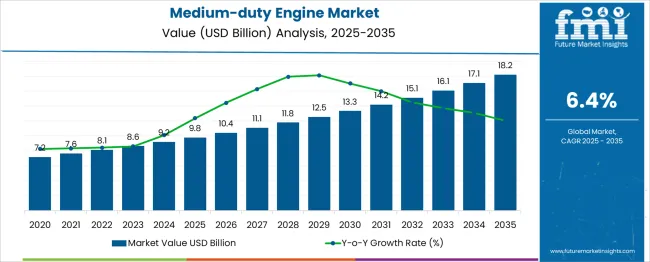
The medium-duty engine market is estimated to be valued at USD 9.8 billion in 2025 and is projected to reach USD 18.2 billion by 2035, registering a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.4% over the forecast period.
The medium-duty engine market is forecast to grow from USD 9.8 billion in 2025 to USD 18.2 billion by 2035, creating an incremental opportunity of USD 8.4 billion over the decade, supported by a CAGR of 6.4%. A 10-year growth trajectory analysis shows the market multiplier reaching 1.86x, indicating that the sector will nearly double in size during the forecast period.
The first five years, from 2025 to 2030, will take the market from USD 9.8 billion to 13.3 billion, delivering USD 3.5 billion or 41.6% of total growth, while the second half from 2030 to 2035 adds USD 4.9 billion, representing 58.4%, signaling a back-weighted growth curve.
Annual increments also display widening gaps, with early-phase growth averaging USD 0.6 billion per year, rising to over USD 1 billion per year in later years, reflecting stronger adoption of advanced powertrain technologies and compliance-driven upgrades. The consistent rise aligns with expanding demand for mid-range engines in logistics, vocational fleets, and construction applications, combined with a shift toward emission-optimized platforms and hybrid-ready designs.
The multiplier dynamics confirm that capacity planning and R&D investments in high-efficiency combustion systems, modular architectures, and fuel-flexible configurations will be critical for manufacturers seeking scale and competitiveness in the next decade.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Medium-duty Engine Market Estimated Value in (2025 E) | USD 9.8 billion |
| Medium-duty Engine Market Forecast Value in (2035 F) | USD 18.2 billion |
| Forecast CAGR (2025 to 2035) | 6.4% |
The medium-duty engine market holds a defined yet modest portion within various broader segments. Within the commercial vehicle engine market, medium-duty engines contribute 18–20%, as this category includes light-duty and heavy-duty powertrains as well. In the diesel engine market, their share reaches 22-25%, reflecting widespread use in delivery trucks, buses, and vocational vehicles. In the industrial engine market, medium-duty units account for 10-12%, given the larger presence of stationary and heavy machines. Within the fleet operations and logistics market, their share is 14–16%, since many urban and regional fleets rely on medium-duty vehicles. In the off-road vehicle engine market, the share is 8–10%, as this includes agricultural, construction, and mining engines. Although these figures are not dominant, demand is growing due to increasing urban deliveries, last-mile logistics, and emissions regulations. Manufacturers are investing in hybridization and cleaner combustion, reinforcing the medium-duty engine segment as a strategic choice for efficient fleet performance and regulatory compliance.
Technological enhancements in diesel combustion efficiency, engine downsizing, and exhaust after-treatment systems are supporting this transformation. Increased fleet upgrades are further influencing the market in response to stricter emission norms and Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) optimization.
The emergence of cleaner internal combustion technologies, including low-NOx engines and partial hybrid integrations, has enabled extended operational performance while maintaining compliance with sustainability objectives. Medium-duty vehicles equipped with such engines are being adopted in greater numbers across urban delivery fleets, school buses, and utility service trucks.
The integration of smart engine diagnostics and performance mapping tools is allowing fleet operators to gain greater visibility into operational efficiency, reducing unplanned downtime. Looking ahead, the market is expected to evolve through a blend of electrification pilots and continuous innovation in ICE platforms aligned with global decarbonization targets.
The medium-duty engine market is segmented by vehicle class, horsepower, sales channel, end use, and geographic regions. By vehicle class of the medium-duty engine market is divided into Class 6, Class 4, and Class 5. The medium-duty engine market is classified into 150 HP-250 HP, Below 150 HP, and Above 250 HP. The sales channel of the medium-duty engine market is segmented into OEM and Aftermarket. The medium-duty engine market is segmented by end use into Construction machinery, Agricultural machinery, Commercial vehicles, and Special vehicles. Regionally, the medium-duty engine industry is classified into North America, Latin America, Western Europe, Eastern Europe, Balkan & Baltic Countries, Russia & Belarus, Central Asia, East Asia, South Asia & Pacific, and the Middle East & Africa.
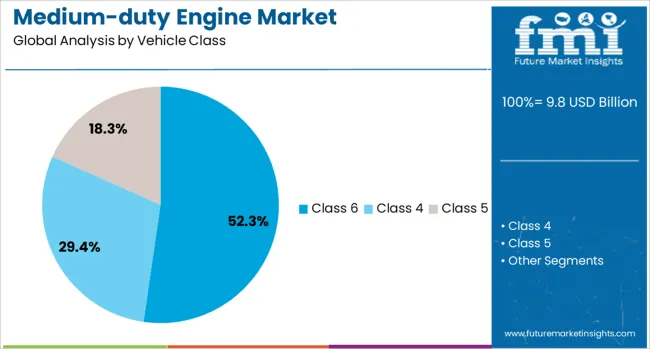
The Class 6 vehicle segment is projected to contribute 52.3% of the total revenue share in the medium-duty engine market in 2025, making it the most significant vehicle class segment. This dominance is being driven by the segment’s widespread use in urban logistics, public utility, and vocational fleets that demand high engine reliability, consistent payload handling, and compliance with regional transportation standards.
Class 6 trucks have been preferred for their ability to deliver optimal performance within weight regulations while offering flexibility in upfitting across multiple commercial applications. The integration of medium-duty engines with advanced emission control systems, including SCR and EGR technologies, has enhanced operational efficiency while ensuring compliance with regulatory mandates.
Fleet modernization programs undertaken by municipal and private operators have supported the deployment of Class 6 vehicles featuring digitally controlled engine systems and telematics. As infrastructure spending and last-mile delivery networks continue to grow, the demand for Class 6 platforms powered by compliant and efficient medium-duty engines is expected to remain elevated.
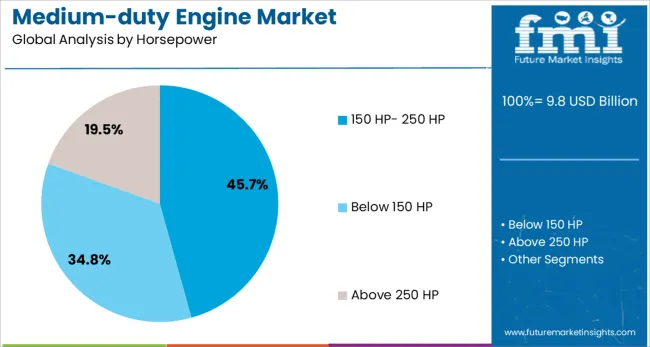
Engines within the 150 HP to 250 HP range are estimated to hold 45.7% of the total market revenue share in the medium-duty engine category by 2025. The growth of this subsegment is attributed to its alignment with the performance requirements of medium-duty applications, offering an ideal balance between fuel economy, torque delivery, and engine durability.
These engines are well-suited for daily urban and regional transport, where payload demands are moderate but consistent uptime and route efficiency are crucial. The subsegment has gained further traction due to OEM strategies focusing on engine platforms that offer modularity and compliance with global emission norms such as Euro VI and EPA Phase 2.
Their adaptability in both diesel and hybrid configurations has expanded their deployment across various body types, including refrigerated trucks, tankers, and shuttle buses. Advancements in electronic control modules and predictive maintenance systems have enabled this engine class to meet evolving operational expectations while maintaining competitive lifecycle costs for fleet owners.
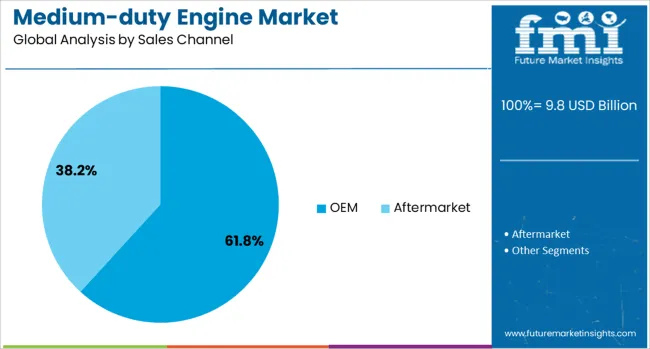
The OEM segment is anticipated to account for 61.8% of the medium-duty engine market’s revenue share in 2025, establishing it as the dominant sales channel. This prominence has been reinforced by the increasing trend among commercial vehicle manufacturers to offer integrated engine solutions that are optimized for compatibility, emissions performance, and warranty alignment. OEMs have expanded their offerings of factory-installed medium-duty engines that incorporate the latest in thermal management, cylinder deactivation, and energy recovery technologies.
This approach allows for more efficient vehicle assembly, reduced integration costs, and streamlined aftersales support. The preference for OEM-installed engines is also being driven by the availability of data-driven engine calibration tools and over-the-air diagnostics, enhancing engine lifecycle management and predictive servicing.
OEM channels benefit from broader distribution networks and established service infrastructures, making them the preferred choice for large fleet operators and government procurement contracts. As demand continues to grow for compliant and technologically advanced engine platforms, OEMs are expected to remain the primary route for engine sales.
Medium‑duty engines are being utilized across commercial vehicles including delivery trucks, vocational work trucks, shuttle buses, and utility vehicles. Demand has been supported by requirements for dependable torque delivery, fuel efficiency, and compliance with emissions regulations. Integration of advanced combustion control, turbocharging, and exhaust after‑treatment systems has improved performance in mixed‑duty cycles. Manufacturers offering modular engine platforms adaptable to biodiesel or renewable fuel blends are positioned to meet diverse operator needs in regional logistics and municipal fleets.
Medium‑duty engines have been specified due to tighter regional emissions standards and the need for clean, efficient power in commercial transport sectors. High‑pressure fuel injection, electronic throttle control, and variable geometry turbochargers have enabled precise combustion and torque delivery across changing load demands. Exhaust after‑treatment systems including selective catalytic reduction and diesel particulate filters have allowed compliance with nitrogen oxide and particulate emissions limits in urban and suburban operating zones. Diagnostic systems featuring built‑in fault detection and remote monitoring have supported preventative maintenance and reduced downtime. As fleet operators have prioritized operational cost savings and regulatory compliance, engine upgrades with digital control and modular compatibility have gained increasing deployment in mixed vehicle fleets.
Adoption of medium‑duty engines has been limited by high upfront costs associated with advanced systems and certification requirements. Retrofit or replacement in existing vehicle chassis may require modifications to accommodate packaging, cooling systems, or new exhaust hardware. Fuel compatibility issues can arise when engines optimized for diesel are integrated with biodiesel or renewable blends without recalibration, risking performance degradation or warranty voidance. Emissions service contracts and after‑treatment maintenance add to the total lifecycle expense. Regional differences in emissions thresholds and approval cycles have created delays in engine deployment across borders. Smaller fleet operators have been cautious due to financing challenges and uncertainty around return on investment for upgraded power units.
Notable opportunities are being realized through electrification initiatives in commercial fleets, where hybrid and integrated engine systems are gaining traction. Demand is being stimulated by vocational trucks, buses, and utility vehicles transitioning to cleaner powertrain configurations. Engine platforms are being integrated with telematics and predictive diagnostics for optimized uptime and maintenance scheduling. Use cases in food delivery, urban logistics, and waste management have created openings for modular medium‑duty engines tailored to specialized vehicle platforms. Collaboration with vehicle OEMs and upfitters has been leveraged to deliver turnkey power solutions. Incentive programs targeting emission reductions in municipal and corporate fleets are encouraging the deployment of advanced engine technologies, especially in urban and suburban operational environments.
Strong trends are being observed toward engine downsizing combined with turbocharging and optimized fuel injection systems to boost power density while reducing fuel consumption. Deployment of exhaust aftertreatment systems such as selective catalytic reduction and diesel particulate filters is being expanded to meet tightening emission requirements. Incremental use of alternative fuels, including renewable diesel, biodiesel blends, and drop‑in fuels, has been initiated to lower carbon impact. Predictive maintenance tools and engine performance monitoring are being embedded within powertrain control architectures for real‑time diagnostics. Modular engine designs compatible with hybrid-electric powertrains are being favored for flexibility. Tier regulations and fleet decarbonization strategies are steering innovation toward low‑NOₓ, low‑PM engine platforms with enhanced reliability.
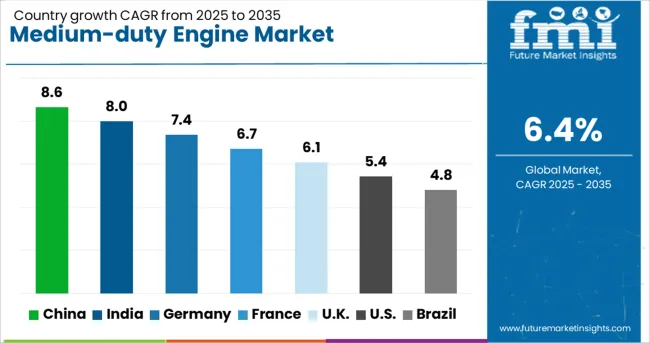
| Country | CAGR |
|---|---|
| China | 8.6% |
| India | 8.0% |
| Germany | 7.4% |
| France | 6.7% |
| UK | 6.1% |
| USA | 5.4% |
| Brazil | 4.8% |
The global medium-duty engine market is expected to grow at 6.4% CAGR from 2025 to 2035, driven by increasing demand in commercial vehicles, construction equipment, and agricultural machinery. China leads with 8.6% CAGR, supported by rising e-commerce logistics and extensive regional freight networks. India follows at 8.0%, fueled by rural infrastructure projects and demand for mid-range trucks in last-mile connectivity.
Germany posts 7.4%, benefiting from advanced powertrain technologies and adoption of low-emission engines for fleet modernization. France records 6.7%, where growth is shaped by strict emission standards and integration of hybrid engine platforms. The UK, growing at 6.1%, focuses on replacement demand and efficiency upgrades in municipal and distribution fleets. The report analyzes more than 40 countries, with five highlighted here.
China is forecast to expand at 8.6% CAGR, supported by increasing domestic freight activity and large-scale e-commerce distribution that depends on medium-duty trucks. National investments in highway expansion and regional connectivity strengthen the use of diesel and hybrid mid-range engines.
Chinese OEMs are developing engines with integrated exhaust after-treatment systems to comply with evolving emissions standards. Export opportunities are growing as domestic manufacturers scale engine production for ASEAN and African markets. Advancements in fuel-efficient turbocharged engines and optimized cooling systems improve engine life and operating efficiency in high-demand logistics and construction applications.
India is expected to grow at 8.0% CAGR, driven by rising deployment of medium-duty engines in tipper trucks, agricultural haulers, and intercity buses. Infrastructure development under programs like Bharatmala and Pradhan Mantri Gram Sadak Yojana is expanding demand for engines optimized for heavy-haul conditions.
Domestic engine manufacturers are investing in alternative fuel platforms, including CNG and LNG-based engines, to reduce operational costs for fleet operators. Government emission standards under Bharat Stage VI are accelerating adoption of advanced engine designs with electronic fuel injection systems. Growth in regional transportation for FMCG and agricultural produce also strengthens market penetration.
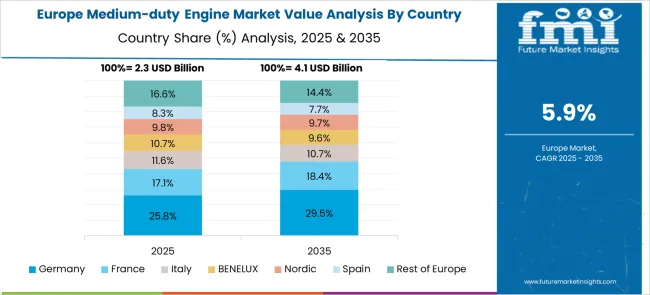
Germany is projected to grow at 7.4% CAGR, supported by a strong base in advanced powertrain innovation and stringent CO₂ emission compliance. The country is witnessing increased demand for hybrid and mild-hybrid engines in regional haulage and public transport fleets. German OEMs lead in integrating telematics for engine performance optimization, improving operational cost efficiency.
Demand from agricultural machinery and specialized municipal vehicles further supports segment growth. Export-oriented manufacturers are investing in Euro VI-compliant engines to cater to both domestic and EU markets. Lightweight engine block development using aluminum alloys enhances efficiency for medium-duty commercial platforms.
France is expected to grow at 6.7% CAGR, with demand driven by regional freight modernization and construction sector recovery. Fleet operators are shifting to engines featuring start-stop systems and advanced thermal management for better fuel utilization.
Manufacturers are introducing mid-power engines with SCR (Selective Catalytic Reduction) and EGR (Exhaust Gas Recirculation) technologies to comply with EU environmental norms. Agricultural cooperatives and rental service providers are significant contributors to engine demand for light-duty loaders and transporters. Integration of advanced diagnostics and predictive maintenance systems in engines is emerging as a trend for reducing lifecycle costs.
The UK is forecast to expand at a 6.1% CAGR, supported by replacement demand in municipal vehicles, refuse trucks, and mid-size delivery vans. Transition toward cleaner engines is reinforced by Ultra Low Emission Zone (ULEZ) compliance, pushing adoption of hybrid-compatible engine platforms. Engine suppliers are focusing on modular design to cater to both diesel and alternative fuel variants.
Growth in e-commerce logistics and last-mile delivery is stimulating demand for mid-duty engines with optimized torque profiles for stop-and-go operations. Partnerships between engine manufacturers and local fleet operators are driving trials for hydrogen-ready and biofuel-compatible engine systems.
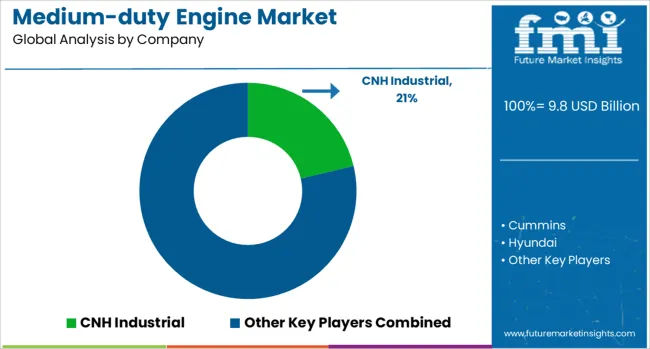
The ocean freight forwarding market is highly competitive, dominated by global logistics leaders such as Kuehne+Nagel, DHL, DB Schenker, DSV A/S, Expeditors International, GEODIS, and Sinotrans, each leveraging extensive global networks, advanced digital platforms, and integrated supply chain solutions to capture market share. The industry operates under a moderately consolidated structure with high entry barriers due to the need for international compliance, carrier partnerships, and digital freight management capabilities.
Buyer power remains significant as large shippers demand competitive pricing and The medium-duty engine market is characterized by intense competition among global manufacturers such as CNH Industrial, Cummins, Hyundai, Isuzu, MAN, Mercedes-Benz, PACCAR, Scania, Tata Motors, and Volvo, each leveraging advanced engineering capabilities, strong OEM partnerships, and extensive distribution networks to sustain leadership in commercial vehicle and industrial applications. Cummins stands out as a technology leader with a focus on fuel efficiency, aftertreatment systems, and alternative fuel compatibility, while Volvo, Scania, and Mercedes-Benz emphasize integrated powertrain solutions tailored for medium-duty trucks and buses, ensuring compliance with stringent emission norms like Euro VI and EPA standards.
PACCAR and MAN capitalize on vertical integration and modular engine platforms to reduce production costs and improve scalability across global markets. Asian manufacturers such as Hyundai, Isuzu, and Tata Motors remain competitive through cost-efficient engines optimized for regional conditions and growing demand for mid-range cargo and passenger vehicles. The market faces moderate entry barriers due to high R&D costs, complex emission regulations, and the need for robust service networks, limiting new entrants. Key competitive factors include engine durability, fuel economy, low NOx emissions, and compatibility with hybrid and electrification trends. Industry rivalry is high, driven by the transition toward low-carbon technologies and digital diagnostics integration for predictive maintenance.
Strategic moves include investments in hydrogen combustion, LNG compatibility, and connected engine management systems to address sustainability mandates and operational efficiency. Performance benchmarks revolve around lifecycle cost, thermal efficiency, power-to-weight ratio, and regulatory compliance, positioning manufacturers for long-term competitiveness in a rapidly evolving transportation ecosystem.
On March 5, 2025, Cummins unveiled the B7.2 diesel engine, part of its B‑Series HELM platform, at NTEA Work Truck Week in Indianapolis. Designed for medium‑duty and vocational trucks, the 7.2 L displacement engine delivers 240-340 hp and 650-1,000 lb‑ft torque, features stop‑start capability, compression‑release engine brake, and digital integration via the Acumen platform. Full North American production begins in 2027 at its Rocky Mount facility.
| Item | Value |
|---|---|
| Quantitative Units | USD 9.8 Billion |
| Vehicle Class | Class 6, Class 4, and Class 5 |
| Horsepower | 150 HP- 250 HP, Below 150 HP, and Above 250 HP |
| Sales Channel | OEM and Aftermarket |
| End Use | Construction machinery, Agricultural machinery, Commercial vehicles, and Special vehicles |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America, Middle East & Africa |
| Country Covered | United States, Canada, Germany, France, United Kingdom, China, Japan, India, Brazil, South Africa |
| Key Companies Profiled | CNH Industrial, Cummins, Hyundai, Isuzu, MAN, Mercedes Benz, PACCAR, Scania, Tata Motors, and Volvo |
| Additional Attributes | Dollar sales by engine type (diesel, natural gas, hybrid) and application (trucks, buses, construction, agriculture), driven by rising demand for fuel efficiency, reduced emissions, and enhanced torque for regional haul and vocational vehicles. Asia-Pacific leads adoption due to growing infrastructure projects and commercial fleets, while Europe focuses on hybrid integration and emission-compliant engines. |
The global medium-duty engine market is estimated to be valued at USD 9.8 billion in 2025.
The market size for the medium-duty engine market is projected to reach USD 18.2 billion by 2035.
The medium-duty engine market is expected to grow at a 6.4% CAGR between 2025 and 2035.
The key product types in medium-duty engine market are class 6, class 4 and class 5.
In terms of horsepower, 150 hp- 250 hp segment to command 45.7% share in the medium-duty engine market in 2025.






Our Research Products

The "Full Research Suite" delivers actionable market intel, deep dives on markets or technologies, so clients act faster, cut risk, and unlock growth.

The Leaderboard benchmarks and ranks top vendors, classifying them as Established Leaders, Leading Challengers, or Disruptors & Challengers.

Locates where complements amplify value and substitutes erode it, forecasting net impact by horizon

We deliver granular, decision-grade intel: market sizing, 5-year forecasts, pricing, adoption, usage, revenue, and operational KPIs—plus competitor tracking, regulation, and value chains—across 60 countries broadly.

Spot the shifts before they hit your P&L. We track inflection points, adoption curves, pricing moves, and ecosystem plays to show where demand is heading, why it is changing, and what to do next across high-growth markets and disruptive tech

Real-time reads of user behavior. We track shifting priorities, perceptions of today’s and next-gen services, and provider experience, then pace how fast tech moves from trial to adoption, blending buyer, consumer, and channel inputs with social signals (#WhySwitch, #UX).

Partner with our analyst team to build a custom report designed around your business priorities. From analysing market trends to assessing competitors or crafting bespoke datasets, we tailor insights to your needs.
Supplier Intelligence
Discovery & Profiling
Capacity & Footprint
Performance & Risk
Compliance & Governance
Commercial Readiness
Who Supplies Whom
Scorecards & Shortlists
Playbooks & Docs
Category Intelligence
Definition & Scope
Demand & Use Cases
Cost Drivers
Market Structure
Supply Chain Map
Trade & Policy
Operating Norms
Deliverables
Buyer Intelligence
Account Basics
Spend & Scope
Procurement Model
Vendor Requirements
Terms & Policies
Entry Strategy
Pain Points & Triggers
Outputs
Pricing Analysis
Benchmarks
Trends
Should-Cost
Indexation
Landed Cost
Commercial Terms
Deliverables
Brand Analysis
Positioning & Value Prop
Share & Presence
Customer Evidence
Go-to-Market
Digital & Reputation
Compliance & Trust
KPIs & Gaps
Outputs
Full Research Suite comprises of:
Market outlook & trends analysis
Interviews & case studies
Strategic recommendations
Vendor profiles & capabilities analysis
5-year forecasts
8 regions and 60+ country-level data splits
Market segment data splits
12 months of continuous data updates
DELIVERED AS:
PDF EXCEL ONLINE
Engineering Machinery Counterweight Iron Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Engine-Driven Endodontic File Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Engine Fixture Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Engine Piston Ring Set Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Engine Cylinder Liners Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Engineering Service Outsourcing Industry Analysis in North America Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Engine Fogging Oil Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Engine Valve Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Engine Starter Fluid Market Growth - Demand, Trends & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Engineering Service Outsourcing Market Analysis - Size, Share, & Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Engineering Analytics Market Growth & Demand 2025 to 2035
Engineering Plastic Market Analysis - Size, Share & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Engineered Cell Therapy - Market Trends & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Engine Tuner Market - Growth & Demand 2025 to 2035
Engine Flush Market Growth – Trends & Forecast 2025-2035
Engine Actuators Market
Engine Mounting Brackets Market
Engineered Wood Market
Geoengineering Market Analysis – Size, Demand & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Aeroengine Accessory Drive Train Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035

Thank you!
You will receive an email from our Business Development Manager. Please be sure to check your SPAM/JUNK folder too.
Chat With
MaRIA