The district heating and cooling market is projected to increase from USD 327.2 billion in 2025 to USD 569.7 billion by 2035, representing a stable and sustainable expansion pattern. The year-on-year (YoY) growth analysis of the provided dataset highlights consistent incremental gains that reflect steady market demand and gradual capacity expansion. From 2025 to 2026, the market rises from USD 327.2 billion to USD 345.9 billion, marking a YoY growth of approximately 5.7%. Similar proportional increases are maintained across the forecast horizon, with values advancing to USD 365.6 billion in 2027 and USD 386.5 billion in 2028.
This consistent percentage change underlines the reliability of the growth drivers, which may include infrastructure upgrades, energy efficiency projects, and district-level integration of renewable energy sources. Mid-term data, such as the movement from USD 456.4 billion in 2031 to USD 482.4 billion in 2032, maintains the steady rise with minimal deviation in growth rates, indicating low volatility. By 2035, the market is expected to reach USD 569.7 billion, with uniform year-over-year percentage increments, completing the forecast. The YoY growth analysis shows a predictable and balanced upward curve for the District Heating Cooling Market, supported by stable demand, ongoing technological improvements, and long-term investment in centralized energy networks.
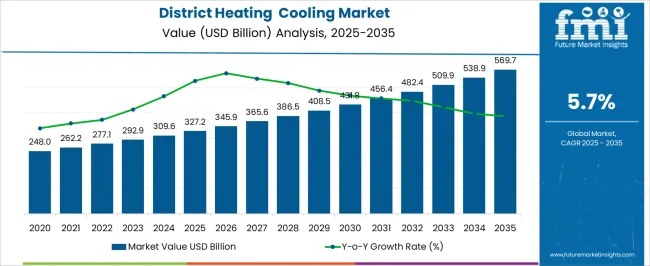
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| District Heating and Cooling Market Estimated Value in (2025 E) | USD 327.2 billion |
| District Heating and Cooling Market Forecast Value in (2035 F) | USD 569.7 billion |
| Forecast CAGR (2025 to 2035) | 5.7% |
The district heating and cooling market is experiencing steady growth, driven by increased demand for energy-efficient urban infrastructure and stringent emissions reduction mandates in key economies. Urbanization and increasing investments in smart city frameworks have encouraged governments and utility providers to transition toward centralized thermal energy systems that reduce environmental footprints and improve supply reliability.
Integration of renewable and surplus heat sources such as geothermal, biomass, and waste heat recovery is being accelerated through policy-driven incentives and carbon-neutrality targets. Technological improvements in thermal storage, heat exchangers, and control systems are supporting wider adoption in both new and retrofit projects.
As climate change resilience becomes a central pillar in urban planning, district-level thermal networks are expected to see expanded use, particularly in regions with high energy density requirements.
The district heating and cooling market is segmented by energy source, application, and geographic regions. By energy source of the district heating and cooling market is divided into District Heating and District Cooling. In terms of application of the district heating and cooling market is classified into Commercial, Residential, and Industrial. Regionally, the district heating and cooling industry is classified into North America, Latin America, Western Europe, Eastern Europe, Balkan & Baltic Countries, Russia & Belarus, Central Asia, East Asia, South Asia & Pacific, and the Middle East & Africa.
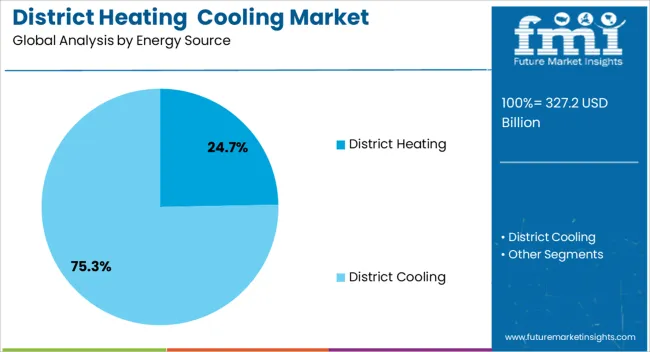
District heating is projected to contribute 24.70% of the total revenue in the district heating and cooling market by 2025, making it the dominant energy source within the segment. Its prominence is being reinforced by increasing deployment in urban centers and colder climate regions where centralized heating offers operational efficiency and environmental compliance.
The ability to harness multiple energy streams such as combined heat and power (CHP), biomass combustion, and industrial waste heat—has strengthened the cost-benefit profile of district heating systems. Advancements in pipeline insulation and low-temperature distribution technologies have further improved network viability.
In parallel, public infrastructure investments and decarbonization roadmaps are encouraging municipalities to expand existing grids and develop new systems to support low-carbon building heating solutions. As energy security and efficiency become policy imperatives, district heating continues to gain traction as a scalable and integrated solution.
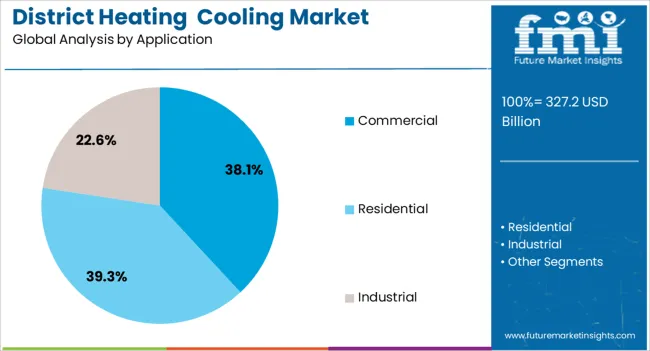
Commercial applications are anticipated to account for 38.10% of the market revenue in 2025, establishing it as the leading segment by application. This growth is being driven by increasing energy consumption across office complexes, retail centers, hospitals, and institutional buildings that require stable thermal regulation year-round.
The commercial sector has been actively investing in district-based systems to reduce lifecycle operating costs and meet tightening environmental performance standards. Building owners and facility managers are aligning with energy performance contracts and sustainability certifications that prioritize high-efficiency thermal systems.
Moreover, the ability to consolidate heating and cooling into a single infrastructure platform has improved space utilization and service scalability in commercial developments. As regulatory frameworks push for net-zero carbon buildings and enhanced energy monitoring, commercial facilities are projected to remain key adopters of district heating and cooling technologies.
The market has gained momentum as centralized energy systems are increasingly implemented to supply thermal energy to multiple buildings through a network of insulated pipes. These systems enable efficient production and distribution of heating and cooling by leveraging combined heat and power plants, renewable energy integration, and waste heat recovery. Advances in thermal storage and smart grid integration have improved operational flexibility and energy efficiency. Urban energy planning has incorporated district systems to optimize resource utilization, lower carbon emissions, and reduce peak load demand.
Innovations in heat exchangers, advanced control systems, and high-performance piping have improved the efficiency of district heating and cooling networks. The incorporation of variable flow systems and predictive maintenance tools based on IoT sensors has enhanced operational control, enabling precise temperature regulation and reduced energy losses. Thermal storage units, including large-scale hot water tanks and phase-change materials, allow systems to store excess heat or cold for later use, balancing supply and demand fluctuations. Integration with renewable sources such as biomass, geothermal, and solar thermal energy has reduced dependence on fossil fuels. These technological improvements have positioned district systems as a cost-effective and environmentally beneficial solution for meeting long-term energy needs.
Government regulations promoting energy efficiency and emission reduction have been instrumental in the expansion of district heating and cooling infrastructure. Subsidies, tax incentives, and financing programs have supported the transition to low-carbon energy sources within district networks. Many municipalities have adopted strategic energy master plans that prioritize the integration of district systems in new developments and retrofits. International climate agreements have further motivated nations to invest in centralized thermal energy distribution. Standards for pipeline insulation, thermal efficiency, and network monitoring have improved system performance and reliability. Such policy-driven initiatives have accelerated adoption, particularly in regions with cold climates and high heating demand, while creating opportunities in emerging economies with growing urban centers.
The integration of waste heat from industrial processes, data centers, and power generation into district heating and cooling systems has increased energy efficiency while reducing greenhouse gas emissions. Renewable sources, particularly biomass and geothermal energy, are being widely deployed to diversify energy inputs. Combined heat and power plants have been optimized to operate in synergy with district networks, maximizing fuel use efficiency. Seasonal thermal energy storage systems allow excess renewable energy to be stored for use during peak demand periods, ensuring system stability. This diversification of energy sources enhances resilience against fuel price volatility and supports decarbonization targets. Market players have increasingly invested in hybrid systems that blend renewable and conventional energy to ensure consistent supply under variable conditions.
High initial capital investment for pipeline networks, distribution stations, and centralized plants remains a significant barrier to market entry, particularly in regions with dispersed populations. Retrofitting existing buildings to connect with district networks can be complex and costly, requiring careful planning and stakeholder coordination. Aging infrastructure in established markets often demands modernization, which can disrupt services and require substantial funding. Seasonal demand fluctuations pose operational challenges, particularly for cooling-dominant networks in warmer regions. Furthermore, the integration of intermittent renewable sources requires advanced storage and balancing mechanisms. Overcoming these challenges involves leveraging public-private partnerships, deploying modular systems, and adopting phased expansion strategies to reduce financial risk while ensuring reliable service delivery.
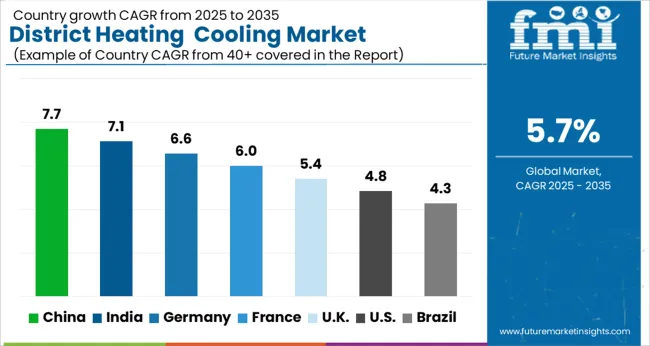
| Country | CAGR |
|---|---|
| China | 7.7% |
| India | 7.1% |
| Germany | 6.6% |
| France | 6.0% |
| UK | 5.4% |
| USA | 4.8% |
| Brazil | 4.3% |
The market is projected to expand at a CAGR of 5.7% between 2025 and 2035, supported by increased adoption of energy-efficient thermal networks and integration of renewable heat sources. China, with an 8.0% CAGR, is advancing through large-scale infrastructure upgrades and the use of waste heat recovery systems. India follows at 7.0%, with urban energy systems increasingly adopting centralized thermal solutions. Germany, also at 7.0%, benefits from government programs promoting low-carbon heating and cooling technologies. The U.K., growing at 5.0%, is focusing on decarbonizing building energy consumption, while the U.S., at 4.8%, is investing in modernized district energy grids to improve efficiency and reduce emissions. This report includes insights on 40+ countries; the top markets are shown here for reference.
China is expected to witness a CAGR of 8% in the district heating cooling market, supported by significant modernization of existing networks and expansion of new centralized energy systems. Large urban clusters and industrial hubs are increasingly connected to upgraded pipelines equipped with automated control technologies. Renewable energy integration, particularly from geothermal and biomass sources, is reducing the dependence on coal-based heating. Strong governmental mandates and regional subsidies are accelerating adoption across northern and central provinces. Collaboration between domestic engineering firms and global technology suppliers is enhancing efficiency, reliability, and environmental performance of district systems.
India is forecast to record a CAGR of 7% in the district heating cooling market, largely influenced by demand growth in metropolitan commercial complexes, high-density residential projects, and large industrial parks. Urban development initiatives in major cities are facilitating the installation of centralized cooling systems that offer both cost efficiency and improved environmental compliance. International collaborations are introducing high-efficiency chillers, advanced heat exchangers, and AI-driven monitoring tools into the market. State-level energy conservation programs and regulatory incentives are encouraging investment in sustainable district systems. Industrial estates are increasingly shifting towards shared cooling plants to optimize operational expenditure while meeting emission control standards.
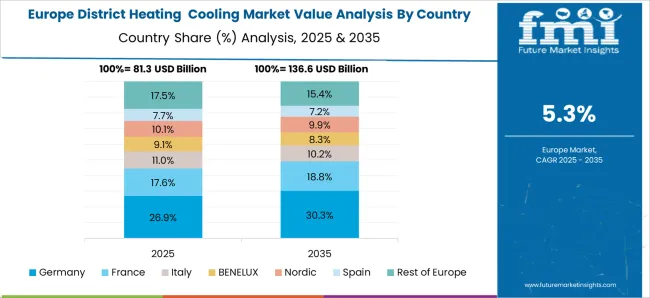
Germany is set to achieve a CAGR of 7% in the district heating cooling market, supported by policies promoting renewable integration and network digitalization. The replacement of coal-based facilities with biomass, geothermal, and waste heat recovery systems is expanding rapidly. Municipal utilities are collaborating with private operators to deploy smart grid technologies for heat distribution monitoring and optimization. Industrial manufacturing regions are incorporating combined heat and power units to enhance energy utilization. The ongoing transition towards climate-neutral heating is backed by substantial funding under federal green energy programs, ensuring rapid expansion of sustainable district energy infrastructure.
The United Kingdom is projected to grow at a CAGR of 5% in the district heating cooling market, backed by targeted investments in low-carbon networks and efficiency improvements. Local authorities, housing developers, and energy companies are implementing heat networks with advanced insulation, smart metering, and integrated leak detection. Hybrid systems that blend renewable sources with existing gas-based plants are expanding in urban and semi-urban zones. National decarbonization objectives are accelerating replacement of older, inefficient boilers with centralized, scalable heating and cooling infrastructure, particularly in social housing projects and large commercial complexes.
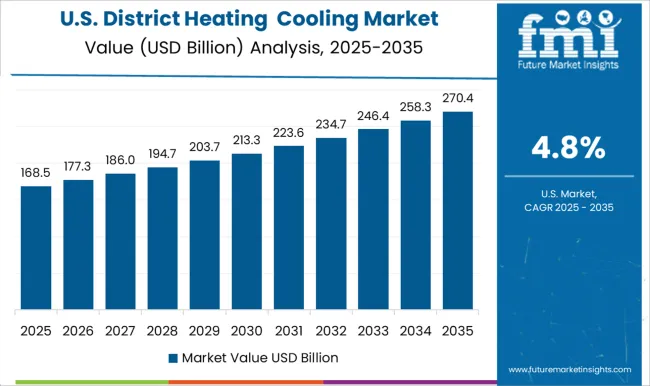
The United States is anticipated to maintain a CAGR of 4.8% in the district heating cooling market, driven by modernization programs targeting universities, healthcare facilities, military bases, and corporate parks. Providers are deploying advanced control systems, thermal energy storage units, and renewable-powered heating sources to boost resilience and efficiency. Federal and state funding is supporting infrastructure renewal in older urban networks, replacing outdated distribution pipelines with insulated, corrosion-resistant alternatives. The adoption of heat recovery systems from industrial processes is gaining momentum, improving overall system sustainability.
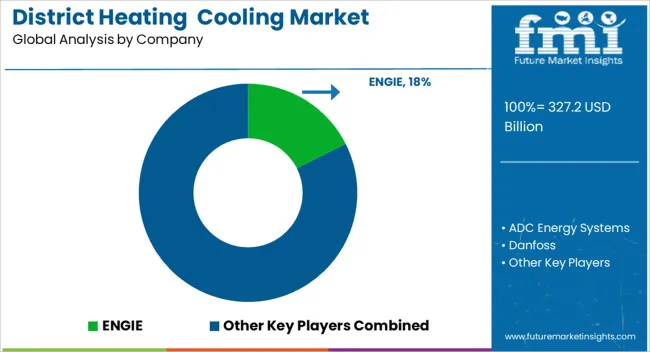
The market features a mix of global leaders and strong regional operators delivering large-scale energy distribution solutions. ENGIE and Veolia dominate with extensive operational networks and strategic investments in expanding service capacity across Europe, Asia, and the Middle East. Vattenfall AB and Fortum remain significant in the Nordic region, leveraging long-standing infrastructure and diversified energy portfolios. Tabreed and Emirates Central Cooling Systems Corporation PJSC are major Middle Eastern providers, offering high-capacity cooling networks tailored for urban districts and commercial hubs. LOGSTOR Denmark Holding ApS supplies advanced pre-insulated pipe systems, supporting operational efficiency for multiple operators worldwide. Danfoss contributes through specialized control systems that optimize heat exchange and energy efficiency in networks. Regional companies like Helen Oy, Göteborg Energi, and Korea District Heating Corporation maintain strong market positions by integrating modern plant upgrades with reliable service delivery. Engineering specialists such as Ramboll Group A/S, DC Pro Engineering, and SNC-Lavalin Group focus on turnkey project execution and network optimization for both heating and cooling applications. The competitive landscape is driven by capacity expansion, network modernization, and long-term municipal contracts. New entrants face barriers including high capital investment, complex regulatory compliance, established operator dominance, technical expertise requirements, and long project development timelines, making market penetration challenging for smaller companies.
Dollar sales by system type and end user, demand dynamics across residential, commercial, and industrial sectors, regional trends in deployment across Europe, North America, and Asia-Pacific, innovation in heat pump integration, thermal energy storage, and smart grid connectivity, environmental impact of carbon emissions reduction and renewable energy integration, and emerging use cases in waste heat recovery, decentralized energy systems, and district-level microgrid development.
| Item | Value |
|---|---|
| Quantitative Units | USD 327.2 Billion |
| Energy Source | District Heating and District Cooling |
| Application | Commercial, Residential, and Industrial |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America, Middle East & Africa |
| Country Covered | United States, Canada, Germany, France, United Kingdom, China, Japan, India, Brazil, South Africa |
| Key Companies Profiled | ENGIE, ADC Energy Systems, Danfoss, DC Pro Engineering, Emicool, Emirates Central Cooling Systems Corporation PJSC, Fortum, Göteborg Energi, Helen Oy, Keppel Corporation Limited, Korea District Heating Corporation, LOGSTOR Denmark Holding ApS, Ørsted A/S, Pal Group, Ramboll Group A/S, RWE, Shinryo Corporation, Siemens, SNC-Lavalin Group, Statkraft AS, STEAG GMBH, Tabreed, Vattenfall AB, and Veolia |
| Additional Attributes | Dollar sales by system type and end user, demand dynamics across residential, commercial, and industrial sectors, regional trends in deployment across Europe, North America, and Asia-Pacific, innovation in heat pump integration, thermal energy storage, and smart grid connectivity, environmental impact of carbon emissions reduction and renewable energy integration, and emerging use cases in waste heat recovery, decentralized energy systems, and district-level microgrid development. |






Our Research Products

The "Full Research Suite" delivers actionable market intel, deep dives on markets or technologies, so clients act faster, cut risk, and unlock growth.

The Leaderboard benchmarks and ranks top vendors, classifying them as Established Leaders, Leading Challengers, or Disruptors & Challengers.

Locates where complements amplify value and substitutes erode it, forecasting net impact by horizon

We deliver granular, decision-grade intel: market sizing, 5-year forecasts, pricing, adoption, usage, revenue, and operational KPIs—plus competitor tracking, regulation, and value chains—across 60 countries broadly.

Spot the shifts before they hit your P&L. We track inflection points, adoption curves, pricing moves, and ecosystem plays to show where demand is heading, why it is changing, and what to do next across high-growth markets and disruptive tech

Real-time reads of user behavior. We track shifting priorities, perceptions of today’s and next-gen services, and provider experience, then pace how fast tech moves from trial to adoption, blending buyer, consumer, and channel inputs with social signals (#WhySwitch, #UX).

Partner with our analyst team to build a custom report designed around your business priorities. From analysing market trends to assessing competitors or crafting bespoke datasets, we tailor insights to your needs.
Supplier Intelligence
Discovery & Profiling
Capacity & Footprint
Performance & Risk
Compliance & Governance
Commercial Readiness
Who Supplies Whom
Scorecards & Shortlists
Playbooks & Docs
Category Intelligence
Definition & Scope
Demand & Use Cases
Cost Drivers
Market Structure
Supply Chain Map
Trade & Policy
Operating Norms
Deliverables
Buyer Intelligence
Account Basics
Spend & Scope
Procurement Model
Vendor Requirements
Terms & Policies
Entry Strategy
Pain Points & Triggers
Outputs
Pricing Analysis
Benchmarks
Trends
Should-Cost
Indexation
Landed Cost
Commercial Terms
Deliverables
Brand Analysis
Positioning & Value Prop
Share & Presence
Customer Evidence
Go-to-Market
Digital & Reputation
Compliance & Trust
KPIs & Gaps
Outputs
Full Research Suite comprises of:
Market outlook & trends analysis
Interviews & case studies
Strategic recommendations
Vendor profiles & capabilities analysis
5-year forecasts
8 regions and 60+ country-level data splits
Market segment data splits
12 months of continuous data updates
DELIVERED AS:
PDF EXCEL ONLINE
District Heating Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
District Heating Pipeline Network Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
District Cooling Market - Growth & Demand 2025 to 2035
Heating and Cooling Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Cooling and Heating as a Service Market Growth – Trends & Forecast 2025-2035
Solar District Heating Market Analysis - Size, Share, and Forecast 2025 to 2035
Ductless Heating & Cooling Systems Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Radiant Heating And Cooling Systems Market
Cooling Tower Fans Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Cooling Skincare Gels Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Cooling Laser Power Measurement Sphere Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Heating Agents Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Cooling Agents Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Cooling Pump Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Cooling Essences Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Cooling Tower Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Cooling Boxes Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Cooling Tower Rental Market Size, Growth, and Forecast 2025 to 2035
Cooling Management System Market - Growth & Demand 2025 to 2035
Cooling Fans Market Growth - Trends & Forecast 2025 to 2035

Thank you!
You will receive an email from our Business Development Manager. Please be sure to check your SPAM/JUNK folder too.
Chat With
MaRIA