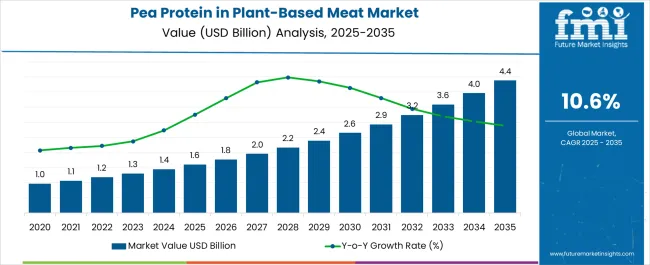
Global demand for pea protein in plant-based meat alternatives is estimated at USD 1.6 billion in 2025, with projections indicating a rise to USD 4.5 billion by 2035, reflecting a CAGR of approximately 10.6% over the forecast period. This expansion reflects both a broadening consumer base and increased per capita consumption across key international territories. The rise in demand is linked to shifting dietary preferences, growing awareness of sustainability, and evolving protein sourcing trends.
By 2025, per capita consumption in leading global territories averages between 0.8 to 1.2 kilograms annually, with projections reaching 1.8 kilograms by 2035. India leads among other countries and is expected to generate the highest growth trajectory at 12.5% CAGR, followed by China (11.8% CAGR), USA (10.9% CAGR), Germany (10.5% CAGR), and UK (9.9% CAGR).
The largest contribution to demand continues to come from burgers and patties, which are expected to account for 42% of total sales in 2025, owing to strong consumer familiarity, extensive foodservice adoption, and retailer support. By application type, textured pea protein represents the dominant processing format, responsible for 55% of all utilization, while isolates and concentrates are expanding across premium formulations.
Consumer adoption is particularly concentrated among flexitarian households and sustainability-focused demographics, with income levels and urban density emerging as significant drivers of demand. While price premiums persist compared to conventional animal proteins, manufacturing scale improvements and supply chain optimization are expected to accelerate affordability across mid-income segments. Regional disparities remain evident, but per capita demand in emerging territories is narrowing the gap with traditionally strong Western consumption hubs.
The increasing demand for clean-label, sustainable, and high-protein alternatives to animal meat is driving growth in pea protein use within plant-based meat. Pea protein offers excellent functionality, including water-binding, emulsification, and gelation properties, which help replicate the texture, juiciness, and bite of traditional meat. Its neutral flavor profile and hypoallergenic nature make it a preferred ingredient over soy or wheat gluten, catering to a broader consumer base including those with food allergies or sensitivities.
Rising adoption of flexitarian and vegan diets, combined with consumer focus on health, wellness, and environmental sustainability, is fueling demand for pea protein-based meat products. Producers are increasingly investing in extrusion technologies and flavor-masking techniques to enhance meat-like sensory experiences. Pea protein’s sustainability advantages-requiring less water and fertilizer while supporting soil health-align with the global shift toward climate-conscious eating. Expanded retail availability, strategic partnerships between food tech companies and major meat producers, and continuous product innovation are further accelerating growth and giving brands a competitive edge in the plant-based meat category.
The pea protein segment in plant-based meat alternatives is classified across several segments. By product format, the key categories include burgers and patties, sausages, nuggets and strips, and other formats including mince and specialty cuts. By application of pea protein, the segment spans textured pea protein, isolates, and concentrates. By distribution channel, the segment covers retail through supermarkets and hypermarkets, foodservice and quick-service restaurants, and online direct-to-consumer platforms. By country, the segmentation is as India, China, USA, Germany, along with other countries.
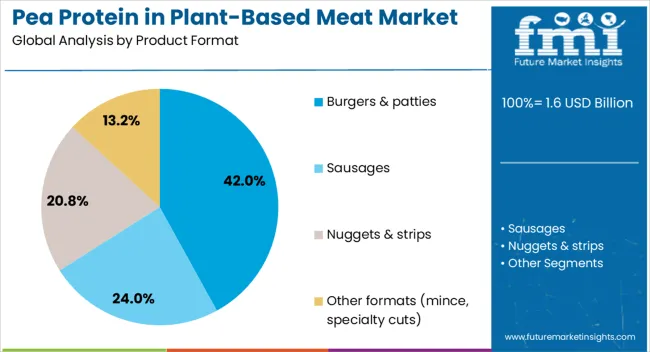
Burgers and patties are projected to dominate sales in 2025, supported by widespread foodservice adoption, consumer familiarity, and strong retail placement. Other formats such as sausages, nuggets, and specialty cuts are growing steadily, each serving distinct consumption patterns.
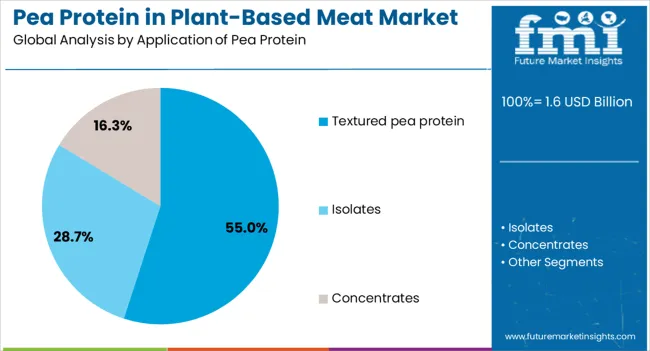
Pea protein applications in plant-based meat span three primary processing categories. Textured pea protein is expected to remain the dominant application in 2025, followed by isolates and concentrates. Processing strategies are evolving to match functional requirements, with growth coming from both traditional and advanced extraction methods.
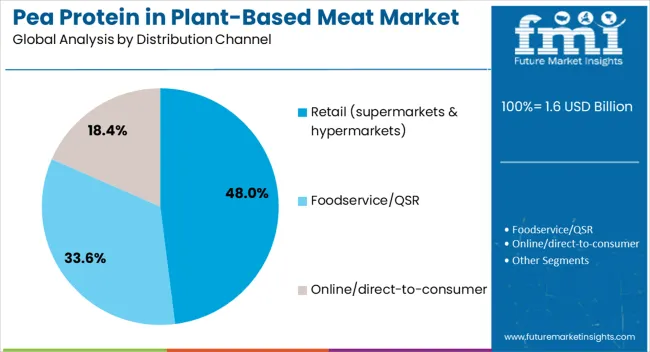
Pea protein-based plant meat products reach consumers through multiple distribution pathways. Retail through supermarkets and hypermarkets is expected to remain the primary sales channel in 2025, followed by foodservice and online platforms. Distribution strategies are adapting to match consumer purchasing behavior, with growth emerging from both physical and digital channels.
Pea protein is becoming a core ingredient in plant-based meat formulations, driven by consumer demand for high-protein, allergen-free, and clean-label options. Unlike soy or wheat, pea protein is non-GMO, gluten-free, and dairy-free, making it ideal for flexitarians, vegans, and individuals with dietary restrictions. Its strong emulsification, gelling, and water-binding properties enable texture and juiciness in burgers, sausages, nuggets, and minced meat alternatives. The sustainability advantage-peas require less water, improve soil fertility through nitrogen fixation, and reduce greenhouse gas emissions-strengthens its role in climate-friendly food systems. Backed by food-tech investments and regulatory support for plant-based innovation, pea protein is positioned as a strategic building block in next-gen meat alternatives.
Despite its strengths, pea protein adoption in meat analogues is constrained by sensory challenges, notably its earthy/green flavor and gritty mouthfeel, which require additional processing or masking agents. Compared to soy, achieving the same fibrous, meat-like texture can be more difficult, leading to higher reliance on extrusion technologies. Cost structures remain elevated due to processing intensity and supply variability, limiting competitiveness against soy- and wheat-based proteins in large-scale applications. Global supply chain risks, including pea crop yield fluctuations and concentration of production in a few geographies, impact price stability. In emerging markets, price-sensitive consumers may favor cheaper soy-based options, restricting market penetration.
Key trends include hybrid formulations where pea protein is blended with soy, fava, chickpea, or mycoprotein to optimize flavor, texture, and nutrition. Precision fermentation and enzymatic processing are being deployed to eliminate off-notes, enhance meaty umami flavors, and improve protein functionality. Advances in high-moisture extrusion and 3D food printing are enabling closer replication of animal muscle fibers. Fortification with iron, vitamin B12, and omega-3s is positioning pea-based meats as nutritionally competitive with animal protein. AI-driven R&D platforms are helping brands predict consumer sensory preferences and accelerate product development cycles. Sustainability-linked branding is leveraging regenerative pea agriculture and circular by-product utilization, aligning with the circular economy and carbon-neutral food manufacturing trends.
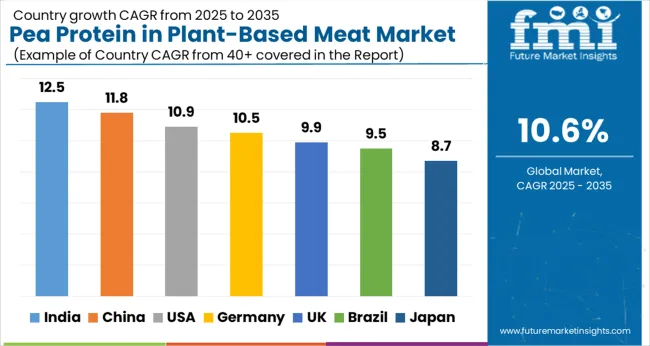
Rising vegetarian populations and faster adoption rates in Asian territories give India and China measurable advantages, while mature Western territories expand more steadily from established consumption bases. The table below shows the compound annual growth rate (CAGR) each of the seven largest countries is expected to record between 2025 and 2035.
| Country | CAGR (2025 to 2035) |
|---|---|
| India | 12.5% |
| China | 11.8% |
| USA | 10.9% |
| Germany | 10.5% |
| UK | 9.9% |
| Brazil | 9.5% |
| Japan | 8.7% |
Between 2025 and 2035, demand for pea protein in plant-based meat is projected to expand across all major global territories, but growth rates will vary based on demographic shifts, dietary preferences, and regulatory frameworks.
Among the top countries analyzed, India is expected to register the fastest compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 12.5%, driven by its substantial vegetarian population base and increasing quick-service restaurant launches featuring pea-protein-based burger alternatives. The country's growing middle class and urbanization trends support expanded retail distribution, while traditional dietary preferences align naturally with plant-based protein acceptance. Rising disposable incomes in tier-one and tier-two cities are enabling premium plant-based product adoption, with pea protein becoming increasingly accessible through modern retail formats.
China is forecast to achieve an 11.8% CAGR over the same period, supported by local alternative meat startups scaling pea protein sourcing and manufacturing capabilities. Government sustainability initiatives and growing health consciousness among urban populations are driving demand for plant-based alternatives. Domestic companies are investing heavily in pea protein processing facilities, reducing import dependence and improving cost competitiveness. The country's large population base and expanding middle class create substantial scale opportunities for pea-protein-based products across retail and foodservice channels.
The USA is expected to grow at a CAGR of 10.9%, reflecting the maturity of its plant-based meat segment and continued innovation by leading brands using pea isolates for clean-label alternatives. Established companies are refining pea protein applications to improve taste, texture, and nutritional profiles. Consumer awareness of plant-based benefits remains high, supported by extensive retail distribution and foodservice integration. The country's advanced food technology sector enables sophisticated pea protein processing, creating premium products that appeal to health-conscious and environmentally aware demographics.
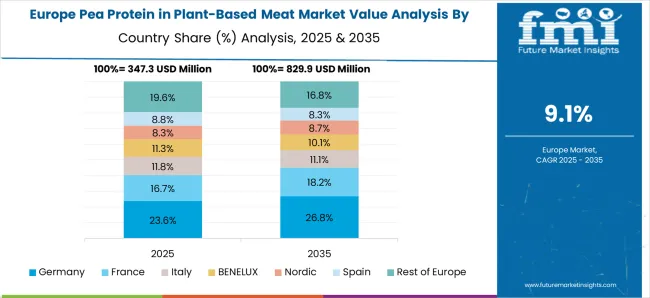
Germany is projected to expand at a 10.5% CAGR, driven by European Union sustainability targets and strong flexitarian demand across the population. The country's well-developed retail infrastructure supports widespread plant-based product availability, while regulatory frameworks encourage sustainable protein development. German consumers demonstrate high environmental consciousness, creating favorable conditions for pea-based meat alternatives. Premium positioning and quality focus align with local purchasing preferences, supporting higher-value pea protein applications in specialized meat substitute products.
The UK is forecast to achieve a 9.9% CAGR, supported by retailer-led plant-based private labels expanding across major supermarket chains. British consumers show increasing interest in meat reduction, driven by health, environmental, and ethical considerations. Major retailers are developing exclusive pea-protein-based products, improving affordability and accessibility. The country's established food processing sector enables efficient pea protein utilization, while strong foodservice integration supports consumption growth across restaurants and quick-service establishments.
Brazil is expected to grow at a 9.5% CAGR, driven by the country's traditionally meat-heavy dietary patterns creating interest in sustainable protein alternatives. Urban populations are increasingly aware of environmental impacts associated with conventional meat production, supporting plant-based adoption. Local food companies are exploring pea protein applications, adapting products to Brazilian taste preferences and cooking methods. The country's large agricultural sector provides opportunities for domestic pea cultivation, potentially reducing ingredient costs and improving supply chain efficiency.
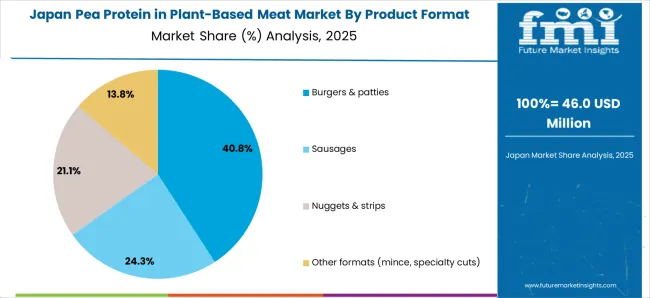
Japan is projected to expand at an 8.7% CAGR, reflecting alternative meat innovation in convenience foods and traditional food applications. Japanese consumers value product quality and innovation, creating opportunities for premium pea-protein-based alternatives. The country's advanced food technology sector enables sophisticated processing methods, improving taste and texture profiles. Convenience store distribution and ready-to-eat applications support consumption growth, while health-conscious aging populations show interest in high-protein, plant-based alternatives.
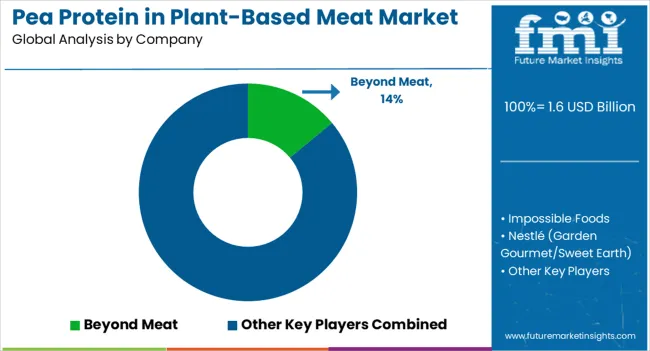
The competitive environment is characterized by a mix of established plant-based meat companies and protein ingredient suppliers. Distribution capabilities and processing expertise remain decisive success factors, with leading suppliers collectively serving thousands of retail outlets and foodservice establishments worldwide.
Beyond Meat maintains the leading position with a 14% share in 2025. The company has established pea protein as a core ingredient across its burger, sausage, and ground meat alternatives, leveraging proprietary processing methods to achieve meat-like texture and taste profiles. Beyond Meat's global distribution network and brand recognition support continued expansion across retail and foodservice channels.
Impossible Foods focuses on innovative protein applications beyond traditional pea-based formulations, but maintains significant pea protein utilization across product lines. The company's emphasis on taste replication and culinary applications drives demand for specialized pea protein ingredients optimized for specific cooking methods and flavor profiles.
Nestlé operates through its Garden Gourmet and Sweet Earth brands, utilizing extensive food processing expertise and global distribution capabilities. The company's integrated supply chain and manufacturing scale enable cost-effective pea protein sourcing and processing, supporting competitive pricing across mass retail channels.
Maple Leaf Foods through its Lightlife brand emphasizes clean-label formulations featuring pea protein as a primary ingredient. The company's focus on natural ingredients and minimal processing appeals to health-conscious consumers seeking recognizable protein sources in plant-based alternatives.
The Vegetarian Butcher, owned by Unilever, leverages corporate sustainability commitments and global reach to expand pea-protein-based products across international territories. The brand's premium positioning and innovative product development drive demand for high-quality pea protein ingredients.
Ingredient suppliers including Roquette Frères, Cargill, Ingredion, Bühler Group, and ADM provide essential pea protein processing capabilities and supply chain infrastructure. These companies invest in extraction technologies, processing equipment, and agricultural partnerships to ensure consistent ingredient availability and quality for plant-based meat manufacturers.
| Item | Value |
|---|---|
| Quantitative Units | USD 1.6 Billion |
| Product Format | Burgers & patties, sausages, nuggets & strips, and other formats |
| Application | Textured pea protein, isolates, and concentrates |
| Distribution channel | Retail (supermarkets & hypermarkets), foodservice/QSR, and online/direct to consumer |
| Regions Covered | North America, Latin America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Middle East & Africa |
| Countries Covered | India, China, Brazil, USA, Germany, UK, Japan and 40+ Countries |
| Key Companies Profiled | Beyond Meat, Impossible Foods; Nestlé (Garden Gourmet/Sweet Earth); Maple Leaf Foods (Lightlife); The Vegetarian Butcher (Unilever); Roquette Frères; Cargill; Ingredion; Bühler Group; ADM |
| Additional Attributes | Dollar sales by CAGR (2025 to 2035), Share by segment, Country growth rates, Usage patterns by product, distribution channel, and application, Competitive landscape, Regulatory environment |
The global demand for pea protein in plant-based meat is estimated to be valued at USD 1.6 billion in 2025.
The market size for the demand for pea protein in plant-based meat is projected to reach USD 4.4 billion by 2035.
The demand for pea protein in plant-based meat is expected to grow at a 10.6% CAGR between 2025 and 2035.
The key product types in demand for pea protein in plant-based meat are burgers & patties, sausages, nuggets & strips and other formats (mince, specialty cuts).
In terms of application of pea protein, textured pea protein segment to command 55.0% share in the demand for pea protein in plant-based meat in 2025.






Full Research Suite comprises of:
Market outlook & trends analysis
Interviews & case studies
Strategic recommendations
Vendor profiles & capabilities analysis
5-year forecasts
8 regions and 60+ country-level data splits
Market segment data splits
12 months of continuous data updates
DELIVERED AS:
PDF EXCEL ONLINE
Demand Signal Repository Solutions Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Demand Side Management Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Demand Response Market Analysis - Size, Share, and Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
North America Shipping Supplies Market Trends – Innovations & Growth 2024-2034
Demand of Kozani Saffron in Greece Analysis - Size, Share & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Demand of No-acid Whey Strained Dairy Processing Concepts in European Union Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Demand for Bronte Pistachio in Italy Analysis - Size, Share & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Demand and Trend Analysis of Gaming Monitor in Western Europe Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Demand and Trend Analysis of Gaming Monitor in Japan Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Demand and Trend Analysis of Gaming Monitor in Korea Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Glycine Soja (Soybean) Seed Extract Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Demand and Trend Analysis of Yeast in Japan - Size, Share, and Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Demand and Trends Analysis of Stevia in Japan Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Demand of Pistachio-based desserts & ingredients in France Analysis - Size, Share & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Japan Women’s Intimate Care Market Trends – Growth & Forecast 2024-2034
Western Europe Men’s Skincare Market Analysis – Forecast 2023-2033
Demand and Trend Analysis of Fabric Stain Remover in Korea Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Demand and Sales Analysis of Paper Cup in Japan Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Demand and Sales Analysis of Paper Cup in Korea Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Demand and Sales Analysis of Paper Cup in Western Europe Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035

Thank you!
You will receive an email from our Business Development Manager. Please be sure to check your SPAM/JUNK folder too.
Chat With
MaRIA