The Reciprocating Power Generating Engine Market is estimated to be valued at USD 48.8 billion in 2025 and is projected to reach USD 77.2 billion by 2035, registering a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4.7% over the forecast period. Analysis of price evolution and Average Selling Price (ASP) trends indicates a moderate and steady increase over the forecast period, consistent with the underlying demand growth and technological enhancements in engine efficiency, emissions control, and fuel flexibility. The market’s annual progression from USD 48.8 billion in 2025 to USD 56.0 billion by 2029, and further to USD 77.2 billion in 2035, suggests that price adjustments are incremental rather than abrupt, with manufacturers balancing cost increases against competitive pressures and end-user adoption sensitivity.
The gradual integration of advanced components, such as higher-grade alloys, digital monitoring systems, and enhanced fuel injection technologies influences the ASP trajectory. These innovations, while improving performance and reliability, contribute to marginally higher unit costs, which are partially offset by economies of scale as production volumes expand. Regional variations in ASP are observed, with mature markets reflecting higher unit prices due to stringent regulatory compliance requirements. In contrast, emerging markets benefit from cost-optimized configurations targeting industrial and commercial applications. The market demonstrates a stable price evolution scenario, where steady ASP growth aligns with incremental technological upgrades and operational efficiencies. The balance between value delivery and competitive pricing ensures sustained adoption while maintaining profitability, reflecting a controlled yet positive pricing environment across the 2025–2035 period.
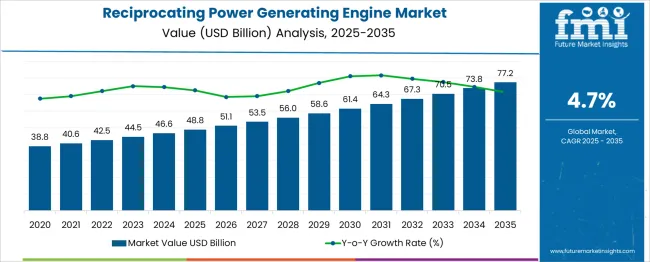
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Reciprocating Power Generating Engine Market Estimated Value in (2025 E) | USD 48.8 billion |
| Reciprocating Power Generating Engine Market Forecast Value in (2035 F) | USD 77.2 billion |
| Forecast CAGR (2025 to 2035) | 4.7% |
The reciprocating power generating engine market is witnessing robust growth as industries prioritize dependable and scalable power sources to meet fluctuating energy demands. Gas-fired engines have gained prominence due to their cleaner emissions, higher fuel efficiency, and adaptability to various operational conditions compared to conventional fuel types. The increasing integration of these engines in distributed power generation and backup systems is a key factor shaping the market landscape.
Additionally, growing industrialization and expanding manufacturing activities have escalated the need for engines capable of delivering consistent power output, especially in regions where grid reliability is challenged. Rated power capacities above 1 MW to 2 MW are preferred for their balance of performance and operational flexibility, making them suitable for a wide range of industrial applications.
The focus on reducing carbon footprints alongside regulatory incentives for cleaner energy sources further supports the adoption of gas-fired reciprocating engines. Moving forward, advancements in engine design and emissions control technologies are expected to bolster the market’s long-term outlook.
The reciprocating power-generating engine market is segmented by fuel type, rated power, application, end use, and geographic regions. By fuel type, the reciprocating power-generating engine market is divided into Gas-fired, Diesel-fired, dual-fuel, and others. In terms of rated power of the reciprocating power generating engine market is classified into > 1 MW - 2 MW, 0.5 MW - 1 MW, > 2 MW - 3.5 MW, > 3.5 MW - 5 MW, > 5 MW - 7.5 MW> 7.5 MW. Based on the application, the reciprocating power-generating engine market is segmented into Industrial, CHP, Energy & utility, Landfill & biogas, Oil & gas, and others. The end use of the reciprocating power-generating engine market is segmented into backup and prime power. Regionally, the reciprocating power-generating engine industry is classified into North America, Latin America, Western Europe, Eastern Europe, Balkan & Baltic Countries, Russia & Belarus, Central Asia, East Asia, South Asia & Pacific, and the Middle East & Africa.
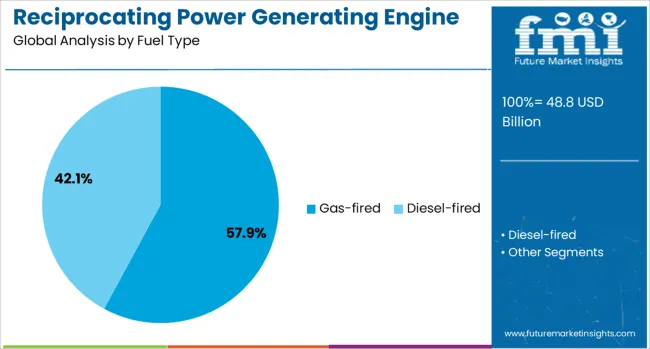
Gas-fired reciprocating engines are anticipated to hold 57.9% of the market revenue share by 2025, marking them as the dominant fuel type segment. This position is attributed to the growing global emphasis on lowering greenhouse gas emissions and meeting stringent environmental regulations.
Gas-fired engines offer significant advantages such as higher thermal efficiency, reduced particulate emissions, and compatibility with renewable natural gas sources, which make them increasingly attractive in both developed and emerging markets. Their flexibility to operate on various types of gaseous fuels and ability to adjust to load changes rapidly have contributed to their adoption in combined heat and power (CHP) applications.
Furthermore, technological advancements improving combustion processes and fuel utilization have enhanced operational economics, making gas-fired engines a preferred choice for industries seeking both environmental compliance and cost-effective power generation.
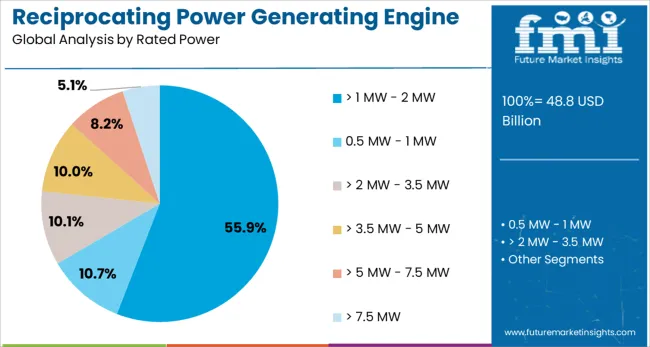
The rated power segment above 1 MW and up to 2 MW is expected to account for 55.9% of the revenue share in 2025, reflecting its widespread acceptance across multiple industrial domains. Engines within this power range provide an optimal combination of capacity and efficiency, enabling their deployment in medium-scale power generation systems and cogeneration plants.
Their scalability supports industrial customers in managing varying load profiles while maintaining a reliable power supply. The segment benefits from improved engine designs that facilitate lower maintenance needs and extended operational lifespans, which are critical factors for industrial operators focused on minimizing downtime and operational costs.
Additionally, this power range aligns well with regulations targeting emissions reduction without compromising on performance, thus driving its strong market position.
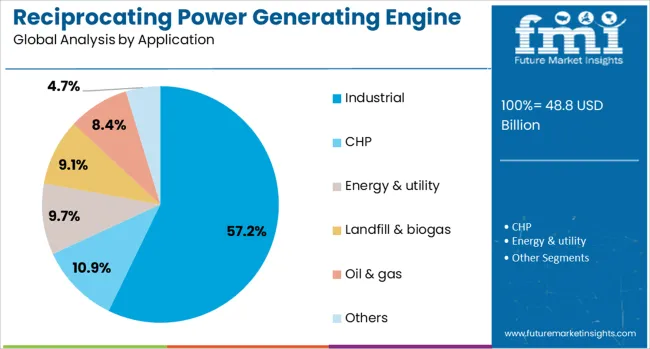
Industrial applications are projected to contribute 57.2% of the overall market revenue by 2025, underscoring their importance in driving demand for reciprocating power-generating engines. This growth is fueled by expanding manufacturing activities and the rising need for on-site power generation solutions to support continuous and reliable operations.
Industries such as chemical processing, food and beverage, and textiles are increasingly adopting reciprocating engines to ensure energy security, reduce reliance on grid power, and manage energy costs effectively. The ability of these engines to provide combined heat and power capabilities enhances their value proposition by improving overall energy efficiency within industrial plants.
Furthermore, the adaptability of reciprocating engines to diverse fuel types and load requirements makes them well-suited for complex industrial environments. The emphasis on sustainability and reducing operational emissions in industrial sectors is expected to accelerate adoption in this segment further.
The market has been growing steadily due to rising global energy demand, industrial expansion, and the need for reliable decentralized power solutions. These engines have been utilized in power plants, commercial facilities, and remote locations for continuous electricity generation. Adoption has been supported by advancements in fuel efficiency, emission reduction technologies, and integration with hybrid energy systems. The market has been influenced by government incentives for cleaner energy and the demand for flexible, scalable, and cost-effective power generation solutions across diverse sectors.
The industrial and commercial sectors have been primary drivers of the reciprocating power generating engine market due to the need for reliable, continuous electricity supply for operations. Manufacturing facilities, data centers, and processing plants have relied on these engines to ensure uninterrupted power and maintain operational efficiency. Remote commercial facilities, including hospitals, hotels, and educational institutions, have utilized reciprocating engines to supplement grid electricity and provide emergency backup during outages. The growing demand for high-capacity engines capable of handling variable load requirements has influenced product development, emphasizing efficiency, fuel flexibility, and operational reliability. Furthermore, industrialization in emerging economies has intensified energy consumption, prompting the deployment of reciprocating engines for localized power generation. By providing a balance between capital cost, scalability, and operational resilience, these engines have been increasingly adopted across commercial and industrial applications globally.
Advancements in reciprocating engine technology have significantly enhanced efficiency, durability, and environmental performance. Modern engines have been designed to reduce fuel consumption while delivering higher power output, supporting cost-effective electricity generation. Emission reduction technologies, including catalytic converters, selective catalytic reduction, and exhaust gas recirculation, have minimized the environmental impact of fuel combustion. Integration with digital monitoring, remote diagnostics, and automation systems has allowed real-time performance optimization, predictive maintenance, and operational safety. Engine designs capable of utilizing multiple fuel types, including natural gas, diesel, and biofuels, have expanded flexibility and market reach. These technological improvements have enabled reciprocating engines to meet stringent regulatory standards, support sustainable power generation, and maintain competitiveness against alternative energy systems in both developed and emerging markets.
Decentralized power generation has been a significant driver for the reciprocating engine market, particularly in regions with unreliable grid infrastructure. Reciprocating engines have been deployed in remote communities, off-grid industrial sites, and temporary facilities to provide consistent electricity where central generation is unavailable. The engines’ ability to operate independently, handle varying load demands, and integrate with storage or renewable systems has made them suitable for microgrids and hybrid energy solutions. Utility providers and independent power producers have increasingly utilized these engines to enhance grid stability, manage peak demand, and support distributed generation strategies. In addition, emergency and backup power applications for critical infrastructure such as hospitals, airports, and telecom facilities have further reinforced adoption. The flexibility, reliability, and modularity of reciprocating engines have positioned them as essential solutions for decentralized energy generation worldwide.
The integration of reciprocating engines with renewable energy and hybrid power systems has created new growth opportunities. Engines have been paired with solar, wind, and energy storage solutions to provide stable, dispatchable power while addressing intermittency issues in renewable generation. Advanced control systems have allowed seamless load sharing, rapid start-stop capabilities, and optimized fuel usage, enhancing overall system efficiency. The increasing deployment of microgrids and off-grid hybrid projects in emerging markets has created demand for engines capable of flexible operation in conjunction with renewable energy sources. Furthermore, engines designed to utilize cleaner fuels, including biogas and hydrogen-enriched blends, have supported decarbonization initiatives and reduced greenhouse gas emissions. The convergence of renewable energy adoption, grid modernization, and hybrid power solutions is expected to continue driving the expansion of the reciprocating power generating engine market globally.
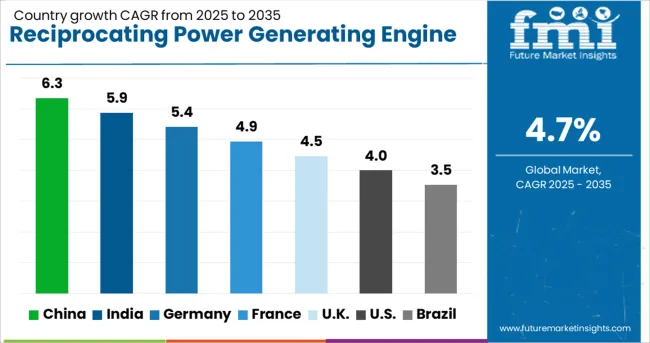
| Country | CAGR |
|---|---|
| China | 6.3% |
| India | 5.9% |
| Germany | 5.4% |
| France | 4.9% |
| UK | 4.5% |
| USA | 4.0% |
| Brazil | 3.5% |
The market is expected to expand at a CAGR of 4.7% between 2025 and 2035, driven by increasing demand for decentralized power generation, backup energy systems, and industrial power solutions. China leads with a 6.3% CAGR, supported by rapid industrialization and growing energy infrastructure projects. India follows at 5.9%, fueled by rising energy demands and adoption of reliable power solutions for remote and industrial areas. Germany, at 5.4%, benefits from government initiatives promoting efficient power generation technologies. The UK, with a 4.5% CAGR, experiences moderate growth through modernization of energy systems. The USA, at 4.0%, reflects steady adoption tied to industrial and emergency power applications. This report includes insights on 40+ countries; the top markets are shown here for reference.
The demand for reciprocating power generating engines in China is expected to grow at a CAGR of 6.3% from 2025 to 2035, driven by rising adoption in industrial, commercial, and municipal power applications. Domestic manufacturers such as Weichai Power and Yuchai are expanding capacity to meet demand for efficient, low-emission engines. Integration of advanced control systems and compliance with national emission standards is enhancing engine performance and durability. Growth in small and medium-sized enterprises requiring decentralized power generation has strengthened the market. Strategic partnerships with component suppliers and investment in research and development are contributing to the advancement of innovative solutions.
India’s reciprocating engine demand is projected to expand at a CAGR of 5.9%, supported by decentralized power solutions for rural and industrial regions. Manufacturers like Cummins India and Kirloskar Electric have introduced high-efficiency models to meet growing electricity demand. Government initiatives to strengthen off-grid and backup power infrastructure are promoting engine adoption. Focus on emission control and fuel optimization has increased reliability, while service networks are expanding to improve customer support across major industrial hubs.
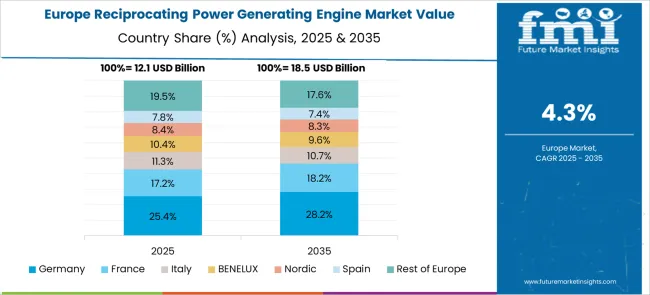
Sales of reciprocating power generating engines in Germany are forecast to grow at a CAGR of 5.4%, fueled by demand in commercial, industrial, and microgrid applications. Companies including MAN Energy Solutions and Rolls-Royce Power Systems are emphasizing emission reduction technologies and engine monitoring systems. Expansion of industrial parks and renewable integration has increased demand for hybrid engine setups. Investment in precision manufacturing and predictive maintenance has improved engine longevity and performance reliability.
The United Kingdom is expected to see reciprocating engine sales expand at a CAGR of 4.5%, driven by industrial and marine power requirements. Engine manufacturers are investing in emission reduction solutions to comply with EU environmental standards. Growth in backup power demand for hospitals, data centers, and commercial complexes is supporting market expansion. Technological enhancements including automated control systems and fuel efficiency optimization have improved operational performance.
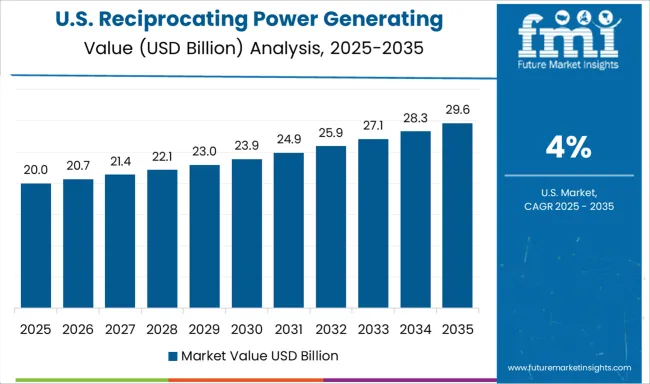
In the United States, the reciprocating engine industry is projected to grow at a CAGR of 4.0%, led by demand in industrial, commercial, and emergency power sectors. Key players such as Caterpillar and Generac have focused on high-efficiency and low-emission engines. Investment in distributed power generation and smart monitoring solutions has strengthened reliability and reduced operational costs. Strategic partnerships with fuel and component suppliers are accelerating product innovation while compliance with environmental regulations drives adoption.
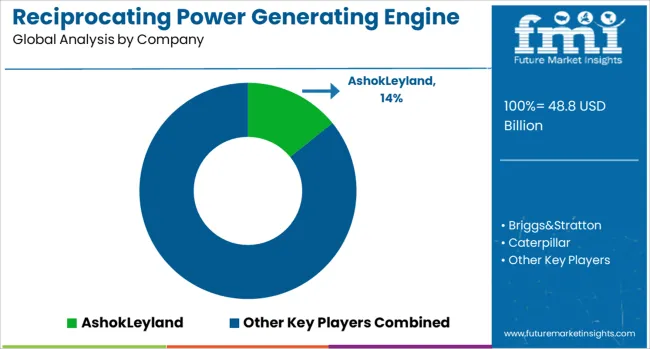
Companies such as Caterpillar, Wärtsilä, MAN Energy Solutions, Cummins, and Rolls-Royce Power Systems compete less on initial equipment cost and more on lifecycle value. Extended service agreements, emissions compliance packages, and digital monitoring platforms are central to their strategy, making after-sales contracts as commercially significant as original engine sales.
The threat of new entrants is limited. Developing large-bore engines requires significant capital investment, advanced metallurgical capability, and long validation cycles. Entry is further constrained by customer risk aversion; utilities and industrial operators prefer proven suppliers with extensive operating references. While smaller regional players may assemble or refurbish units, the competitive weight remains with established OEMs. Supplier power is moderate but growing in sensitivity. Precision components, high-performance alloys, and electronic control systems are sourced from specialized suppliers, some of whom hold proprietary technologies. OEMs mitigate this by vertical integration of critical systems and by building long-term partnerships. Still, supply chain fragility, especially around high-strength alloys and advanced electronics, continues to shape cost structures.
Buyer power varies. Industrial buyers in mining, oil and gas, and heavy manufacturing have options between multiple global OEMs, enabling price negotiations. However, in remote or islanded power applications, switching costs are high because once an engine platform is chosen, operator training, spare parts inventories, and digital monitoring systems create lock-in. The threat of substitutes is intensifying. Gas turbines and, increasingly, hybrid renewable-battery systems compete directly in many applications. Engines retain strength in distributed generation, fast start-up peaking plants, and dual-fuel flexibility, but competitive pressure from non-engine technologies is gradually redefining growth prospects.
| Item | Value |
|---|---|
| Quantitative Units | USD 48.8 Billion |
| Fuel Type | Gas-fired, Diesel-fired, Dual fuel, and Others |
| Rated Power | > 1 MW - 2 MW, 0.5 MW - 1 MW, > 2 MW - 3.5 MW, > 3.5 MW - 5 MW, > 5 MW - 7.5 MW, and > 7.5 MW |
| Application | Industrial, CHP, Energy & utility, Landfill & biogas, Oil & gas, and Others |
| End Use | Backup and Prime power |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America, Middle East & Africa |
| Country Covered | United States, Canada, Germany, France, United Kingdom, China, Japan, India, Brazil, South Africa |
| Key Companies Profiled | AshokLeyland, Briggs&Stratton, Caterpillar, Cummins, Deere&Company, DeutzAG, Enerflex, EscortsLimited, GEVernova, GuascorEnergy, KawasakiHeavyIndustries, KirloskarOilEngines, KohlerEngines, MANEnergySolutions, MitsubishiHeavyIndustries, Rolls-Royce, Scania, TRITONDURO, Wärtsilä, and YANMARHOLDINGS |
| Additional Attributes | Dollar sales by engine type and power rating, demand dynamics across industrial power generation, marine propulsion, and backup electricity supply, regional trends in deployment across Asia-Pacific, North America, and Europe, innovation in fuel efficiency, emission reduction technologies, and hybrid integration, environmental impact of fuel consumption, exhaust emissions, and engine lifecycle, and emerging use cases in decentralized power generation, renewable fuel adaptation, and remote or off-grid energy solutions. |
The global reciprocating power generating engine market is estimated to be valued at USD 48.8 billion in 2025.
The market size for the reciprocating power generating engine market is projected to reach USD 77.2 billion by 2035.
The reciprocating power generating engine market is expected to grow at a 4.7% CAGR between 2025 and 2035.
The key product types in reciprocating power generating engine market are gas-fired, _0.5 mw - 1 mw, _> 1 mw - 2 mw, _> 2 mw - 3.5 mw, _> 3.5 mw - 5 mw, _> 5 mw - 7.5 mw, _> 7.5 mw, diesel-fired, _0.5 mw - 1 mw, _> 1 mw - 2 mw, _> 2 mw - 3.5 mw, _> 3.5 mw - 5 mw, _> 5 mw - 7.5 mw, _> 7.5 mw, dual fuel, _0.5 mw - 1 mw, _> 1 mw - 2 mw, _> 2 mw - 3.5 mw, _> 3.5 mw - 5 mw, _> 5 mw - 7.5 mw, _> 7.5 mw, others, _0.5 mw - 1 mw, _> 1 mw - 2 mw, _> 2 mw - 3.5 mw, _> 3.5 mw - 5 mw, _> 5 mw - 7.5 mw and _> 7.5 mw.
In terms of rated power, > 1 mw - 2 mw segment to command 55.9% share in the reciprocating power generating engine market in 2025.






Our Research Products

The "Full Research Suite" delivers actionable market intel, deep dives on markets or technologies, so clients act faster, cut risk, and unlock growth.

The Leaderboard benchmarks and ranks top vendors, classifying them as Established Leaders, Leading Challengers, or Disruptors & Challengers.

Locates where complements amplify value and substitutes erode it, forecasting net impact by horizon

We deliver granular, decision-grade intel: market sizing, 5-year forecasts, pricing, adoption, usage, revenue, and operational KPIs—plus competitor tracking, regulation, and value chains—across 60 countries broadly.

Spot the shifts before they hit your P&L. We track inflection points, adoption curves, pricing moves, and ecosystem plays to show where demand is heading, why it is changing, and what to do next across high-growth markets and disruptive tech

Real-time reads of user behavior. We track shifting priorities, perceptions of today’s and next-gen services, and provider experience, then pace how fast tech moves from trial to adoption, blending buyer, consumer, and channel inputs with social signals (#WhySwitch, #UX).

Partner with our analyst team to build a custom report designed around your business priorities. From analysing market trends to assessing competitors or crafting bespoke datasets, we tailor insights to your needs.
Supplier Intelligence
Discovery & Profiling
Capacity & Footprint
Performance & Risk
Compliance & Governance
Commercial Readiness
Who Supplies Whom
Scorecards & Shortlists
Playbooks & Docs
Category Intelligence
Definition & Scope
Demand & Use Cases
Cost Drivers
Market Structure
Supply Chain Map
Trade & Policy
Operating Norms
Deliverables
Buyer Intelligence
Account Basics
Spend & Scope
Procurement Model
Vendor Requirements
Terms & Policies
Entry Strategy
Pain Points & Triggers
Outputs
Pricing Analysis
Benchmarks
Trends
Should-Cost
Indexation
Landed Cost
Commercial Terms
Deliverables
Brand Analysis
Positioning & Value Prop
Share & Presence
Customer Evidence
Go-to-Market
Digital & Reputation
Compliance & Trust
KPIs & Gaps
Outputs
Full Research Suite comprises of:
Market outlook & trends analysis
Interviews & case studies
Strategic recommendations
Vendor profiles & capabilities analysis
5-year forecasts
8 regions and 60+ country-level data splits
Market segment data splits
12 months of continuous data updates
DELIVERED AS:
PDF EXCEL ONLINE
Prime Power Reciprocating Power Generating Engine Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Backup Reciprocating Power Generating Engine Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Diesel Power Engine Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Marine Reciprocating Engine Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Mechanical Reciprocating Engine Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Engineering Machinery Counterweight Iron Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Engine-Driven Endodontic File Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Power Grid Fault Prediction Service Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Power Plant Boiler Market Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Power Ring Rolling Machine Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Engine Fixture Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Power Supply Equipment for Data Center Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Engine Piston Ring Set Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Power Electronics Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Power Quality Equipment Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Power Generator for Military Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Engine Cylinder Liners Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Power Tools Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Power Supply Isolation Equipment Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Engineering Service Outsourcing Industry Analysis in North America Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035

Thank you!
You will receive an email from our Business Development Manager. Please be sure to check your SPAM/JUNK folder too.
Chat With
MaRIA