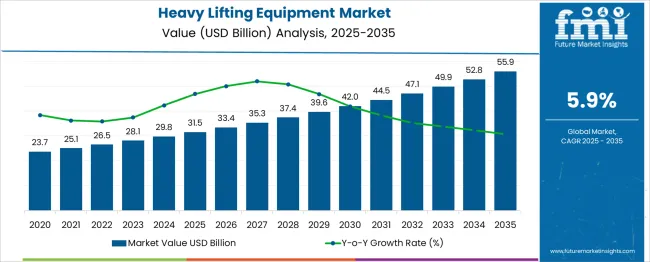
The Heavy Lifting Equipment Market is estimated to be valued at USD 31.5 billion in 2025 and is projected to reach USD 55.9 billion by 2035, registering a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.9% over the forecast period. The year-on-year increments expand gradually from USD 1.9 billion in the first year to USD 3.1 billion in the final year. This progression demonstrates a gently sloped exponential growth curve, where the market compounds consistently without sudden inflections or plateaus.
The CAGR of 5.9% signals a moderate yet dependable expansion profile. Between 2025 and 2030, the market gains USD 10.5 billion, rising from USD 31.5 billion to USD 42.0 billion. In contrast, the period from 2030 to 2035 adds a larger increment of USD 13.9 billion, from USD 42.0 billion to USD 55.9 billion.
This illustrates that the latter half of the period contributes disproportionately more to the overall growth, supporting a convex curve structure. The increase in yearly additions suggests a compound growth mechanism at work rather than a linear trend. Despite the absence of any sharp spikes, the rising marginal gains reflect increasing market depth.
The curve shape leans toward a moderate compound trajectory, marked by incremental acceleration over time and consistent compounding rather than aggressive surges or visible maturity slowdowns.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Heavy Lifting Equipment Market Estimated Value in (2025 E) | USD 31.5 billion |
| Heavy Lifting Equipment Market Forecast Value in (2035 F) | USD 55.9 billion |
| Forecast CAGR (2025 to 2035) | 5.9% |
The heavy lifting equipment market is experiencing steady growth driven by rising infrastructure investments, expansion in industrial manufacturing, and increasing energy and construction projects worldwide. Emphasis on automation, safety compliance, and productivity has compelled end users to adopt advanced lifting solutions with higher load capacities and mobile functionality.
Government-backed urbanization initiatives, port modernization, and renewable energy projects are stimulating demand for versatile lifting systems. Furthermore, the shift toward modular construction, offshore maintenance, and mining development is accelerating deployment of mobile and high-capacity equipment.
Technological innovations including remote control, load monitoring, and telematics integration are enhancing equipment performance and reliability. Looking ahead, the market is expected to benefit from sustained capital expenditure in logistics, oil & gas, and utility sectors, where efficiency, safety, and portability remain key operational priorities.
The heavy lifting equipment market is segmented by product type, capacity, mobility, power source, application, end-use, and geographic regions. By product type, the heavy lifting equipment market is divided into Cranes, Forklifts, Hoists, Winches, Lifts, and others (Handlers, etc.).
In terms of capacity, the heavy lifting equipment market is classified into 100 - 200 Tons, 50 - 100 Tons, and above 200 Tons. The heavy lifting equipment market is segmented into Mobile Lifting Equipment, Fixed Lifting Equipment, and Portable Lifting Equipment. The power source of the heavy lifting equipment market is segmented into Diesel-Powered, Electric-Powered, and Hybrid-Powered.
The heavy lifting equipment market is segmented into Construction, Mining, Industrial Manufacturing, Warehousing & Logistics, Oil & Gas, Energy & Power, Marine & Shipbuilding, and Others (Aerospace & Defense, etc.). The end-use of the heavy lifting equipment market is segmented into Construction Companies, Rental Service Providers, Logistics & Warehousing Firms, Manufacturing Plants, Mining Companies, and Others (Utilities & Power Plants, etc.).
Regionally, the heavy lifting equipment industry is classified into North America, Latin America, Western Europe, Eastern Europe, Balkan & Baltic Countries, Russia & Belarus, Central Asia, East Asia, South Asia & Pacific, and the Middle East & Africa.
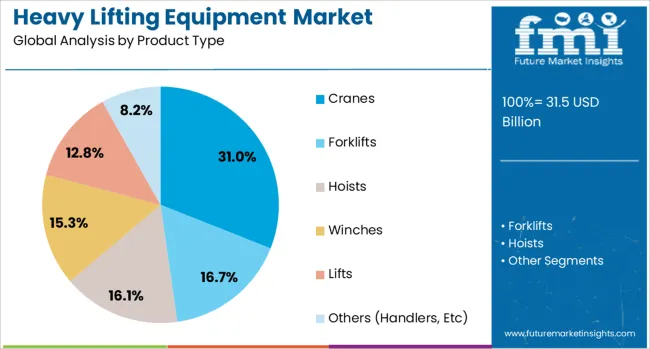
Cranes are anticipated to contribute 31.0% of the total revenue in the heavy lifting equipment market by 2025, establishing them as the leading product type segment. Their dominance is being reinforced by their adaptability across industrial, construction, maritime, and energy operations requiring vertical and horizontal lifting flexibility.
Technological enhancements such as advanced hydraulic systems, operator-assist controls, and modular boom configurations have improved operational precision and safety. Cranes offer multi-purpose utility across terrain types and are favored for their ability to handle both light-duty and extreme-load applications.
The expansion of smart city developments, urban transit systems, and high-rise infrastructure is contributing to sustained crane demand, particularly in projects requiring precise material handling over constrained workspaces.
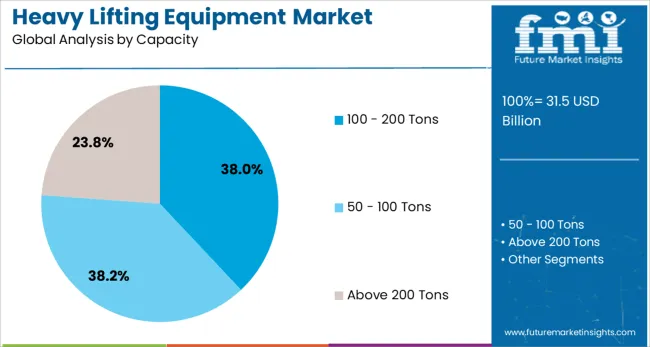
The 100–200 tons capacity range is projected to command 38.0% of the total market share in 2025, making it the most preferred capacity bracket. This segment’s growth is attributed to its optimal balance between lifting capability and equipment mobility, suitable for a broad range of heavy industrial applications.
Equipment in this capacity range is being adopted in large-scale infrastructure, mining, petrochemical, and utility installations, where mid-range loads are common. Advancements in load stability systems and material strength have enabled safer and more efficient handling at this scale.
The ability to customize attachments and integrate digital controls has made this capacity range suitable for increasingly complex operational environments, aligning with safety standards and performance expectations.
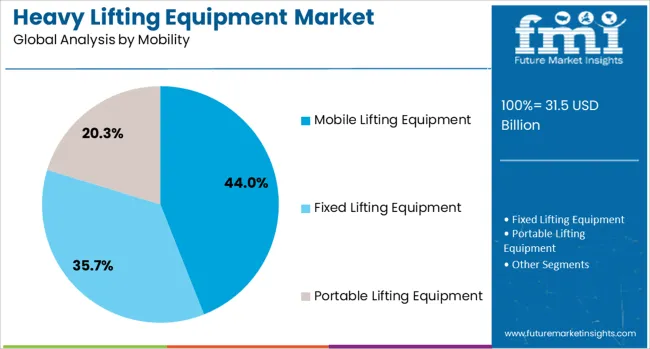
Mobile lifting equipment is expected to account for 44.0% of the market revenue in 2025, positioning it as the leading mobility type. This leadership is driven by increasing demand for flexible, transportable lifting solutions that reduce downtime and enhance site productivity.
Equipment in this category includes truck-mounted cranes, all-terrain lifts, and self-propelled units capable of accessing confined or remote project sites. Their growing adoption in sectors like oil & gas, wind energy, and infrastructure repair stems from the reduced setup time, fuel efficiency, and ease of repositioning.
Integration of GPS tracking, real-time diagnostics, and automated leveling systems is improving operational visibility and compliance, making mobile equipment essential for time-sensitive and multi-site operations. As global construction schedules tighten and urban project logistics become more complex, mobile lifting equipment continues to outperform stationary alternatives.
The heavy lifting equipment market has played a pivotal role in enabling material handling across construction, mining, shipbuilding, manufacturing, and oil and gas industries. These machines have facilitated the movement of oversized loads, steel frameworks, turbines, and prefabricated components in time-sensitive and spatially constrained environments. Growth in this market has been underpinned by the expansion of industrial facilities, power generation projects, and infrastructure development. Demand has also been influenced by upgrades in lifting capacity, enhanced maneuverability, and adherence to safety regulations. Manufacturers have focused on automation, remote monitoring, and electrification to increase operational efficiency while reducing workplace risk and environmental impact.
Global infrastructure initiatives have served as one of the most prominent contributors to sustained demand for heavy lifting equipment. Equipment such as mobile cranes, tower cranes, gantry systems, and hydraulic lifters has been utilized in the erection of bridges, highways, airports, and high-rise buildings. The deployment of these machines has allowed for the vertical and horizontal transportation of concrete beams, steel girders, and prefabricated panels within tight project timelines. Governments and private developers have procured high-capacity cranes with extended reach and load indicators for use in constrained urban sites. In regions undergoing reconstruction or industrialization, heavy lifting equipment has remained essential for executing foundational and superstructure works efficiently and safely.
Adoption of automation and digital control systems in heavy lifting equipment has transformed operator control, maintenance planning, and load safety assurance. Integration of load moment indicators, anti-collision systems, GPS-enabled positioning, and condition monitoring platforms has minimized manual oversight while reducing downtime. Semi-autonomous cranes and hoists have improved load handling precision, especially in complex or hazardous lifting scenarios. Equipment telematics have facilitated real-time data collection on fuel consumption, cycle times, and usage rates, enabling predictive maintenance and fleet optimization. These advancements have lowered total cost of ownership while enhancing worker safety and lifting accuracy, making automated systems increasingly attractive to equipment rental companies and large contractors.
Rising attention to air quality standards and emissions control has led to a notable shift toward electrified and hybrid models in the heavy lifting equipment sector. Electric-powered cranes, hoists, and forklifts have been deployed in indoor facilities, ports, and tunnel projects to minimize particulate emissions and noise. In urban construction zones, the use of battery-powered lifting systems has been preferred to comply with stringent zoning regulations. Manufacturers have invested in lithium-ion battery packs, energy recovery systems, and regenerative braking features to extend operational hours without compromising lifting performance. These models have also reduced fuel expenses and improved compliance with environmental certifications required on large-scale public infrastructure projects.
Equipment rental providers have played a vital role in enhancing accessibility to heavy lifting machines for contractors and small- to mid-sized construction firms. Short- and long-term rental agreements have enabled users to avoid capital expenditures while gaining access to high-capacity and specialized lifting systems. Rental companies have diversified their fleets with all-terrain cranes, telescopic handlers, crawler cranes, and aerial lifts to cater to different project needs. Maintenance, operator training, and transport logistics have been bundled as value-added services, reducing downtime for end-users. This shift toward flexible usage models have expanded the customer base and accelerated fleet modernization. As more contractors seek scalable lifting capacity without ownership liabilities, equipment rental has remained a resilient driver of market activity.
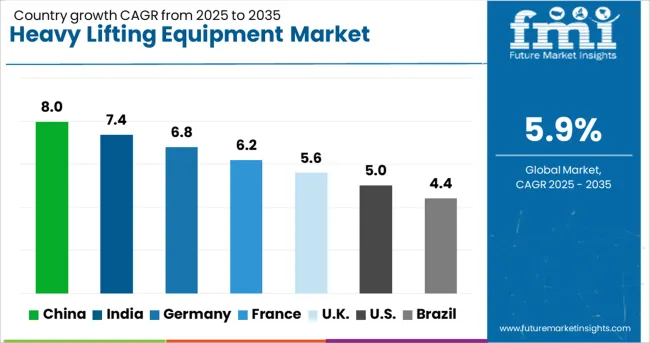
| Country | CAGR |
|---|---|
| China | 8.0% |
| India | 7.4% |
| Germany | 6.8% |
| France | 6.2% |
| UK | 5.6% |
| USA | 5.0% |
| Brazil | 4.4% |
The heavy lifting equipment market is anticipated to grow at a CAGR of 5.9% from 2025 to 2035, driven by rising infrastructure development, increasing warehouse automation, and the expansion of energy and utility sectors. China, with a projected growth of 8.0%, remains dominant due to large-scale construction activities and domestic equipment production. India, growing at 7.4%, benefits from industrial corridor expansion and private investments in logistics. Germany is forecast to grow at 6.8%, supported by continued innovation in load handling systems and demand across manufacturing hubs. The UK, advancing at 5.6%, emphasizes modernization of public infrastructure and retrofitting of lifting fleets. The USA, with a CAGR of 5.0%, experiences steady adoption in oil and gas, mining, and port operations. This report includes insights on 40+ countries; the top markets are shown here for reference.
China is expected to register a CAGR of 8.0% in the heavy lifting equipment market between 2025 and 2035, supported by expansive infrastructure construction and port modernization. State-backed initiatives have propelled demand for advanced gantry cranes, mobile hoists, and high-capacity tower systems. The Belt and Road Initiative has driven adoption of automated heavy lifters for freight logistics, while smart factory development across Shanghai and Shenzhen has increased robotic lifting installations. Chinese firms are advancing in sensor-integrated hydraulic systems for remote load coordination.
India is projected to grow at a CAGR of 7.4% driven by rising public infrastructure projects and urban redevelopment plans. Rapid metro construction, high-rise building growth, and warehouse automation are expanding demand for telescopic handlers and crawler cranes. Indian heavy equipment firms are partnering with global OEMs to localize component production. Government investment through the National Infrastructure Pipeline is accelerating procurement of lifting solutions for rail, road, and energy projects. Tier-2 cities have emerged as new hotspots for equipment rental services.
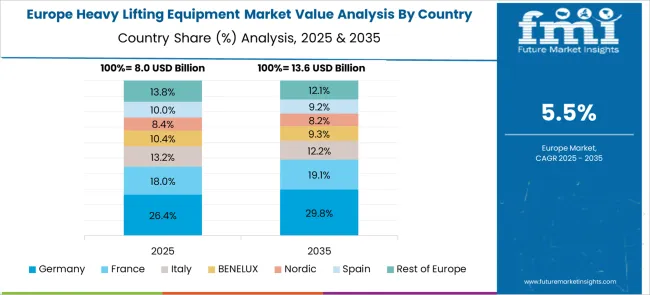
Germany is anticipated to expand at a CAGR of 6.8% owing to its focus on electrification and automation of heavy lifting fleets. German manufacturers are transitioning toward battery-powered hoists, smart winches, and semi-autonomous lifting platforms for logistics and manufacturing hubs. Retrofit projects to improve energy efficiency in older crane installations have risen, particularly in the Ruhr and Bavarian regions. Use of AI for predictive load balancing is gaining momentum in automotive and chemical industries where safety-critical lifting is essential.
The United Kingdom is forecasted to achieve a CAGR of 5.6%, supported by logistics infrastructure upgrades and warehouse expansion. Demand for compact and all-terrain mobile cranes has grown due to spatial limitations in urban centers. British ports and logistics hubs are investing in container handling equipment with real-time positioning controls. Construction projects associated with rail electrification and energy storage facilities have driven demand for heavy lifting platforms with modular setups. Post-Brexit import patterns are reshaping logistics equipment specifications.
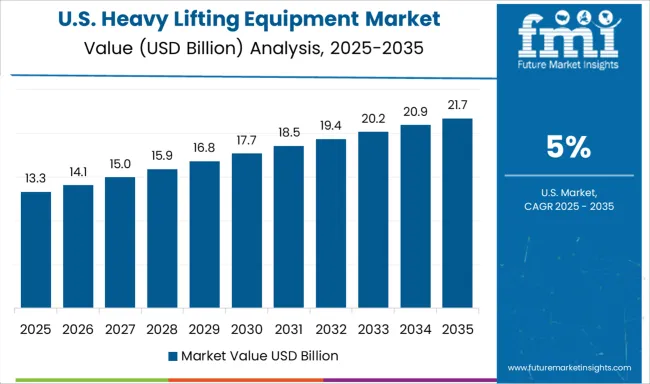
The United States is expected to grow at a CAGR of 5.0% due to factory modernization, warehouse robotics, and aerospace-related installations. American manufacturers are integrating programmable hoisting systems for large assembly lines, especially in automotive and aerospace industries. Adoption of AI-assisted load management software and overhead crane automation has risen in logistics parks across Texas, Ohio, and Illinois. Infrastructure bills have spurred procurement of heavy lifting vehicles for power grid expansions and wind turbine installations.
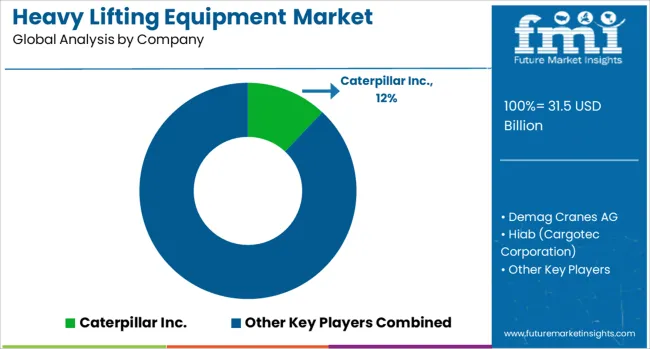
The heavy lifting equipment market forms the backbone of infrastructure development, mining, shipbuilding, oil and gas, and industrial construction activities worldwide. This sector features a highly consolidated but competitive landscape comprising globally entrenched players and regionally dominant manufacturers. These companies engineer and supply cranes, hoists, forklifts, winches, and hydraulic lifting systems designed for extreme load-bearing and operational safety in challenging environments.
Caterpillar Inc., Komatsu Ltd., and Hyundai Construction Equipment dominate the earthmoving and mining verticals with robust lifting machines integrated into large-scale excavators and loaders. Liebherr Group and Tadano Ltd. have built extensive reputations through their tower cranes and mobile lifting platforms, particularly in high-rise and offshore wind projects.
The Manitowoc Company and Terex Corporation supply advanced crawler cranes and rough terrain models tailored for heavy civil construction. Konecranes and Demag Cranes AG cater to factory automation and industrial manufacturing through technologically enhanced overhead cranes and hoist systems.
Mammoet operates as a specialized service provider for engineered heavy lifting and transport solutions in nuclear, petrochemical, and offshore oil segments. Meanwhile, Zoomlion, XCMG Group, and Sany Heavy Industry represent China’s rapid ascent in exporting competitively priced, high-capacity lifting equipment. Palfinger AG and Hiab (Cargotec Corporation) lead in loader cranes and truck-mounted lifting systems optimized for logistics and municipal operations.
Demand is guided by megaproject deployment, equipment replacement cycles, and compliance with safety and emission norms, positioning innovation and durability as decisive market differentiators.
| Item | Value |
|---|---|
| Quantitative Units | USD 31.5 Billion |
| Product Type | Cranes, Forklifts, Hoists, Winches, Lifts, and Others (Handlers, Etc) |
| Capacity | 100 - 200 Tons, 50 - 100 Tons, and Above 200 Tons |
| Mobility | Mobile Lifting Equipment, Fixed Lifting Equipment, and Portable Lifting Equipment |
| Power Source | Diesel-Powered, Electric-Powered, and Hybrid-Powered |
| Application | Construction, Mining, Industrial Manufacturing, Warehousing & Logistics, Oil & Gas, Energy & Power, Marine & Shipbuilding, and Others (Aerospace & Defense, Etc) |
| End-Use | Construction Companies, Rental Service Providers, Logistics & Warehousing Firms, Manufacturing Plants, Mining Companies, and Others (Utilities & Power Plants, Etc) |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America, Middle East & Africa |
| Country Covered | United States, Canada, Germany, France, United Kingdom, China, Japan, India, Brazil, South Africa |
| Key Companies Profiled | Caterpillar Inc., Demag Cranes AG, Hiab (Cargotec Corporation), Hyundai Construction Equipment, Komatsu Ltd., Konecranes, Liebherr Group, Mammoet, Palfinger AG, Sany Heavy Industry Co., Ltd., Tadano Ltd., Terex Corporation, The Manitowoc Company, Inc., XCMG Group, and Zoomlion Heavy Industry Science & Technology Co., Ltd. |
| Additional Attributes | Dollar sales by equipment type and application industry, demand dynamics across construction, mining, shipping, and manufacturing sectors, regional trends in deployment across Asia-Pacific, North America, and Europe, innovation in load monitoring systems, remote operation technologies, and energy-efficient hydraulic mechanisms, environmental impact of fuel consumption, emissions during operations, and equipment lifecycle waste, and emerging use cases in modular infrastructure assembly, offshore wind turbine installation, and automated material handling in industrial megaprojects. |
The global heavy lifting equipment market is estimated to be valued at USD 31.5 billion in 2025.
The market size for the heavy lifting equipment market is projected to reach USD 55.9 billion by 2035.
The heavy lifting equipment market is expected to grow at a 5.9% CAGR between 2025 and 2035.
The key product types in heavy lifting equipment market are cranes, forklifts, hoists, winches, lifts and others (handlers, etc).
In terms of capacity, 100 - 200 tons segment to command 38.0% share in the heavy lifting equipment market in 2025.






Our Research Products

The "Full Research Suite" delivers actionable market intel, deep dives on markets or technologies, so clients act faster, cut risk, and unlock growth.

The Leaderboard benchmarks and ranks top vendors, classifying them as Established Leaders, Leading Challengers, or Disruptors & Challengers.

Locates where complements amplify value and substitutes erode it, forecasting net impact by horizon

We deliver granular, decision-grade intel: market sizing, 5-year forecasts, pricing, adoption, usage, revenue, and operational KPIs—plus competitor tracking, regulation, and value chains—across 60 countries broadly.

Spot the shifts before they hit your P&L. We track inflection points, adoption curves, pricing moves, and ecosystem plays to show where demand is heading, why it is changing, and what to do next across high-growth markets and disruptive tech

Real-time reads of user behavior. We track shifting priorities, perceptions of today’s and next-gen services, and provider experience, then pace how fast tech moves from trial to adoption, blending buyer, consumer, and channel inputs with social signals (#WhySwitch, #UX).

Partner with our analyst team to build a custom report designed around your business priorities. From analysing market trends to assessing competitors or crafting bespoke datasets, we tailor insights to your needs.
Supplier Intelligence
Discovery & Profiling
Capacity & Footprint
Performance & Risk
Compliance & Governance
Commercial Readiness
Who Supplies Whom
Scorecards & Shortlists
Playbooks & Docs
Category Intelligence
Definition & Scope
Demand & Use Cases
Cost Drivers
Market Structure
Supply Chain Map
Trade & Policy
Operating Norms
Deliverables
Buyer Intelligence
Account Basics
Spend & Scope
Procurement Model
Vendor Requirements
Terms & Policies
Entry Strategy
Pain Points & Triggers
Outputs
Pricing Analysis
Benchmarks
Trends
Should-Cost
Indexation
Landed Cost
Commercial Terms
Deliverables
Brand Analysis
Positioning & Value Prop
Share & Presence
Customer Evidence
Go-to-Market
Digital & Reputation
Compliance & Trust
KPIs & Gaps
Outputs
Full Research Suite comprises of:
Market outlook & trends analysis
Interviews & case studies
Strategic recommendations
Vendor profiles & capabilities analysis
5-year forecasts
8 regions and 60+ country-level data splits
Market segment data splits
12 months of continuous data updates
DELIVERED AS:
PDF EXCEL ONLINE
Heavy-Duty Pallet Warehouse Racking Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Heavy Duty Pallet Rack Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Heavy Duty Pump Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Heavy Duty Corrugated Packaging Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Heavy-Truck Composite Component Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Heavy-duty Truck AMT Transmission Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Heavy-duty Truck AMT Synchronizer Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Heavy-Duty Hydrogen Compressors Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Heavy Duty Bins Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Heavy Duty Pick Up Trucks Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Heavy Duty Gas Turbine Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Heavy Duty Vehicle Rental Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Heavy Duty Engine Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Heavy Cordless Tools Market Analysis Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Heavy Haul Truck Market Analysis - Size, Share, and Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Heavy Commercial Vehicle Eps Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Heavyweight Motorcycles Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Heavy Duty Trucks Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Heavy Oil Cracking Catalyst Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Heavy Wall Bottles Market Size, Share & Forecast 2025 to 2035

Thank you!
You will receive an email from our Business Development Manager. Please be sure to check your SPAM/JUNK folder too.
Chat With
MaRIA