The mechanical reciprocating engine market is estimated to be valued at USD 2.1 billion in 2025 and is projected to reach USD 4.7 billion by 2035, registering a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 8.3% over the forecast period. A rolling CAGR analysis reveals a consistent compounding pattern, with steady growth across all overlapping five-year periods. From 2025 to 2030, the market expands from USD 2.1 billion to USD 3.1 billion, yielding a five-year CAGR of approximately 8.1%. This early phase reflects reliable demand from decentralized power generation, marine propulsion, and industrial mechanical systems.
In the next window, from 2026 to 2031, the market grows from USD 2.3 billion to USD 3.4 billion, maintaining a rolling CAGR of around 8.2%. Each subsequent rolling window shows marginal increases in value but stays within a narrow CAGR range of 8.1% to 8.3%, indicating low deviation. The final five-year window, from 2030 to 2035, shows the market rising from USD 3.1 billion to USD 4.7 billion, producing a rolling CAGR close to 8.7%. This rolling CAGR structure reflects a stable acceleration trend, underpinned by rising fuel efficiency standards, backup power installations, and replacement demand in industrial and transport segments. No sharp fluctuations are observed, confirming consistent long-term growth potential across all forecast intervals.
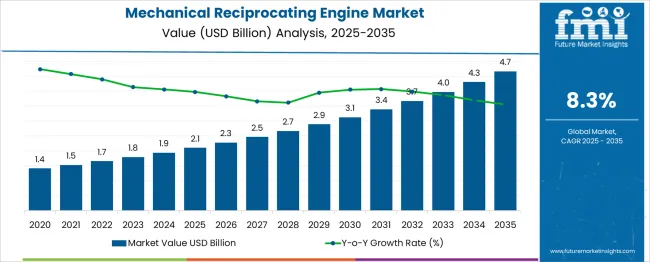
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Mechanical Reciprocating Engine Market Estimated Value in (2025 E) | USD 2.1 billion |
| Mechanical Reciprocating Engine Market Forecast Value in (2035 F) | USD 4.7 billion |
| Forecast CAGR (2025 to 2035) | 8.3% |
The mechanical reciprocating engine market is advancing due to growing needs for distributed power, off-grid electricity, and propulsion in marine and industrial sectors. Prominent manufacturers include Caterpillar, Cummins, MAN Energy Solutions, Wärtsilä, Rolls Royce, Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, and General Electric. These companies focus on hybrid integration, dual-fuel flexibility, hydrogen readiness, and modular engine platforms. Markets in Asia Pacific expand rapidly due to infrastructure growth and energy demand while Europe and North America emphasize emissions reduction and fuel efficiency. New developments include opposed piston configurations, real-time monitoring systems, and adaptive control for improved combustion, reliability, and reduced lifecycle operating costs across applications.
The market is driven by five major parent sectors, each offering distinct contributions. Automotive powertrains account for around 35% of demand, where piston engines remain dominant in passenger cars, light trucks, and hybrid systems. Roughly 25% comes from industrial machinery, such as generators, compressors, and off-road equipment. Small and medium-sized marine vessels account for about 18%, relying on reliable reciprocating engines for propulsion and auxiliary systems. Construction and agricultural equipment contribute close to 15%, with engines powering tractors, harvesters, and earthmoving machinery. The remaining 7% is linked to stationary power generation in backup systems and remote installations. These sectors influence performance standards, emissions norms, and fuel-type selection across the market.
The market is undergoing significant expansion, driven by the increasing need for distributed power generation, industrial resilience, and fuel-efficient mechanical drive systems. Growth has been supported by the rising global demand for reliable backup and prime power solutions, particularly in remote and industrial regions where centralized power infrastructure is limited or unstable.
Manufacturers are increasingly focusing on high-performance, fuel-flexible engines that can be deployed across diverse end-use industries. Emphasis on energy efficiency and the transition toward lower-emission alternatives has also reinforced the relevance of reciprocating engines, especially in applications where operational stability, quick start capability, and load-following performance are essential.
Advancements in combustion technology, emissions control, and digital engine monitoring systems have further strengthened the market’s position. With industries seeking dependable solutions for mechanical drive and power generation, mechanical reciprocating engines are expected to maintain long-term viability, supported by technological innovation and regional infrastructure development..
The mechanical reciprocating engine market is segmented by fuel, rated power, and geographic regions. The fuel of the mechanical reciprocating engine market is divided into Gas, Diesel, and Others. In terms of rated power, the mechanical reciprocating engine market is classified into 1 MW – 2 MW. Regionally, the mechanical reciprocating engine industry is classified into North America, Latin America, Western Europe, Eastern Europe, Balkan & Baltic Countries, Russia & Belarus, Central Asia, East Asia, South Asia & Pacific, and the Middle East & Africa.
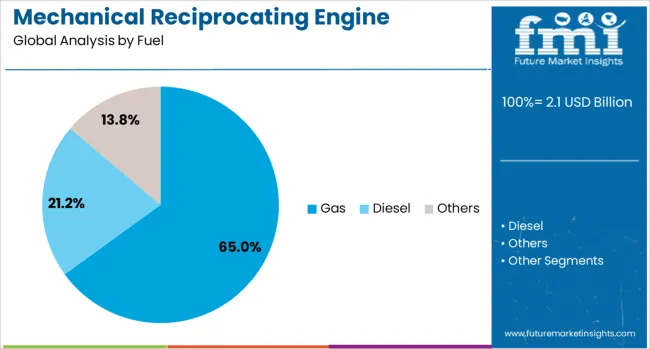
The gas fuel segment is projected to account for 65% of the Mechanical Reciprocating Engine market revenue share in 2025, making it the leading fuel type. A global shift toward cleaner combustion fuels and the growing availability of natural gas across industrialized and developing markets has supported this dominant position. Gas engines have been preferred for their lower emissions profile, higher thermal efficiency, and regulatory compliance with tightening environmental standards.
Their adaptability to various applications, including power generation, mechanical drive, and cogeneration systems, has further expanded their deployment. Operational advantages such as reduced fuel costs and lower maintenance frequency compared to liquid-fueled counterparts have enhanced their attractiveness to end-users.
As industries seek energy reliability with improved sustainability, the adoption of gas-fueled mechanical reciprocating engines has been accelerated. Ongoing infrastructure development for gas transmission and increasing investments in decentralized power systems are expected to sustain this segment’s leadership in the coming years..
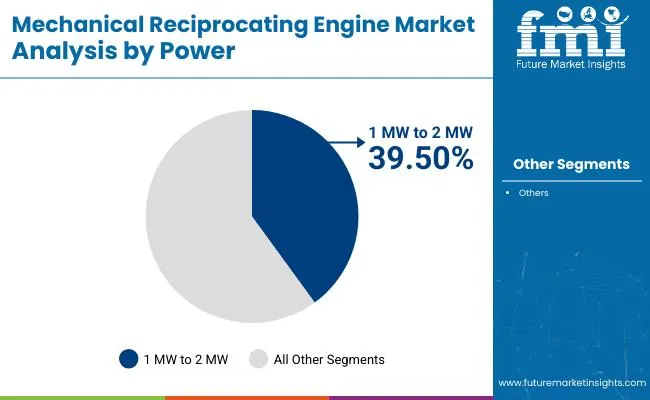
The 1 MW to 2 MW rated power segment is expected to hold 39.50% of the Mechanical Reciprocating Engine market revenue share in 2025, emerging as the dominant power range category. This segment has been favored for its optimal balance between power output and operational efficiency, making it suitable for both industrial and commercial applications. Engines in this range have been widely deployed in distributed power generation, small-scale utilities, and critical backup systems due to their ability to provide stable and immediate power cost-effectively.
Flexibility in fuel usage and ease of integration into modular or containerized systems have further driven adoption. Industries operating in off-grid or semi-grid environments have prioritized engines within this power band for their reliability and adaptability.
Compliance with emissions standards and the ability to incorporate digital control systems have increased their value proposition. Market momentum for this segment is expected to continue as sectors invest in scalable and resilient energy infrastructure..
Global demand for mechanical reciprocating engines has been sustained by industrial, agricultural, and power generation applications where reliability and robustness are essential. About 46% of small-scale generator sets sold in 2024 incorporated reciprocating piston engines. The use of these systems in irrigation pump sets, stationary backup generators, and remote microgrid systems was significant. Asia Pacific and Latin America led deployment, followed by Eastern Europe and Africa. Growth has been supported by retrofits of aging units and demand for improved disassembly serviceability.
Reciprocating engines have been selected because of compatibility with multiple fuel types, ease of service, and modular scalability. Nearly 51% of industrial standby power units now support dual-fuel or gaseous fuel operation, enabling use of natural gas, biogas, or ethanol-derived fuels. In agricultural irrigation applications, 38% of pump engine models were designed with multi-fuel intake. Cold-start ability and high torque at low RPMs have supported adoption in small marine craft and remote rental generators. Field technicians and local workshops maintain high serviceability, reducing downtime by up to 17 %. Fuel substitution pathways have enabled use in waste-to-energy or rural electrification systems, reinforcing adaptability.
Despite fuel flexibility, reciprocating engines are constrained by lower thermal efficiency and higher emissions compared with turbine or generator alternatives. Conversion efficiencies remained around 30% in 2024, while modern gensets approached 40%. Compliance with Tier 3 or Stage IIIA emission regulations added retrofitting and after-treatment costs averaging 18% per unit. In urban zones where low-emission zones were enforced, usage restrictions reduced adoption in 12% of municipal generator installs. Noise and vibration levels were rated as unacceptable in up to 9% of critical infrastructure, requiring additional muffler systems. Fuel sensitivity in ethanol blends caused knock issues in some older engine models when blends exceeded 15% ethanol content, reducing operational consistency.
Growth has emerged from retrofitting aging units with lean-burn or electronically controlled fuel injection systems. Retrofit programs captured 23% of new installations in commercial microgrid projects. Portable rental fleets and remote construction sites adopted modular engine packages for backup and temporary power needs. Biogas-compatible engine variants entered food processing, dairy farms, and wastewater treatment sector use cases. In developing country zones, small-scale electrification through mini-grid and engine-based generators accounted for 28% of new electrification nodes. Partnerships between engine OEMs and local energy system integrators offer service-based leasing models, enabling scalability and structured maintenance frameworks.
Engine modules with remote telemetry, fuel consumption tracking, and predictive diagnostics were installed in 34 % of newer commercial units. Adaptive fuel injection management was embedded in 29 % of dual-fuel models to optimize the mixture under manual control conditions. Lightweight aluminum alloy engine blocks and modular crankcases have lowered unit mass by around 14 % for portable gensets. Integrated urea injection and SCR systems are increasingly specified in Tier 4-compliant models. Compact skid-mounted generator packs with full corner lifting and rapid-connect fuel lines are being adopted in hospitality and event sectors. Condition-based maintenance programs using vibration and temperature sensors are being piloted to reduce unplanned downtime and extend service intervals.
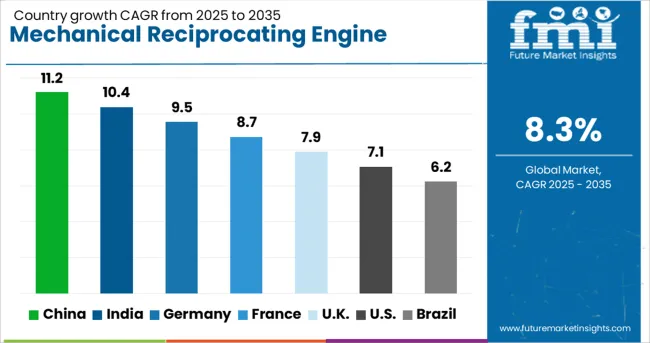
| Country | CAGR |
|---|---|
| China | 11.2% |
| India | 10.4% |
| Germany | 9.5% |
| France | 8.7% |
| UK | 7.9% |
| USA | 7.1% |
| Brazil | 6.2% |
The mechanical reciprocating engine market is projected to expand globally at a CAGR of 8.3% from 2025 to 2035. China is advancing at 11.2%, nearly 1.35 times the global average, due to rising deployment in distributed power systems and backup generation. India follows with a 10.4% CAGR, driven by industrial expansion and energy access initiatives, growing 1.25 times faster than the global rate. Germany registers 9.5%, slightly above the global benchmark, supported by clean energy transitions and retrofit programs. The UK, at 7.9%, and the US, at 7.1%, are growing below the global average, primarily due to slower fleet turnover and established infrastructure. The report covers detailed analysis of 40+ countries, with the top five countries shared as a reference.
China has maintained its status as a top contributor in the mechanical reciprocating engine sector, supported by widespread deployment across thermal power, shipbuilding, and locomotive industries. Engine OEMs have expanded manufacturing capacity in Shandong and Zhejiang to meet demand for dual-fuel and medium-speed engines. Demand from inland shipping and freight rail networks has driven a shift toward higher efficiency and longer maintenance cycle designs. Stringent emissions standards in select provinces have increased adoption of electronically controlled fuel injection systems in large-scale engines.
In India, mechanical reciprocating engines have remained integral to decentralized power generation, backup systems, and agricultural pumping. Expansion in rural infrastructure and off-grid solar-diesel hybrid systems has increased reliance on smaller engines with improved thermal performance. Indian manufacturers have focused on compact diesel and CNG-powered models below 500 kW, particularly for irrigation and industrial welding segments. Government support for Make-in-India has led to component indigenization, particularly crankshaft machining and precision piston casting.
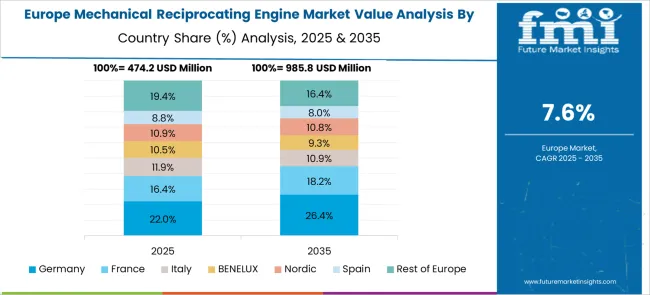
Germany has emphasized cleaner reciprocating engine development, largely for combined heat and power (CHP) and industrial cogeneration plants. A steady shift toward natural gas and biogas-compatible engines has been observed, particularly in the 1 to 5 MW segment. OEMs have prioritized lean-burn engine development to comply with EU emission directives while extending TBO (time between overhaul) intervals. Domestic research has centered around reducing NOx output through advanced turbocharging and Miller-cycle engine technologies.
The United Kingdom has observed moderate growth in this segment, with utility backup, emergency gensets, and renewable-energy hybrids serving as key use cases. OEMs have increased production of mid-range diesel and gas reciprocating engines tailored for data centers and NHS facilities. Government decarbonization goals have steered investments toward cleaner dual-fuel engines integrated into standby and peaking power plants. The market has also responded to a growing demand for engine-based generators supporting frequency response and spinning reserve services.
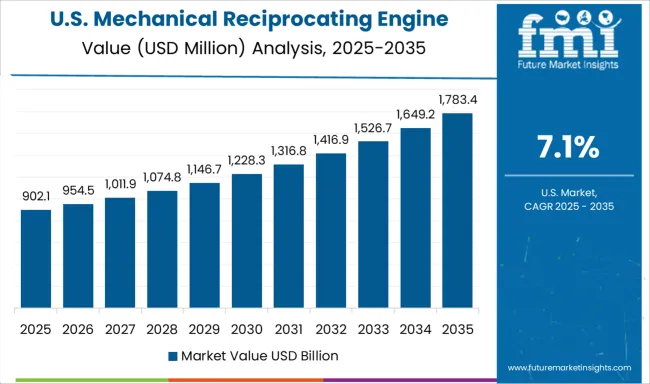
In the United States, this market has been driven by natural gas-fueled engines for distributed generation and oilfield applications. Rural electrification, especially in Texas and North Dakota, has continued to utilize robust reciprocating engines for localized power and pumpjack operations. Federal resilience programs have increased engine deployment in grid-edge and disaster response setups. US manufacturers have introduced variable compression ratio engines with remote diagnostics, increasing utility-grade applicability.
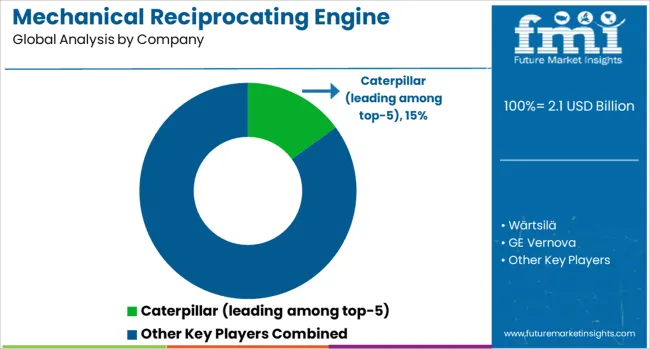
Global suppliers in the mechanical reciprocating engine space provide robust power units designed for marine, industrial, utility, and off-grid applications. Caterpillar leads among the top five, offering high-speed and medium-speed engines tailored for mechanical drives and prime power generation. These engines are deployed in oilfield pumping, drilling, and mining operations. Wärtsilä manufactures large-bore units suited for heavy marine propulsion and hybrid power plants, with dual-fuel capability enabling compliance with varying emissions requirements. GE Vernova supplies engines for industrial cogeneration and decentralized energy production, incorporating digital monitoring and low-emission combustion systems for emerging markets.
Rolls Royce supports industrial and defense sectors through mtu-branded systems that provide scalable, high-torque engines for naval vessels and rail traction. MAN Energy Solutions delivers low- and medium-speed marine engines used in commercial shipping and floating production platforms, recognized for low maintenance intervals and long operational life. Companies like Cummins and Mitsubishi also serve mobile field units and regional utilities, offering modular platforms optimized for variable load profiles. Competitive positioning is influenced by combustion efficiency, dual-fuel adaptability, maintenance logistics, and integration with hybrid energy management systems. Product selection varies by torque output, lifecycle costs, and end-user requirements for reliability across continuous and peak-shaving operations.
Between 2023 and 2025, the mechanical reciprocating engine market advanced through fuel-flexible models, digital integration, and tailored regional offerings. Caterpillar and Cummins introduced engines compatible with hydrogen and biofuels.
MAN Energy Solutions and Wärtsilä expanded dual-fuel marine and power plant engines. GE Vernova and Rolls-Royce improved remote monitoring features. Mid-tier players focused on cost-effective, regulation-compliant systems for local markets. Across sectors, demand rose for modular, efficient engines used in distributed energy, marine propulsion, and industrial backup power applications.
| Item | Value |
|---|---|
| Quantitative Units | USD 2.1 Billion |
| Fuel | Gas, Diesel, and Others |
| Rated Power | 1 MW – 2 MW |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America, Middle East & Africa |
| Country Covered | United States, Canada, Germany, France, United Kingdom, China, Japan, India, Brazil, South Africa |
| Key Companies Profiled | Caterpillar (leading among top‑5), Wärtsilä, GE Vernova, Rolls‑Royce, MAN Energy Solutions, and [Others: Cummins, Mitsubishi, etc.] |
| Additional Attributes | Dollar sales by engine type (diesel, gasoline, natural gas) and application (automotive, industrial power generation, marine), demand driven by transportation, backup power and construction, regional trends led by Asia Pacific with North America catching up, innovation in dual fuel engines, turbocharging, and hybrid assisted designs, and environmental impact via lower emissions, improved efficiency and compliance with IMO and CAFE regulations. |
The global mechanical reciprocating engine market is estimated to be valued at USD 2.1 billion in 2025.
The market size for the mechanical reciprocating engine market is projected to reach USD 4.7 billion by 2035.
The mechanical reciprocating engine market is expected to grow at a 8.3% CAGR between 2025 and 2035.
The key product types in mechanical reciprocating engine market are gas, diesel and others.
In terms of rated power, 1 mw – 2 mw segment to command 39.5% share in the mechanical reciprocating engine market in 2025.






Our Research Products

The "Full Research Suite" delivers actionable market intel, deep dives on markets or technologies, so clients act faster, cut risk, and unlock growth.

The Leaderboard benchmarks and ranks top vendors, classifying them as Established Leaders, Leading Challengers, or Disruptors & Challengers.

Locates where complements amplify value and substitutes erode it, forecasting net impact by horizon

We deliver granular, decision-grade intel: market sizing, 5-year forecasts, pricing, adoption, usage, revenue, and operational KPIs—plus competitor tracking, regulation, and value chains—across 60 countries broadly.

Spot the shifts before they hit your P&L. We track inflection points, adoption curves, pricing moves, and ecosystem plays to show where demand is heading, why it is changing, and what to do next across high-growth markets and disruptive tech

Real-time reads of user behavior. We track shifting priorities, perceptions of today’s and next-gen services, and provider experience, then pace how fast tech moves from trial to adoption, blending buyer, consumer, and channel inputs with social signals (#WhySwitch, #UX).

Partner with our analyst team to build a custom report designed around your business priorities. From analysing market trends to assessing competitors or crafting bespoke datasets, we tailor insights to your needs.
Supplier Intelligence
Discovery & Profiling
Capacity & Footprint
Performance & Risk
Compliance & Governance
Commercial Readiness
Who Supplies Whom
Scorecards & Shortlists
Playbooks & Docs
Category Intelligence
Definition & Scope
Demand & Use Cases
Cost Drivers
Market Structure
Supply Chain Map
Trade & Policy
Operating Norms
Deliverables
Buyer Intelligence
Account Basics
Spend & Scope
Procurement Model
Vendor Requirements
Terms & Policies
Entry Strategy
Pain Points & Triggers
Outputs
Pricing Analysis
Benchmarks
Trends
Should-Cost
Indexation
Landed Cost
Commercial Terms
Deliverables
Brand Analysis
Positioning & Value Prop
Share & Presence
Customer Evidence
Go-to-Market
Digital & Reputation
Compliance & Trust
KPIs & Gaps
Outputs
Full Research Suite comprises of:
Market outlook & trends analysis
Interviews & case studies
Strategic recommendations
Vendor profiles & capabilities analysis
5-year forecasts
8 regions and 60+ country-level data splits
Market segment data splits
12 months of continuous data updates
DELIVERED AS:
PDF EXCEL ONLINE
Mechanical Shaft Seal Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Mechanical And Electronic Fuzes Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Mechanical Testing Equipment Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Mechanical Locks Market Analysis - Size, Share, and Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Mechanical Coil Tester Market Analysis - Size, Share, & Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Mechanical Performance Tuning Components Market Growth - Trends & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Mechanical Ventilator Market - Demand & Growth Outlook 2025 to 2035
Mechanical Seals Market Growth - Trends & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Understanding Market Share Trends in the Mechanical Locks Industry
Mechanical Keyboard Market
Electromechanical Timers Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Bicycle Mechanical Disc Brake Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Dynamic Mechanical Analyzer Market
Chemical Mechanical Planarization Market Growth – Size & Forecast 2025 to 2035
5G Electromechanical RF Switch Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Nanoelectromechanical Systems (NEMS) Market - Trends & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Micro-electromechanical System (MEMS) Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Micro-Electro Mechanical Systems Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
High Precision Mechanical Machine Components Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Reciprocating Sabre Saws Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035

Thank you!
You will receive an email from our Business Development Manager. Please be sure to check your SPAM/JUNK folder too.
Chat With
MaRIA