The global power line communication (PLC) market is estimated at USD 14.7 billion in 2025 and is projected to reach USD 57.0 billion by 2035, expanding at a CAGR of 14.5% during the forecast period. Growth is underpinned by the rising adoption of smart grid infrastructure, demand for advanced metering solutions, and the increasing role of PLC in energy management systems. Leveraging existing electrical wiring for data transmission allows for cost-efficient and rapid deployment across residential, commercial, and industrial sectors.
In 2025, the hardware segment is expected to dominate with a 38.6% share, while North America, Asia-Pacific, and Europe emerge as key growth regions. Leading companies shaping the market include Siemens AG, Schneider Electric, General Electric, Hitachi Energy Ltd., STMicroelectronics, Renesas Electronics Corporation, and AMETEK Inc.
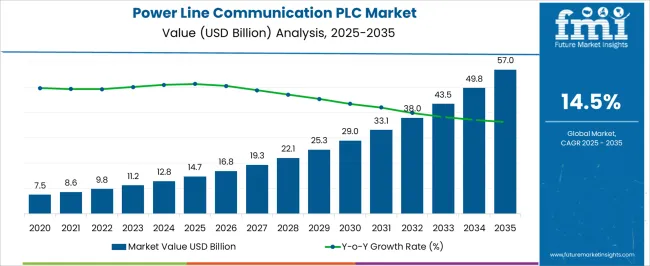
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Power Line Communication (PLC) Market Estimated Value in (2025 E) | USD 14.7 billion |
| Power Line Communication (PLC) Market Forecast Value in (2035 F) | USD 57.0 billion |
| Forecast CAGR (2025 to 2035) | 14.5% |
The power line communication (PLC) market is expanding steadily, driven by the growing need for reliable and cost-effective communication infrastructure across utility and industrial sectors. Increasing deployment of smart grid systems, energy-efficient solutions, and remote monitoring technologies is propelling adoption of PLC systems due to their ability to transmit data over existing electrical wiring.
Regulatory emphasis on energy optimization, grid modernization, and intelligent metering infrastructure has encouraged large-scale investments in PLC-compatible devices. Advancements in narrowband and broadband PLC technologies are improving system performance across long distances and high-noise environments.
Future growth is expected to be supported by the integration of PLC with IoT platforms, advancements in semiconductor components, and rising demand for seamless data transmission in emerging economies. Government-backed smart infrastructure initiatives and the convergence of data communication and energy distribution systems continue to position PLC as a core enabler of digital grid transformation.
The power line communication (PLC) market is segmented by offering, frequency, application, industry vertical, and geographic regions. By offering, the market is divided into Hardware, Software, and Services. In terms of frequency, the market is classified into Narrowband and Broadband. Based on application, the market is segmented into Smart Grid, Networking, and Long-haul. By industry vertical, the market is categorized into Energy & Power, Commercial, Residential, Industrial, and Automotive & Transportation. Regionally, the PLC industry is segmented into North America, Latin America, Western Europe, Eastern Europe, Balkan & Baltic Countries, Russia & Belarus, Central Asia, East Asia, South Asia & Pacific, and the Middle East & Africa.
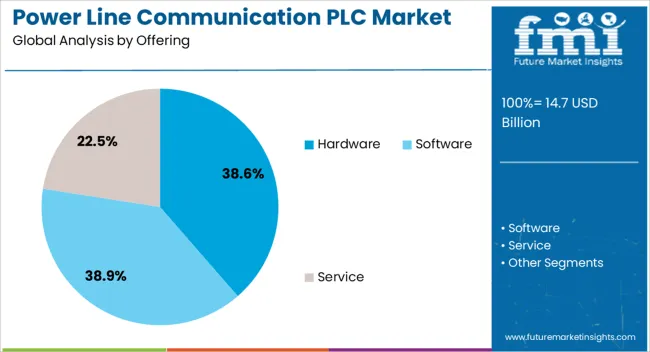
Hardware is expected to account for 38.60% of the total market revenue in 2025, making it the leading segment by offering in the PLC market. This leadership is being attributed to the rising deployment of physical communication modules, couplers, and transceivers across smart grid and home automation systems.
Hardware components serve as critical enablers of signal modulation, power injection, and data integrity in high-interference electrical environments. Demand has been supported by the expansion of grid infrastructure and increased installation of smart meters that rely on hardware-based PLC integration.
The need for high-speed, stable, and interference-resistant communication equipment is reinforcing investment in robust hardware platforms. In addition, continuous improvements in chip design and compact module architecture are reducing cost and power consumption, supporting long-term growth.
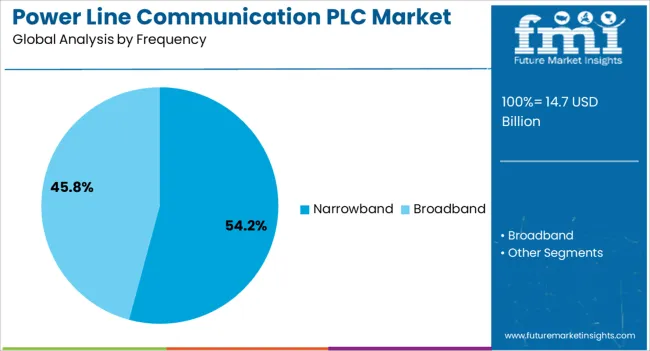
Narrowband PLC is projected to hold 54.20% of total revenue share in 2025, establishing it as the dominant frequency type in the market. The segment’s growth is being driven by its suitability for long-distance, low-data-rate communication applications, particularly in power distribution and utility monitoring.
Narrowband PLC systems offer enhanced noise immunity, stable performance over aging grid infrastructure, and lower operational complexity key factors for scalable deployment in diverse environments. Its compatibility with legacy infrastructure has reduced the need for extensive network overhauls, making it the preferred solution for smart grid automation, remote asset monitoring, and outage management.
Regulatory encouragement for grid reliability and energy efficiency is further reinforcing the adoption of narrowband PLC as a core communications standard for utilities.
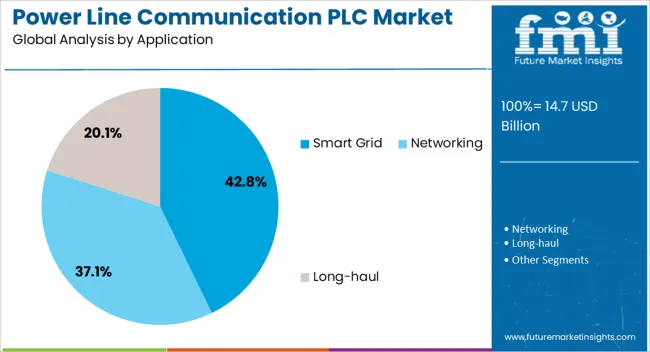
Smart grid applications are expected to represent 42.80% of total market revenue in 2025, positioning this segment as the most prominent in the PLC landscape. This dominance is being supported by the increasing integration of digital communication systems within energy transmission and distribution networks.
PLC technology enables real-time data exchange between substations, transformers, and end-user meters, enhancing grid visibility, fault detection, and load management. The shift toward predictive maintenance, distributed energy resource coordination, and demand-side energy analytics is accelerating PLC deployment across smart grid projects.
Government-led smart infrastructure initiatives, funding programs, and technical standards are also fostering adoption. The segment is further benefiting from the expansion of advanced metering infrastructure (AMI), which heavily relies on PLC to deliver efficient, low-latency communication in cost-sensitive environments.
Power line communication is advancing as a versatile solution for smart grids, industrial automation, and building management, driven by cost efficiency and broad application potential. Hybrid PLC models and evolving standards are expanding its commercial reach.
Adoption of power line communication is expanding as utilities prioritize advanced metering infrastructure and grid modernization programs. Leveraging existing electrical wiring reduces installation costs and accelerates network rollout compared to new cabling systems. Utilities use PLC to enable real-time monitoring, fault detection, and load management across transmission and distribution networks. This technology facilitates bidirectional communication between utilities and end-users, improving demand response capabilities and outage management. Government-led initiatives for energy efficiency and digital grid transformation are reinforcing deployment, particularly in regions undergoing large-scale renewable integration. PLC’s compatibility with hybrid communication architectures is further strengthening its role in building resilient, cost-efficient, and interoperable smart grid solutions for both developed and emerging markets.
Industrial sectors are increasingly adopting PLC for machine-to-machine communication and monitoring of production assets. Its capability to transmit data reliably over long distances without additional cabling supports deployment in challenging factory environments. PLC networks integrate seamlessly with SCADA systems, enabling real-time process control, predictive maintenance, and remote diagnostics. The technology’s noise-resistant design allows stable performance in electrically noisy settings such as manufacturing plants, oil refineries, and mining operations. The push toward Industry 4.0 connectivity is boosting PLC adoption as companies seek unified infrastructure for power and data transmission. This dual-function capability reduces capital expenditure while enhancing operational efficiency and uptime in critical industrial processes.
PLC is gaining traction in residential and commercial building automation due to its compatibility with existing wiring infrastructure. It supports applications such as lighting control, HVAC management, security systems, and energy monitoring without requiring complex rewiring. PLC-enabled smart plugs and connected appliances allow centralized control, enhancing user convenience and reducing energy costs. Its high penetration in retrofitting projects makes it appealing for property owners seeking cost-effective upgrades. Vendors are introducing hybrid PLC-wireless devices to improve coverage and performance in larger buildings. This trend is supported by growing interest in integrated building energy management systems that link lighting, climate control, and access systems through a unified communication network.
Developments in both broadband and narrowband PLC are widening the technology’s application scope. Broadband PLC supports high-speed internet and multimedia services, making it viable for in-home networking and rural broadband delivery. Narrowband PLC offers lower data rates but longer transmission distances, ideal for smart metering, grid control, and remote monitoring. The combination of these two formats allows tailored solutions for different industry needs. Enhanced modulation techniques and noise filtering are improving signal quality, while interoperability standards are ensuring seamless integration across devices. This evolution is positioning PLC as a flexible, scalable solution capable of meeting diverse communication requirements in energy, industrial, and consumer markets.
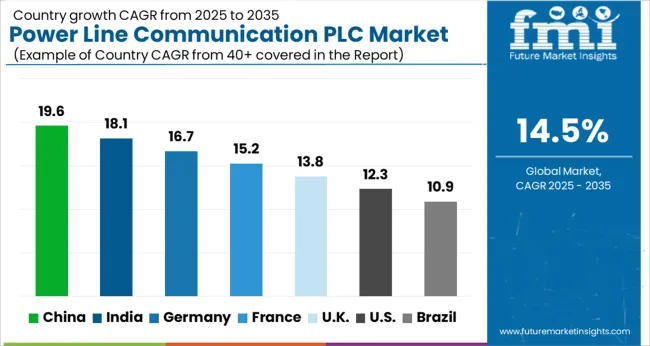
The power line communication market is projected to expand steadily from 2025 to 2035, supported by smart grid integration, industrial automation, and connected building applications. China leads with a 19.6% share, driven by large-scale utility modernization, government-backed smart energy initiatives, and extensive adoption of PLC-enabled metering infrastructure. India follows at 18.1%, benefitting from rapid electrification in rural areas, growth in industrial energy monitoring systems, and cost-effective building automation projects. Germany holds 16.7%, supported by advanced manufacturing, grid optimization programs, and high adoption in renewable energy control systems.
France accounts for 15.2%, driven by integration of PLC in public infrastructure projects and energy efficiency programs. The United Kingdom holds 13.8%, with adoption led by broadband PLC applications and deployment in urban smart grid projects. The United States captures 12.3%, supported by hybrid PLC-wireless solutions in industrial settings and rural broadband expansion programs. This distribution highlights how infrastructure readiness, government policy, and application diversity are shaping PLC adoption across major global economies.
China registered a CAGR of about 18.4% from 2020–2024, which increased to 19.6% for 2025–2035, driven by nationwide deployment of PLC-enabled smart meters and large-scale energy management projects. Early growth was supported by state-led utility upgrades and expansion of PLC for grid stability in major provinces. Over the next decade, integration of PLC in electric vehicle charging networks, renewable energy monitoring, and industrial automation systems will accelerate adoption. Strategic collaborations between utilities and technology providers are enhancing interoperability, ensuring wider penetration across residential and commercial applications.
India saw a CAGR of approximately 17.2% during 2020–2024, which moved up to 18.1% for 2025–2035, propelled by rural electrification programs and urban energy management solutions. The initial period’s growth came from adoption in industrial control systems and emerging deployment in smart city projects. Looking ahead, broader implementation of PLC for automated meter reading, energy theft detection, and building management systems is expected to fuel growth. Partnerships between public utilities and PLC solution providers are enabling faster deployments and reducing integration costs, strengthening India’s position as a key market in the Asia-Pacific region.
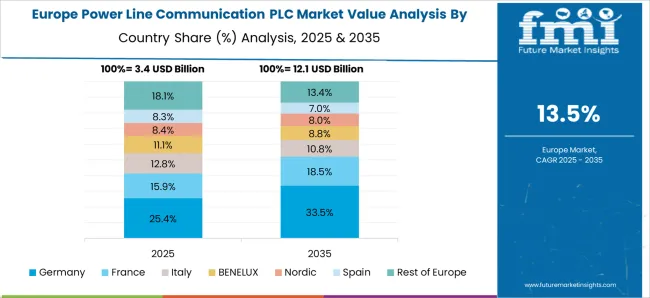
France posted a CAGR of about 14.6% from 2020–2024, which grew to 15.2% in the 2025–2035 period, driven by modern grid digitization and energy optimization programs. The earlier phase saw demand concentrated in utility PLC applications for distribution automation. Going forward, the growth will be fueled by increased adoption in public infrastructure monitoring, electric mobility infrastructure, and residential energy control systems. The presence of established energy companies and technology developers is encouraging cross-sector integration of PLC for improved efficiency and grid stability.
The UK registered a CAGR of around 12.5% between 2020–2024, which rose to 13.8% during 2025–2035, in line with the global CAGR of 14.5%. The earlier phase saw deployments primarily in broadband-over-power-line services and pilot smart grid programs. In the coming decade, growth will be shaped by large-scale smart meter rollouts, energy efficiency regulations, and hybrid PLC-wireless solutions in both residential and industrial setups. Expansion into rural broadband connectivity using PLC infrastructure is also expected to drive adoption. Collaborative projects between utility providers and telecom companies are enhancing scalability and cost-effectiveness.
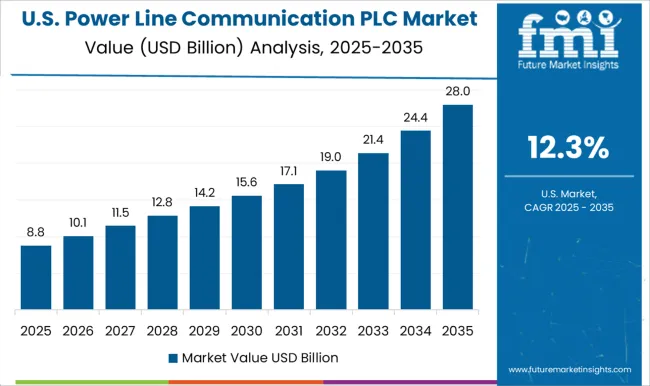
The USA recorded a CAGR of nearly 11.4% from 2020–2024, which increased to 12.3% in 2025–2035, reflecting stable yet growing adoption. Early growth was driven by industrial automation and broadband-over-power-line pilots. The next decade will see wider use in utility automation, EV charging networks, and rural connectivity projects supported by federal funding. Technological enhancements for cybersecurity and integration with IoT devices will strengthen market adoption in both commercial and residential segments.
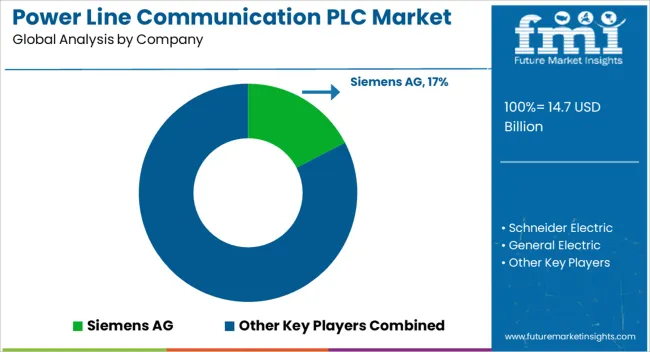
Global reach in utilities and industrial plants gives these firms meaningful channel strength. Siemens AG is positioned through smart grid platforms where PLC couplers, data concentrators, and AMI head-end software are integrated for outage detection and load control. Schneider Electric emphasizes substation automation and feeder equipment with PLC gateways to support distribution management. General Electric focuses on distribution automation and line monitoring that uses PLC for teleprotection and status telemetry.
Hitachi Energy Ltd. supports narrowband PLC for utility signaling, HV and MV feeder communications, and remote asset control. STMicroelectronics supplies PLC SoCs and analog front ends that support OFDM schemes for G3-PLC and PRIME, enabling meter and gateway vendors to reach certified performance. Renesas Electronics Corporation offers modem ICs, power-line transceivers, and reference modules for smart metering and street lighting. AMETEK Inc contributes through carrier communication, power quality instrumentation, and condition monitoring that relies on PLC links in harsh environments.
| Item | Value |
|---|---|
| Quantitative Units | USD Billion |
| Offering | Hardware, Software, and Service |
| Frequency | Narrowband and Broadband |
| Application | Smart Grid, Networking, and Long-haul |
| Industry Vertical | Energy & Power, Commercial, Residential, Industrial, and Automotive & Transportation |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America, Middle East & Africa |
| Country Covered | United States, Canada, Germany, France, United Kingdom, China, Japan, India, Brazil, South Africa |
| Key Companies Profiled | Siemens AG, Schneider Electric, General Electric, Hitachi Energy Ltd., STMicroelectronics, Renesas Electronics Corporation, and AMETEK Inc |
| Additional Attributes | Dollar sales, share, growth by application, regional demand trends, competitive benchmarking, technology adoption rates, regulatory impacts, and utility procurement patterns. |






Our Research Products

The "Full Research Suite" delivers actionable market intel, deep dives on markets or technologies, so clients act faster, cut risk, and unlock growth.

The Leaderboard benchmarks and ranks top vendors, classifying them as Established Leaders, Leading Challengers, or Disruptors & Challengers.

Locates where complements amplify value and substitutes erode it, forecasting net impact by horizon

We deliver granular, decision-grade intel: market sizing, 5-year forecasts, pricing, adoption, usage, revenue, and operational KPIs—plus competitor tracking, regulation, and value chains—across 60 countries broadly.

Spot the shifts before they hit your P&L. We track inflection points, adoption curves, pricing moves, and ecosystem plays to show where demand is heading, why it is changing, and what to do next across high-growth markets and disruptive tech

Real-time reads of user behavior. We track shifting priorities, perceptions of today’s and next-gen services, and provider experience, then pace how fast tech moves from trial to adoption, blending buyer, consumer, and channel inputs with social signals (#WhySwitch, #UX).

Partner with our analyst team to build a custom report designed around your business priorities. From analysing market trends to assessing competitors or crafting bespoke datasets, we tailor insights to your needs.
Supplier Intelligence
Discovery & Profiling
Capacity & Footprint
Performance & Risk
Compliance & Governance
Commercial Readiness
Who Supplies Whom
Scorecards & Shortlists
Playbooks & Docs
Category Intelligence
Definition & Scope
Demand & Use Cases
Cost Drivers
Market Structure
Supply Chain Map
Trade & Policy
Operating Norms
Deliverables
Buyer Intelligence
Account Basics
Spend & Scope
Procurement Model
Vendor Requirements
Terms & Policies
Entry Strategy
Pain Points & Triggers
Outputs
Pricing Analysis
Benchmarks
Trends
Should-Cost
Indexation
Landed Cost
Commercial Terms
Deliverables
Brand Analysis
Positioning & Value Prop
Share & Presence
Customer Evidence
Go-to-Market
Digital & Reputation
Compliance & Trust
KPIs & Gaps
Outputs
Full Research Suite comprises of:
Market outlook & trends analysis
Interviews & case studies
Strategic recommendations
Vendor profiles & capabilities analysis
5-year forecasts
8 regions and 60+ country-level data splits
Market segment data splits
12 months of continuous data updates
DELIVERED AS:
PDF EXCEL ONLINE
Power Line Communication System Market
Power Line Filters Market
Online Powersports Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Power Transmission Lines and Towers Market Analysis & Forecast by Product, Conductor, Insulation, Voltage, Current, Application, and Region Through 2035
Power Grid Fault Prediction Service Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Lined Dip Pipes Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Power Plant Boiler Market Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Power Ring Rolling Machine Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Power Supply Equipment for Data Center Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Linear Regulator ICs (LDOs) Market Forecast and Outlook 2025 to 2035
Line Post Porcelain Insulator Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Power Electronics Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Power Quality Equipment Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Power Generator for Military Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Linerless Label Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Power Tools Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Power Supply Isolation Equipment Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Power Window Lift Motor Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Communication Test and Measurement Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Powered Surgical Staplers Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035

Thank you!
You will receive an email from our Business Development Manager. Please be sure to check your SPAM/JUNK folder too.
Chat With
MaRIA