The Satellite As A Service Market is estimated to be valued at USD 5.3 billion in 2025 and is projected to reach USD 21.5 billion by 2035, registering a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 15.0% over the forecast period.
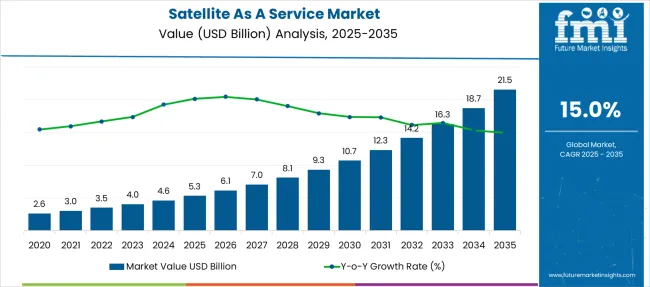
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Satellite As A Service Market Estimated Value in (2025E) | USD 5.3 billion |
| Satellite As A Service Market Forecast Value in (2035F) | USD 21.5 billion |
| Forecast CAGR (2025 to 2035) | 15.0% |
The Satellite as a Service market is expanding rapidly, driven by the growing demand for accessible, scalable, and cost-effective satellite solutions across diverse industries. With advancements in satellite miniaturization, cloud integration, and reusable launch technologies, service-based satellite models are increasingly favored over traditional ownership structures.
These models reduce capital expenditure and enable flexible deployment, making satellite capabilities more attainable for governments, enterprises, and research institutions. Rising adoption of satellite-based connectivity, Earth observation, and IoT integration is pushing the boundaries of how space-based services are consumed.
The shift toward data-as-a-service models and increasing reliance on near real-time analytics further amplify market growth. Looking forward, strong investment inflows, public-private partnerships, and policy frameworks encouraging private sector participation are expected to sustain momentum. This evolving ecosystem is positioned to reshape space accessibility while supporting a wide array of terrestrial applications.
The satellite as a service market is segmented by services, applications, end-users and geographic regions. By services of the satellite, the market is divided into Satellite launch, Payload design & integration, Ground station management, Data processing & management, and Satellite operations management. In terms of application of the satellite as a service market, it is classified into Satellite IoT, Earth observation, Ship tracking, Air traffic monitoring, Weather forecasting, and Others. Based on the end-user of the satellite as a service market, it is segmented into Government & defense, Commercial, and Academics. Regionally, the satellite as a service industry is classified into North America, Latin America, Western Europe, Eastern Europe, Balkan & Baltic Countries, Russia & Belarus, Central Asia, East Asia, South Asia & Pacific, and the Middle East & Africa.
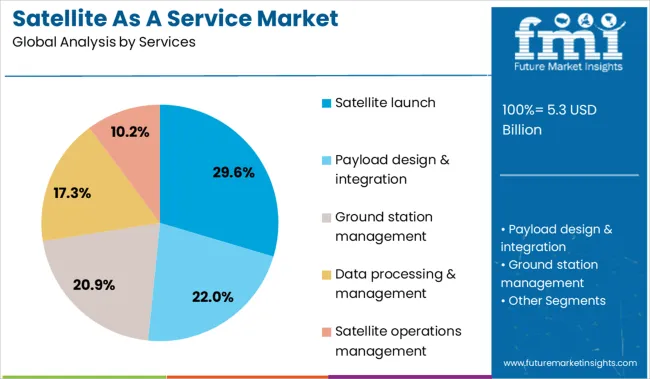
The satellite launch segment leads the services category with a 29.6% market share, reflecting its foundational role in enabling downstream space services. The rise of commercial launch providers, particularly those leveraging reusable rocket technology, has significantly lowered launch costs and accelerated service availability.
These developments have enabled organizations to focus on satellite utility rather than the complexities of deployment, making launch-as-a-service an essential component in the broader market. The segment continues to benefit from government contracts, commercial collaborations, and emerging space programs from developing nations.
Increased frequency of small satellite launches and rapid satellite constellation development are further supporting the growth of this service model. The continued evolution of low-cost launch systems and the emergence of on-demand launch capabilities are expected to enhance accessibility and scalability, ensuring the satellite launch segment remains pivotal to market expansion.
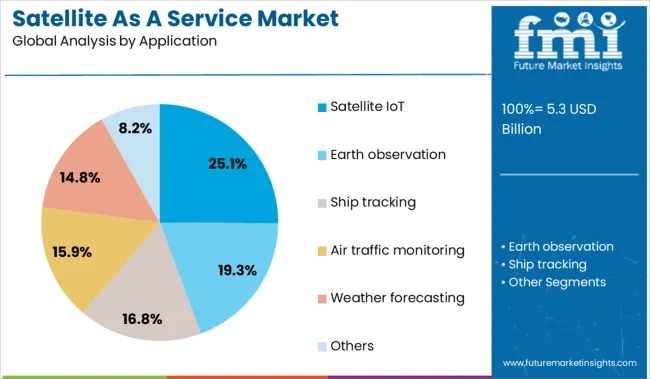
The satellite IoT segment holds a 25.1% share in the application category, driven by the increasing need for ubiquitous connectivity across remote and underserved regions. As terrestrial networks face coverage limitations, satellite-enabled IoT has become critical for sectors such as agriculture, logistics, maritime, and environmental monitoring.
The segment has gained traction through the deployment of low-Earth orbit (LEO) constellations that support low-latency, high-frequency data transmission. Companies are increasingly adopting satellite IoT services to monitor assets, track movement, and optimize operations in geographically dispersed locations.
The integration of IoT platforms with cloud and AI technologies is further improving data utilization, supporting predictive insights and automation. Ongoing demand for resilient and scalable connectivity solutions is expected to solidify the position of satellite IoT applications as a key driver within the Satellite as a Service market.
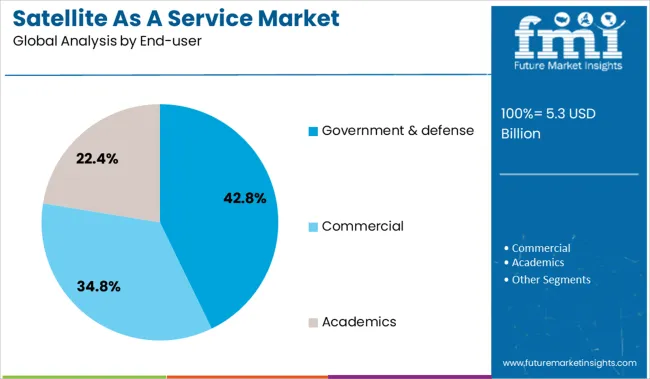
The government and defense sector dominates the end-user category with a commanding 42.8% market share, highlighting its critical role in driving demand for secure and mission-critical satellite services. Government agencies and defense organizations rely heavily on satellite systems for communication, surveillance, navigation, and reconnaissance, particularly in conflict zones and remote areas.
The segment is supported by consistent investments in national security infrastructure, joint space initiatives, and space situational awareness programs. Governments are increasingly outsourcing specific satellite capabilities through service-based models to enhance operational efficiency and reduce lifecycle costs.
The adoption of secure, flexible, and rapidly deployable satellite solutions aligns with the strategic objectives of modern defense systems. This trend is expected to persist as geopolitical tensions, cyber threats, and demand for real-time intelligence continue to shape satellite service procurement in the public sector.
Satellite as a Service platforms are expanding rapidly as companies demand turnkey satellite connectivity and analytics. Emerging opportunities lie in modular payload services, edge computing in orbit, and customized coverage bundles for new industry sectors.
Commercial operators are increasingly leveraging satellite infrastructure as a service to access bandwidth, Earth observation data, IoT connectivity, and geospatial analytics without owning hardware. These platforms allow rapid deployment of satellite-based services in sectors such as agriculture, maritime logistics, energy exploration, and disaster response. Pay per use access to imaging supports real-time mapping and environmental monitoring. Hosted payloads enable global machine-to-machine communication in remote areas where terrestrial networks are unavailable. Service providers handle licensing, data delivery, and infrastructure, reducing the operational burden on end users. This model appeals to enterprises and public agencies seeking affordable and efficient access to satellite data without high capital expenditure or long lead times.
Growth potential lies in modular payload options including sensors, radios, IoT repeaters, or onboard data processors. Providers can offer tailored packages that include specific coverage areas, bandwidth limits, and data refresh rates suited to different industry needs. Partnerships with telecom firms, analytics platforms, and logistics providers expand reach into emerging sectors like remote mining, environmental compliance, and infrastructure monitoring. By offering flexible pricing models such as subscriptions or project-based access, providers make satellite data more accessible to small and midsize enterprises. These developments help extend satellite service applications beyond traditional aerospace and defense markets, creating demand in new commercial segments that benefit from reliable space-based insights.
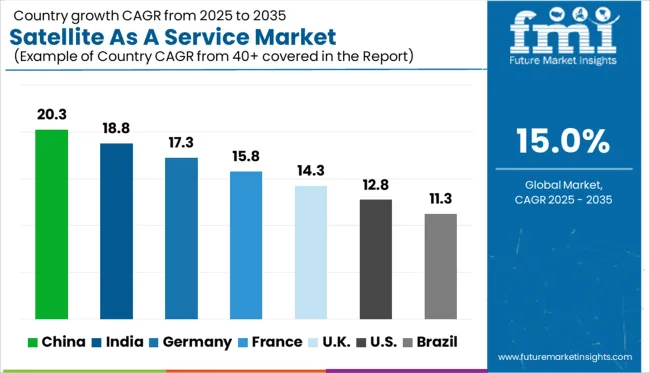
| Country | CAGR |
|---|---|
| China | 20.3% |
| India | 18.8% |
| Germany | 17.3% |
| France | 15.8% |
| UK | 14.3% |
| USA | 12.8% |
| Brazil | 11.3% |
The global market is anticipated to grow at a strong CAGR of 15% from 2025 to 2035, driven by miniaturization of satellite hardware, rising demand for real-time data, and advancements in low-earth orbit infrastructure. Among BRICS nations, China leads with a remarkable 20.3% CAGR, supported by major governmental and private space initiatives. India follows closely at 18.8%, bolstered by cost-effective satellite programs and expanding commercial applications across agriculture and disaster management. Germany, a leading OECD member, shows a 17.3% CAGR, reflecting robust aerospace R&D and adoption in logistics and security. France contributes a 15.8% CAGR due to innovation in satellite communication systems. The UK and US grow at 14.3% and 12.8% respectively, amid increased adoption by telecom and defense sectors. This report covers detailed analysis of 40+ countries, and the top five countries have been shared as a reference.
China is expanding at a rapid 20.3% CAGR, the highest among major countries, with strong YoY demand driven by national data policies and institutional contracts. Satellite services are being used extensively in weather forecasting, maritime monitoring, and resource mapping. Commercial uptake is accelerating through bundled services offered to logistics and telecom sectors. Government support for low-Earth orbit deployment is helping private providers scale analytics platforms linked to earth observation. Demand from agriculture and mining regions is creating localized opportunities for subscription-based satellite imagery and transmission models. Pricing flexibility is also allowing smaller clients to access customized satellite outputs without needing ground infrastructure.
India is growing at a 18.8% CAGR, with clear YoY momentum driven by public-private collaboration and satellite-based agricultural support systems. State-led procurement is being complemented by enterprise-level demand from insurance, urban planning, and telecom sectors. Local firms are offering affordable satellite data services, targeting mid-sized firms with crop monitoring and asset tracking needs. Capacity constraints are being addressed through partnerships with international providers. Remote monitoring solutions are now being bundled with analytics dashboards, making space-based services more practical for rural administrators. Government tenders are increasingly including satellite data components in land management and flood risk mitigation programs.
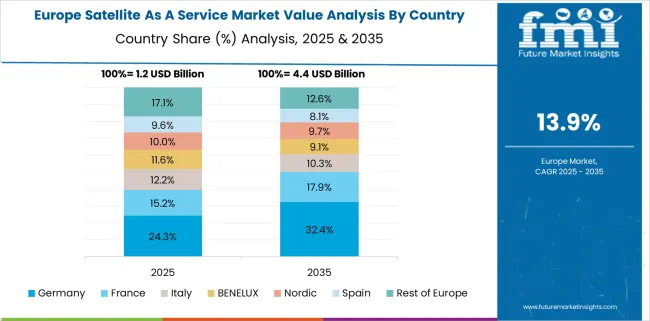
Germany is progressing at a 17.3% CAGR, with solid YoY growth supported by industrial demand for satellite-driven analytics across automotive, construction, and forestry sectors. Earth observation data is now integrated into engineering planning and infrastructure maintenance tools. Large corporations are licensing continuous satellite feeds to monitor logistics, fuel usage, and remote operations. Academic and research institutions also play a key role in data testing and validation for commercial models. Satellite-as-a-service solutions are being offered through European consortiums that bundle orbital capacity with processing tools. High trust in satellite-derived information is accelerating corporate adoption in precision-heavy industries.
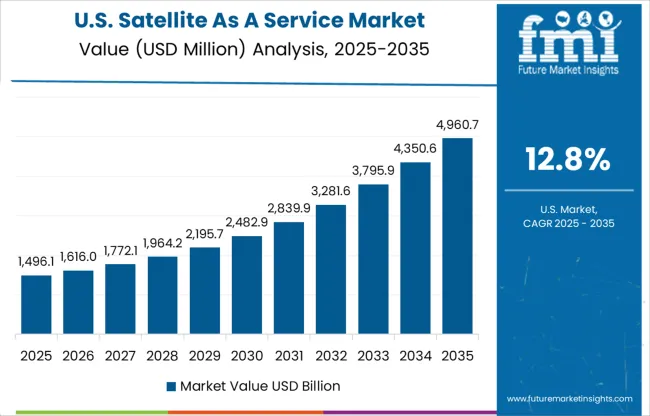
The United States is advancing at a 12.8% CAGR, showing steady YoY growth across enterprise applications such as geofencing, asset tracking, and wildfire detection. Commercial clients are demanding high-frequency updates, pushing service providers to rely on multi-satellite constellations. Most adoption is concentrated in energy, agriculture, and national park surveillance. Government agencies continue to lead in procurement, but private sector use is expanding via subscription platforms offering API-based satellite feeds. Satellite service bundling with geographic information systems is becoming more common, especially for utilities and infrastructure operators. Although growth is slower than in Asia, recurring revenue models are maturing.
The United Kingdom is expanding at a 14.3% CAGR, showing consistent YoY growth through defense contracting, precision farming, and transportation logistics. Satellite service providers are focusing on low-latency imagery and geospatial alerts for clients requiring real-time insights. Data compliance and processing security are top considerations, especially in defense and public infrastructure projects. Uptake is also growing among rail and maritime operators seeking predictive tracking and route optimization. Several firms are offering SaaS models bundled with analytics subscriptions that reduce the need for in-house processing. Policy alignment with European space regulations is ensuring service continuity across borders.
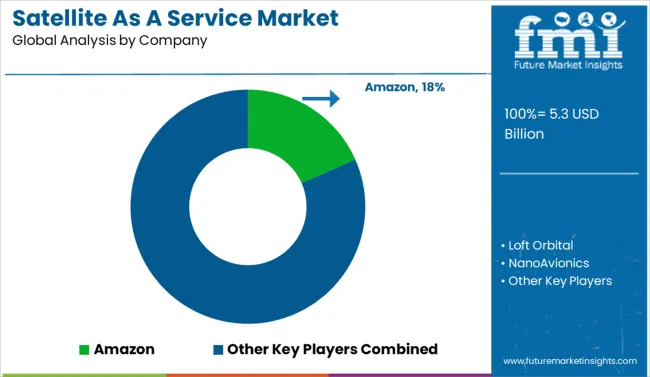
The Satellite as a Service (SataaS) market is emerging and niche-consolidated, characterized by rapid innovation and partnerships between cloud giants and space-tech startups. Amazon, through its AWS Ground Station and Project Kuiper, dominates early growth by integrating satellite data with cloud-based analytics. Loft Orbital and Spire Global offer payload-as-a-service platforms, democratizing access to space infrastructure. Mid-tier firms like York Space Systems and NanoAvionics focus on modular, rapidly deployable microsatellite buses. CesiumAstro and Spacety strengthen the ecosystem with customizable communications payloads. Key success levers include service agility, low latency data delivery, and vertical integration from orbit to cloud.
On March 4, 2024, Spire Global, Inc. announced via Business Wire that it successfully launched four satellites on SpaceX’s Transporter 10 mission. Two were built for Myriota to scale its IoT service, while the satellites leverage Spire’s “Space-as-a-Service” model, enhancing low-cost, global IoT connectivity with faster data transfer and scalable deployment.
| Item | Value |
|---|---|
| Quantitative Units | USD 5.3 Billion |
| Services | Satellite launch, Payload design & integration, Ground station management, Data processing & management, and Satellite operations management |
| Application | Satellite IoT, Earth observation, Ship tracking, Air traffic monitoring, Weather forecasting, and Others |
| End-user | Government & defense, Commercial, and Academics |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America, Middle East & Africa |
| Country Covered | United States, Canada, Germany, France, United Kingdom, China, Japan, India, Brazil, South Africa |
| Key Companies Profiled | Amazon, Loft Orbital, NanoAvionics, Spire Global, Inc., York Space Systems, CesiumAstro, Inc., and Spacety |
| Additional Attributes | Dollar sales by service type, satellite function, and end-user industry; regional demand driven by connectivity gaps, space democratization, and cloud integration; innovation in payload flexibility, on-demand satellite tasking, and AI-based data analytics; cost dynamics shaped by launch economics, subscription models, and satellite miniaturization; environmental impact from orbital debris and deorbiting practices; and emerging use cases in precision agriculture, disaster monitoring, and remote asset tracking. |
The global satellite as a service market is estimated to be valued at USD 5.3 billion in 2025.
The market size for the satellite as a service market is projected to reach USD 21.5 billion by 2035.
The satellite as a service market is expected to grow at a 15.0% CAGR between 2025 and 2035.
The key product types in satellite as a service market are satellite launch, payload design & integration, ground station management, data processing & management and satellite operations management.
In terms of application, satellite iot segment to command 25.1% share in the satellite as a service market in 2025.






Full Research Suite comprises of:
Market outlook & trends analysis
Interviews & case studies
Strategic recommendations
Vendor profiles & capabilities analysis
5-year forecasts
8 regions and 60+ country-level data splits
Market segment data splits
12 months of continuous data updates
DELIVERED AS:
PDF EXCEL ONLINE
Satellite Launch Vehicle Market Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Satellite Simulator Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Satellite Communication Components Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Satellite Vessel Tracking Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Satellite IoT Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Satellite Solar Cell Materials Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Satellite Launch Vehicle (SLV) Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Satellite Manufacturing Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Satellite Component Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Satellite Payloads Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Satellite Modem Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Satellite Ground Station Market Trends – Growth & Forecast 2024-2034
Satellite Antenna Market
Satellite Laser Communication Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Satellite-based 5G Network Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Satellite Phased Array Antenna Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Satellite Cables And Assemblies Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
4K Satellite Broadcasting Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
UAV Satellite Communication Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Nanosatellite And Microsatellite Market

Thank you!
You will receive an email from our Business Development Manager. Please be sure to check your SPAM/JUNK folder too.
Chat With
MaRIA