Structural Analysis Software Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Offshore ROV Market Growth – Trends & Forecast 2024-2034
Offshore Equipment Market
Offshore Wind Market Forecast and Outlook 2025 to 2035
Offshore Wind Energy Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Offshore Wind Energy Infrastructure Market
Fixed Offshore Wind Energy Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Export Offshore Wind Cable Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Floating Offshore Wind Energy Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Inter Array Offshore Wind Cable Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Wind Energy Consulting Service Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Window Air Conditioner Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Wind Power Coatings Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035

Thank you!
You will receive an email from our Business Development Manager. Please be sure to check your SPAM/JUNK folder too.
Chat With
MaRIA