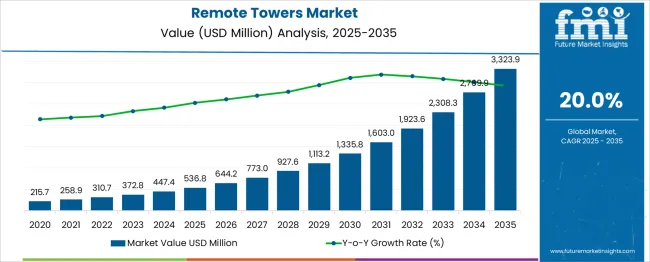
The Remote Towers Market is estimated to be valued at USD 536.8 million in 2025 and is projected to reach USD 3323.9 million by 2035, registering a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 20.0% over the forecast period.
Phase-wise analysis indicates a distinctly back-loaded growth structure. In the first half (2025-2030), the market rises from USD 536.8 million to 1,335.8 million, adding USD 799 million, which accounts for 28.7% of total growth.
This early phase is driven by initial adoption in regional airports and regulatory approvals for single remote tower solutions. Annual gains increase from USD 107.4 million in 2026 to USD 222.6 million by 2030, showing steady progress. The second half (2030-2035) contributes a significantly higher USD 1,988.1 million, representing 71.3% of incremental growth, as large-scale deployments accelerate through multi-airport remote tower systems and AI-based traffic management integration.
Annual growth exceeds USD 400 million after 2032, signaling rapid scalability supported by digital infrastructure upgrades and increased investment in advanced surveillance and automation platforms. Companies that invest in modular architectures, real-time analytics, and robust cybersecurity for remote operations will be best positioned to capture the expanding demand in this high-growth segment as air traffic control modernization gains global momentum.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Remote Towers Market Estimated Value in (2025 E) | USD 536.8 million |
| Remote Towers Market Forecast Value in (2035 F) | USD 3323.9 million |
| Forecast CAGR (2025 to 2035) | 20.0% |
The remote towers market occupies an important niche within advanced aviation infrastructure. In the airport operations and air traffic management solutions market, remote towers represent 6–8 %, as traditional towers and integrated ATC systems dominate spending. Within the digital air traffic control systems market, their share is higher at 12–14 %, reflecting the growing shift from physical to virtual control environments.
In the remote and virtual air traffic services (VATS) market, remote towers lead with a 35–38 % share, as they form the core technology for consolidating air traffic management across multiple airports. For the airspace modernization and automation systems market, remote towers account for 5–6 %, since large investments are directed toward surveillance radars, communication systems, and automation software. In the aviation infrastructure and smart airport technology market, the share is about 4–5 %, given the significant allocation to passenger processing, biometric systems, and IoT-enabled airport solutions.
Although the shares appear modest across broader infrastructure markets, demand is accelerating due to cost efficiencies, the ability to control multiple airports remotely, and compliance with safety and capacity requirements. Adoption of AI-based object detection, high-definition video, and real-time data links is reshaping tower operations, making remote towers a critical enabler for future-ready, digitalized air traffic management globally.
The remote towers market is witnessing accelerated growth as air navigation service providers and airport authorities seek scalable and cost-effective solutions for air traffic management. The evolution from conventional control towers to remote digital platforms has been influenced by rising pressure on operational efficiency, infrastructure modernization, and the need to support low-traffic and regional airports.
Advancements in high-resolution video surveillance, real-time data transmission, and sensor fusion technologies have enabled controllers to manage multiple airports remotely while maintaining high safety and performance standards. The deployment of intelligent vision systems, combined with automated decision support tools, has reduced dependency on physical infrastructure and optimized staffing resources.
Regulatory acceptance and pilot programs across Europe, Asia, and the Middle East are further strengthening the commercial viability of remote towers. As civil aviation continues to evolve, the integration of AI-driven analytics, edge computing, and secured communication networks is expected to expand the role of remote towers in both single-airport and multi-airport configurations, creating new opportunities for market expansion globally.
The remote towers market is segmented by operation type, system type, application, end user, and geographic regions. The remote towers market is divided by operation type into Single/Sequential, Multiple/Simultaneous, Contingency, and Supplementary Remote Tower. The remote towers market is classified by system type into Cameras (180/360/Pan), Remote Tower Module, and Solutions & Software. Based on the application, the remote towers market is segmented into Surveillance, Communication, Information & Control, Flight Data Handling, and Visualization. The end users of the remote towers market are segmented into Commercial airports and Military airports. Regionally, the remote towers industry is classified into North America, Latin America, Western Europe, Eastern Europe, Balkan & Baltic Countries, Russia & Belarus, Central Asia, East Asia, South Asia & Pacific, and the Middle East & Africa.
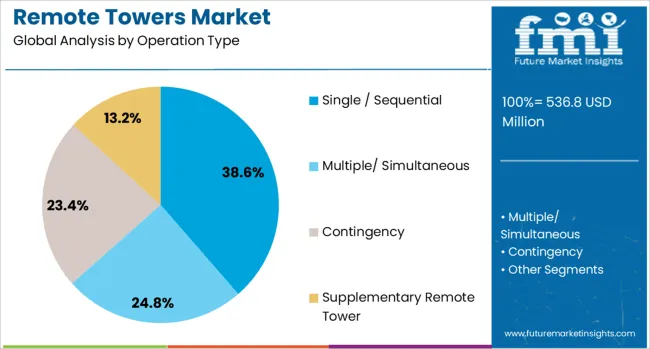
The single sequential operation type segment is projected to account for 38.6% of the overall revenue share in the remote towers market in 2025. This segment's dominance is being driven by its operational simplicity, regulatory readiness, and widespread suitability for regional airport environments. The model has enabled remote control of one airport at a time, offering significant cost reductions without compromising safety or performance.
Its adoption has been accelerated by successful validation in live airport settings and alignment with existing air traffic management protocols. Furthermore, the single sequential approach requires less complex integration, making it ideal for airports undergoing initial digital transformation.
The segment has also benefited from faster certification timelines, as well as reduced training and infrastructure requirements, allowing for faster deployment. As remote tower adoption scales, this operation model is serving as the foundational architecture upon which more advanced multi-airport configurations are built, reinforcing its importance in the early and mid-term growth phases of the market.
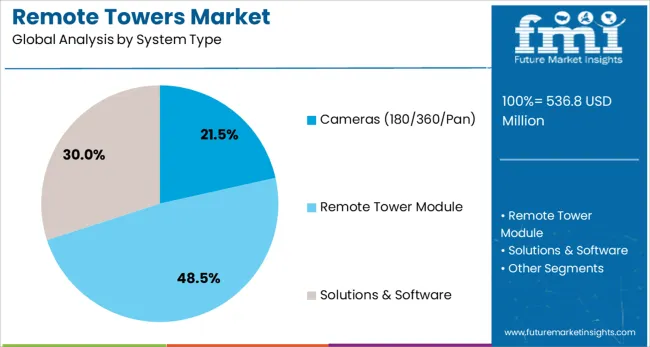
The cameras 180/360/pan system type segment is expected to contribute 21.5% of the total market share in the remote towers market by 2025. This segment has gained traction due to its ability to replicate and enhance the visual capabilities of traditional control towers using high-resolution, panoramic imaging. The integration of 180 and 360 degree panoramic cameras has enabled continuous situational awareness with wide-area coverage, supporting real-time tracking of aircraft, vehicles, and ground movements.
These systems have been instrumental in reducing blind spots, improving visibility during adverse weather conditions, and providing enhanced night vision capabilities. With the integration of real-time analytics and dynamic zoom functions, operators can monitor specific zones with high precision while retaining full-field awareness.
Their modular configuration and software-defined adaptability allow for quick upgrades and remote diagnostics. As regulatory bodies approve more remote tower implementations, the demand for flexible and advanced visual systems is expected to remain high, sustaining the growth of this segment.
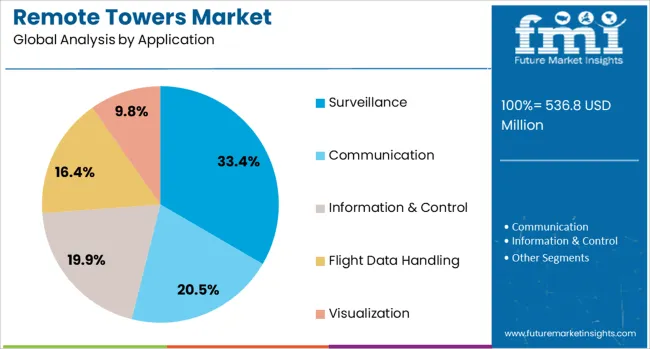
The surveillance application segment is projected to hold 33.4% of the remote towers market revenue share in 2025. This leadership is attributed to the critical need for continuous monitoring of airport perimeters, runways, taxiways, and surrounding airspace to maintain safety and compliance. Surveillance capabilities have been significantly enhanced through the deployment of advanced imaging sensors, intelligent detection algorithms, and real-time data processing.
Remote towers configured for surveillance purposes enable early threat identification, anomaly detection, and situational control without requiring a physical presence on-site. Their implementation has reduced infrastructure overhead while increasing operational coverage. Moreover, real-time integration with air traffic control and emergency response systems has elevated the effectiveness of surveillance-based operations in both civil and military aviation.
These solutions are being prioritized across global airport modernization projects to enhance security, support autonomous systems, and comply with evolving regulatory standards. As digital transformation accelerates in aviation infrastructure, surveillance will continue to serve as a primary use case driving the demand for remote tower systems.
Remote towers are being introduced to provide air traffic control services without requiring fully staffed onsite facilities at every airport. These systems use high-definition cameras, communication systems, and centralized command platforms to manage multiple airfields from a single hub. Adoption has grown among regional and low-traffic airports seeking cost-effective control solutions. Providers offering certified video surveillance, redundant communication networks, and secure data transmission capabilities are positioned to meet the rising demand for advanced air traffic management systems globally.
Remote towers have been implemented to reduce operational costs and enhance control efficiency at airports with low traffic density. Advanced visual monitoring systems capture full panoramic views, streaming real-time data to remote centers for managing takeoffs and landings. Integration with radar feeds and standardized communication protocols has improved coordination across multiple sites. Operational flexibility has been achieved as one control center can manage several airports, minimizing staffing needs. Technological developments in network reliability and fail-safe backup systems have reinforced the safety and resilience of remote operations. As aviation authorities seek scalability and cost control, remote towers have emerged as a strategic solution for modern air traffic control systems.
The deployment of remote tower systems has faced challenges due to stringent regulatory approvals, safety certifications, and operational licensing requirements. Long validation timelines arise from diverse airport conditions and traffic complexities. High-speed data links with reliable redundancy are required to prevent service disruption, increasing infrastructure costs. Technical integration with existing navigation systems and radar units has been complex, requiring specialized engineering. System performance in image resolution, latency, and operator awareness must undergo rigorous testing before deployment. Workforce training on new remote management interfaces and multi-airport coordination adds further implementation complexity. These factors combined with high setup costs have limited adoption across smaller and resource-constrained airports.
Significant opportunities have been created by deployment of remote tower systems at smaller or low‑traffic airports where traditional control towers are not economically viable. Remote towers enable centralized air traffic control services to be provided from regional hubs, reducing infrastructure costs and enabling scalable airspace management. Countries with numerous regional airports have adopted remote solutions to expand coverage without constructing physical towers. Partnership models between aviation authorities and technology providers have facilitated combined implementation and operational services. Systems are being upgraded to support sensor fusion, including high‑definition cameras, radar, and multilateration tracking. Expansion into heliport and military airfield operations is being explored as additional use cases for remote air traffic services.
Prevailing trends include integration of high-definition cameras, radar feeds, and infrared sensors into unified digital tower platforms that replicate a traditional tower view via video walls. Virtualization of air traffic control workstations is becoming common, whereby controllers access remote feeds from secure data centres rather than being stationed onsite. Redundancy protocols and secure cloud infrastructure are being implemented to ensure uptime and data integrity. Augmented reality overlays are being tested to provide controllers with additional situational information such as aircraft identification and distance metrics. Adoption of standardized communication protocols and interoperability frameworks is advancing to enable cross-border remote tower operations. Training simulators in digital formats are being used to certify controller performance under virtual tower scenarios.
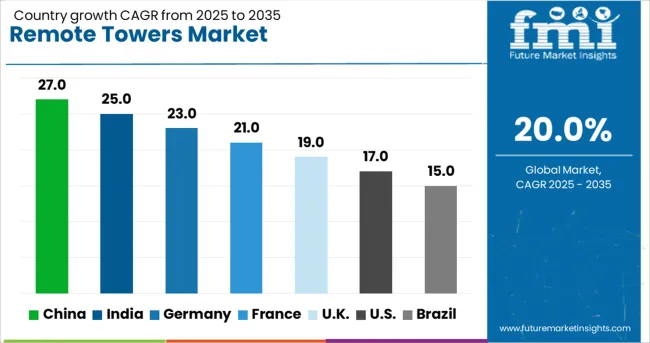
| Country | CAGR |
|---|---|
| China | 27.0% |
| India | 25.0% |
| Germany | 23.0% |
| France | 21.0% |
| UK | 19.0% |
| USA | 17.0% |
| Brazil | 15.0% |
The global remote towers market is projected to grow at a robust 20.0% CAGR from 2025 to 2035, fueled by air traffic modernization, digital ATC solutions, and cost optimization initiatives by airports. Among BRICS economies, China leads at 27.0%, leveraging large-scale airport expansion and automation programs. India follows with 25.0%, supported by regional connectivity schemes and rapid integration of remote ATC solutions for tiered airports. OECD nations show strong adoption, with Germany at 23.0%, France at 21.0%, and the UK at 19.0%, driven by advanced airspace management, collaborative decision-making systems, and cybersecurity integration. This analysis includes data for over 40 countries, with the top five markets detailed below.
China is projected to grow at a 27.0% CAGR, supported by the rapid deployment of digital tower systems in major airport hubs and secondary cities. The Civil Aviation Administration of China (CAAC) is promoting remote ATC solutions to manage rising flight volumes efficiently. Domestic suppliers are developing integrated platforms combining surveillance, AI-assisted decision support, and advanced communication systems. Large-scale airport construction projects, including smart terminals, reinforce the adoption of remote tower technologies. Strategic collaborations with European technology firms accelerate system standardization and ensure compliance with international air traffic norms. Investments in automation and multi-airport monitoring further strengthen the Chinese remote towers ecosystem.
India is expected to grow at a 25.0% CAGR, driven by regional airport development under UDAN (Ude Desh Ka Aam Nagrik) and cost-efficient ATC management solutions. Remote towers are being prioritized for airports with low to medium traffic, reducing infrastructure costs and staffing requirements. Strategic partnerships between Airports Authority of India (AAI) and international technology providers are expediting implementation timelines. Domestic OEMs are investing in scalable remote tower platforms integrated with real-time surveillance and AI-based flight management tools. The rise of greenfield airports and air cargo hubs is further amplifying demand for digital ATC solutions. India’s regulatory frameworks emphasize cybersecurity and data privacy for all digital tower deployments.
France is projected to grow at a 21.0% CAGR, with remote tower adoption led by DSNA (Direction des Services de la Navigation Aérienne) modernization programs. Deployment is concentrated in regional airports and secondary hubs to reduce operational costs. French OEMs and system integrators are developing cloud-enabled ATC platforms with high-definition video surveillance and data analytics capabilities. Partnerships with European aviation authorities ensure compliance with SESAR (Single European Sky ATM Research) standards. Growing investments in training simulators for remote ATC controllers are strengthening workforce readiness. Remote tower integration with advanced airspace monitoring systems further enhances operational efficiency in complex traffic environments.
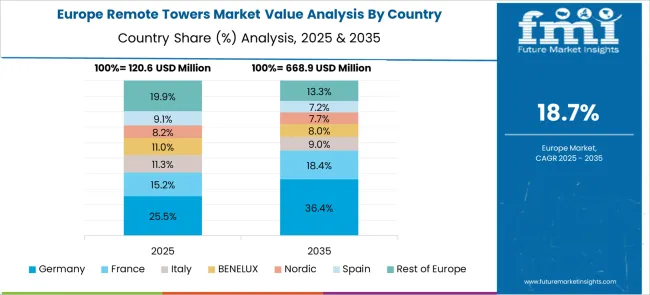
Germany is forecast to grow at a 23.0% CAGR, supported by the modernization of ATC infrastructure under the Single European Sky initiative. Remote tower technology is being deployed for multi-airport control centers, optimizing operations for smaller airports with reduced on-site resources. DFS (Deutsche Flugsicherung) and leading OEMs are investing in platforms integrating AI-based decision-making, remote monitoring, and virtual reality visualization for enhanced situational awareness. Investments in cybersecurity and redundant communication channels ensure operational reliability. The focus on interoperability standards and collaborative decision-making systems aligns with EU aviation digitalization goals. Export opportunities for German technology firms in remote ATC solutions are also expanding across emerging markets.
The UK is expected to record a 19.0% CAGR, driven by the transition from traditional ATC systems to remote digital solutions under airspace modernization programs. NATS (National Air Traffic Services) is piloting remote tower solutions for regional airports, optimizing operational efficiency and cost structure. Private airport operators are adopting hybrid systems that combine on-site and remote ATC capabilities. Domestic suppliers are focusing on systems with AI-driven analytics and redundant communication protocols to maintain safety and compliance. Strategic alliances with technology firms are accelerating deployment timelines across critical hubs. Integration of remote towers with collaborative decision-making tools ensures improved traffic flow management.
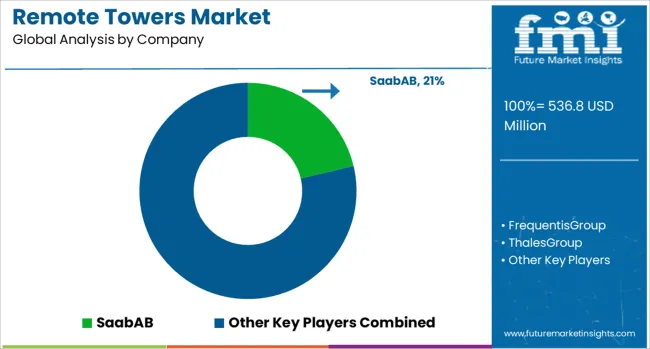
Leading players include Saab AB, Frequentis Group, Thales Group, Indra Sistemas S.A., Raytheon Technologies Corporation, L3Harris Technologies, Inc., and Northrop Grumman Corporation, each leveraging advanced surveillance systems, real-time data processing, and remote air traffic control technologies. Saab AB holds a strong position with its pioneering remote tower systems deployed across multiple European airports, while Frequentis and Thales focus on integrating advanced voice communication, data sharing, and virtual visualization systems into ATC workflows. Indra Sistemas delivers scalable remote tower solutions with AI-driven analytics to support both single and multiple airport operations.
Raytheon Technologies and L3Harris Technologies emphasize cybersecurity-enabled platforms and secure data transmission, catering to increasing demands for safety compliance in high-traffic zones.
Northrop Grumman extends its expertise in defense-grade technologies to ensure resilient and secure remote tower infrastructure. The market operates under high regulatory oversight, with certification requirements by authorities like EASA and FAA creating substantial entry barriers for new entrants. Competitive differentiation revolves around system interoperability, latency reduction, integration with radar and camera-based sensors, and predictive maintenance through digital twins.
Industry rivalry is intense as vendors compete for global contracts driven by cost savings, scalability, and modernization initiatives across regional and international airports. Future growth will hinge on AI integration, 5G-enabled communication, and multi-airport remote operations, positioning technology-driven companies to capitalize on digital transformation in global air traffic management.
| Item | Value |
|---|---|
| Quantitative Units | USD 536.8 Million |
| Operation Type | Single / Sequential, Multiple/ Simultaneous, Contingency, and Supplementary Remote Tower |
| System Type | Cameras (180/360/Pan), Remote Tower Module, and Solutions & Software |
| Application | Surveillance, Communication, Information & Control, Flight Data Handling, and Visualization |
| End User | Commercial Airport and Military Airport |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America, Middle East & Africa |
| Country Covered | United States, Canada, Germany, France, United Kingdom, China, Japan, India, Brazil, South Africa |
| Key Companies Profiled | SaabAB, FrequentisGroup, ThalesGroup, IndraSistemas,S.A., RaytheonTechnologiesCorporation, L3harrisTechnologies,Inc., and NorthropGrummanCorporation |
| Additional Attributes | Dollar sales are segmented by deployment type (digital tower, remote tower center, hybrid control) and by airport category (regional, medium, large hubs). Demand is driven by cost optimization, talent scarcity, and push for CADP (cost‑efficient air traffic management) in underused airports. Europe and North America lead early adoption; Asia-Pacific is expanding regional projects. Innovation focuses on high-definition pan‑tilt‑zoom cameras, AI‑enabled situational awareness, HD sensor fusion, and edge computing resilience. Key trends include multi‑airport remote tower centers and secure high- |
The global remote towers market is estimated to be valued at USD 536.8 million in 2025.
The market size for the remote towers market is projected to reach USD 3,323.9 million by 2035.
The remote towers market is expected to grow at a 20.0% CAGR between 2025 and 2035.
The key product types in remote towers market are single / sequential, multiple/ simultaneous, contingency and supplementary remote tower.
In terms of system type, cameras (180/360/pan) segment to command 21.5% share in the remote towers market in 2025.






Our Research Products

The "Full Research Suite" delivers actionable market intel, deep dives on markets or technologies, so clients act faster, cut risk, and unlock growth.

The Leaderboard benchmarks and ranks top vendors, classifying them as Established Leaders, Leading Challengers, or Disruptors & Challengers.

Locates where complements amplify value and substitutes erode it, forecasting net impact by horizon

We deliver granular, decision-grade intel: market sizing, 5-year forecasts, pricing, adoption, usage, revenue, and operational KPIs—plus competitor tracking, regulation, and value chains—across 60 countries broadly.

Spot the shifts before they hit your P&L. We track inflection points, adoption curves, pricing moves, and ecosystem plays to show where demand is heading, why it is changing, and what to do next across high-growth markets and disruptive tech

Real-time reads of user behavior. We track shifting priorities, perceptions of today’s and next-gen services, and provider experience, then pace how fast tech moves from trial to adoption, blending buyer, consumer, and channel inputs with social signals (#WhySwitch, #UX).

Partner with our analyst team to build a custom report designed around your business priorities. From analysing market trends to assessing competitors or crafting bespoke datasets, we tailor insights to your needs.
Supplier Intelligence
Discovery & Profiling
Capacity & Footprint
Performance & Risk
Compliance & Governance
Commercial Readiness
Who Supplies Whom
Scorecards & Shortlists
Playbooks & Docs
Category Intelligence
Definition & Scope
Demand & Use Cases
Cost Drivers
Market Structure
Supply Chain Map
Trade & Policy
Operating Norms
Deliverables
Buyer Intelligence
Account Basics
Spend & Scope
Procurement Model
Vendor Requirements
Terms & Policies
Entry Strategy
Pain Points & Triggers
Outputs
Pricing Analysis
Benchmarks
Trends
Should-Cost
Indexation
Landed Cost
Commercial Terms
Deliverables
Brand Analysis
Positioning & Value Prop
Share & Presence
Customer Evidence
Go-to-Market
Digital & Reputation
Compliance & Trust
KPIs & Gaps
Outputs
Full Research Suite comprises of:
Market outlook & trends analysis
Interviews & case studies
Strategic recommendations
Vendor profiles & capabilities analysis
5-year forecasts
8 regions and 60+ country-level data splits
Market segment data splits
12 months of continuous data updates
DELIVERED AS:
PDF EXCEL ONLINE
Remote ICU Monitoring System Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Remote Lockout Tool Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Remote Desktop Software Market Forecast and Outlook 2025 to 2035
Remote Patient Monitoring Devices Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Remote Assist Headrest Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Remote Endarterectomy Devices Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Remote Electrocardiogram Monitoring Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Remote Valve Tissue Expanders Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Remote Patient Monitoring System Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Remote Imaging Collaboration Market Analysis - Size, Share, and Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Remote Operated Vehicle Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Remote DC Microgrid Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Remote Microgrid Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Remote AF Detection Tools Market Analysis Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Remote Vehicle Diagnostics Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Remote Home Monitoring Systems Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Remote Asset Management Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Remote Learning Technology Spending Market Analysis by Technology Software, Technology Services, Learning Mode, End User and Region Through 2025 to 2035
Remote Sensing Services Market Trends - Growth & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Remote Cooled Cube Ice Machines Market – Advanced Refrigeration & Industry Growth 2025 to 2035

Thank you!
You will receive an email from our Business Development Manager. Please be sure to check your SPAM/JUNK folder too.
Chat With
MaRIA