The Synthetic Food Market is estimated to be valued at USD 19.7 billion in 2025 and is projected to reach USD 39.5 billion by 2035, registering a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.2% over the forecast period. A year-on-year growth examination shows that annual increments vary modestly, indicating low growth rate volatility across the forecast horizon. Between 2025 and 2026, the market grows by USD 1.4 billion, followed by annual increases ranging from USD 1.6 billion to USD 2.5 billion in the later years.
The growth rate volatility index, in this context, can be gauged by evaluating the variability of these annual growth figures. Over the 10 years, changes remain within a narrow absolute range, with the smallest year-on-year gain of USD 1.4 billion and the largest at USD 2.6 billion. This produces a low deviation from the mean annual increase of around USD 1.98 billion. Such consistency indicates that external shocks, substitution risks, or regulatory disruptions are not projected to have a material impact on growth acceleration or deceleration. The steady slope of growth suggests that the market will not exhibit sharp growth spikes or contractions. The market reflects a low Growth Rate Volatility Index, signaling a mature pace of adoption supported by incremental innovation and predictable demand expansion.
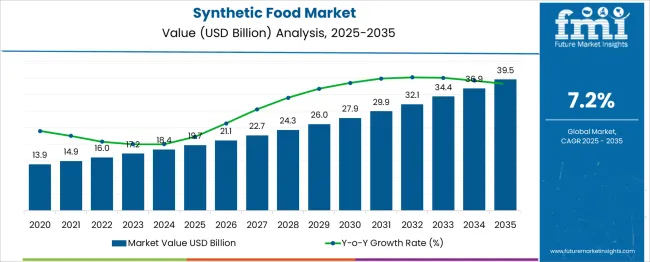
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Synthetic Food Market Estimated Value in (2025 E) | USD 19.7 billion |
| Synthetic Food Market Forecast Value in (2035 F) | USD 39.5 billion |
| Forecast CAGR (2025 to 2035) | 7.2% |
The synthetic food market is witnessing sustained growth due to increasing demand for cost-efficient, scalable, and shelf-stable ingredients that meet the sensory and functional needs of processed foods. The rise in global population, combined with urbanization and lifestyle shifts, has led to surging consumption of ready-to-eat and packaged products, accelerating the need for synthetic alternatives in coloring, flavoring, and preservation.
Regulatory allowances and advancements in food-grade chemical synthesis have enabled consistent quality and performance across batches, making synthetic ingredients highly attractive for industrial-scale food production. Additionally, synthetic inputs offer formulation flexibility, longer product life, and protection from seasonal variability of natural alternatives.
Growing consumer acceptance of synthetic options in low-dose, safety-assured formulations especially in emerging markets is expected to reinforce future growth opportunities, particularly as food manufacturers focus on affordability, appearance, and taste consistency.
The synthetic food market is segmented by product, application, and geographic regions. By product of the synthetic food market is divided into Colors. In terms of application of the synthetic food market is classified into Flavour & Fragrances, Colors, Antioxidants, Hydrocolloids, Emulsifiers Fat Replacers. Regionally, the synthetic food industry is classified into North America, Latin America, Western Europe, Eastern Europe, Balkan & Baltic Countries, Russia & Belarus, Central Asia, East Asia, South Asia & Pacific, and the Middle East & Africa.
The colors segment is expected to lead the synthetic food product landscape, contributing 26.0% of total revenue in 2025. This segment's dominance is being driven by the growing emphasis on visual appeal in packaged foods and beverages, where synthetic colorants provide vibrant, stable, and cost-effective alternatives to natural dyes.
Their ability to withstand heat, pH variations, and light exposure makes them highly suitable for applications requiring extended shelf life and consistency. Technological improvements in encapsulation and dispersion systems have further enhanced their performance across diverse food matrices.
Moreover, the limited availability and instability of certain natural pigments continue to position synthetic colors as the preferred choice among manufacturers striving for precise shade reproduction and scalability across global markets.
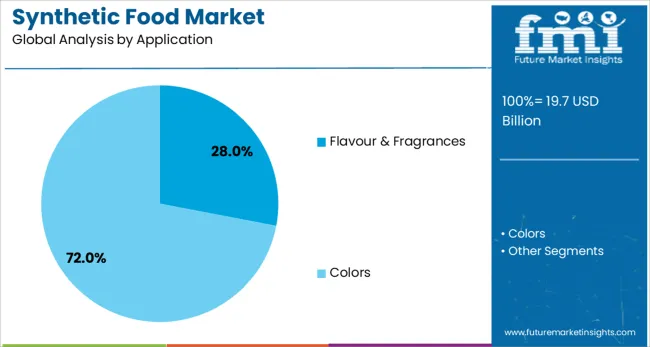
Flavour & fragrances are projected to account for 28.0% of the synthetic food market revenue in 2025, making it the leading application segment. This prominence is attributed to the critical role of synthetic flavors in enhancing taste profiles, masking off-notes, and improving consumer acceptance of processed and fortified foods.
Synthetic compounds provide reliable, repeatable outcomes and are essential in developing complex sensory profiles unattainable through natural extraction alone. Their cost-effectiveness and high potency allow precise dosage control, reducing waste and ensuring regulatory compliance.
Expanding product lines in categories such as functional beverages, confectionery, and meal replacements are further boosting demand. Additionally, the versatility of synthetic fragrances in aligning food aroma with flavor perception has reinforced their significance in brand differentiation and consumer retention.
Synthetic food has been developed to address evolving dietary preferences, supply constraints, and the need for scalable alternatives to traditional agriculture-based ingredients. These food products have been formulated using biotechnology, fermentation, or lab-based synthesis to replicate the taste, texture, and nutritional profiles of conventional meat, dairy, and other food categories. Their adoption has been supported by research institutions, food technology companies, and ingredient manufacturers focused on expanding food access and enhancing efficiency in raw material sourcing. The synthetic food market has matured into a viable parallel supply chain across beverages, bakery, ready meals, and protein-based product categories.
Fermentation and cellular agriculture have enabled scalable production of synthetic proteins that replicate those found in meat, eggs, or milk. Microbial fermentation has been applied to generate casein, whey, or albumin alternatives without animal involvement. Precision fermentation using engineered microorganisms has allowed the synthesis of specific functional proteins used in food formulation. Lab-cultured meat, though at an early stage of commercialization, has presented potential for producing muscle tissue from animal cells under controlled bioreactors. These methods have addressed supply volatility associated with livestock and provided consistent ingredient quality for downstream food production. Industrial-scale protein fermenters have supported the foodservice and ingredient blending industries with predictable input availability.
Flavor replication has remained a critical aspect of synthetic food development. Advanced compound libraries and AI-based formulation tools have been employed to create synthetic analogs of meat, dairy, or seafood flavors. Texturization techniques, including shear-cell structuring and microencapsulation, have allowed plant or synthetic proteins to imitate the mouthfeel of animal-based ingredients. These approaches have improved the consumer experience across ready meals, snack foods, and alternative dairy products. Synthetic fat emulsions and customized binders have been integrated to mimic cooking behavior and visual appearance. As a result, synthetic food manufacturers have been able to match sensory expectations of mainstream consumers and foodservice operators.
The synthetic food industry has emphasized consistent ingredient supply and scalable manufacturing as essential growth levers. Continuous bioprocessing, modular fermentation infrastructure, and downstream purification systems have been deployed to support bulk production of key inputs. Standardized formulations and ingredient blends have allowed food brands to expand synthetic product lines with predictable performance. Stability under varying storage and processing conditions has been ensured through encapsulation and formulation techniques. Manufacturers have invested in closed-loop facilities to reduce contamination and operational costs. These manufacturing frameworks have enabled broad deployment of synthetic ingredients in packaged foods, beverage concentrates, and plant-based analogues on a global scale.
While synthetic food products have achieved technical feasibility, market expansion has been limited by regulatory fragmentation, raw material input costs, and consumer perception. Approvals for novel ingredients and production processes have varied across regions, creating barriers to international scaling. High costs associated with precision fermentation and cell culturing have restricted affordability compared to conventional food systems. Concerns related to processing methods, labeling, and long-term health outcomes have influenced buyer adoption. Public understanding of synthetic food production has remained limited, requiring targeted outreach and transparent communication. Regulatory convergence, input cost optimization, and consumer education are expected to be key to unlocking broader growth in the synthetic food market.
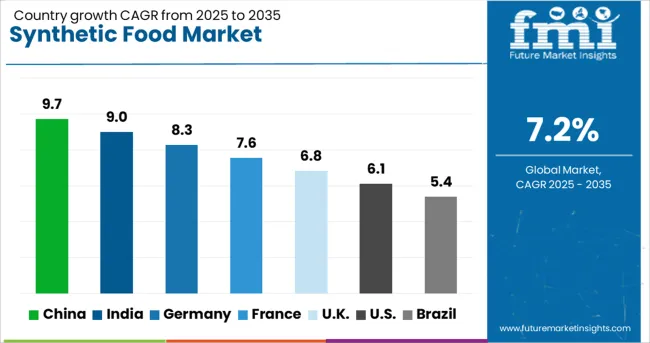
| Country | CAGR |
|---|---|
| China | 9.7% |
| India | 9.0% |
| Germany | 8.3% |
| France | 7.6% |
| UK | 6.8% |
| USA | 6.1% |
| Brazil | 5.4% |
The synthetic food market is anticipated to expand at a CAGR of 7.2% from 2025 to 2035, driven by regulatory shifts, climate-resilient food innovation, and demand for scalable protein alternatives. China is expected to grow at 9.7%, supported by its investment in cell-based meat and fermentation technologies. India follows with 9.0%, as plant-derived food ingredients and cultured dairy receive support through policy and startups. Germany, with a projected 8.3% growth, gains momentum from consumer awareness and EU-backed alternative protein initiatives. The UK market is likely to grow at 6.8%, owing to food-tech investments and demand for cruelty-free nutrition. The USA, expanding at 6.1%, is shaped by biotech-driven startups, sustainability regulations, and changing dietary preferences. This report includes insights on 40+ countries; the top markets are shown here for reference.
China is projected to expand at a CAGR of 9.7% in the synthetic food market between 2025 and 2035. This is supported by growing urban acceptance of lab-grown proteins, bioengineered dairy, and precision-fermented ingredients. State-backed biotechnology zones in cities like Shenzhen and Chengdu are promoting domestic synthetic food startups. Public demand for food security and controlled nutrition sources has pushed local players to develop allergen-free alternatives and nutrient-modified food products. E-commerce platforms have enabled early access to new food types among younger demographics.
India is expected to register a CAGR of 9.0% with increasing experimentation in synthetic eggs, cultured dairy, and bio-enhanced spices. Startups are using indigenous plant DNA for molecular food engineering tailored to local palates. State governments in Karnataka and Maharashtra have allocated grants for alternative protein labs. Rising middle-class health awareness, along with growing vegan interest, is creating demand for clean-label synthetic ingredients across cities. Partnerships with cloud kitchens are driving sampling of synthetically engineered items.
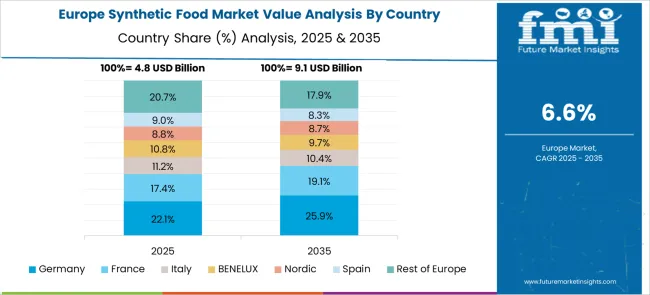
Germany is forecasted to grow at a CAGR of 8.3%, driven by demand for environmentally sustainable proteins, enzyme-enhanced flavors, and synthetic fats. Bioengineering research labs are collaborating with food brands to replicate traditional tastes in synthetic formats. Federal policy emphasis on circular bioeconomy supports the use of cell culture and fermentation technologies for alternative food sources. Consumer acceptance is rising due to clean nutrition and animal-welfare perceptions.
The United Kingdom is projected to grow at a CAGR of 6.8% due to the rising use of precision fermentation for hypoallergenic and fortified foods. Demand is driven by public health programs promoting synthetic food options for dietary-sensitive populations. Universities in London and Edinburgh are supporting early-stage development of lab-derived ingredients for school meals and elderly care. Ethical food consumers are embracing synthetic substitutes for traditional animal-based items.
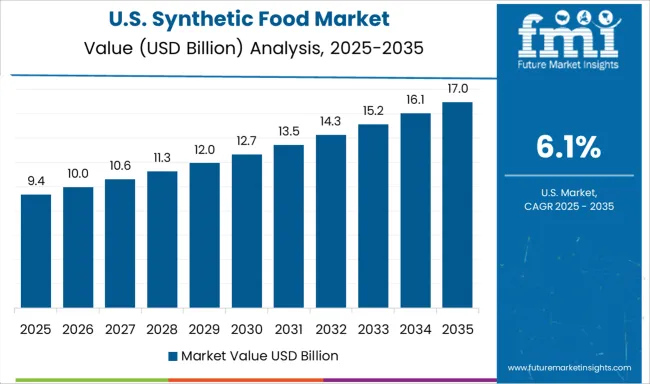
The United States is expected to register a CAGR of 6.1% with heavy investments from food-tech incubators and venture funds backing synthetic beef, gelatin, and oils. Silicon Valley and Boston remain the core hubs for lab-grown food innovation. Synthetic food is increasingly promoted through fitness platforms and meal-subscription services targeting performance-based nutrition. Regulatory reviews have focused on transparency and labeling, while acceptance is rising among urban Gen Z consumers.
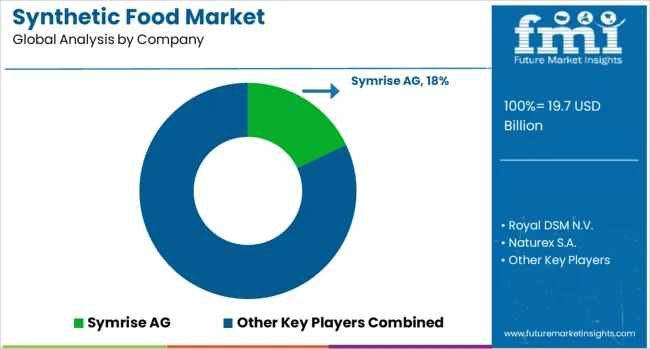
The synthetic food market comprises companies delivering artificial flavors, colors, preservatives, and enhancers designed to replicate or intensify sensory profiles in processed food applications. Market dynamics are shaped by rising demand for consistent product taste, appearance, and shelf life across mass-produced packaged foods, beverages, and confectionery. The sector’s competitiveness hinges on regulatory adherence, stability in extreme processing environments, and technological advancements in formulation accuracy and safety validation. Symrise AG, Sensient Technologies, and Flavorchem Corporation lead through diverse portfolios that cover synthetic flavors, emulsions, and aromatic chemicals used in global FMCG lines.
Royal DSM N.V. and BASF SE maintain strong positions in synthetic micronutrients, offering tailored solutions for fortified food and beverage products. Naturex S.A. and Döhler Group, though historically tied to natural ingredients, continue to supplement their synthetic lines to meet large-scale volume demands. Chr. Hansen A/S and Fiorio Colori focus on synthetic food dyes engineered for brightness, solubility, and heat resistance across applications in bakery, dairy, and beverage sectors. D.D. Williamson & Co. Inc. and Allied Biotech Corp provide high-performance coloring systems adaptable to pH, light, and oxidative challenges. FMC Corporation and Falcon Essential Oils maintain visibility in synthetic texturizers and flavoring agents. Biolandes SAS and Aarkay Food Products target niche bulk supply chains, while Archer Daniels Midland Company reinforces synthetic additive production as part of its broader food ingredient operations.
| Item | Value |
|---|---|
| Quantitative Units | USD 19.7 Billion |
| Product | Colors |
| Application | Flavour & Fragrances, Colors, Antioxidants, Hydrocolloids, Emulsifiers, and Fat Replacers |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America, Middle East & Africa |
| Country Covered | United States, Canada, Germany, France, United Kingdom, China, Japan, India, Brazil, South Africa |
| Key Companies Profiled | Symrise AG, Royal DSM N.V., Naturex S.A., Sensient Technologies, Falcon Essential Oils, Fiorio Colori, Flavorchem Corporation, FMC Corporation, D.D. Williamson & Co. Inc., Döhler Group, Chr. Hansen A/S, Biolandes SAS, BASF SE, Allied Biotech Corp, Archer Daniels Midland Company, and Aarkay Food Products |
| Additional Attributes | Dollar sales by product category and distribution channel, demand dynamics across meat analogs, dairy substitutes, and flavor enhancers, regional trends in consumption across North America, Europe, and Asia-Pacific, innovation in precision fermentation, cell-based food synthesis, and molecular gastronomy applications, environmental impact of land use reduction, water savings, and energy intensity of lab-based production, and emerging use cases in personalized nutrition, space exploration diets, and allergen-free food system development. |
The global synthetic food market is estimated to be valued at USD 19.7 billion in 2025.
The market size for the synthetic food market is projected to reach USD 39.5 billion by 2035.
The synthetic food market is expected to grow at a 7.2% CAGR between 2025 and 2035.
The key product types in synthetic food market are colors, _antioxidants, _flavour & fragrances, _hydrocolloids, _emulsifiers, _fat replacers and _enzymes.
In terms of application, flavour & fragrances segment to command 28.0% share in the synthetic food market in 2025.






Our Research Products

The "Full Research Suite" delivers actionable market intel, deep dives on markets or technologies, so clients act faster, cut risk, and unlock growth.

The Leaderboard benchmarks and ranks top vendors, classifying them as Established Leaders, Leading Challengers, or Disruptors & Challengers.

Locates where complements amplify value and substitutes erode it, forecasting net impact by horizon

We deliver granular, decision-grade intel: market sizing, 5-year forecasts, pricing, adoption, usage, revenue, and operational KPIs—plus competitor tracking, regulation, and value chains—across 60 countries broadly.

Spot the shifts before they hit your P&L. We track inflection points, adoption curves, pricing moves, and ecosystem plays to show where demand is heading, why it is changing, and what to do next across high-growth markets and disruptive tech

Real-time reads of user behavior. We track shifting priorities, perceptions of today’s and next-gen services, and provider experience, then pace how fast tech moves from trial to adoption, blending buyer, consumer, and channel inputs with social signals (#WhySwitch, #UX).

Partner with our analyst team to build a custom report designed around your business priorities. From analysing market trends to assessing competitors or crafting bespoke datasets, we tailor insights to your needs.
Supplier Intelligence
Discovery & Profiling
Capacity & Footprint
Performance & Risk
Compliance & Governance
Commercial Readiness
Who Supplies Whom
Scorecards & Shortlists
Playbooks & Docs
Category Intelligence
Definition & Scope
Demand & Use Cases
Cost Drivers
Market Structure
Supply Chain Map
Trade & Policy
Operating Norms
Deliverables
Buyer Intelligence
Account Basics
Spend & Scope
Procurement Model
Vendor Requirements
Terms & Policies
Entry Strategy
Pain Points & Triggers
Outputs
Pricing Analysis
Benchmarks
Trends
Should-Cost
Indexation
Landed Cost
Commercial Terms
Deliverables
Brand Analysis
Positioning & Value Prop
Share & Presence
Customer Evidence
Go-to-Market
Digital & Reputation
Compliance & Trust
KPIs & Gaps
Outputs
Full Research Suite comprises of:
Market outlook & trends analysis
Interviews & case studies
Strategic recommendations
Vendor profiles & capabilities analysis
5-year forecasts
8 regions and 60+ country-level data splits
Market segment data splits
12 months of continuous data updates
DELIVERED AS:
PDF EXCEL ONLINE
Synthetic Food Color Market Analysis - Size, Share, and Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Food & Beverage OEE Software Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Food Grade Crosslinked Polyvinylpolypyrrolidone (PVPP) Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Food Grade Cassia Gum Powder Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Food Grade Dry Film Lubricant Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Synthetic Dye Market Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Synthetic Data Generation Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Foodservice Equipment Market Analysis - Size, Share, and Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Food Basket Market Forecast and Outlook 2025 to 2035
Food Grade Tremella Polysaccharide Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Food Sorting Machine Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Synthetic Biology Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Foodservice Paper Bag Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Food Stabilizers Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Food Packaging Film Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Food Certification Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Food Tray Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Food & Beverage Industrial Disinfection and Cleaning Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Synthetic Abrasives Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Synthetic Zeolite Y Adsorbent Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035

Thank you!
You will receive an email from our Business Development Manager. Please be sure to check your SPAM/JUNK folder too.
Chat With
MaRIA