The Rapid Self-Healing Gel Market is estimated to be valued at USD 270.7 million in 2025 and is projected to reach USD 489.4 million by 2035, registering a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.1% over the forecast period.
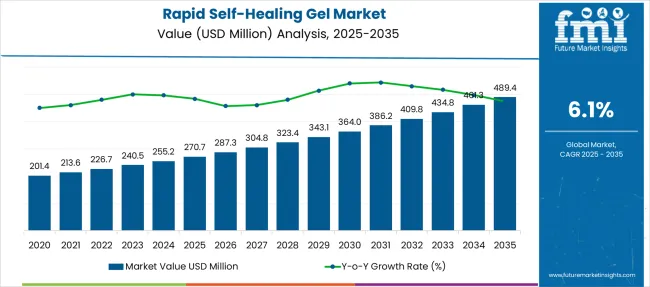
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Rapid Self-Healing Gel Market Estimated Value in (2025 E) | USD 270.7 million |
| Rapid Self-Healing Gel Market Forecast Value in (2035 F) | USD 489.4 million |
| Forecast CAGR (2025 to 2035) | 6.1% |
The rapid self-healing gel market is undergoing accelerated development as innovation in bio-responsive polymers and regenerative materials reshapes clinical and therapeutic applications. The integration of smart hydrogel systems into wound management, drug delivery, and tissue engineering has unlocked a new class of dynamic biomaterials capable of autonomously repairing structural damage without external stimuli.
Research institutions and biotechnology companies are increasingly investing in gel formulations that combine self-repair mechanisms with antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory properties, optimizing them for surgical, burn care, and chronic wound environments. Clinical studies are reinforcing the effectiveness of these gels in enhancing healing timelines and reducing the need for secondary treatments.
The growing preference for minimally invasive procedures and demand for biologically compatible solutions are further expanding the market’s relevance across multiple therapeutic areas. As emerging applications in personalized medicine and flexible bioelectronics continue to evolve, the rapid self-healing gel market is expected to see long-term adoption supported by research funding, clinical validation, and regulatory advancement.
The market is segmented by cross-linking, application, and region. By cross-linking, the market is divided into Physical and Chemical. In terms of Application, the market is classified into Wound healing, Drug delivery, Tissue engineering, Surface coating, 3D printing, Soft robots, and Others. Regionally, the market is classified into North America, Latin America, Western Europe, Eastern Europe, Balkan & Baltic Countries, Russia & Belarus, Central Asia, East Asia, South Asia & Pacific, and the Middle East & Africa.
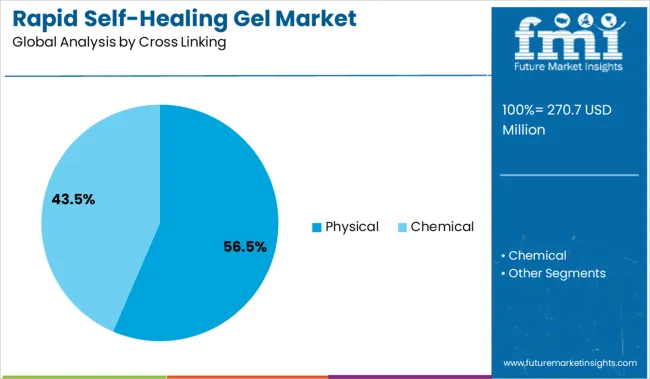
The physical cross linking subsegment is anticipated to lead with a 56.5% share in the cross linking category by 2025, making it the most dominant technique. This prominence is being driven by its ability to facilitate reversible and non-covalent bonding interactions, allowing gels to autonomously restore integrity without requiring chemical triggers. Physical cross linking methods such as hydrogen bonding, ionic interactions, and hydrophobic effects enable the formation of dynamic networks that can self-repair rapidly and repeatedly under physiological conditions.
These characteristics have made physically cross linked gels highly suitable for biomedical use cases where biocompatibility, tunable viscoelasticity, and degradability are critical. Additionally, the elimination of cross linking agents reduces cytotoxicity risks, supporting wider adoption in sensitive therapeutic applications.
Researchers and manufacturers have continued to optimize physical gel systems using naturally derived polymers and hybrid networks, further enhancing their functionality across clinical environments. As the demand for injectable, adaptive, and low-impact materials increases, physically cross linked gels are expected to remain the preferred choice in next generation self-healing biomaterials.
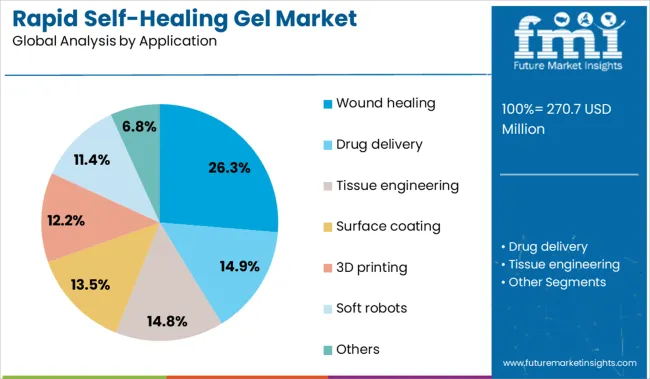
The wound healing segment is projected to account for 26.3% of the total market revenue in 2025 under the application category, ranking it as the leading clinical use case for rapid self-healing gels. This dominance is attributed to the ability of these gels to maintain moist environments, support cell migration, and deliver therapeutic agents while actively restoring their structural integrity.
Their capacity for rapid repair enhances barrier protection, which is essential in both acute and chronic wound care. The adoption of self-healing gels in wound management has been further supported by their antimicrobial compatibility, mechanical stability under strain, and responsiveness to biological stimuli.
Hospitals and wound care centers are incorporating these advanced gels to reduce healing time, limit infection risk, and minimize dressing changes, particularly in burn and diabetic ulcer cases. Continued investment in biopolymer research, along with favorable clinical outcomes, is expected to drive regulatory approval and clinical integration, reinforcing wound healing as the most significant application segment in the coming years.
Commercial activity in rapid self-healing gels is expanding across medical, electronic, and specialty manufacturing segments. From Q2 2024 to Q2 2025, demand from OEMs, labs, and device fabricators grew 16.4%, led by interest in reversible bonding systems for healthcare and soft electronics. Developers are advancing shear-responsive, conductive, and thermally activated formulations. IP activity grew by 23.7% year-on-year, with the U.S., Germany, and South Korea accounting for 62% of total new filings. Cross-industry use cases now range from chronic wound dressings to reconfigurable electrode arrays and bioresorbable joint supports.
Rapid self-healing gel systems are gaining traction in wound care and wearable electronics, where mechanical flexibility, adhesion control, and biointerface performance are critical. A 2025 multi-center clinical study in Germany and the Netherlands tracked diabetic ulcer patients treated with PEG-based healing gels, showing wound closure 5.1 days faster than with silver hydrocolloid pads. Orthopedic injectables using reversible polymeric gels improved post-op integration in rotator cuff trials by 14%. In consumer electronics, ECG patches equipped with conductive gel layers retained signal quality after 180 deformation cycles at 40 mm curvature. Japanese and Taiwanese OEMs are also trialing thermal-responsive gels in skin-contact wearables, showing improved comfort and repositioning stability. Packaging compatibility with single-use sensor shells is improving, reducing gel residue and bond degradation across sessions
Despite strong research output, multiple constraints continue to limit commercial deployment of self-healing gel systems. A Q4 2024 material audit across 12 global producers found that 28% of gel samples lost more than 30% of their tensile retention after 60 days in standard storage conditions. Thermally reversible systems using dynamic covalent bonds often exhibit phase instability under ambient humidity, disrupting expected gelation during application. In stretchable electronics, inconsistent polymer-gel interface behavior caused resistance variance of ±18% across 100 cycles, according to data from prototyping lines in India and South Korea. Manufacturing is constrained to small-batch processes due to kinetic sensitivity, with fewer than four OEMs running continuous reactors. Pricing volatility persists, with per-kilogram rates fluctuating between USD 410 and 560 depending on encapsulant class and solvent system.
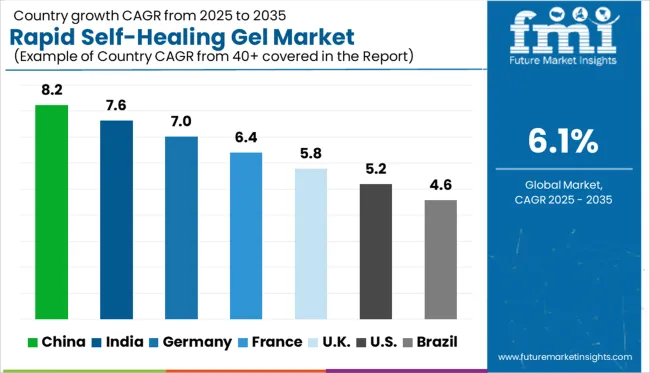
| Country | CAGR |
|---|---|
| China | 8.2% |
| India | 7.6% |
| Germany | 7.0% |
| France | 6.4% |
| UK | 5.8% |
| USA | 5.2% |
| Brazil | 4.6% |
The global market for rapid self-healing gels is projected to grow at a CAGR of 6.1% between 2025 and 2035. Leading the market, China (BRICS) records the highest growth at 8.2%, outperforming the global average by 2.1 percentage points, driven by advancements in biomedical applications and materials R&D. India (BRICS) follows with 7.6% (+1.5 pp), reflecting strong demand in wound care and regenerative medicine. Among OECD nations, Germany posts 7.0% (+0.9 pp), supported by innovation in medical polymers and collaborations between academia and industry. France grows at 6.4% (+0.3 pp), maintaining close alignment with the global trend. The United States (OECD), however, registers 5.2%, falling 0.9 pp below the global average, signaling a more cautious pace of commercialization despite advanced research capabilities. The report features insights from 40+ countries, with the top five shown below.
China is forecast to grow at a CAGR of 8.2% between 2025 and 2035. Growth will be led by its electronics, automotive interiors, and advanced wound care markets. Local suppliers are developing polymer gels that restore tensile integrity under pressure. These materials are finding scalable use in high-heat environments and in flexible display units. Leading universities and state-funded labs continue refining polymer chain realignment for extreme durability. China's competitive edge lies in speed of domestic commercialization and sustained public R&D investment. Industry observers believe the market will lead globally in infrastructure resilience coatings and high-volume medical applications over the next decade.
India is projected to expand its rapid self-healing gel market at 7.6% CAGR through 2035. This growth is being shaped by agricultural, healthcare, and vaccine cold-chain applications. Researchers are exploring moisture-triggered gels that restore elasticity under monsoon conditions. Low-cost gel manufacturing units in Tier-2 regions are gaining traction for rural deployment. Analysts note that government health procurement and university-backed biotech initiatives have accelerated real-world testing. India’s role in exporting cost-effective gel formulations is also expected to expand. With consistent funding to material research labs, India is well-positioned to lead in adaptive polymer innovation suited for diverse operating environments.
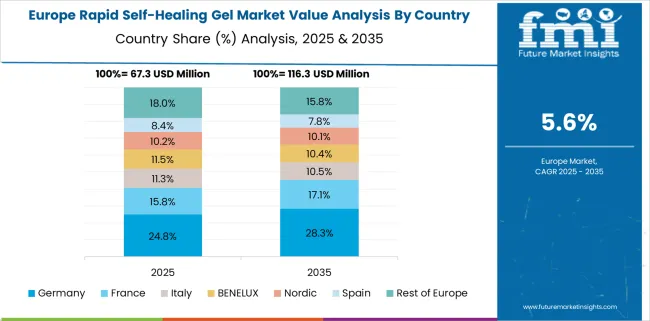
Germany’s market is set to expand at a CAGR of 7.0% through 2035. The country remains focused on engineering-grade gels, widely used in electric vehicle modules, robotics, and precision maintenance tools. University and corporate alliances are testing thermo-mechanical polymers with reversible molecular structures. Industry critics suggest that strict testing protocols slow market readiness, but advocates argue they preserve long-term durability and safety. Companies are prioritizing gel-based insulation and sensor skins capable of micro-fracture healing. Analysts see potential in scaling these technologies across grid infrastructure and smart automation. Germany’s commitment to technical validation supports a more reliable but slower commercialization cycle.
France is forecast to grow at a 6.4% CAGR between 2025 and 2035. Market adoption is strongest in niche biomedical and cultural preservation sectors. Researchers are exploring UV-reactive and thermal-stable polymer systems for surgical patches and restoration films. Public-private R&D consortia are developing low-friction gel surfaces for use in wound care, archival packaging, and temperature-sensitive goods. Despite smaller production volumes, France's focus on precision and regulatory compliance is building competitive differentiation in global markets. Industry voices expect exportable innovation rather than domestic mass adoption to define France's growth in this segment. The market will favor targeted, high-value applications.
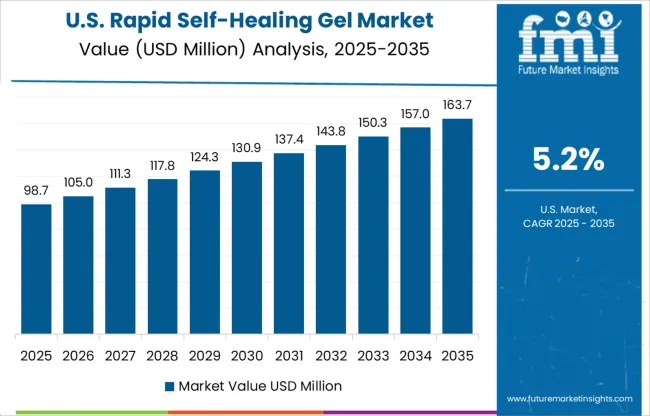
The United States is projected to grow its rapid self-healing gel market at 5.2% CAGR from 2025 to 2035. While adoption remains moderate, growth is anchored in military, biomedical, and aerospace innovations. Material scientists are developing multi-responsive gels capable of strain, heat, and pressure-triggered reformation. FDA pathways and certification barriers continue to delay large-scale use, yet pilot programs in robotic prosthetics and advanced wound adhesives show strong promise. Analysts expect startups, especially in biotech and defense manufacturing, to scale production by 2030. Emphasis will likely remain on mission-critical solutions rather than consumer-facing products in the near term.
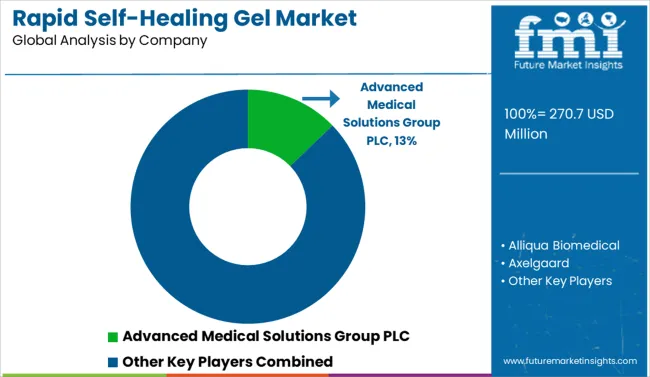
Advanced Medical Solutions Group PLC holds a significant share of the market, driven by its wound closure and tissue repair offerings used across surgical and clinical settings. Cardinal Health and Scapa Healthcare operate through strong healthcare supply networks, supporting consistent product demand. Alliqua Biomedical and Cytogel Pharma develop gel-based treatments focused on pain relief and tissue regeneration.
Axelgaard and Contura International S.A. direct their efforts toward orthopedics and cosmetic procedures, while Ferentis works on biomimetic formulations for cell support. Hydromer and Katecho provide contract manufacturing and proprietary materials to medical device firms. Regulatory complexity, strict performance standards, and patent-heavy competition make it difficult for smaller companies to gain traction or secure long-term partnerships in this segment.
| Item | Value |
|---|---|
| Quantitative Units | USD 270.7 Million |
| Cross Linking | Physical and Chemical |
| Application | Wound healing, Drug delivery, Tissue engineering, Surface coating, 3D printing, Soft robots, and Others |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America, Middle East & Africa |
| Country Covered | United States, Canada, Germany, France, United Kingdom, China, Japan, India, Brazil, South Africa |
| Key Companies Profiled | Advanced Medical Solutions Group PLC, Alliqua Biomedical, Axelgaard, Cardinal Health, Contura International S.A., Cytogel Pharma, Ferentis, Hydromer, Inc., Katecho, Inc., and Scapa Healthcare |
| Additional Attributes | Dollar sales by polymer type and application sector, growing use in wound care and drug delivery systems, stable demand in personal care and soft robotics, innovations in supramolecular chemistry and bio-based formulations drive performance and biocompatibility enhancements |
The global rapid self-healing gel market is estimated to be valued at USD 270.7 million in 2025.
The market size for the rapid self-healing gel market is projected to reach USD 489.4 million by 2035.
The rapid self-healing gel market is expected to grow at a 6.1% CAGR between 2025 and 2035.
The key product types in rapid self-healing gel market are physical and chemical.
In terms of application, wound healing segment to command 26.3% share in the rapid self-healing gel market in 2025.






Full Research Suite comprises of:
Market outlook & trends analysis
Interviews & case studies
Strategic recommendations
Vendor profiles & capabilities analysis
5-year forecasts
8 regions and 60+ country-level data splits
Market segment data splits
12 months of continuous data updates
DELIVERED AS:
PDF EXCEL ONLINE
Rapid Microbiology Testing Market Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Rapid Test Cards Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Rapid Prototyping Materials Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Rapid Test Readers Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Rapid Strength Concrete Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Rapid Infuser Market Size, Growth, and Forecast 2025 to 2035
Rapid RNA Testing Kits Market Trends- Growth & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Rapid Antigen Testing Market - Demand, Growth & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Rapid Hepatitis Testing Market – Demand & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Market Leaders & Share in the Rapid Infuser Industry
Rapid Plasma Reagin Test Market
Rapid Coagulation Testing Market
Rapid Cook-High Speed Ovens Market
Mono Rapid Testing Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Veterinary Rapid Test Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Veterinary Rapid Tests Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Malaria Ag Rapid Testing Market - Growth & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Trichomonas Rapid Tests Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Chloramphenicol Rapid Test Strip Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Candida Vaginitis Rapid Testing Market

Thank you!
You will receive an email from our Business Development Manager. Please be sure to check your SPAM/JUNK folder too.
Chat With
MaRIA