The phosphate fertilizer market is valued at USD 61.42 billion in 2025 and is forecast to reach USD 101.00 billion by 2035, advancing at a 5.1 % CAGR across the period. Within the phosphate fertilizer market, China remains the most lucrative country in 2025, accounting for about one-third of global demand, while India is poised to be the fastest-growing national market as balanced-nutrient subsidy schemes boost MAP and DAP adoption.
Supply-chain volatility, raw-material price swings, and tightening runoff regulations are reshaping the phosphate fertilizer market. Government food-security drives and precision-farming incentives underpin demand, yet price spikes for phosphate rock and environmental curbs on excessive phosphorus use restrain widespread application.
Key trends include enhanced-efficiency phosphate fertilizers (EEPFs) with controlled-release coatings, water-soluble grades for fertigation, and farmer demand for custom blends informed by real-time soil tests.
Looking ahead, the phosphate fertilizer market will pivot toward regenerative and climate-smart agriculture. Edge-analytics spreaders, variable-rate technology, and blockchain traceability will optimize every kilogram of applied P₂O₅, while circular-economy investments in wastewater-derived phosphates reduce import dependence. Suppliers that integrate low-carbon extraction, slow-release formulations, and “fertilizer-as-a-service” financing models are set to capture outsized share through 2035.
Consolidation across the phosphate-fertilizer value chain is intensifying as miners, chemical processors, and ag-retail networks seek end-to-end control over supply security and farmer relationships. Integrated majors are locking in long-term offtake for low-cadmium rock, investing in on-site sulfuric-acid cogeneration to dampen energy shocks, and partnering with ag-tech startups to embed real-time nutrient-advisory tools into dealer portals. Meanwhile, regional co-operatives and specialty blenders are leveraging toll-granulation and white-label MAP/DAP output to capture niche demand for micronutrient-fortified or organic-certified grades.
This competitive jostling-combined with stricter ESG disclosure rules-will push lagging producers to modernize wet-process assets, cut process-water consumption, and publish cradle-to-gate carbon intensities or risk market share erosion by 2035.
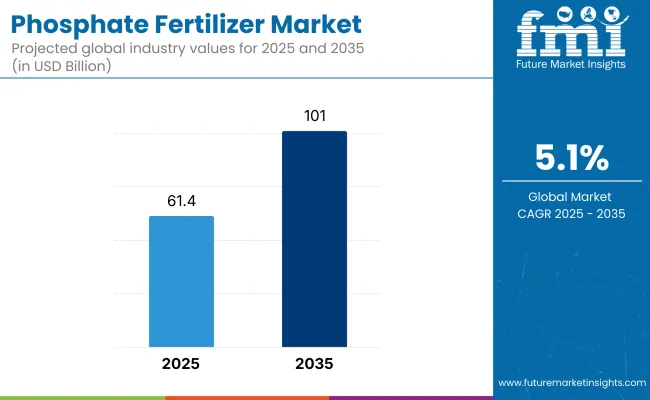
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Industry Size (2025E) | USD 61.42 billion |
| Industry Value (2035F) | USD 101.00 billion |
| CAGR (2025 to 2035) | 5.1% |
MAP’s high phosphorus content and compatibility with cereals, grains, and oilseeds position it for rapid uptake-especially in precision-farming regions shifting toward balanced N-P-K programs. Controlled-release MAP and MAP-sulfur blends further lift its appeal versus legacy SSP or TSP grades. Conversely, DAP retains volume dominance in subsidy-driven Asian markets, while SSP serves cost-sensitive growers in Africa and India.
| Product Type | CAGR (2025 to 2035) |
|---|---|
| Monoammonium Phosphate (MAP) | 6.3% |
Expansion of soy, canola, and sunflower acreage for biofuels and vegetable oils-particularly in Brazil, Argentina, and Canada-drives above-average phosphate demand. Cereals & grains remain the largest application block, but their growth is steadier as yield gains plateau. Fruits & vegetables leverage specialty water-soluble phosphates in hydroponics, while pulses and forage crops post moderate growth under tailored blends.
| Application | CAGR (2025 to 2035) |
|---|---|
| Oilseeds | 5.8% |
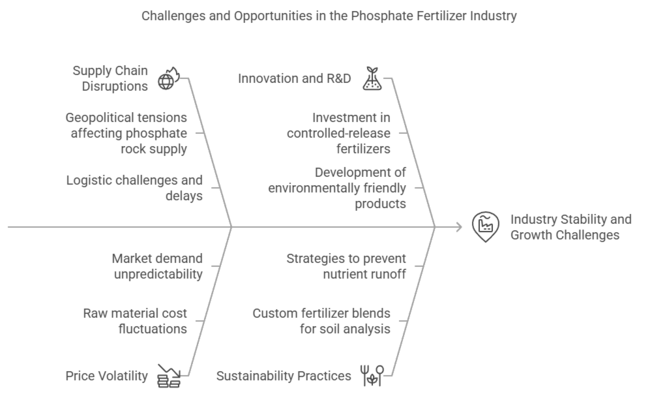
Future Market Insights (FMI) has analyzed the phosphate fertilizer industry for the period 2015 to 2025 and provided key industry insight from stakeholders, including manufacturers, distributors, agronomists, and large farmers. Over 70 percent of people surveyed expected demand to grow further as issues of global food security widened and high-yield per hectare agricultural methods were adopted.
Among the trends established above, one of the most important findings was the growing use of efficient phosphate fertilizers (EEPFs). Approximately 60% of fertilizer manufacturers continue to invest in R&D for controlled-release and environmentally friendly products to prevent nutrient runoff and enhance soil quality. Distributors saw farmers' buying habits changing, too, with more requests for custom fertilizer blends based on real-time soil analysis.
However, the main worries are supply chain disruption and price volatility for raw materials. Most prominently, almost two-thirds of the stakeholders identified risks related to the supply of phosphate rock.
Tensions arise from the production and export of phosphate rock, particularly in regions of North Africa and the Middle East, where geopolitical disputes pose a significant risk to producers. Both sources also emphasized the need for diversified supply chains and increased investment in sustainable phosphate extraction and production methods to ensure long-term industry stability.
The survey reflected a generally cautiously optimistic outlook for the phosphate fertilizer industry. Demand will continue to grow, but all stakeholders agree that the standard bearers of industry performance in the coming decade will be where innovation, sustainability, and policy facilitation come together.
| Countries | Key Regulations & Policies |
|---|---|
| The United States | In addition, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) regulates phosphate runoff under the Clean Water Act. The USDA encourages the sound use of fertilizer through subsidy programs, such as EQIP. |
| United Kingdom | Phosphate is regulated in the UK under the Fertilizer Regulations 1991 and the Farming Rules for Water (2018) to help mitigate environmental impacts and promote balanced nutrient management. |
| France | The Eau et Agriculture Law requires reducing phosphorus use in farming next to waterways. In France, there are also incentives for organic and low-phosphate fertilizers. |
| Germany | The Fertilizer Ordinance (DüV), comparable to the EU Nitrates Directive, restricts phosphate application per soil analysis. |
| Italy | The government encourages precision agriculture practices to maximize fertilizer applications. European Union environmental regulations also impose limits on phosphate applications. |
| South Korea | The Act on the Control of Agricultural and Fisheries Pollution limits the excessive use of phosphates, supports the use of environmentally friendly fertilizers, and provides sustainable farming incentives. |
| Japan | Some laws also relate to fertilizers, like the Soil Fertilizer Law, which governs labeling as well as phosphate fertilizer quality. Japan also advocates smart farming practices that maximize fertilizer efficiency. |
| China | China's "Zero Growth Policy for Fertilizers" aims to limit the use of chemical fertilizers by promoting more sustainable and efficient agricultural practices. |
| Australia & NZ | National Environment Protection Measures (NEPM) control phosphate access to sensitive water areas. New Zealand Freshwater Reforms restrict phosphorus runoff in dairy. |
| India | The policy acts as an incentive to use a balanced fertilizer. In addition, the government supports domestic production to alleviate imports dependency on excess phosphate. |
| 2020 to 2024 | 2025 to 2035 |
|---|---|
| COVID-19-led disruptions, supply chain disruptions, and volatile raw material prices created volatility for the stock industry. | Expected to stabilize as supply chain resilience improves alongside strategic phosphate mining expansion. |
| Increased Demand by Global Concerns on Food Security and Growing Adoption by Precision Farming Techniques. | Demand will continue to grow due to population growth and government-backed sustainable agriculture initiatives. |
| Geopolitical dynamics also affected phosphate supply, especially from North Africa and China. | Diversified sourcing and investments in alternative phosphate extraction methods aim to reduce supply risks. |
| The industry is shifting towards green fertilizers and controlled-release formulations. | Cutting-edge technologies in enhanced phosphorus fertilizers, precision agriculture, and regenerative agriculture. |
| Governments stepped up regulations to limit phosphate runoff and overuse. | There should be more stringent regulation of sustainable fertilizer application methods, with support for organic and slow-release phosphate fertilizers. |
Over two-thirds of the domestic USA phosphate fertilizer industry is underpinned by large-scale commercial farming, particularly corn, soybeans, and wheat. The country is dependent on domestic phosphate, which is also imported from Morocco and China. Phosphate runoff is being pushed over by increasingly strict environmental regulations, contributing to greater use of enhanced efficiency fertilizers (EEFs).
The industry segment growth is created by precision agriculture and sustainable farming initiatives. Demand for rock phosphate-based fertilizers is also being driven by increased organic and regenerative farming practices. With the USA government advocating for climate-smart agriculture, phosphate use will likely be increasingly regulated, and e fficient application methods such as variable rate technology (VRT) will be encouraged.
Climate regulations and sustainable agriculture policies guide the phosphate fertilizers industry in the UK. And with domestic phosphate production dipping, the country relies on imports from North Africa and Russia. Precision farming and policies to apply less phosphates are responsible for the growing use of slow-release fertilizers and water-soluble phosphates.
The organic farming industry is expanding, resulting in demand for natural sources of phosphate, such as rock phosphate and bio-based fertilizers. Post-Brexit agricultural policies have further pushed for self-sufficiency in food production that will continue to underpin steady demand for phosphate fertilizer in the cultivation of wheat, barley, and oilseed rape.
As one of Europe's most productive agricultural nations, the French phosphate fertilizer industry is well-established and dominated by wheat, maize, and grapeseed cultivation. The government's regulation of phosphate applications to combat eutrophication makes low-runoff fertilizers desirable.
Increased interest in sustainable agriculture, coupled with EU Green Deal policies, is promoting the use of bio-based phosphate fertilizers and precise nutrient management. Interest in the circular economy is also growing as France pursues phosphate recycling technologies. TSP and MAP continue to be widely used for high-value crop production and vineyard applications.
Stringent European Union environmental laws and sophisticated agricultural practices constrain Germany's phosphate fertilizer industry. There is a growing movement among farmers to embrace phosphate efficiency programs that link soil testing with precision application and fertigation technologies. The country is investing in recovering phosphate from wastewater, thereby decreasing the need to import phosphate rock.
The growth of organic farming is also fuelled by demand for natural phosphate sources. Key crops such as wheat, barley, and sugar beets drive phosphate consumption. Germany is aligning with sustainability targets, including the EU Farm to Fork Strategy, which advocates for the use of enhanced-efficiency phosphate fertilizers to reduce environmental impact and improve nutrient management.
In South Korea, intensive vegetable farming, rice cultivation, and greenhouse agriculture drive the phosphate fertilizer industry. The country largely relies on imports from Morocco and China due to its scarcity of domestic phosphate. The government has recently not officially called for the use of precision farming and controlled-release fertilizers to increase nutrient use phase capacity.
The rising demand for hydroponics & vertical farming is spurring the use of water-soluble phosphates. To mitigate reliance on imports, South Korea is working on phosphate recycling projects. Anticipated sustainable agriculture policies are likely to spur phosphate-efficient fertilizers and cropping systems in the years ahead.
China is the world’s biggest producer and consumer of phosphate fertilizers, with a global industry share of 33% in 2024, which is mainly needed in rice, wheat, and maize farming. Restrictions on phosphate use have been implemented by the government to prevent soil degradation and to avoid polluting the water.
There is a growing trend in the industry towards phosphate-efficient fertilizers, tailored blends, and coated DAP formulations. China is another player looking to cater to global demand, particularly in India, Southeast Asia, and Africa, which are largely phosphate fertilizers. Research on phosphate recycling and precision agriculture is gaining momentum, paving the way for sustained growth at a reduced environmental cost.
Phosphate fertilizers are consumed in massive amounts in the wheat, barley, and pasture cropping industries here in Australia and New Zealand. In Australia, SSP is also in demand, especially for legume and pasture crops, with DAP and MAP predominating in cereal production. Dairy farming and sustainable land management drive New Zealand’s phosphate industry.
Both countries are currently implementing programs that enhance precision agriculture and phosphorus efficiency, allowing for more efficient fertilizer usage. Phosphate rock imports from North Africa are crucial, but interest in alternative and organic sources of phosphate is growing.
Phosphate fertilizers are among the biggest consumers in India, driven by the demand for rice, wheat, pulses, and oilseeds. So, DAP and SSP are given by the government at a subsidized price to small and medium-scale farmers. India is a key industry for imports of phosphate rock from two major suppliers-China and Morocco.
The phenomenon has raised soil degradation concerns and promoted balanced fertilizer application strategies. In high-value crops, the adoption of personalized phosphate blends and water-soluble fertilizers is increasing. The phosphate fertilizer industry in India is projected to grow further as consumption of food increases, and agriculture intensifies, while efficient and sustainable use of fertilizers is also being prioritized.
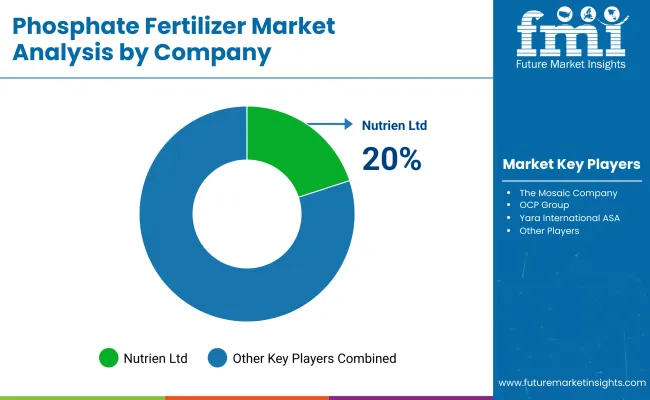
The global phosphate fertilizers industry size was estimated at USD 68.3 billion in 2021 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate of 5.8% during the forecast period. Here’s a breakdown of the top players-and their projected industry shares-by 2024
Nutrien Ltd.
Industry Share: ~20%
Nutrien is one of the largest international providers of crop inputs and services. It produces phosphate fertilizers. It is a leader in North America, South America, and other important agricultural regions.
The Mosaic Company
Industry Share: ~18%
Mosaic is a producer of concentrated phosphate and potash fertilizers. The company has sizable operations across both North and South America, as well as Asia.
OCP Group
Industry Share: ~15%
OCP Group is a Moroccan state-owned company and among the largest producers of phosphate and phosphate-based fertilizers in the world. The company has a notable footprint across Africa, Europe, and Asia.
Yara International ASA
Industry Share: ~12%
Yara is a Norwegian chemical company that produces nitrogen- and phosphate-based fertilizers. It operates primarily in Europe, Africa, and the Americas.
EuroChem Group
Industry Share: ~10%
EuroChem is a Swiss-based chemical company that is one of the world's leading producers of nitrogen, phosphate, and potash fertilizers. The firm is well-established in Europe and Asia.
Other Players
Industry Share: ~25%
When it comes to the remaining segment of the industry, it is shared by smaller regional players as well as emerging entrants, many of whom target niche industries or specialized fertilizer products.
Expansion of Production Capacity Nutrien
Nutrien expands USA phosphate production capacity. This position is in line with the growing trend of high-efficiency fertilizers in the global industry and strengthens Nutrien's leadership status.
Mosaic's Partnership Deal in Brazil
Mosaic also partnered with Brazilian agricultural cooperatives to expand the distribution network in South America. With this collaboration, the company will be able to augment its reach in the area.
The Increasing Role of Customized Fertilizers: OCP Group
OCP Group introduces a range of customized phosphate fertilizers adapted to the specificities of crops and soils. This will , in turn, increase crop yields and soil health.
Yara's Acquisition in Europe
Yara, a global producer of crop nutrition and one of the largest producers of nitrogen-based fertilizers, announced that it had bought another small producer in Europe. Part of Yara's product range would come under this acquisition, likely cementing its industry position further.
Expansion of EuroChem production capacity in Russia
EuroChem increased its output of phosphate fertilizers in Russia to meet growing demand in Eastern Europe and Asia. This expansion will bolster EuroChem's capabilities and extend its industry reach.
Global food demand has a significant impact on the phosphate fertilizer industry, as it is essential for improving soil fertility and crop production. A growing world population (9.7 billion by 2050) and the need for sustainable agricultural productivity ensure that phosphate-based fertilizer demand remains high in the long run.
Fertilizer consumption is rising in many developing economies, mainly in Asia-Pacific, Latin America, and Africa, as they strive to boost food production. Commodity prices such as natural gas and phosphate rock are important factors affecting production costs and price increases in key areas.
General geopolitical tensions, particularly in China, Morocco, and Russia, impact global phosphate supply chains. Supply deficiencies and price fluctuations are consequences of trade barriers and export quotas in these regions.
Environmental issues are also shaking up the industry, as governments around the world-in response to climate change and sustainability policies-are imposing limits on phosphate runoff water pollution. This shift is propelling the even wider use of enhanced-efficiency fertilizers and phosphate recycling tech.
Currency exchange rates, inflation, and global trade agreements influence the industry, as phosphate fertilizers are highly sought-after commodities. Over the long term, precision farming technologies, organic fertilizers, and phosphate alternatives will take center stage in determining the course of the industry.
There are various opportunities in the phosphate fertilizer industry due to several factors, like global demand for food, the sustainable agriculture trend, technological advancements, and others. Areas for expansion include:
Agricultural practices are evolving to tackle global challenges, such as nutrient runoff, by optimizing fertilizer use and improving soil health. Data-driven farming also includes developing other solutions, such as AI and IoT-based soil monitoring, to improve phosphorus management.
Sustainable and organic fertilizers The growing transition to a more sustainable and organic production network has created a demand for rock phosphate, bio-based phosphates, and phosphate recycling solutions. The phosphate industry will benefit from low-impact extraction and manufacturing methods.
The rapid agricultural expansion in Africa, Latin America, and Southeast Asia can provide considerable growth opportunities. Local partnerships will help to secure industry share in these regions. Phosphate recycling from wastewater and industrial products can also provide insights for sustainable long-term investments.
The industry is segmented into mono ammonium phosphate (MAP), diammonium phosphate (DAP), single superphosphate (SSP), triple superphosphate (TSP), and others.
It is segmented into cereals and grains, oilseeds, pulses and legumes, fruits and vegetables, and others.
It is fragmented into North America, Latin America, Western Europe, Eastern Europe, Central Asia, Russia and Belarus, Balkan and Baltic, South Asia Pacific, East Asia, Middle East, and Africa.
Soil nutrient depletion and population growth are increasing food production needs.
The consumption of phosphate fertilizers is prominent across Asia-Pacific, North America, and Europe.
Tightened regulations curtail overuse, encouraging sustainable and targeted approaches.
The industry is shifting toward ethical sourcing, phosphate recycling, and innovative nutrient delivery methods.
OCP Group, The Mosaic Company, Nutrien Ltd., Yara International, CF Industries Holdings, Inc., PhosAgro, ICL Group Ltd., Incitec Pivot Limited, EuroChem Group, and Saudi Arabian Mining Company (Ma'aden).
Table 01: Global Market Size (US$ Million) and Volume (Tons) Analysis and Forecast by Product Type, 2018 to 2033
Table 02: Global Market Size (US$ Million) and Volume (Tons) Analysis and Forecast by Application, 2018 to 2033
Table 03: Global Market Size Volume (Tons) Analysis and Forecast by Region, 2018 to 2033
Table 04: Global Market Size (US$ Million) Analysis and Forecast by Region, 2018 to 2033
Table 05: North America Market Size (US$ Million) and Volume (Tons) Analysis and Forecast by Country, 2018 to 2033
Table 06: North America Market Size (US$ Million) and Volume (Tons) Analysis and Forecast by Product Type, 2018 to 2033
Table 07: North America Market Size (US$ Million) and Volume (Tons) Analysis and Forecast by Application, 2018 to 2033
Table 08: Latin America Market Size (US$ Million) and Volume (Tons) Analysis and Forecast by Country, 2018 to 2033
Table 09: Latin America Market Size (US$ Million) and Volume (Tons) Analysis and Forecast by Product Type, 2018 to 2033
Table 10: Latin America Market Size (US$ Million) and Volume (Tons) Analysis and Forecast by Application, 2018 to 2033
Table 11: Western Europe Market Size (US$ Million) and Volume (Tons) Analysis and Forecast by Country, 2018 to 2033
Table 12: Western Europe Market Size (US$ Million) and Volume (Tons) Analysis and Forecast by Product Type, 2018 to 2033
Table 13: Western Europe Market Size (US$ Million) and Volume (Tons) Analysis and Forecast by Application, 2018 to 2033
Table 14: Eastern Europe Market Size (US$ Million) and Volume (Tons) Analysis and Forecast by Country, 2018 to 2033
Table 15: Eastern Europe Market Size (US$ Million) and Volume (Tons) Analysis and Forecast by Product Type, 2018 to 2033
Table 16: Eastern Europe Market Size (US$ Million) and Volume (Tons) Analysis and Forecast by Application, 2018 to 2033
Table 17: Russia and Belarus Market Size (US$ Million) and Volume (Tons) Analysis and Forecast by Product Type, 2018 to 2033
Table 18: Russia and Belarus Market Size (US$ Million) and Volume (Tons) Analysis and Forecast by Application, 2018 to 2033
Table 19: Balkan and Baltics Market Size (US$ Million) and Volume (Tons) Analysis and Forecast by Product Type, 2018 to 2033
Table 20: Balkan and Baltics Market Size (US$ Million) and Volume (Tons) Analysis and Forecast by Application, 2018 to 2033
Table 21: Central Asia Market Size (US$ Million) and Volume (Tons) Analysis and Forecast by Product Type, 2018 to 2033
Table 22: Central Asia Market Size (US$ Million) and Volume (Tons) Analysis and Forecast by Application, 2018 to 2033
Table 23: South Asia Pacific Market Size (US$ Million) and Volume (Tons) Analysis and Forecast by Country, 2018 to 2033
Table 24: South Asia Pacific Market Size (US$ Million) and Volume (Tons) Analysis and Forecast by Product Type, 2018 to 2033
Table 25: South Asia Pacific Market Size (US$ Million) and Volume (Tons) Analysis and Forecast by Application, 2018 to 2033
Table 26: East Asia Market Size (US$ Million) and Volume (Tons) Analysis and Forecast by Country, 2018 to 2033
Table 27: East Asia Market Size (US$ Million) and Volume (Tons) Analysis and Forecast by Product Type, 2018 to 2033
Table 28: East Asia Market Size (US$ Million) and Volume (Tons) Analysis and Forecast by Application, 2018 to 2033
Table 29: Middle East and Africa Market Size (US$ Million) and Volume (Tons) Analysis and Forecast by Country, 2018 to 2033
Table 30: Middle East and Africa Market Size (US$ Million) and Volume (Tons) Analysis and Forecast by Product Type, 2018 to 2033
Table 31: Middle East and Africa Market Size (US$ Million) and Volume (Tons) Analysis and Forecast by Application, 2018 to 2033
Figure 01: Global Market Historical Volume (Tons), 2018 to 2022
Figure 02: Global Market Current and Forecast Volume), 2023 to 2033
Figure 03: Global Market Historical Value (US$ Million), 2018 to 2022
Figure 04: Global Market Current and Forecast Value (US$ Million), 2023 to 2033
Figure 05: Global Market Incremental $ Opportunity (US$ Million), 2023 to 2033
Figure 06: Global Market Share and BPS Analysis by Product Type, 2023 and 2033
Figure 07: Global Market Y-o-Y Growth Projections by Product Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 08: Global Market Attractiveness Analysis by Product Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 09: Global Market Absolute $ Opportunity by Monoammonium Phosphate (MAP) Segment, 2018 to 2033
Figure 10: Global Market Absolute $ Opportunity by Diammonium Phosphate (DAP)Segment, 2018 to 2033
Figure 11: Global Market Absolute $ Opportunity by Single Superphosphate (SSP) Segment, 2018 to 2033
Figure 12: Global Market Absolute $ Opportunity by Triple Superphosphate (TSP) Segment, 2018 to 2033
Figure 13: Global Market Absolute $ Opportunity by Others Segment, 2018 to 2033
Figure 14: Global Market Share and BPS Analysis by Application, 2023 and 2033
Figure 15: Global Market Y-o-Y Growth Projections by Application, 2023 to 2033
Figure 16: Global Market Attractiveness Analysis by Application, 2023 to 2033
Figure 17: Global Market Absolute $ Opportunity by Cereals & Grains Segment, 2018 to 2033
Figure 18: Global Market Absolute $ Opportunity by Oilseeds Segment, 2018 to 2033
Figure 19: Global Market Absolute $ Opportunity by Pulses & legumes Segment, 2018 to 2033
Figure 20: Global Market Absolute $ Opportunity by Fruits & Vegetables Segment, 2018 to 2033
Figure 21: Global Market Absolute $ Opportunity by Others Segment, 2018 to 2033
Figure 22: Global Market Share and BPS Analysis by Region, 2023 and 2033
Figure 23: Global Market Y-o-Y Growth Projections by Region, 2023 to 2033
Figure 24: Global Market Attractiveness Analysis by Region, 2023 to 2033
Figure 25: Global Market Absolute $ Opportunity by North America Segment, 2018 to 2033
Figure 26: Global Market Absolute $ Opportunity by Latin America Segment, 2018 to 2033
Figure 27: Global Market Absolute $ Opportunity by Western Europe Segment, 2018 to 2033
Figure 28: Global Market Absolute $ Opportunity by Eastern Europe Segment, 2018 to 2033
Figure 29: Global Market Absolute $ Opportunity by Russia and Belarus Segment, 2018 to 2033
Figure 30: Global Market Absolute $ Opportunity by Balkan and Baltic Segment, 2018 to 2033
Figure 31: Global Market Absolute $ Opportunity by Central Asia Segment, 2018 to 2033
Figure 32: Global Market Absolute $ Opportunity by South Asia Pacific Segment, 2018 to 2033
Figure 33: Global Market Absolute $ Opportunity by East Asia Segment, 2018 to 2033
Figure 34: Global Market Absolute $ Opportunity by Middle East and Africa Segment, 2018 to 2033
Figure 35: North America Market Share and BPS Analysis by Country, 2023 and 2033
Figure 36: North America Market Y-o-Y Growth Projections by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 37: North America Market Attractiveness Analysis by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 38: North America Market Share and BPS Analysis by Product Type, 2023 and 2033
Figure 39: North America Market Y-o-Y Growth Projections by Product Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 40: North America Market Attractiveness Analysis by Product Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 41: North America Market Share and BPS Analysis by Application, 2023 and 2033
Figure 42: North America Market Y-o-Y Growth Projections by Application, 2023 to 2033
Figure 43: North America Market Attractiveness Analysis by Application, 2023 to 2033
Figure 44: Latin America Market Share and BPS Analysis by Country, 2023 and 2033
Figure 45: Latin America Market Y-o-Y Growth Projections by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 46: Latin America Market Attractiveness Analysis by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 47: Latin America Market Share and BPS Analysis by Product Type, 2023 and 2033
Figure 48: Latin America Market Y-o-Y Growth Projections by Product Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 49: Latin America Market Attractiveness Analysis by Product Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 50: Latin America Market Share and BPS Analysis by Application, 2023 and 2033
Figure 51: Latin America Market Y-o-Y Growth Projections by Application, 2023 to 2033
Figure 52: Latin America Market Attractiveness Analysis by Application, 2023 to 2033
Figure 53: Western Europe Market Share and BPS Analysis by Country, 2023 and 2033
Figure 54: Western Europe Market Y-o-Y Growth Projections by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 55: Western Europe Market Attractiveness Analysis by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 56: Western Europe Market Share and BPS Analysis by Product Type, 2023 and 2033
Figure 57: Western Europe Market Y-o-Y Growth Projections by Product Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 58: Western Europe Market Attractiveness Analysis by Product Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 59: Western Europe Market Share and BPS Analysis by Application, 2023 and 2033
Figure 60: Western Europe Market Y-o-Y Growth Projections by Application, 2023 to 2033
Figure 61: Western Europe Market Attractiveness Analysis by Application, 2023 to 2033
Figure 62: Eastern Europe Market Share and BPS Analysis by Country, 2023 and 2033
Figure 63: Eastern Europe Market Y-o-Y Growth Projections by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 64: Eastern Europe Market Attractiveness Analysis by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 65: Eastern Europe Market Share and BPS Analysis by Product Type, 2023 and 2033
Figure 66: Eastern Europe Market Y-o-Y Growth Projections by Product Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 67: Eastern Europe Market Attractiveness Analysis by Product Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 68: Eastern Europe Market Share and BPS Analysis by Application, 2023 and 2033
Figure 69: Eastern Europe Market Y-o-Y Growth Projections by Application, 2023 to 2033
Figure 70: Eastern Europe Market Attractiveness Analysis by Application, 2023 to 2033
Figure 71: Russia and Belarus Market Share and BPS Analysis by Product Type, 2023 and 2033
Figure 72: Russia and Belarus Market Y-o-Y Growth Projections by Product Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 73: Russia and Belarus Market Attractiveness Analysis by Product Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 74: Russia and Belarus Market Share and BPS Analysis by Application, 2023 and 2033
Figure 75: Russia and Belarus Market Y-o-Y Growth Projections by Application, 2023 to 2033
Figure 76: Russia and Belarus Market Attractiveness Analysis by Application, 2023 to 2033
Figure 77: Balkan and Baltics Market Share and BPS Analysis by Product Type, 2023 and 2033
Figure 78: Balkan and Baltics Market Y-o-Y Growth Projections by Product Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 79: Balkan and Baltics Market Attractiveness Analysis by Product Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 80: Balkan and Baltics Market Share and BPS Analysis by Application, 2023 and 2033
Figure 81: Balkan and Baltics Market Y-o-Y Growth Projections by Application, 2023 to 2033
Figure 82: Balkan and Baltics Market Attractiveness Analysis by Application, 2023 to 2033
Figure 83: Central Asia Market Share and BPS Analysis by Product Type, 2023 and 2033
Figure 84: Central Asia Market Y-o-Y Growth Projections by Product Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 85: Central Asia Market Attractiveness Analysis by Product Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 86: Central Asia Market Share and BPS Analysis by Application, 2023 and 2033
Figure 87: Central Asia Market Y-o-Y Growth Projections by Application, 2023 to 2033
Figure 88: Central Asia Market Attractiveness Analysis by Application, 2023 to 2033
Figure 89: South Asia Pacific Market Share and BPS Analysis by Country, 2023 and 2033
Figure 90: South Asia Pacific Market Y-o-Y Growth Projections by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 91: South Asia Pacific Market Attractiveness Analysis by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 92: South Asia Pacific Market Share and BPS Analysis by Product Type, 2023 and 2033
Figure 93: South Asia Pacific Market Y-o-Y Growth Projections by Product Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 94: South Asia Pacific Market Attractiveness Analysis by Product Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 95: South Asia Pacific Market Share and BPS Analysis by Application, 2023 and 2033
Figure 96: South Asia Pacific Market Y-o-Y Growth Projections by Application, 2023 to 2033
Figure 97: South Asia Pacific Market Attractiveness Analysis by Application, 2023 to 2033
Figure 98: East Asia Market Share and BPS Analysis by Country, 2023 and 2033
Figure 99: East Asia Market Y-o-Y Growth Projections by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 100: East Asia Market Attractiveness Analysis by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 101: East Asia Market Share and BPS Analysis by Product Type, 2023 and 2033
Figure 102: East Asia Market Y-o-Y Growth Projections by Product Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 103: East Asia Market Attractiveness Analysis by Product Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 104: East Asia Market Share and BPS Analysis by Application, 2023 and 2033
Figure 105: East Asia Market Y-o-Y Growth Projections by Application, 2023 to 2033
Figure 106: East Asia Market Attractiveness Analysis by Application, 2023 to 2033
Figure 107: Middle East and Africa Market Share and BPS Analysis by Country, 2023 and 2033
Figure 108: Middle East and Africa Market Y-o-Y Growth Projections by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 109: Middle East and Africa Market Attractiveness Analysis by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 110: Middle East and Africa Market Share and BPS Analysis by Product Type, 2023 and 2033
Figure 111: Middle East and Africa Market Y-o-Y Growth Projections by Product Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 112: Middle East and Africa Market Attractiveness Analysis by Product Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 113: Middle East and Africa Market Share and BPS Analysis by Application, 2023 and 2033
Figure 114: Middle East and Africa Market Y-o-Y Growth Projections by Application, 2023 to 2033
Figure 115: Middle East and Africa Market Attractiveness Analysis by Application, 2023 to 2033






Our Research Products

The "Full Research Suite" delivers actionable market intel, deep dives on markets or technologies, so clients act faster, cut risk, and unlock growth.

The Leaderboard benchmarks and ranks top vendors, classifying them as Established Leaders, Leading Challengers, or Disruptors & Challengers.

Locates where complements amplify value and substitutes erode it, forecasting net impact by horizon

We deliver granular, decision-grade intel: market sizing, 5-year forecasts, pricing, adoption, usage, revenue, and operational KPIs—plus competitor tracking, regulation, and value chains—across 60 countries broadly.

Spot the shifts before they hit your P&L. We track inflection points, adoption curves, pricing moves, and ecosystem plays to show where demand is heading, why it is changing, and what to do next across high-growth markets and disruptive tech

Real-time reads of user behavior. We track shifting priorities, perceptions of today’s and next-gen services, and provider experience, then pace how fast tech moves from trial to adoption, blending buyer, consumer, and channel inputs with social signals (#WhySwitch, #UX).

Partner with our analyst team to build a custom report designed around your business priorities. From analysing market trends to assessing competitors or crafting bespoke datasets, we tailor insights to your needs.
Supplier Intelligence
Discovery & Profiling
Capacity & Footprint
Performance & Risk
Compliance & Governance
Commercial Readiness
Who Supplies Whom
Scorecards & Shortlists
Playbooks & Docs
Category Intelligence
Definition & Scope
Demand & Use Cases
Cost Drivers
Market Structure
Supply Chain Map
Trade & Policy
Operating Norms
Deliverables
Buyer Intelligence
Account Basics
Spend & Scope
Procurement Model
Vendor Requirements
Terms & Policies
Entry Strategy
Pain Points & Triggers
Outputs
Pricing Analysis
Benchmarks
Trends
Should-Cost
Indexation
Landed Cost
Commercial Terms
Deliverables
Brand Analysis
Positioning & Value Prop
Share & Presence
Customer Evidence
Go-to-Market
Digital & Reputation
Compliance & Trust
KPIs & Gaps
Outputs
Full Research Suite comprises of:
Market outlook & trends analysis
Interviews & case studies
Strategic recommendations
Vendor profiles & capabilities analysis
5-year forecasts
8 regions and 60+ country-level data splits
Market segment data splits
12 months of continuous data updates
DELIVERED AS:
PDF EXCEL ONLINE
Fertilizer Packaging Market Forecast and Outlook 2025 to 2035
Phosphated Ester Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Fertilizer Tester Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Fertilizer Value Added Coatings Market Analysis - Size, Share, and Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Fertilizer Applicators Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Phosphate Salts Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Fertilizer Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Fertilizer Bags Market Growth - Demand & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Fertilizer Additive Market Report – Growth, Demand & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Phosphate Conversion Coatings Market 2025 to 2035
Phosphate Market Growth - Trends & Forecast 2024 to 2034
Fertilizer Injection Pumps Market
Phosphate Esters Market
Phosphated Distarch Phosphate Market
Diphosphates Market Analysis - Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Biofertilizers Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
NPK Fertilizers Market Analysis - Size, Share, and Forecast 2025 to 2035
Polyphosphate Market Food-Grade, Feed Grade, Cosmetic Grade and Other Grades through 2035
Wet Fertilizer Spreaders Market
Iron Phosphate Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035

Thank you!
You will receive an email from our Business Development Manager. Please be sure to check your SPAM/JUNK folder too.
Chat With
MaRIA