The global automotive market is expected to reach USD 4544 billion in 2025, advancing at a CAGR of 5.6% through 2035. This places the projected market size at approximately USD 7822.1 billion by 2035.
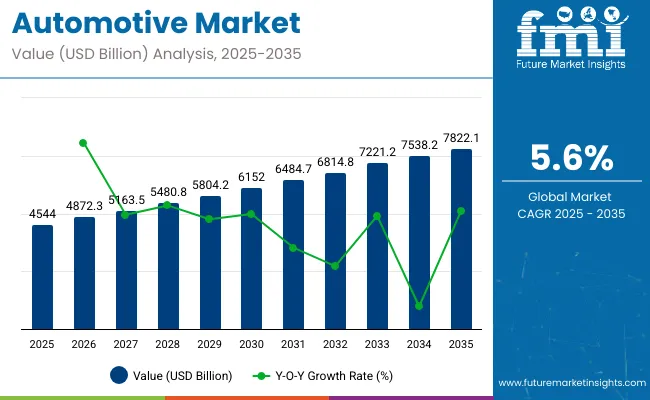
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Industry Size (2025E) | USD 4544 billion |
| Industry Value (2035F) | USD 7822.1 billion |
| CAGR (2025 to 2035) | 5.6% |
Year-on-year progression exhibits a balanced curve with consistent expansion driven by EV integration, connected mobility, and aftermarket digitalization. From 2025 to 2026, incremental revenue is projected near USD 254 billion, followed by rising annual contributions averaging USD 300 billion between 2027 and 2030. The YoY growth rate remains within a controlled band of 5.2% to 5.8%, indicating equilibrium between supply chain recalibration and vehicle demand resurgence across ASEAN, NAFTA, and select OECD economies.
Mild YoY growth spikes are expected in 2029 and 2032, coinciding with policy resets related to emission standards and green vehicle subsidies. The luxury and utility vehicle segments remain volume stabilizers, while alternative drivetrains and fleet electrification contribute to above-average YoY gains post-2030. The curve does not suggest volatility, it reflects structured step-wise growth, typical of high-capex sectors under regulatory oversight.
The absence of negative or erratic YoY dips supports the interpretation that the market is shifting toward predictable scale, aligned with macroeconomic normalization. This structure favors OEM capacity planning and ecosystem-level demand forecasting over the long term.ult, Ford, BMW, Nissan
The automotive sector operates across several industrial parent categories. Roughly 60% of global vehicle output has been attributed to automotive manufacturing, encompassing personal and fleet transport segments. It occupies close to 70% of the transportation equipment sector, reflecting extensive integration across on-road mobility infrastructure.
As part of the machinery and equipment industry, it contributes about 40% of operational share due to complex assembly and component integration. Approximately 25% of total steel usage has been absorbed by this sector, particularly in structural frames, drive systems, and underbody components. Automotive electronics now account for 35% of system architecture, reinforcing the transition toward electrical and digital vehicle ecosystems.
Investment strategies have shifted toward software-based integration, with over 30% of product development focusing on digital control modules, adaptive navigation, and semi-automated driving capabilities. Electrified vehicle sales now comprise 15% of global new vehicle purchases, supported by charging infrastructure build-outs.
Materials substitution practices such as composite alloy usage have been adopted across 45% of new production lines to reduce mass and improve efficiency. Localization efforts across component sourcing networks have been accelerated to counter delays and regional exposure risks. Autonomous driving features at limited automation levels have entered 20% of models produced in high-volume manufacturing regions.
The automotive market has been reshaped by shifting vehicle demand, electrified drivetrains, and digitized control systems. SUVs and hybrid formats have driven production alignment and procurement patterns across OEMs and suppliers. Regulatory frameworks in OECD and ASEAN countries have pushed R&D toward emission-reduction technologies and alternative powertrains.
Infotainment, ADAS, and in-vehicle connectivity features have entered mass adoption cycles, restructuring value chains from Tier 1 to assembly. Over the 2025 to 2035 period, EV incentives and digital upgrades are expected to drive consistent volume shifts.
Electric drivetrains have become integrated across 15% of global vehicle production platforms. Investment prioritization has shifted to support hybrid formats and connected services, particularly across OECD cities. Low-emission vehicle incentives have encouraged EV uptake in Europe, China, and India.
Fleet electrification in ASEAN and North America has led to logistics cost reductions. OEMs have retooled production to accommodate these new architectures. Connected vehicles have expanded OEM revenue via telematics and OTA updates. Hybrid vehicle usage has grown in Japan and Germany.
Global supply chains have faced disruptions due to rare earth shortages and semiconductor deficits. Battery costs have become volatile due to fluctuations in cobalt and lithium pricing. OEMs in Southeast Asia and Eastern Europe have experienced delayed production cycles.
Supplier networks have struggled to pivot from legacy parts to EV-compatible systems. High capital requirements for electrification and infrastructure have delayed fleet transitions. Regulatory inconsistencies across LATAM and ASEAN have slowed platform certification. Labor shortages continue to impact high-skill assembly operations.
Aftermarket platforms have captured consumer spending via predictive maintenance and subscription models. Lightweighting with aluminum and composites has improved fuel efficiency in hybrid vehicles. Digital upgrades for navigation, diagnostics, and vehicle security have drawn urban buyers.
Software collaborations have enabled real-time vehicle analytics across new models. Fleet operators have increasingly adopted hybrid low-maintenance formats. Circular design using modular components has reduced production waste. EV systems with V2G capabilities have gained pilot traction in Japan and select EU zones.
Vehicle manufacturers have shifted toward mobility services and real-time connectivity. Shared mobility models have expanded urban use cases across OECD economies. Subscription-based ownership and ride-hailing have changed consumer access patterns.
Fuel cell trucks are being deployed in long-haul routes in California, Korea, and Germany. Software-defined architectures now allow frequent feature updates and diagnostics. Manufacturing units have begun sourcing renewable energy across multiple zones. Autonomous and robotics-driven testing is underway in Japan, Israel, and the United States.
The automotive market in 2025 will be shaped by high-performing segments that continue to dominate global demand patterns. Passenger cars will retain the largest share by type, followed by internal combustion engines as the primary fuel category despite rising electrification.
Dealerships remain the leading sales channel due to customer dependence on physical interactions and bundled service options. Compact vehicles will lead based on size preference driven by cost and urban space limitations. While electric vehicles are gaining momentum, they still represent a smaller portion of the total market volume.
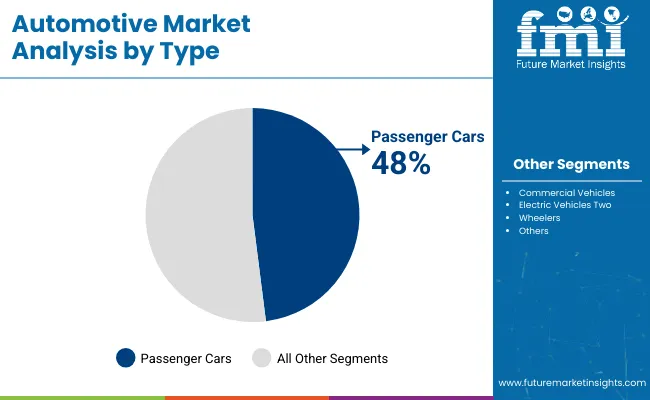
in 2025 Passenger cars are forecasted to hold a dominant 48% market share in 2025 by type, driven by continuous demand from both developed and emerging economies. Companies like Toyota, Hyundai, and Volkswagen are scaling production and investing in new variants, especially hybrid sedans and compact crossovers.
Urban population density and reliance on personal mobility have kept passenger vehicles ahead of other types. Automakers are enhancing fuel efficiency, infotainment systems, and in-vehicle safety features to maintain their competitive edge. The flexibility in design, affordability, and usability across age groups and income classes keeps this segment consistently high in purchase frequency.
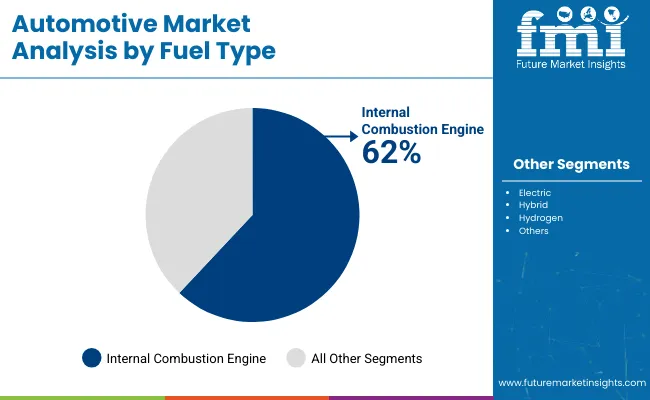
Iin 2025 Internal combustion engines are expected to maintain their leadership with a 62% market share by fuel type in 2025, supported by widespread infrastructure and affordability across multiple regions. Brands including Honda, Suzuki, and Ford continue to manufacture combustion-powered vehicles for regions with limited EV infrastructure.
The lack of universal EV charging networks, especially in Africa, ASEAN, and Latin America, has allowed ICE models to remain competitive. Enhancements in emission control technologies and dual-fuel variants are helping automakers meet evolving regulatory benchmarks without drastically changing vehicle platforms, making ICEs a transitional solution for most emerging and middle-income automotive markets.
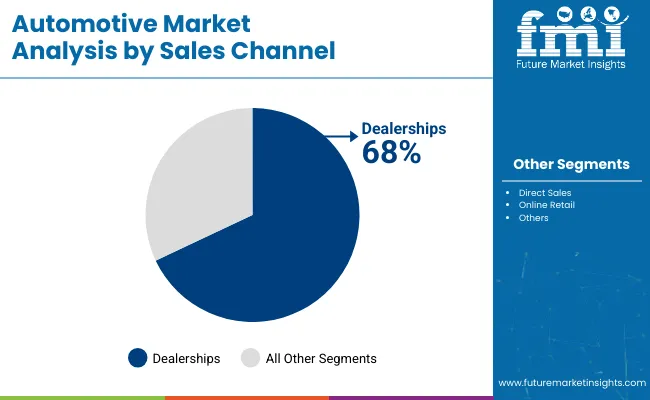
in 2025 Dealerships will continue to dominate the automotive distribution landscape with a 68% share by sales channel in 2025, supported by consumer trust, financing services, and test-drive access. Brands such as Tata Motors, Kia, and Nissan are expanding dealership footprints in lower-tier cities to capture rural and semi-urban demand.
Digital sales portals remain supplementary, especially for premium and high-value vehicles where physical verification is crucial. Dealerships also manage vehicle registration, insurance, and warranty processing, offering bundled advantages that digital platforms cannot yet replicate at scale. Despite the growth of e-commerce, the value proposition of in-person sales continues to deliver better conversion rates.
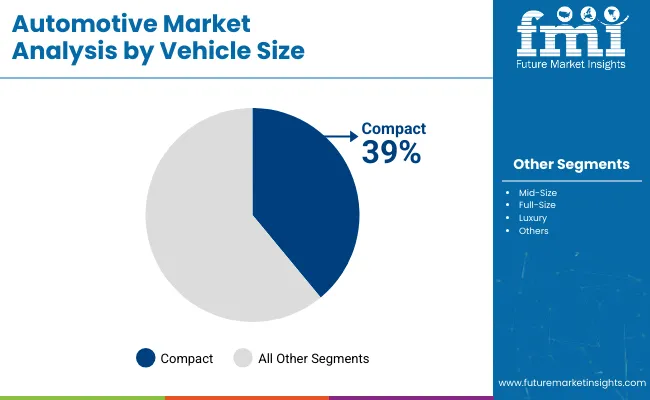
Compact vehicles are projected to lead by vehicle size with a 39% share in 2025, reflecting sustained consumer interest in low-maintenance, city-friendly, and budget-oriented models. Automakers such as Maruti, Dacia, and Renault are strengthening their position through diverse compact offerings, including hatchbacks and small sedans.
These vehicles benefit from lower registration costs, tax breaks, and fuel savings, especially in urban environments with limited parking. Regulatory frameworks in countries like India and Brazil incentivize sub-4 meter cars, ensuring higher adoption rates. Enhancements such as smart infotainment, crash sensors, and digital dashboards are being added without significantly affecting price brackets.
Electric vehicles are anticipated to capture 15% of the global automotive market by type in 2025, underpinned by government incentives and OEM investments in battery technology. Tesla, BYD, and Volkswagen are leading EV innovation through localized manufacturing and integrated battery supply chains.
EV sales are growing across urban regions in Europe and Asia, where charging infrastructure is more developed and policy support is stronger. Adoption in commercial fleets and car-sharing models is also contributing to volume growth. While EVs still face adoption barriers in terms of price and infrastructure in many countries, OEMs are focusing on modular EV platforms for long-term cost reduction.
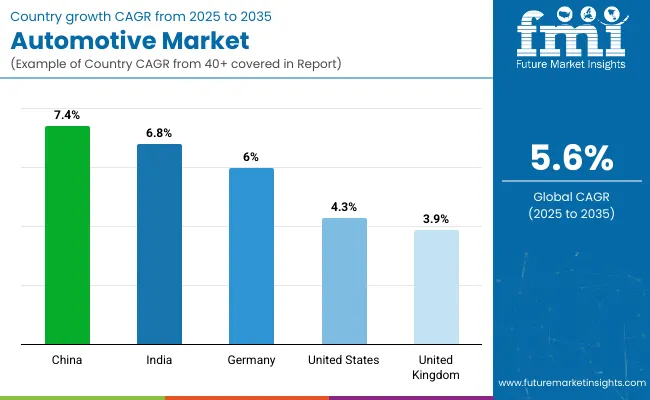
The global automotive market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 5.6% from 2025 to 2035. China (BRICS) records the highest growth at 7.4%, which is 1.8% above the global average. India (BRICS) follows at 6.8%, exceeding the average by 1.2%. Among OECD economies, Germany posts 6.0%, showing a 0.4% advantage. The United States is projected at 4.3%, trailing the global rate by 1.3%, while the United Kingdom shows the lowest at 3.9%, falling short by 1.7%.
The higher growth in BRICS countries reflects volume-led domestic production and policy-linked vehicle manufacturing incentives. OECD markets show lower growth due to mature ownership levels and tighter regulatory compliance timelines. ASEAN countries, although not listed, continue to build local supply chains, with some outperforming OECD averages in assembly and sales growth, especially where tariff-free trade and CKD strategies are being applied within the bloc.
United States is forecast to grow at a CAGR of 4.3%, placing it 23% below the global average. EV growth has remained strongest in coastal states while rural regions continue to favor gasoline-based vehicles. Infrastructure rollouts for electric vehicle charging have been initiated, but regional disparities limit uniform adoption.
Automotive manufacturing has been influenced by retooling delays and semiconductor constraints. Expansion has focused on larger vehicle formats including SUVs and pickups, with sedans experiencing steady decline. Domestic output is being impacted by shifting consumer preferences, labor costs, and the pace of technological integration across OEMs.
United Kingdom is anticipated to grow at a CAGR of 3.9%, trailing the global rate by 30%. Trade complexities following Brexit and raw material sourcing limitations have disrupted momentum. Low-emission zones have created urban demand for hybrid models, while battery electric vehicles have underperformed relative to continental benchmarks.
Manufacturing remains reliant on export-oriented luxury models, but localized production volumes have not yet recovered to pre-pandemic levels. Capacity and workforce issues persist, particularly in the Midlands. Strategic repositioning has focused on emissions regulation compliance and retention of European market access.
Germany is expected to expand at a CAGR of 6.0%, slightly above the global benchmark. Regulatory alignment with the European Green Deal has accelerated hybrid and electric vehicle production. Strong performance has been driven by high-margin vehicle exports, with OEM concentration in Bavaria and Baden-Württemberg.
Government-supported battery initiatives have improved production independence. Hydrogen-fueled vehicle R&D has gained public sector backing. Growth has been supported by efficient integration between Tier 1 suppliers and final assemblers, particularly in energy-dense vehicle formats for global export markets.
China is forecast to grow at a CAGR of 7.4%, outperforming the global average by 32%. Electrification has been pushed through subsidy-supported policies in Tier 2 and Tier 3 cities. NEV (New Energy Vehicle) programs have created dominant domestic brands while reducing dependence on imported components.
Provincial-level manufacturing hubs have been integrated into global trade routes, enabling cost-effective export of assembled vehicles. Sectoral growth has concentrated on low-emission compact models and mid-range EVs serving Southeast Asia and Latin America.
India is projected to grow at a CAGR of 6.8%, second only to China among the profiled nations. Growth has been supported by surging two-wheeler and compact car registrations, primarily in Tier 2 cities. Fiscal incentives have been introduced to localize electric vehicle manufacturing and battery production.
State-level EV policies have encouraged adoption through reduced GST rates and infrastructure grants. Market composition remains dominated by low-cost segments, although mid-range hybrid offerings are gaining traction. Logistics fleet electrification and charging station expansions are supporting broader ecosystem growth.
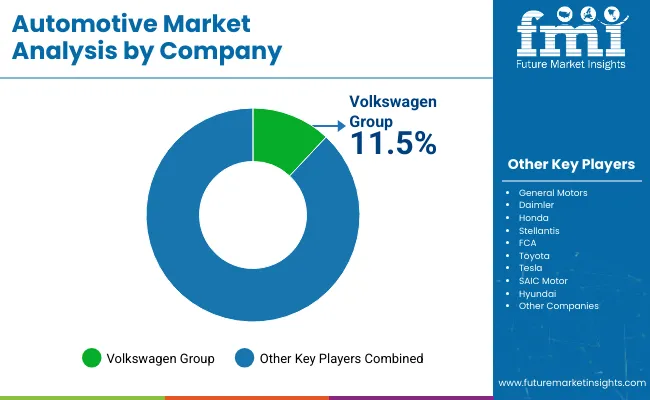
The automotive sector is shaped by dominant manufacturers and evolving regional suppliers who are expanding through model upgrades, dealership growth, and production realignment. Volkswagen Group has maintained market depth by expanding domestic production hubs and upgrading core vehicle lines across multiple regions. General Motors has shifted focus toward localized procurement strategies and platform consolidation, targeting cost optimization in Latin America and Southeast Asia.
Toyota and Honda have refined mid-range offerings to strengthen distribution in high-volume regions. Ford and Groupe Renault have pursued commercial fleet partnerships to improve distribution scale. Tesla has continued to build vertically integrated supply chains through large-scale gigafactory projects in Germany, China, and the USA.
Stellantis and FCA are maximizing shared platforms to reduce production complexity. BMW and Daimler have restructured R&D allocation, with a focus on driveline efficiency and global platform modularity. Hyundai and SAIC Motor are building region-specific models aligned with local demand.
Mid-tier and emerging automotive suppliers have entered new markets through small-scale production, regionally tailored vehicle types, and local distribution alliances. Eastern European and ASEAN-based companies have focused on cost-effective variants supported by government procurement. Distribution partnerships and model co-development with local vendors have enabled faster access to regulated markets. Brand recognition, logistics scale, and compliance costs continue to favor long-term incumbents.
Recent Industry News
| Report Attributes | Details |
|---|---|
| Market Size (2025) | USD 4544 billion |
| Projected Market Size (2035) | USD 7822.1 billion |
| CAGR (2025 to 2035) | 5.6% |
| Base Year for Estimation | 2024 |
| Historical Period | 2020 to 2024 |
| Projections Period | 2025 to 2035 |
| Quantitative Units | USD billion for value and volume units as applicable |
| Vehicle Types Analyzed (Segment 1) | Passenger Cars, Commercial Vehicles, Electric Vehicles, Two Wheelers |
| Fuel Types Analyzed (Segment 2) | Internal Combustion Engine, Electric, Hybrid, Hydrogen |
| Sales Channels Analyzed (Segment 3) | Direct Sales, Dealerships, Online Retail |
| Vehicle Sizes Analyzed (Segment 4) | Compact, Mid-Size, Full-Size, Luxury |
| Regions Covered | North America; Latin America; Western Europe; Eastern Europe; Asia Pacific; Middle East and Africa |
| Countries Covered | United States, Canada, Brazil, Mexico, Germany, United Kingdom, France, Italy, China, Japan, India, UAE, South Africa |
| Key Players Influencing the Market | Volkswagen Group, General Motors, Daimler, Honda, Stellantis, FCA, Toyota, Tesla, SAIC Motor, Hyundai, Groupe Renault, Ford, BMW, Nissan, Others |
| Additional Attributes | Dollar sales by vehicle type (EVs, ICE, hybrids) and segment (passenger, commercial), demand driven by electrification and shared mobility, regional leadership in China and North America, innovation in autonomous systems and lightweight materials, environmental gain via lower emissions, and emerging use cases in mobility-as-a-service ecosystems and smart fleet operations. |
The market is expected to reach USD 7822.1 billion by 2035.
The global market is projected to grow at a 5.6% CAGR during this period.
Passenger cars are forecast to account for 48% of total vehicle sales in 2025.
Internal combustion engines are anticipated to hold a 62% share by fuel type in 2025.
Volkswagen Group leads with an 11.5% share of the global automotive market.






Our Research Products

The "Full Research Suite" delivers actionable market intel, deep dives on markets or technologies, so clients act faster, cut risk, and unlock growth.

The Leaderboard benchmarks and ranks top vendors, classifying them as Established Leaders, Leading Challengers, or Disruptors & Challengers.

Locates where complements amplify value and substitutes erode it, forecasting net impact by horizon

We deliver granular, decision-grade intel: market sizing, 5-year forecasts, pricing, adoption, usage, revenue, and operational KPIs—plus competitor tracking, regulation, and value chains—across 60 countries broadly.

Spot the shifts before they hit your P&L. We track inflection points, adoption curves, pricing moves, and ecosystem plays to show where demand is heading, why it is changing, and what to do next across high-growth markets and disruptive tech

Real-time reads of user behavior. We track shifting priorities, perceptions of today’s and next-gen services, and provider experience, then pace how fast tech moves from trial to adoption, blending buyer, consumer, and channel inputs with social signals (#WhySwitch, #UX).

Partner with our analyst team to build a custom report designed around your business priorities. From analysing market trends to assessing competitors or crafting bespoke datasets, we tailor insights to your needs.
Supplier Intelligence
Discovery & Profiling
Capacity & Footprint
Performance & Risk
Compliance & Governance
Commercial Readiness
Who Supplies Whom
Scorecards & Shortlists
Playbooks & Docs
Category Intelligence
Definition & Scope
Demand & Use Cases
Cost Drivers
Market Structure
Supply Chain Map
Trade & Policy
Operating Norms
Deliverables
Buyer Intelligence
Account Basics
Spend & Scope
Procurement Model
Vendor Requirements
Terms & Policies
Entry Strategy
Pain Points & Triggers
Outputs
Pricing Analysis
Benchmarks
Trends
Should-Cost
Indexation
Landed Cost
Commercial Terms
Deliverables
Brand Analysis
Positioning & Value Prop
Share & Presence
Customer Evidence
Go-to-Market
Digital & Reputation
Compliance & Trust
KPIs & Gaps
Outputs
Full Research Suite comprises of:
Market outlook & trends analysis
Interviews & case studies
Strategic recommendations
Vendor profiles & capabilities analysis
5-year forecasts
8 regions and 60+ country-level data splits
Market segment data splits
12 months of continuous data updates
DELIVERED AS:
PDF EXCEL ONLINE
Automotive Direct Liquid Cooling IGBT Module Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Automotive Hoses and Assemblies Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Automotive Network Testing Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Automotive Performance Part Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Automotive Carbon Ceramic Brake Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Automotive Camshaft Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Automotive Stamping Industry Analysis in India Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Automotive Cylinder Liner Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Automotive Microcontroller Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Automotive Roof Rails Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Automotive Active Safety System Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Automotive Diagnostic Scan Tool Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Automotive Test Equipment Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Automotive Dynamic Map Data Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Automotive Green Tires Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Automotive E-Tailing Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Automotive Interior Market Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Automotive Key Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Automotive Appearance Chemical Market Forecast and Outlook 2025 to 2035
Automotive Seating Market Forecast and Outlook 2025 to 2035

Thank you!
You will receive an email from our Business Development Manager. Please be sure to check your SPAM/JUNK folder too.
Chat With
MaRIA