The voluntary carbon credit market is projected to expand from USD 2.1 billion in 2025 to USD 19.8 billion by 2035, reflecting a robust compound annual growth rate of 25.0%. Analysis of the cost structure reveals that primary expenditures are concentrated in project development, verification, and certification, which together account for a substantial portion of total costs.
Project development encompasses activities such as site identification, feasibility studies, and implementation of carbon reduction or sequestration initiatives. Verification and certification costs include third-party audits, monitoring systems, and compliance with standards set by recognized registries, ensuring credibility and market acceptance of carbon credits. Downstream, the value chain extends to brokers, exchanges, and corporate purchasers, where transaction fees, market liquidity, and pricing volatility influence margins. Trading platforms add value through aggregation, standardization, and facilitation of credit transactions, while corporate and institutional buyers contribute demand-driven revenue flows.
The market also incurs administrative and regulatory compliance costs, which are necessary to maintain transparency and integrity within voluntary carbon markets. Cost optimization along this value chain is increasingly achieved through technological adoption, including digital monitoring, blockchain-based verification, and remote sensing, which reduce operational expenditures and enhance traceability. The value chain demonstrates a vertically integrated model where project developers, verifiers, and intermediaries collectively contribute to market growth, and efficiency improvements at each stage are critical to sustaining profitability while meeting the escalating demand for verified carbon credits.
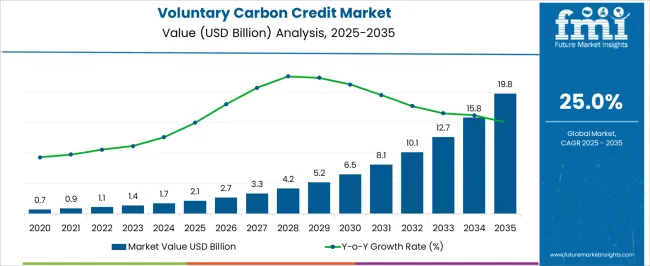
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Voluntary Carbon Credit Market Estimated Value in (2025 E) | USD 2.1 billion |
| Voluntary Carbon Credit Market Forecast Value in (2035 F) | USD 19.8 billion |
| Forecast CAGR (2025 to 2035) | 25.0% |
The voluntary carbon credit market represents a specialized segment within the broader carbon trading and environmental finance industry, emphasizing emissions offsetting and corporate climate action. Within the overall carbon markets sector, it accounts for about 6.2%, driven by corporate commitments to reduce net carbon footprints. In the renewable energy and forestry project development segment, it holds nearly 5.7%, reflecting credits generated from reforestation, wind, solar, and methane capture projects. Across the corporate sustainability and ESG initiatives market, the segment captures 4.3%, supporting voluntary reporting and climate pledges.
Within the green finance and investment category, it represents 3.9%, highlighting integration into ESG-linked investment portfolios. In the environmental consulting and certification sector, it secures 2.8%, emphasizing verification, auditing, and market credibility. Recent developments in this market have focused on transparency, digitalization, and diversified project types. Innovations include blockchain-enabled tracking platforms for secure and verifiable carbon credit issuance and retirement. Key players are collaborating with project developers, corporations, and financial institutions to expand credit supply and ensure quality standards.
Satellite monitoring, AI-based verification, and IoT sensors are increasingly applied to track project performance and emissions reductions. Methodologies for new project types, including blue carbon, regenerative agriculture, and biochar initiatives, are gaining attention. The voluntary carbon credit pricing mechanisms are evolving to incentivize high-impact and co-benefit projects. These advancements demonstrate how integrity, technology integration, and innovative project design are shaping the voluntary carbon credit market.
The voluntary carbon credit market is gaining momentum as organizations across sectors commit to achieving net-zero targets and enhancing sustainability profiles. Corporate disclosures and environmental reports have highlighted a growing shift toward voluntary offset mechanisms as a complementary strategy to emission reduction initiatives.
The market has benefited from increased participation by private enterprises, financial institutions, and multinational corporations seeking to meet investor and consumer expectations for climate accountability. Innovations in carbon offset verification, blockchain-based tracking systems, and standardized certification protocols have improved transparency and trust in credit transactions.
Additionally, expanding awareness of climate risk mitigation and the alignment of carbon credit projects with the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) are strengthening the market’s appeal. Looking ahead, the voluntary carbon credit market is expected to grow through greater integration into corporate ESG frameworks, rising demand for nature-based solutions, and increased investments in renewable energy, reforestation, and carbon capture projects.
The voluntary carbon credit market is segmented by end use and geographic regions. By end use, voluntary carbon credit market is divided into Renewable Energy, Agriculture, Carbon Capture & Storage, Chemical Process, Household & Community, Industrial & Commercial, Forestry & Land use, Waste Management, and Others. Regionally, the voluntary carbon credit industry is classified into North America, Latin America, Western Europe, Eastern Europe, Balkan & Baltic Countries, Russia & Belarus, Central Asia, East Asia, South Asia & Pacific, and the Middle East & Africa.
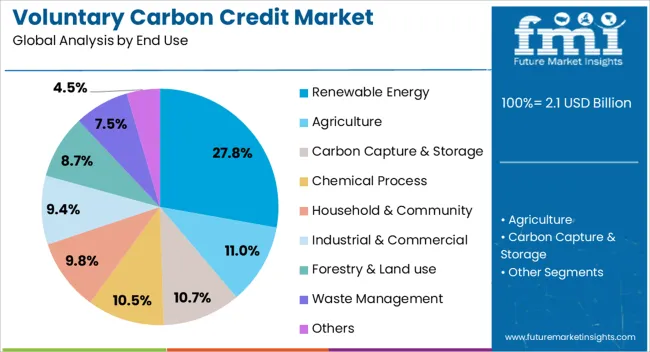
The Renewable Energy segment is projected to account for 27.8% of the voluntary carbon credit market revenue in 2025, establishing itself as one of the leading end-use categories. Growth in this segment has been driven by the role of renewable energy projects in displacing fossil fuel-based electricity generation, thereby generating high-quality, verifiable carbon credits.
Wind, solar, hydro, and geothermal projects have been widely adopted in both developed and emerging markets, supported by favorable policy environments and green financing instruments. Buyers in the voluntary carbon credit market have shown strong interest in renewable energy credits due to their direct link to long-term decarbonization goals and their contribution to sustainable development.
Corporate sustainability programs often prioritize renewable energy offsets as they align with Scope 2 emission reduction strategies while providing co-benefits such as local employment and energy access. With continuous investment in clean energy infrastructure and the global shift toward low-carbon power generation, the Renewable Energy segment is expected to maintain its strong position within the voluntary carbon credit market.
The market has been expanding rapidly as companies, governments, and organizations seek to offset greenhouse gas emissions beyond mandated regulatory requirements. Carbon credits represent quantified, verified reductions or removals of carbon dioxide or equivalent gases, allowing entities to meet sustainability goals, achieve net-zero commitments, and participate in carbon trading initiatives. The market encompasses projects such as reforestation, renewable energy, soil carbon sequestration, and methane capture. Growing corporate responsibility, investor pressure, and public scrutiny on environmental performance have driven demand for verified credits.
Corporate adoption of voluntary carbon credits has been a key driver of market growth as organizations seek to demonstrate climate responsibility and achieve net-zero or carbon-neutral commitments. Companies in energy, transportation, technology, and consumer goods sectors are increasingly incorporating carbon offsetting strategies into ESG frameworks. Voluntary carbon credits are purchased to compensate for emissions that are difficult to eliminate internally, such as scope 3 emissions from supply chains. The integration of carbon credits into sustainability reporting enhances brand reputation and aligns with stakeholder expectations. Investment in renewable energy, reforestation, and methane capture projects has been incentivized by demand from corporations looking for credible and verified reductions. Transparent MRV systems and third-party verification help ensure the reliability of these credits, making corporate participation a major factor in market expansion.
The evolution of monitoring, reporting, and verification technologies has enhanced the integrity and reliability of the voluntary carbon credit market. Satellite imagery, remote sensing, IoT-based monitoring, and blockchain-enabled registries are increasingly used to track carbon sequestration projects and emission reductions. These technological innovations ensure transparency, prevent double counting, and validate carbon removal claims, building confidence among buyers and investors. Digital platforms also allow trading of credits with real-time pricing and project tracking, increasing liquidity and accessibility. Furthermore, improved methodologies for calculating carbon reductions in forestry, agriculture, and renewable energy projects have standardized reporting practices. Technological integration has therefore strengthened market trust, enabling wider adoption by corporations, financial institutions, and voluntary participants seeking high-quality and verifiable carbon credits.
Market growth has been fueled by the diversification of carbon reduction projects, offering a broad spectrum of options for buyers and investors. Forestry-based initiatives, including afforestation, reforestation, and avoided deforestation, remain popular due to their high carbon sequestration potential and co-benefits for biodiversity. Renewable energy projects, such as wind, solar, and biomass generation, provide measurable reductions while supporting clean energy transition. Other innovative projects, including soil carbon enhancement, blue carbon, and methane capture from landfills, are gaining traction. This diversification allows participants to select credits aligned with environmental, social, and governance priorities, while promoting localized sustainable development. By offering a wide range of project types, the market addresses varying corporate sustainability needs, enhancing participation and market liquidity.
Despite growth, the voluntary carbon credit market faces challenges related to standardization, pricing transparency, and regulatory alignment. Differences in methodologies, verification standards, and registries can result in inconsistencies and concerns about credit quality. Price volatility, influenced by demand-supply dynamics, may affect investment decisions. Moreover, alignment with emerging regulatory frameworks, such as national carbon pricing schemes and international climate agreements, is critical to avoid double-counting or invalid credits. Market participants must navigate these complexities while ensuring credible reporting and sustainable project execution. Enhanced governance, adoption of internationally recognized standards, and robust certification mechanisms are expected to improve market confidence, ensuring long-term viability and facilitating the continued growth of voluntary carbon credit initiatives globally.
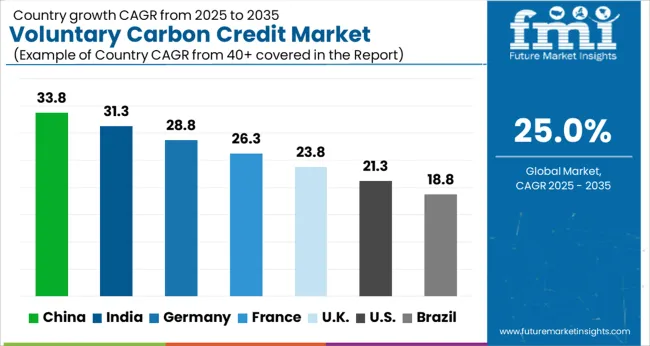
| Country | CAGR |
|---|---|
| China | 33.8% |
| India | 31.3% |
| Germany | 28.8% |
| France | 26.3% |
| UK | 23.8% |
| USA | 21.3% |
| Brazil | 18.8% |
The market is expanding rapidly as governments and corporations increase commitments to carbon neutrality. China leads with a projected growth rate of 33.8%, driven by large-scale carbon trading initiatives and renewable energy projects. India follows at 31.3%, supported by growing adoption of carbon offset programs in the agriculture and energy sectors. Germany records 28.8% due to strong regulatory frameworks and corporate sustainability commitments.
The United Kingdom reaches 23.8%, fueled by investments in carbon capture and green finance mechanisms. The United States maintains 21.3%, where corporate ESG strategies and voluntary offsets continue to drive market activity. Together, these countries represent the primary hubs for trading, innovation, and adoption in the voluntary carbon credit market. This report includes insights on 40+ countries; the top markets are shown here for reference.
China market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 33.8%, fueled by rising government initiatives to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and increasing corporate participation in carbon offset programs. The market is being shaped by rising regulatory frameworks, corporate sustainability targets, and growing awareness of environmental responsibility. Demand is particularly high among the manufacturing, energy, and transport sectors seeking to meet emission reduction commitments. Investments in carbon trading platforms and technology-enabled verification processes are supporting market development. Strategic collaborations between local firms and international sustainability organizations are enabling the adoption of standardized carbon credit solutions. With the increasing focus on net-zero targets, China’s market is witnessing rapid adoption and diversification across various carbon credit mechanisms.
India is expected to expand at a CAGR of 31.3%, driven by government incentives, renewable energy adoption, and corporate ESG commitments. Companies across power, transport, and industrial sectors are increasingly participating in voluntary carbon offset schemes to comply with national climate goals.
Technological advancements in monitoring and verification of carbon credits are supporting transparency and credibility. Rising awareness among businesses and investors regarding climate action is accelerating market adoption. Indian firms are forming strategic alliances with global carbon registries and consulting organizations to facilitate standardization and maximize environmental benefits. The combined effect of regulatory support, renewable energy penetration, and corporate sustainability initiatives is reinforcing strong market growth potential.
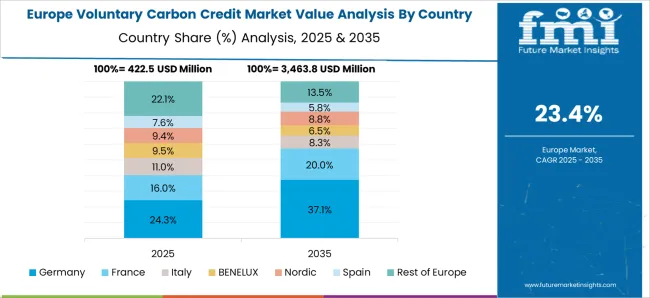
Germany is anticipated to grow at a CAGR of 28.8%, supported by stringent environmental regulations and proactive corporate climate action. Demand is particularly strong in the renewable energy, transportation, and manufacturing sectors, where emissions reduction is a priority. Companies are increasingly adopting standardized carbon credit schemes to meet net-zero and ESG commitments. Germany’s advanced sustainability framework encourages verification, auditing, and reporting of carbon offset initiatives. Strategic collaborations between local enterprises and international organizations are fostering market credibility and innovation. Awareness campaigns, government support, and increasing demand for green products are collectively driving the market. Focus on digital platforms for carbon trading and transparent reporting is further enhancing growth.
The United Kingdom’s market is projected to expand at a CAGR of 23.8%, driven by strong regulatory oversight and heightened corporate environmental responsibility. Adoption is high across energy, transportation, and industrial sectors seeking to offset emissions and achieve net-zero targets. Increasing investments in technology platforms that monitor, validate, and trade carbon credits are enhancing market efficiency. UK companies are collaborating with global carbon standards organizations to ensure the transparency and integrity of carbon offset schemes. Public awareness regarding climate change, along with incentives for corporate sustainability, is stimulating demand. The growing market for green products and services, combined with government-backed initiatives, is expected to accelerate adoption during the forecast period.
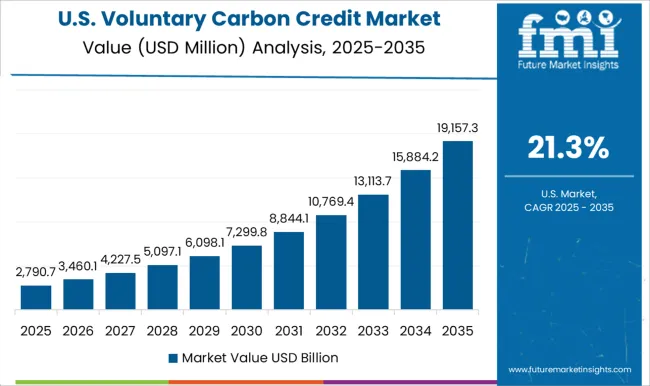
The United States market is anticipated to grow at a CAGR of 21.3%, supported by strong corporate climate commitments and regulatory encouragement. Companies in the energy, manufacturing, and transportation sectors are increasingly participating in voluntary carbon offset programs to meet ESG and net-zero targets. Advanced digital platforms for carbon tracking and validation are improving market transparency and efficiency. Strategic collaborations with international registries and certification bodies are enhancing credibility and adoption. Growing awareness of climate change and consumer preference for environmentally responsible products is driving demand for carbon credits. The combination of technological adoption, regulatory support, and market-driven sustainability initiatives is fostering steady growth across the country.
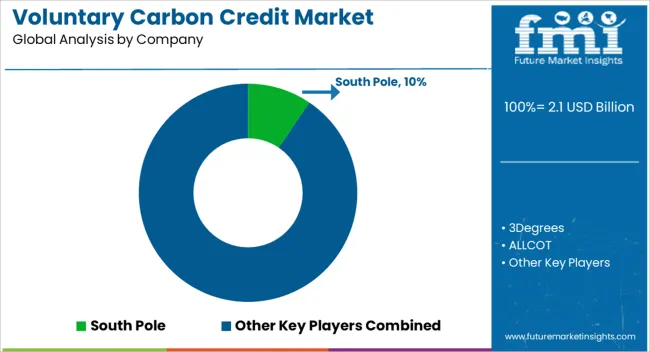
The market is shaped by organizations facilitating carbon offsetting through verified emission reduction projects and sustainability initiatives. South Pole, 3Degrees, and ALLCOT are key players offering diverse carbon credit portfolios from forestry, renewable energy, and community-based projects, enabling corporates and individuals to neutralize their carbon footprint. Atmosfair and CarbonClear specialize in high-quality, certified carbon offsets, emphasizing transparency, traceability, and alignment with global standards for environmental impact. ClimeCo and Climate Impact Partners focus on large-scale industrial and energy sector clients, providing customized solutions for emission reduction and sustainability reporting. EcoAct, Ecosecurities, and The Carbon Trust leverage expertise in project validation, carbon accounting, and advisory services to ensure market credibility.
Leading corporations such as Microsoft, Shell, and PwC actively participate in voluntary carbon markets to achieve net-zero commitments, integrating carbon credits into broader corporate sustainability strategies. TerraPass, VERRA, and The Carbon Collective Company enhance market accessibility, providing standardized, verifiable credits that support global climate action and the transition to low-carbon economies.
| Item | Value |
|---|---|
| Quantitative Units | USD 2.1 Billion |
| End Use | Renewable Energy, Agriculture, Carbon Capture & Storage, Chemical Process, Household & Community, Industrial & Commercial, Forestry & Land use, Waste Management, and Others |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America, Middle East & Africa |
| Country Covered | United States, Canada, Germany, France, United Kingdom, China, Japan, India, Brazil, South Africa |
| Key Companies Profiled | South Pole, 3Degrees, ALLCOT, Atmosfair, CarbonClear, ClimeCo, Climate Impact Partners, EcoAct, Ecosecurities, Microsoft, PwC, Shell, TerraPass, The Carbon Collective Company, The Carbon Trust, and VERRA |
| Additional Attributes | Dollar sales by credit type and project category, demand dynamics across corporate, industrial, and financial sectors, regional trends in carbon offset adoption, innovation in verification, tracking, and reporting technologies, environmental impact of emission reduction projects, and emerging use cases in sustainable supply chains, net-zero strategies, and climate finance initiatives. |
The global voluntary carbon credit market is estimated to be valued at USD 2.1 billion in 2025.
The market size for the voluntary carbon credit market is projected to reach USD 19.8 billion by 2035.
The voluntary carbon credit market is expected to grow at a 25.0% CAGR between 2025 and 2035.
The key product types in voluntary carbon credit market are renewable energy, agriculture, carbon capture & storage, chemical process, household & community, industrial & commercial, forestry & land use, waste management and others.






Full Research Suite comprises of:
Market outlook & trends analysis
Interviews & case studies
Strategic recommendations
Vendor profiles & capabilities analysis
5-year forecasts
8 regions and 60+ country-level data splits
Market segment data splits
12 months of continuous data updates
DELIVERED AS:
PDF EXCEL ONLINE
Carbon Enhanced Lead Acid Battery Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Carbon-negative Cement Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Carbon Tetrabromide Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Carbon Steel Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Carbon Brush Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Carbon Offset Platform Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Carbon Tapes Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Carbon-Free Waste Gas Abatement System Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Carbon Labeled Packaged Meal Market Analysis - Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Carbon Fiber Bike Wheelset Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Carbon Dioxide Lasers Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Carbon-negative Packaging Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Carbon Fiber Construction Repair Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Carbon-Dioxide Synthesis Cosmetics Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Carbon-Neutral Skincare Ingredients Market Analysis - Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Carbonate Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Carbon Fiber Reinforced Plastic Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Carbon Fiber Wraps Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Carbon Fiber Boat Hulls Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Carbon Textile Reinforced Concrete Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035

Thank you!
You will receive an email from our Business Development Manager. Please be sure to check your SPAM/JUNK folder too.
Chat With
MaRIA