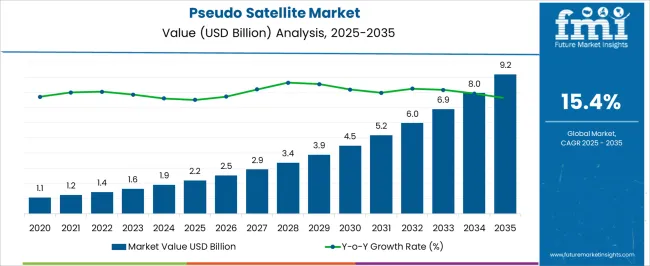
The pseudo satellite market is estimated to be valued at USD 2.2 billion in 2025 and is projected to reach USD 9.2 billion by 2035, registering a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 15.4% over the forecast period.
Pseudo satellites, often operating in the stratosphere, face regulatory overlaps between aviation and satellite domains. Civil aviation authorities are progressively defining standards for high-altitude long-endurance (HALE) platforms, ensuring safe coexistence with commercial aircraft. These guidelines directly affect operational deployment timelines and insurance costs. Spectrum management plays a critical role, as pseudo satellites rely on uninterrupted communication and data relay functions. Regulatory restrictions on frequency usage, combined with growing demand for bandwidth, can influence cost structures and market entry strategies. Additionally, governments are increasingly scrutinizing surveillance and reconnaissance capabilities, which means defense procurement policies and export controls will substantially impact adoption.
Environmental compliance is another emerging factor. With increasing focus on clean technologies, lighter composite materials and solar-powered propulsion are receiving regulatory incentives, particularly in Europe and Asia-Pacific. While these measures support long-term growth, stringent certification processes and prolonged approval cycles may slow short-term adoption. The regulatory harmonization across regions will remain a decisive factor shaping the market trajectory.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Pseudo Satellite Market Estimated Value in (2025 E) | USD 2.2 billion |
| Pseudo Satellite Market Forecast Value in (2035 F) | USD 9.2 billion |
| Forecast CAGR (2025 to 2035) | 15.4% |
The pseudo satellite market is viewed as a strategic and rapidly evolving segment across multiple parent industries. It is estimated to contribute about 18.2% of the aerospace and high altitude platforms market, due to advantages in loiter time and payload flexibility. Within earth observation and remote sensing, a 12.5% share is assessed, as persistent surveillance and high resolution sensing capabilities are enabled. In telecommunications and connectivity services, a 9.1% presence is calculated, supported by use as complementary nodes to terrestrial and space networks. The defense and surveillance sector is estimated at 14.0%, while weather and environmental monitoring is placed at 6.7%, indicating targeted utility across mission profiles and commercial services.
Recent industry trends have been driven by advances in lightweight materials, high efficiency power systems, and autonomous flight control, which have enabled longer endurance pseudo satellites at lower operating cost. Groundbreaking developments include modular payload architectures that allow rapid mission reconfiguration, high altitude solar electric propulsion for continuous operation, and multi node constellations for redundant coverage. Key players have pursued strategic partnerships with telecom operators and government agencies to secure spectrum access and service contracts, while research collaborations have been formed with material science and avionics firms to scale production. Business models based on as a service leasing, persistent surveillance packages, and hybrid network offload strategies have been trialed to commercialize capability and accelerate adoption.
The market is experiencing significant expansion as advancements in unmanned aerial vehicle technology and solar power integration enable persistent, high-altitude operations. These platforms are being increasingly deployed for communication, surveillance, and environmental monitoring applications where traditional satellites may be cost-prohibitive or lack operational flexibility.
The ability to remain airborne for weeks or even months is creating strong interest from both governmental and commercial stakeholders seeking near-space capabilities with lower launch and operational costs. Continuous improvements in lightweight materials, energy storage systems, and autonomous flight control are further enhancing the viability of pseudo satellites for a wide range of missions.
Strategic investments from defense agencies and telecommunication companies are reinforcing the growth momentum, while emerging applications in disaster management, border security, and remote connectivity are expanding the addressable market As regulatory frameworks evolve and technology matures, pseudo satellites are expected to play a pivotal role in augmenting existing satellite networks and delivering high-value, real-time data services.
The pseudo satellite market is segmented by type, application, end use, and geographic regions. By type, pseudo satellite market is divided into solar-powered UAVs, stratospheric balloons, hybrid airships, and tethered drones. In terms of application, pseudo satellite market is classified into intelligence, surveillance, and reconnaissance (ISR), telecommunications, Earth observation, environmental monitoring, commercial IoT, and others. Based on end use, pseudo satellite market is segmented into government/military, commercial enterprises, and research institutions. Regionally, the pseudo satellite industry is classified into North America, Latin America, Western Europe, Eastern Europe, Balkan & Baltic Countries, Russia & Belarus, Central Asia, East Asia, South Asia & Pacific, and the Middle East & Africa.
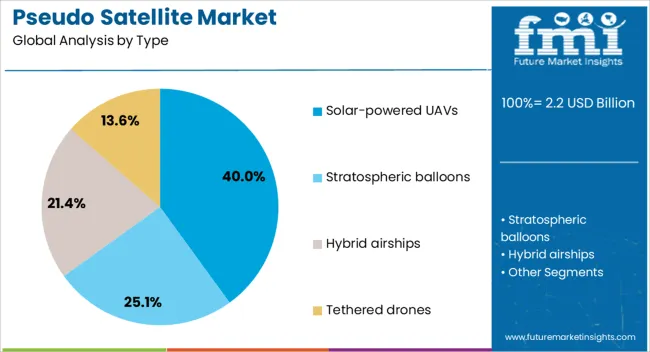
The solar powered UAVs type segment is projected to account for 40% of the market revenue share in 2025, making it the leading type. This growth has been driven by the segment’s ability to harness renewable energy for extended flight durations without the need for frequent refueling or maintenance. Such operational endurance is particularly valued in missions that require continuous coverage over specific areas.
Solar powered UAVs have been adopted in high-altitude applications where uninterrupted operations and minimal ground support are critical. The integration of energy-efficient propulsion systems and high-efficiency solar panels has allowed these platforms to sustain performance in varying atmospheric conditions.
Their flexibility in deployment, coupled with lower operational costs compared to conventional aircraft and satellites, has reinforced their demand As both defense and commercial users seek long-endurance, cost-effective aerial solutions, the segment is expected to maintain its leadership position supported by ongoing advancements in solar technology and lightweight structural design.
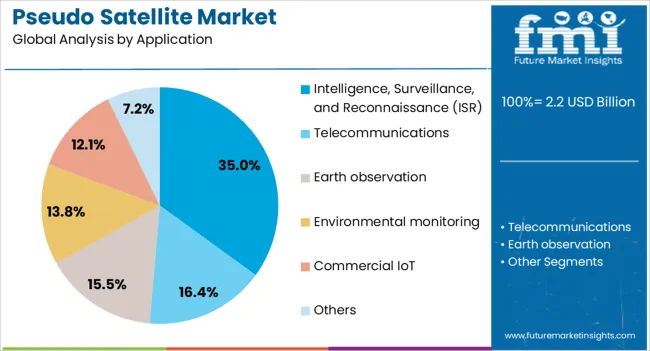
The intelligence surveillance and reconnaissance application segment is anticipated to command 35% of the market revenue share in 2025, positioning it as the dominant application. This growth has been attributed to the increasing demand for persistent and wide-area monitoring capabilities across defense, border security, and strategic infrastructure protection.
Pseudo satellites configured for ISR missions provide high-resolution imagery, signals intelligence, and real-time data transmission without the need for expensive satellite launches or the limitations of low-flying aircraft. Software-defined payload systems allow rapid reconfiguration to meet evolving mission requirements, while the high-altitude platform’s vantage point ensures broad coverage and minimal detection risk.
The ability to operate continuously for extended periods supports critical applications where uninterrupted situational awareness is essential Growing geopolitical tensions and the emphasis on proactive threat detection have further fueled investment in ISR-focused pseudo satellite systems, securing the segment’s dominant position within the market.
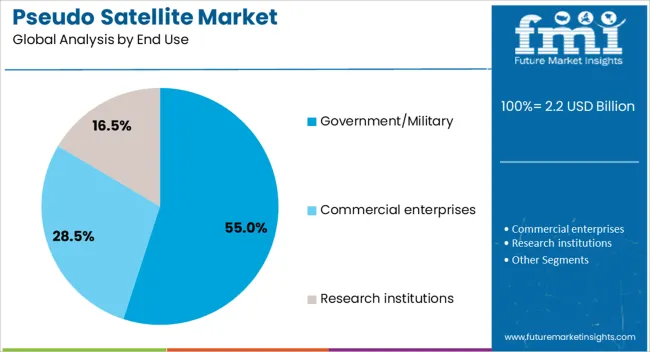
The government military end use segment is expected to hold 55% of the market revenue share in 2025, establishing it as the leading end-use category. This leadership has been driven by strong defense sector demand for strategic intelligence, secure communications, and surveillance solutions that can be rapidly deployed and maintained over critical areas. Pseudo satellites provide cost-effective alternatives to conventional satellites while delivering persistent coverage for border monitoring, maritime surveillance, and battlefield intelligence.
Government and military agencies have increasingly invested in these platforms due to their adaptability, operational resilience, and reduced vulnerability to anti-satellite measures. The segment’s growth has also been supported by the integration of advanced sensors, encrypted communications, and interoperability with existing defense networks.
As defense modernization programs prioritize space and near-space capabilities, pseudo satellites are emerging as an integral component of multi-domain operations This sustained focus on security readiness and strategic advantage is expected to reinforce the segment’s leading position in the years ahead.
The market has emerged as a specialized segment of aerospace and defense, where high altitude pseudo satellites operate in the stratosphere as alternatives or complements to conventional satellites. These platforms, often powered by solar energy, have been designed to remain airborne for extended periods, delivering persistent coverage for communication, surveillance, and Earth observation. Their cost advantage compared to orbital satellites has made them an attractive option for governments, defense agencies, and commercial enterprises. Ongoing collaborations between aerospace manufacturers and communication technology firms have reinforced interest in the development of pseudo satellite systems for global connectivity and monitoring applications.
A major dynamic has been the increasing use of pseudo satellites for defense and surveillance purposes. Their ability to provide real-time, high-resolution imaging and persistent monitoring over specific regions has been seen as a strategic asset for national security. Unlike conventional satellites, pseudo satellites can be repositioned as required and operated at lower costs, making them suitable for border monitoring, intelligence gathering, and maritime security. Defense agencies in technologically advanced nations have invested in trials and prototype projects to assess their operational advantages. This growing defense utility has significantly expanded market interest in high altitude pseudo satellite systems.
The role of pseudo satellites in extending communication coverage has been another significant driver. Positioned in the stratosphere, these platforms have been used to bridge connectivity gaps in rural and remote regions where terrestrial networks are limited. They have also been tested to provide emergency communication in disaster-hit areas, where conventional infrastructure has failed. Technology companies have explored pseudo satellites as part of global broadband initiatives, offering an alternative to satellite constellations. Such connectivity benefits have strengthened commercial interest in the pseudo satellite market, particularly as demand for reliable communication has grown across diverse sectors.
The market has been shaped by innovations in solar power systems, lightweight composite materials, and autonomous flight control technologies. Solar-powered pseudo satellites have been engineered to achieve endurance lasting weeks or months, surpassing traditional unmanned aerial vehicles. Advances in battery storage have also supported nighttime operations, enhancing reliability. Lightweight but strong materials have enabled these platforms to withstand stratospheric conditions while carrying advanced payloads. Continuous improvement in autonomous navigation and control systems has further optimized operational efficiency. These technological breakthroughs have expanded the feasibility of deploying pseudo satellites for multiple commercial and defense applications.
Despite promising applications, the pseudo satellite market has faced notable challenges. Harsh stratospheric conditions, including strong winds and extreme temperatures, have posed technical hurdles for long-duration operations. Payload capacity has remained limited compared to satellites, restricting the range of services that can be offered. High development costs and the need for rigorous testing have also slowed commercialization, as only a few aerospace companies possess the capability to build and operate such systems. These operational and financial constraints have been barriers to widespread deployment, though ongoing advancements suggest that gradual market expansion will be realized.
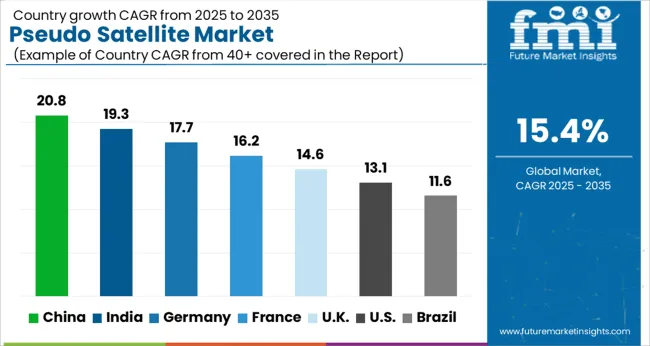
| Country | CAGR |
|---|---|
| China | 20.8% |
| India | 19.3% |
| Germany | 17.7% |
| France | 16.2% |
| UK | 14.6% |
| USA | 13.1% |
| Brazil | 11.6% |
The market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 15.4% from 2025 to 2035, supported by rising demand for high-altitude platforms and advanced communication systems. China, with a 20.8% CAGR, is accelerating adoption through extensive aerospace projects and large-scale R&D programs. India, growing at 19.3%, is focusing on cost-effective deployment strategies for defense and connectivity applications. Germany, at 17.7%, is leveraging strong aerospace engineering expertise to develop advanced endurance and payload systems. The UK, expanding at 14.6%, emphasizes testing and demonstration programs for commercial and military usage, while the USA, with 13.1% growth, is concentrating on next-generation surveillance and communication technologies. This report includes insights on 40+ countries; the top markets are shown here for reference.
The market in China is anticipated to register a CAGR of 20.8%, driven by the nation’s focus on advanced aerospace technologies and unmanned aerial systems. High Altitude Pseudo Satellites (HAPS) are gaining momentum in communication, defense, and environmental monitoring applications. Government programs and private sector collaborations are supporting large-scale projects to establish high-altitude platforms as alternatives to traditional satellites. China is investing in lightweight materials, solar-powered flight systems, and long-endurance designs, strengthening its leadership in this emerging market. The increasing need for secure communication infrastructure and surveillance is further amplifying adoption.
India is forecast to grow at a CAGR of 19.3%, supported by national initiatives in defense modernization and space technology innovation. The Indian Space Research Organisation and defense agencies are actively exploring HAPS systems for communication, navigation, and remote sensing. Focus is being placed on integrating pseudo satellites with existing space and drone infrastructure to reduce costs and enhance surveillance capabilities. Domestic aerospace manufacturers are working toward partnerships with global technology providers to accelerate development, indicating strong potential for adoption across strategic applications in the near future.
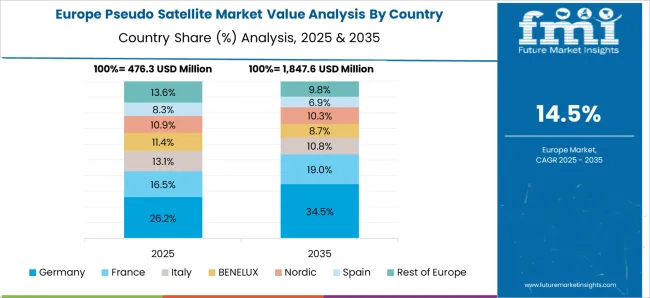
Germany’s market is projected to rise at a CAGR of 17.7%, led by strong aerospace expertise and research funding across the European Union. Applications in secure communication, disaster management, and environmental monitoring are expanding as German companies collaborate with international organizations to develop long-endurance pseudo satellite platforms. The emphasis on renewable energy technologies, particularly solar-powered propulsion, is improving flight durations and efficiency. Germany’s well-established aerospace ecosystem and government support for high-altitude projects place it in a favorable position to strengthen its market presence.
The market in the United Kingdom is expected to expand at a CAGR of 14.6%, supported by defense-led initiatives and innovation in unmanned aerial technologies. The nation is exploring the use of HAPS for military communication, maritime monitoring, and border security operations. Strong collaborations between government, aerospace firms, and research institutions are shaping the early stages of pseudo satellite development. Although the market is at a relatively nascent phase, strategic investments and pilot projects are laying the groundwork for broader adoption in both defense and civilian applications.
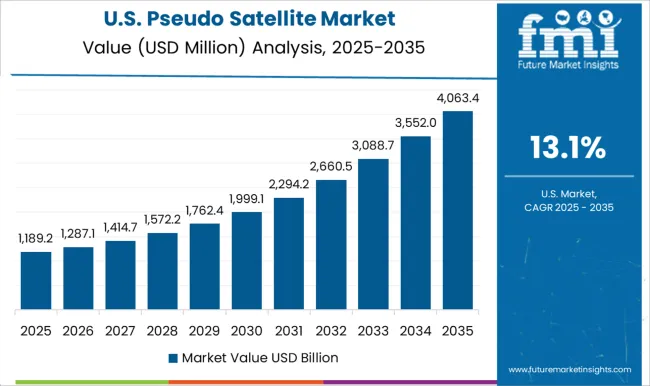
The market in the United States is projected to grow at a CAGR of 13.1%, driven by increasing investments in defense technology and aerospace innovation. High-altitude platforms are being tested for extended intelligence, surveillance, and reconnaissance missions, as well as for augmenting communication infrastructure in remote regions. USA aerospace companies are working on solar-powered and lightweight systems to achieve longer operational durations, reducing dependency on traditional satellites. Government funding, combined with private sector innovation, is expected to strengthen the deployment of pseudo satellites for both defense and commercial purposes.
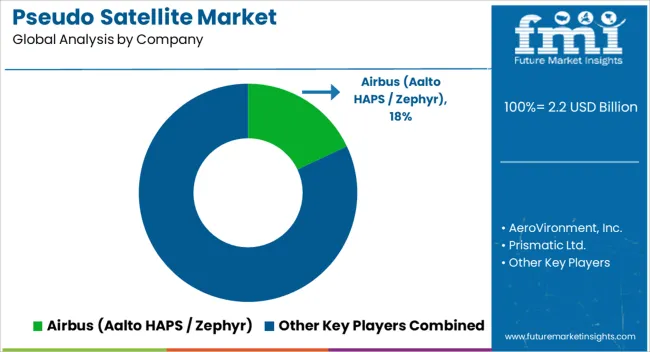
The market is shaped by the rising demand for high-altitude long-endurance platforms that can bridge the functional gap between satellites and unmanned aerial systems. Airbus, through its Aalto HAPS division and the Zephyr program, has established itself as a prominent player, demonstrating solar-powered, ultra-light platforms capable of multi-week endurance at stratospheric altitudes. AeroVironment, Inc. has also been an important contributor, bringing expertise in unmanned systems and high-altitude solar aircraft that target both defense and communication applications. Prismatic Ltd. has focused on efficient stratospheric vehicles designed for persistent surveillance and communication relay missions, adding to the growing ecosystem of innovators.
Thales Alenia Space, as part of the Thales Group, has combined aerospace heritage with next-generation HAPS development, leveraging communication system expertise to expand connectivity services. Sceye Inc. has emphasized advanced materials and stratospheric balloons for environmental monitoring and telecom coverage. Skydweller has pursued solar-powered autonomous aircraft adapted from piloted platforms to achieve long-endurance missions without crew. World View has expanded its focus beyond tourism and research balloons into stratospheric communication and observation systems. Collectively, these companies define a competitive environment where solar efficiency, endurance, and payload integration drive differentiation. The mix of aerospace primes, specialized startups, and dual-use innovators suggests that pseudo satellites are steadily advancing from experimental projects into strategic assets for defense, telecom, and environmental monitoring markets.
| Item | Value |
|---|---|
| Quantitative Units | USD 2.2 Billion |
| Type | Solar-powered UAVs, Stratospheric balloons, Hybrid airships, and Tethered drones |
| Application | Intelligence, Surveillance, and Reconnaissance (ISR), Telecommunications, Earth observation, Environmental monitoring, Commercial IoT, and Others |
| End Use | Government/Military, Commercial enterprises, and Research institutions |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America, Middle East & Africa |
| Country Covered | United States, Canada, Germany, France, United Kingdom, China, Japan, India, Brazil, South Africa |
| Key Companies Profiled | Airbus (Aalto HAPS / Zephyr), AeroVironment, Inc., Prismatic Ltd., Thales Alenia Space / Thales Group, and Sceye Inc. / Skydweller / World View |
| Additional Attributes | Dollar sales by platform type and application, demand dynamics across defense, communication, and environmental monitoring sectors, regional trends in high-altitude platform adoption, innovation in endurance, payload capacity, and energy efficiency, environmental impact of material usage and lifecycle management, and emerging use cases in disaster response, surveillance, and rural connectivity solutions. |
The global pseudo satellite market is estimated to be valued at USD 2.2 billion in 2025.
The market size for the pseudo satellite market is projected to reach USD 9.2 billion by 2035.
The pseudo satellite market is expected to grow at a 15.4% CAGR between 2025 and 2035.
The key product types in pseudo satellite market are solar-powered uavs, stratospheric balloons, hybrid airships and tethered drones.
In terms of application, intelligence, surveillance, and reconnaissance (isr) segment to command 35.0% share in the pseudo satellite market in 2025.






Full Research Suite comprises of:
Market outlook & trends analysis
Interviews & case studies
Strategic recommendations
Vendor profiles & capabilities analysis
5-year forecasts
8 regions and 60+ country-level data splits
Market segment data splits
12 months of continuous data updates
DELIVERED AS:
PDF EXCEL ONLINE
High-Altitude Pseudo-Satellite Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Pseudo Collagen Market Analysis - Size, Share & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Intestinal Pseudo-Obstruction Treatment Market - Trends, Growth & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Satellite Launch Vehicle Market Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Satellite Simulator Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Satellite Communication Components Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Satellite Vessel Tracking Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Satellite IoT Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Satellite Laser Communication Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Satellite Phased Array Antenna Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Satellite Solar Cell Materials Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Satellite-based 5G Network Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Satellite Launch Vehicle (SLV) Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Satellite Manufacturing Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Satellite Cables And Assemblies Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Satellite Component Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Satellite As A Service Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Satellite Payloads Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Satellite Modem Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Satellite Ground Station Market Trends – Growth & Forecast 2024-2034

Thank you!
You will receive an email from our Business Development Manager. Please be sure to check your SPAM/JUNK folder too.
Chat With
MaRIA